Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: Dna Rna and Atp
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: Dna Rna and Atp
Uploaded by
Jemimah MohmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: Dna Rna and Atp
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: Dna Rna and Atp
Uploaded by
Jemimah MohmedCopyright:
Available Formats
DNA RNA and ATP
Draw a DNA nucleotide: Name the 4 DNA bases and the base pairs:
Pyrimidine:
Thymine - T
Cytosine – C
Purine:
Adenine - A
Guanine – G
A–T
G-C
Compare eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA:
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Stored in one long, circular DNA ring Linear DNA
Smaller than Eukaryotic DNA Larger than Prokaryotic DNA
NO Associated Proteins Associated with proteins
DOES NOT form Chromosomes Forms Chromosomes
No non coding DNA in plasmid Contains introns and mini satellites
What do the following terms mean?
Intron Degenerate
Non coding DNA in genes Each codon codes for more than one amino acid
Codon Mini-satellite
Triplet code Non coding DNA between genes
Genome Proteome
The complete set of genes required to build a is the complete set of proteins produced by the
functional organism. genome at any one time.
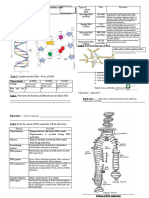
Explain DNA replication:
1. DNA Helicase (enzyme) ‘unzips’ DNA by breaking the H bonds between the bases
2. DNA nucleotides now base -pair with exposed bases on the two separate strands
3. DNA Polymerase (enzyme) joins together these new nucleotides to form a new strand
4. You end up with two copies of DNA. Each have 1 original strand of DNA and 1 new strand of DNA
Draw a diagram to explain the Meselson and Stahl experiment:
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA
Both polymers called nucleic acid
Both have monomers nucleotides
Both have C, G, A
Dna differences
Double stranded
Has T, and no U
Has sugar deoxyribose
Rna differences
Single stranded
Has U, and no T
Has sugar ribose
Draw a condensation reaction to show the production of ATP:
You might also like
- Biology-ModuleSixLessonThreePathwayThreeActivity RedoDocument7 pagesBiology-ModuleSixLessonThreePathwayThreeActivity Redomiranda50% (4)
- How Genes WorkDocument60 pagesHow Genes WorkElla Katarina LaguertaNo ratings yet
- HABB 213 Overal NotesDocument67 pagesHABB 213 Overal NotesAmandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Dna ReplicationDocument55 pagesUnit 5 - Dna Replicationapi-262235970100% (1)
- X-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsDocument5 pagesX-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsYadhirNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication Translation and TrascriptionDocument32 pagesDNA Replication Translation and TrascriptionJero MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Chemistry LectureDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Chemistry LectureHoque Mohammed Newaz Shoriful100% (1)
- DNA: The Genetic MaterialDocument73 pagesDNA: The Genetic MaterialAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna 11Document70 pagesDna Rna 11L CuevasNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna Structurealexagano4321No ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Overview of Molecular Biology: GenomeDocument49 pagesOverview of Molecular Biology: GenomefachriybalafifNo ratings yet
- 03 ApplicationsDocument62 pages03 ApplicationsTorres JeromeNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA Protein SynthesisDocument41 pagesDNA RNA Protein Synthesisjohairah merphaNo ratings yet
- DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA & DNA Replicationvictoria.hugginsNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument69 pagesNucleic AcidsKinjal BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- FHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesFHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionLeena AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationDocument28 pagesNucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationSerap BayramNo ratings yet
- 2016 Y4 IPBio DNA Structure Function ReplicationDocument40 pages2016 Y4 IPBio DNA Structure Function ReplicationAdithiyaHasalotoffeelingsNo ratings yet
- 3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryDocument90 pages3 Bacterial Genetics I & II DentistryMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument67 pagesProtein SynthesisLian Rose MendozaNo ratings yet
- DNA and Genetic EngineeringDocument43 pagesDNA and Genetic EngineeringBlessy Anne GabeloNo ratings yet
- BioChem Lecture 11 (24.dec.16)Document54 pagesBioChem Lecture 11 (24.dec.16)Sunny KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 6 - DNA Structure and Replication - Maha WizrahDocument35 pagesLecture No 6 - DNA Structure and Replication - Maha Wizrah5qntzq6zs9No ratings yet
- PD 8 DnaDocument2 pagesPD 8 Dnaapi-299976291No ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1survey1hloboNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument42 pagesDna StructureCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation PracticeDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation PracticeJohn Philip Napal100% (1)
- Lesson. 14& 15 Extra NotesDocument2 pagesLesson. 14& 15 Extra Notesvenners123No ratings yet
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Genes and Protein SynthesisDocument31 pagesGenes and Protein SynthesisKhadija ShoaibNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNAmonica.perezgaNo ratings yet
- BMS1021 W1L3Document30 pagesBMS1021 W1L3Sophia BeamNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisLaurence PriscillaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control: Dna and RnaDocument18 pagesGenetic Control: Dna and Rnarasha nadaNo ratings yet
