Professional Documents
Culture Documents
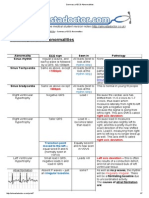
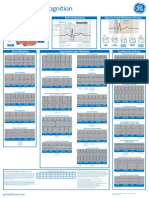
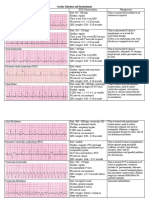
Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrythmias: Conduction, or Both
Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrythmias: Conduction, or Both
Uploaded by
dea0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesOriginal Title
week3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesMechanisms of Cardiac Arrythmias: Conduction, or Both
Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrythmias: Conduction, or Both
Uploaded by
deaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
MECHANISMS OF CARDIAC ARRYTHMIAS
Disorders of heart rhythm result from alterations of impulse formation, impulse
conduction, or both.
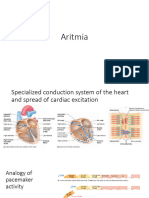
Normal Impulse Formation
Secara umum, electrical impulse itu dihasilkan oleh specialized cardiac cells yang
memiliki intrinsic automaticity (cell’s ability to depolarize itself to a threshold
voltage to generate spontaneous action potential) e.g. SA node, AV node and
ventricular conducting system (bundle of His, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers)
pacemaker cells
1. Ionic Basis of Automaticity
Cells with natural automaticity do not have a static resting voltage
they display gradual depolarization during phase 4 of AP (due to the
pacemaker current)
Threshold pacemaker cells before opening the Na+ channels itu
biasanya around -60mV
Gradual depolarization (beda sama myocyte cell contraction yang
rapid), due to: (1) slow inward Ca2+ current, (2) progressive decline of
an outward K+ current, and (3) additional Na+ current via activation of
Na-Ca exchanger from sarcoplasmic reticulum (“calcium clock”)
Kenapa depolarization pacemaker cells lebih lambat dibandingkan
myocyte? Because membrane potential determines the proportion
of fast Na+ channels capable of depolarization, semakin negatif
membrane voltagenya, semakin banyak fast Na+ channels yang
available for ion exchange.
Repolarization phase of pacemaker cells depends on inactivation of the
Ca2+ channels and the opening of voltage-gated K+ channels for K+
efflux.
2. Native and Latent Pacemakers
The pacemaker cells with the fastest rate of depolarization set the
heart rate.
Dominant pacemaker in the normal heart: SA node (rate: 60-100bpm)
Native pacemakers: SA node (because it sets the heart rate)
Latent pacemakers (ectopic pacemakers): other cells within the
specialized conduction system that has the same potential to act as a
pacemaker (if necessary) e.g. AV node & Purkinje system (firing rate:
30-40 bpm) these latent pacemakers may initiate and take over the
pacemaking function if SA node slows/fails to fire/conduction
abnormalities block the normal wave of depolarization.
3. Overdrive Suppression
The cells preempt all other automatic cells from spontaneously firing
but also directly suppresses their automaticity overdrive
suppression
Overdrive suppression decreases cell’s automaticity when that cell is
driven to depolarize faster than its intrinsic discharge rate.
Hyperpolarization: 3 Na+ keluar, K+ masuk. Ada 1 positive ion diluar to
create the membrane to be more negative cell potential (inside the
membrane) becomes more negative additional time is required for
spontaneous phase 4 (depolarization) to reach the threshold.
Hyperpolarizaton current meningkat apabila cells ini dipaksa untuk
meningkatkan firing rate mereka (lebih dari normal) overdrive
suppression decreases firing rate.
4. Electronic Interactions
Gangerti
Altered Impulse Formation
1. Alterations in SA Node Automaticity
They are regulated primarily by neurohormonal factors.
A. Increased SA Node Automaticity
- Important modulator of normal SA automaticity: ANS
- Sympathetic stimulation (beta-adrenergic receptors): increases
the open probability of the pacemaker channels increase of
pacemaker current steeper slope in phase 4 depolarization
SA node reaches threshold and fire earlier than normal HR
increases.
- Sympathetic activity increases the rate of pacemaker
depolarization via pacemaker current and by causing the action
potential threshold to become more negative.
- E.g: exercise, emotional stress.
B. Decreased SA Node Automaticity
- Caused by PNS
- Cholinergic stimulation via vagus nerve reduce the
probability of pacemaker channels to be opened reduced
pacemaker current and reduced slope of phase 4 depolarization
slowed intrinsic firing rate decreased HR
- Reduced pacemaker current, more negative maximum diastolic
potential, and less negative threshold level slows the intrinsic
firings reduced heart rate
2. Escape Rhythms
Sinus node becomes suppressed fires less frequently site of
impulse formationnya berubah jadi latent pacemaker
Impulse initiated by latent pacemaker = escape beat.
Persistent impairment of SA node will allow a continued series of
escape beats = escape rhythm (they are actually protective, to
prevent the HR becomes pathologically slow)
Decreased HR usually caused by the activation of PNS. Bagian
jantung itu beda-beda sensitivitynya sama PNS stimulation. Yang
paling sensitive SA-AV node atrial tissue ventricular conducting
system
Moderate parasympathetic stimulation: slows SA node pacemaker
shifts to AV node
Strong parasympathetic stimulation: SA&AV node becomes
suppressed ventricular escape pacemaker
The beat is usually late and terminates a pause caused by slowed
sinus rhythm.
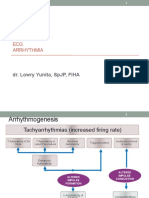
3. Enhanced Automaticity of Latent Pacemakers
Latent pacemaker develops an intrinsic rate of depolarization faster
than SA node = ectopic beat
The impulse is premature (lebih cepet daripada sinus rhythm)
Sequence of similar ectopic beats = ectopic rhythm
Usually caused by: high catecholamine concentration, hypoxemia,
ischemia, electrolyte disturbances, drug toxicities (digoxin intoxication)
4. Abnormal Automaticity
Cardiac tissue injury pathologic changes in impulse formation
myocardial cells diluar specialized conduction system acquire
automaticity & spontaneously depolarize
Injured myocyte membrane nya jadi “leaky” atau bocor unable to
maintain concentration gradient of ion resting potential jadi lebih gak
negatif
Triggered Activity
Action potential can trigger abnormal depolarization extra heart beat
or rapid arrythmias
This type of automaticity is stimulated by a preceeding acton potential
Early after depolarization (EAD): menganggu repolarisasi may
initiate TdP
Delayed after depolarization (DAD): terjadi setelah repolarisasi
biasanya terjadi karena calcium intracellular nya tinggi, biasanya ada di
kondisi intoksiasi digitalis atrial & ventricular tachycardias associated
with digitalis toxicity
Altered Impulse Conduction
1. Conduction Block
Propagating impulse is blocked karena ada bagian dari jatung yang
udh electrically unexcitable
Can be transient or permanent
Caused by ischemia, fibrosis, inflammation, and certain drugs
Functional block: conduction block occurs waktu ada electrical impulse
yang dateng ke cardiac cells yang lagi “rest” (masih di dalam RF period
setelah depolarisasi) (e.g. antiarrythmic drugs)
Fixed block: karena ada barrier yang disebabkan oleh fibrosis/scarring
2. Undirectional Block and Reentry
You might also like
- Key Points/: Study GuideDocument48 pagesKey Points/: Study Guidedanni100% (1)
- Megacode Testing Checklist: Scenarios 1/3/8 Bradycardia Pulseless VT PEA PCACDocument6 pagesMegacode Testing Checklist: Scenarios 1/3/8 Bradycardia Pulseless VT PEA PCACberril_fannyNo ratings yet
- Ecg Made Ridiculously Easy!Document78 pagesEcg Made Ridiculously Easy!momobelle100% (9)
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Clinical Skill ChecklistDocument2 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation Clinical Skill ChecklistCarissa TirtaniaNo ratings yet
- Unswagati, Cirebon Dr. Irwan M. Loebis, SPJPDocument55 pagesUnswagati, Cirebon Dr. Irwan M. Loebis, SPJPApriliani Nur Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- ArrythmiasDocument30 pagesArrythmiasavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - SCOME UNPADDocument73 pagesCardiology - SCOME UNPADastarimediantoNo ratings yet
- Common Cardiovascular Conditions: Lecture Notes - Antiarythmic Agents 1Document6 pagesCommon Cardiovascular Conditions: Lecture Notes - Antiarythmic Agents 1Ernest Patrick MatiasNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsUma MounaNo ratings yet
- Cvs 1,2Document36 pagesCvs 1,2atefmoussaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Arrhythmias: Belay E. MD December 2015Document53 pagesPathophysiology of Arrhythmias: Belay E. MD December 2015Amanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsDocument15 pagesAnti-Arrhythmic DrugsYamin SanjuNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectrophysiologyDocument46 pagesBasic Electrophysiologyiin setiyana100% (1)
- Cardio - Vascular Dr. Mohamed Elsherif المحاضرة الأولىDocument11 pagesCardio - Vascular Dr. Mohamed Elsherif المحاضرة الأولىmb74v6ncpnNo ratings yet
- Core V - Cardiovascular CoreDocument35 pagesCore V - Cardiovascular CoreMatthew LeiNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Thursday, January 17, 2019 1:04 PMDocument3 pagesArrhythmias: Thursday, January 17, 2019 1:04 PMaminath2288No ratings yet
- Or Cardiac Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Some PharmacologyDocument58 pagesOr Cardiac Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Some PharmacologyJacob StoneNo ratings yet
- Normal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharDocument27 pagesNormal Heart Rhythm: Mutiara Budi AzharAditya Fresno Dwi WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument9 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNo ratings yet