- Pogil - Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesPogil - Protein SynthesisSavanna SturgessNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 Intro08 SDocument26 pagesLecture01 Intro08 SHui Ka HoNo ratings yet
- Biology: Third QuarterDocument126 pagesBiology: Third QuarterHill A. D.No ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument18 pagesDNA Structureharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- 2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatDocument35 pages2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Nucleic Acid Chemistry Part 1Document7 pages11.1 Nucleic Acid Chemistry Part 1ChonaNo ratings yet
- DNA NotesDocument25 pagesDNA NotesNeha GoyalNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument23 pagesDNA and RNAHazel SioseNo ratings yet
- I Molecular Biology Basics PJDocument19 pagesI Molecular Biology Basics PJhafeeeNo ratings yet
- Case 1 SummeryDocument11 pagesCase 1 SummeryTtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - DNA The Molecular of InheritanceDocument28 pagesChapter 8 - DNA The Molecular of InheritanceNguyễn ChiNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dna-Rna AamDocument25 pagesStruktur Dna-Rna AamMila DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Cape1 DNA2Document48 pagesCape1 DNA2Matt BarhamNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument2 pagesMolecular GeneticsFaith YeNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument25 pagesDna Code of Liferaym6270No ratings yet
- DNA STRUCTURE LectureDocument44 pagesDNA STRUCTURE Lectureevacarlina1721No ratings yet
- Singapore Junior Biology Olympiad 2018: Chromosomes, Dna and GenesDocument16 pagesSingapore Junior Biology Olympiad 2018: Chromosomes, Dna and Genesaloysius limNo ratings yet
- Weekly Test 2 (T-2) A-LDocument5 pagesWeekly Test 2 (T-2) A-Laqua PiscesNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of Life-1Document25 pagesDna Code of Life-1ngubobomikaziNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Cell Division & Protein SynthesisDocument21 pages4.9 Cell Division & Protein Synthesis2023875802No ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 1 4939 8991 1 PDFDocument359 pages10.1007@978 1 4939 8991 1 PDFGabyMezaCarrasco100% (1)
- 07 10 2021 Bio AssignmentDocument4 pages07 10 2021 Bio AssignmentSuneel ReddyNo ratings yet
- Notes On Molecular Basis of Inheritance by ExamsRoadDocument8 pagesNotes On Molecular Basis of Inheritance by ExamsRoadVogolus machatteNo ratings yet
- Hind III Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument2 pagesHind III Haemophilus InfluenzaeJazmin Nicole AbanesNo ratings yet
- THE CLASSIC - Molecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesTHE CLASSIC - Molecular Structure of Nucleic AcidsP. R. SREENIVASANNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyDocument3 pagesScience 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyRowena Nim100% (2)
- Post Transcriptional ModificationDocument31 pagesPost Transcriptional ModificationranasiddharthNo ratings yet
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocument45 pagesHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - DNA Replication (Short Size) PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 - DNA Replication (Short Size) PDFlelNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. FDocument10 pagesPROTEIN SYNTHESIS. FNikita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bif501 Assignment No 2Document10 pagesBif501 Assignment No 2bc190205832 RIFFAT BANONo ratings yet
- Post It Note Science DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Mini.1.Kreitzer-houslerDocument4 pagesPost It Note Science DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation Mini.1.Kreitzer-houslerCHRISTEROP0% (1)
- Dogma Sentral Biologi Molekuler: Riandini Aisyah Molecular Biology & ImmunologyDocument56 pagesDogma Sentral Biologi Molekuler: Riandini Aisyah Molecular Biology & ImmunologyArkan Adi WidiyaNo ratings yet
- Real-Time PCR BasicsDocument78 pagesReal-Time PCR BasicsSubbagbinfung Rumkit Bhayangkara Palangka RayaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesFrom Gene To ProteincrookedspookNo ratings yet
- Genetic Coding PDFDocument12 pagesGenetic Coding PDFMobileLegends SbNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument108 pagesCell Biology Lecture NotesMert PolatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life Sinhala Model PaperDocument12 pagesChemical Basis of Life Sinhala Model PaperNisal PeirisNo ratings yet
- 04-Aug-2021 A History of DnaDocument15 pages04-Aug-2021 A History of DnanaomiNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument3 pagesTranscriptionprerana23No ratings yet
- Explanatory Chapter: Troubleshooting PCRDocument8 pagesExplanatory Chapter: Troubleshooting PCRLisset Ch GNo ratings yet
- "PROJECT REPORT" ON "RNAi AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN LIFE SCIENCES"Document28 pages"PROJECT REPORT" ON "RNAi AND ITS APPLICATIONS IN LIFE SCIENCES"Nishant SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefDocument2 pages6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefReeNo ratings yet
- Flu Case StudyDocument4 pagesFlu Case StudyaprilweinmanNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet-1Document3 pagesStudent Worksheet-1brenden chapmanNo ratings yet
- q2 Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesq2 Nucleic AcidsPaul TinarwoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFDocument58 pagesGenetics Lecture 2 - DNA and Chromosome Structure PDFMarlee SandersonNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument33 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceJabcv OahdjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Genetic 2Document85 pagesLecture 6. Genetic 2Thanhh ThaooNo ratings yet