- Cvs 1Document37 pagesCvs 1atefmoussaNo ratings yet
- 8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsDocument76 pages8C - Antiarrythmic DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Document44 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Chinenye Akwue100% (1)
- Arrhythmia IMO 2018Document53 pagesArrhythmia IMO 2018EldhaNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalDocument73 pagesArrhythmia: Dian Pratiwi Cardiology Department Chasan Boesoerie HospitalummuabNo ratings yet
- Cardiac L1CVSDocument19 pagesCardiac L1CVSQutaybah JahmanyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Electrical ActivityDocument17 pagesCardiac Electrical ActivitySalah Salah 201-901-341No ratings yet
- Arrhythmia 2021-2022 Semester 1Document42 pagesArrhythmia 2021-2022 Semester 1Omar AlaamNo ratings yet
- CV ED Sem 2 2020 2021Document43 pagesCV ED Sem 2 2020 2021Sarhan AliNo ratings yet
- What Is ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWhat Is ArrhythmiaSharan MurugaboopathyNo ratings yet
- CVS PhysiologyDocument43 pagesCVS Physiologyapi-3705050100% (1)
- Arritmias Rosen SDocument31 pagesArritmias Rosen SFrank RamirezNo ratings yet
- Heart Muscles, Valves & Blood Vessels (I)Document31 pagesHeart Muscles, Valves & Blood Vessels (I)Hussain GauharNo ratings yet
- s1c11 ECG - Supplement PDFDocument108 pagess1c11 ECG - Supplement PDFVisan Andreea Mihaela RamonaNo ratings yet
- AritmiaDocument14 pagesAritmiaDiana ElfandewyNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CHF and ArryhtmiasDocument5 pagesDrugs For CHF and ArryhtmiasConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cardiac Arrythmias M2Document28 pagesIntroduction To Cardiac Arrythmias M2Millicent AwuzieNo ratings yet
- The Heart Has Several Pacemakers Known As Autonomic FociDocument1 pageThe Heart Has Several Pacemakers Known As Autonomic FociAnonymous mLYupGyNNo ratings yet
- Ecg Arrhythmia: Dr. Lowry Yunita, SPJP, FihaDocument48 pagesEcg Arrhythmia: Dr. Lowry Yunita, SPJP, FihaMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- Conductive Systemof The HeartDocument25 pagesConductive Systemof The HeartShreeya PooniaNo ratings yet
- 02 AntiarrhythmicAgentsDocument83 pages02 AntiarrhythmicAgentsSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias GeneralDocument131 pagesArrhythmias GeneralAnonymous IRl5fn6No ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument59 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsCharles YiuNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument12 pages12 - Cardiac ArrhythmiasYassine LaiymaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Activity of The HeartDocument28 pagesElectrical Activity of The Heartsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmias Agents: By: Tirta Darmawan Susanto, Dr.,MkesDocument64 pagesAntiarrhythmias Agents: By: Tirta Darmawan Susanto, Dr.,MkesShally ChandraNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Physiology Exam QuestionsDocument17 pagesCardio-Physiology Exam Questionsjimmy100% (2)
- Campugan - Jay - Patho - AssignmentDocument11 pagesCampugan - Jay - Patho - AssignmentFlower Flower FlowerNo ratings yet
- 12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Document12 pages12 - Cardiac Arrhythmias - 0Ehtiram HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology of HeartDocument46 pagesElectrophysiology of HearthafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- ELEC4810 Notes-3 PDFDocument82 pagesELEC4810 Notes-3 PDFKwan ChanNo ratings yet
- Phys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalDocument10 pagesPhys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Cardiovascular Physiology HandoutDocument7 pagesUnit 4 - Cardiovascular Physiology Handouttilahun aligazNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovasular SystemPhai KoemhienNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of The HeartDocument25 pagesElectrical Properties of The HeartSherwan R Shal100% (3)
- Electrophysiological Properties of Cardiac MyocytesDocument39 pagesElectrophysiological Properties of Cardiac Myocytesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- CVS AnatomyDocument45 pagesCVS AnatomyAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- Characteristic of Cardiac Muscle Cells - CVSK4Document36 pagesCharacteristic of Cardiac Muscle Cells - CVSK4Lydia KosasihNo ratings yet
- Estimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaDocument10 pagesEstimulação Transcutânea Não InvasivaMarcos AcioliNo ratings yet
- الوحدة الثانيهDocument7 pagesالوحدة الثانيهHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Special Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedDocument14 pagesSpecial Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedAzhersyedNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiaDocument135 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiaPERFECT CLASSESNo ratings yet
- Ffisiologi EkgDocument29 pagesFfisiologi EkgRoby4No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Name: Chellya Fanny Alvionitan NIM: 01071200025 Tutor: A26 Group: A26Document4 pagesName: Chellya Fanny Alvionitan NIM: 01071200025 Tutor: A26 Group: A26deaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Document12 pagesQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNo ratings yet
- DasdaDocument17 pagesDasdadeaNo ratings yet
- Table of Content 3Document6 pagesTable of Content 3deaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiac Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagesBasic Cardiac Structure and FunctiondeaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument15 pagesHypertensiondeaNo ratings yet
- Part 02 EP TracingsDocument42 pagesPart 02 EP TracingsHany100% (1)
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument8 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationamesb100% (1)
- Using The Surface Electrocardiogram To Localization of Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaDocument12 pagesUsing The Surface Electrocardiogram To Localization of Idiopathic Ventricular TachycardiaNavojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ecg in Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument173 pagesEcg in Congenital Heart DiseasewasimNo ratings yet
- 058+ +1595+ +Luh+Made+Indrasuari+ +galleyDocument5 pages058+ +1595+ +Luh+Made+Indrasuari+ +galleyLathief CaakNo ratings yet
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDocument6 pagesSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Osce PDFDocument51 pagesOsce PDFAlfonso PeñarroyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 MIDTERMS PG 7Document1 pageNCM 118 MIDTERMS PG 7Kai SamaNo ratings yet
- 439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG BasicsDocument34 pages439 3 Electrophysiology & ECG Basicssrisairampoly0% (1)
- Manual de Service BC - Biomedical - DA-2006 - Defibrillator - Analyzer PDFDocument171 pagesManual de Service BC - Biomedical - DA-2006 - Defibrillator - Analyzer PDFGuillermo ZalazarNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers & Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (Icds) - Anaesthesia Tutorial of The Week 299 25 November 2013Document8 pagesPacemakers & Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (Icds) - Anaesthesia Tutorial of The Week 299 25 November 2013Anup SasalattiNo ratings yet
- Pages From FU784-293-The Only EKG Book You'Ll Ever N - Thaler, Malcolm SDocument3 pagesPages From FU784-293-The Only EKG Book You'Ll Ever N - Thaler, Malcolm Sindri lestari100% (1)
- TplCoverDetailed - Detailed Cover SheetDocument2 pagesTplCoverDetailed - Detailed Cover SheetTara FernandezNo ratings yet
- Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesSummary of ECG AbnormalitiesKarin AdraiNo ratings yet
- Brugada SyndromeDocument5 pagesBrugada SyndromevitriaNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Atrial and Ventricular Pacing During Narrow Complex Tachycardia - The Janus Response. Which One Is True?Document5 pagesSimultaneous Atrial and Ventricular Pacing During Narrow Complex Tachycardia - The Janus Response. Which One Is True?Sahil HasanNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) - Mayo Clinic: People Also AskDocument5 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) - Mayo Clinic: People Also AskHAMMAD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia Recognition Part 1 and 2 DOC1178264 Rev2Document2 pagesArrhythmia Recognition Part 1 and 2 DOC1178264 Rev2Nico Angelo CopoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support With Automated External Defibrillator and Advanced Cardiac Life Support TrainingDocument2 pagesBasic Life Support With Automated External Defibrillator and Advanced Cardiac Life Support TrainingJohn Dalton Marin VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part B: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community CollegeDocument80 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: The Heart: Part B: Prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community CollegeBrianna PinchinatNo ratings yet
- Ecg TestDocument67 pagesEcg TestEm KayNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation GuideDocument7 pagesAtrial Fibrillation GuideFirstglobalsupercopNo ratings yet
- Arrythmias 2-3Document4 pagesArrythmias 2-3cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Sharmin Anak Ngitar 3827 Code BlueDocument2 pagesSharmin Anak Ngitar 3827 Code BlueJoy HavsonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Chapter 45Document4 pagesPharmacology Chapter 45angela garroteNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument3 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasWilbert GuerreroNo ratings yet