Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Literature Review
Literature Review
Uploaded by
Bassam WazirOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Literature Review
Literature Review
Uploaded by
Bassam WazirCopyright:
Available Formats
Subject of research By Research Summary
This paper introduces a high-rise building ambient vibration test project in Laibin. Some results obtained from full-scale
measurements of the dynamic behavior of 10 high-rise buildings are described. Different pre- and post-processing
Operational Modal Analysis and Rational
Yun Zhou, Ph.D.; Yi Zhou; techniques were used for ambient vibration signal analysis, from which the modal parameters were obtained using three
Finite-Element Model Selection for Ten OMA techniques. By rationally analyzing and modeling the stiffness of the infill walls, six finite element (FE) models were
Weijian Yi, Ph.D.; Taiping
High-Rise Buildings based on On-Site built in PKPM and SAP2000 to estimate the analytical modal information. The influences of the infill wall mass and
Chen; Dexian Tan; and Site Mi stiffness on the dynamic properties of a high-rise building are further discussed. According to the identified and calculated
Ambient Vibration Measurements
results, all three modes emerged in each modal dense region in the frequency domain of high-rise buildings. Finally, based
on 25 proposed empirical equations, the fundamental periods of 10 buildings are calculated and summarized.
Numerical model for the dynamic and
Guillermo M. Álamo · Luis A. This paper presents a three–dimensional linear numerical model for the dynamic and seismic analysis of pile-supported
seismic analysis of pile‑supported
Padrón · Juan J. Aznárez · structures that allows to represent simultaneously the structures, pile foundations, soil profile and incident seismic waves and
structures with a meshless integral that, therefore, takes directly into account structure–pile–soil interaction.
Orlando Maeso
representation of the layered soil
This paper aims to develop a simplified but comprehensive approach relating to vulnerability assessment in the form of
Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of a Jungwon Huh ID , Quang Huy fragility curves on a shallow two-story reinforced concrete underground box structure constructed in a highly-weathered
soil. In addition, a comparison of the results of earthquakes per peak ground acceleration (PGA) is conducted to determine
Shallow Two-Story Underground RC Box Tran ID , Achintya Haldar ,
the effective and appropriate number for cost- and time-benefit analysis. The ground response acceleration method for
Structure Innjoon Park and Jin-Hee Ahn buried structures (GRAMBS) is used to analyze the behavior of the structure subjected to transverse seismic loading under
quasi-static conditions.
This thesis consists of two major parts. the first part is about design deep beams by a simply supported beam MS1-2 having
shear span to depth ratio of less than 2 has been first designed using truss modeling in SAP2000 Software, using modeling
thick shell element technique. The results of design obtained from FEM modeling has been compared with design obtain in
Behavior of Reinforced Concrete Deep
the available literature. The second part is about study the behavior of deep beams with high strength reinforcement with
Beam with High Strength Reinforcement Sarah Hashim Ebaid various shear span to depth (a/d) ratios and deferent reinforcement ratio ρ to study the strength parameters such as, first
using SAP2000 Software crack load, the ultimate failure load, load of yielding in main tension reinforcement, strains in main tension reinforcement,
deflection at ultimate load, and mode of failure. The design results obtained from SAP2000 shell thick model was show a
good agreement compared with results obtained in the available literature.
Given in the GEO-HKIE (2011) Report, GEO-HKIE prepared three worked examples pursuant to the new
recommendations, which are presented in this report. The first example demonstrates the procedure for adopting the hybrid
Geotechnical Engineering nail arrangement, which is a novelty to local practitioners. The second example assumes that steeply inclined nails have to
Design Illustrations on the Use of Soil be adopted due to site constraints. The design therefore includes the provision of an embedded concrete footing which aims
Office and The Hong Kong
Nails to Upgrade Loose Fill Slopes to reduce slope deformation. The effectiveness of the nail arrangement is verified by numerical analysis. The last example
Institution of Engineers considers a fill slope with loose fill of a considerable depth, and illustrates the procedure to delineate the non-liquefiable
loose fill zone by limit equilibrium method. Recommendations in respect of the selection of design parameters are also
presented in the worked examples.
Finite element modeling of buildings with Iason Pelekis Frank McKenna This paper addresses the computational modeling of buildings that have either been designed to rock on the soil beneath
their foundation (foundation rocking) or at the foundation–structure interface (structural rocking). Within OpenSees,
structural and foundation rocking on dry Gopal S. P. Madabhushi foundation and structural rocking were modeled using a beam-on-a-nonlinear- Winkler foundation model (BNWF)
sand Matthew J. DeJong combined with flat-slider elements for footing–soil and superstructure–footing interactions, respectively.
In this thesis, soil-structure interaction effects in buildings are studied using relatively simple models prepared by a general-
purpose structural analysis software (SAP2000). A symmetrical, 6-story, 6-bay reinforced concrete moment resisting frame
A STUDY ON MODELING SOIL-
Nawaf Hani Muslim Al- is considered for both two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) building models. Seismic responses of three
STRUCTURE INTERACTION EFFECTS different building structures (with varying dynamic characteristics) on three different homogeneous, elastic soil mediums are
dayyeni computed and compared with the responses of the corresponding fixed base models. Soil-structure interaction effects are
IN BUILDINGS
modeled by two approaches: (i) using soil springs representing the soil impedance functions (substructure method), and (ii)
modeling the soil medium directly along with the structure and the foundation (direct analysis method).
You might also like
- Moving Man Phet Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesMoving Man Phet Lab Activityuflilla50% (4)
- 11 Design of Pile For Initial Load Test: 11.1 Lateral Capacity of PilesDocument5 pages11 Design of Pile For Initial Load Test: 11.1 Lateral Capacity of PilesManvendra NigamNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On Behavior of Flat Slab Under Dynamic LoadingDocument2 pagesReview Paper On Behavior of Flat Slab Under Dynamic LoadingIJSTENo ratings yet
- 265 HcsDocument3 pages265 HcsNaveen NunnaNo ratings yet
- Tociej 6 200 PDFDocument15 pagesTociej 6 200 PDFSaad HneidiNo ratings yet
- Seismic Performance Evaluation of Multistoried RC Framed Buildings With Shear Wall PDFDocument6 pagesSeismic Performance Evaluation of Multistoried RC Framed Buildings With Shear Wall PDFSahil OzaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S235271022201748X MainDocument20 pages1 s2.0 S235271022201748X Maingopa dasNo ratings yet
- Lateral Load Distribution in Frame StructuresDocument8 pagesLateral Load Distribution in Frame Structuresreetika100% (1)
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Jiulin Bai, Huiming Chen, Junfeng Jia, Bohao Sun, Shuangshuang JinDocument7 pagesSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Jiulin Bai, Huiming Chen, Junfeng Jia, Bohao Sun, Shuangshuang JinfadwaissaNo ratings yet
- Soil-Structure Interaction Modelling For Piles in Performance-Based Seismic DesignDocument9 pagesSoil-Structure Interaction Modelling For Piles in Performance-Based Seismic DesignKanumalli PavanNo ratings yet
- Dissertation - M.tech Akshay Uphade Roll.30Document23 pagesDissertation - M.tech Akshay Uphade Roll.30Akshay UphadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Review of LiteratureDocument19 pagesChapter 2. Review of Literatureci_balaNo ratings yet
- PARDO 2014 - Biaxial Capacity of Rigid FootingsDocument9 pagesPARDO 2014 - Biaxial Capacity of Rigid FootingsAnonymous wvLOveDRNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of A Multi Storey BuildingDocument33 pagesPushover Analysis of A Multi Storey BuildingPrakhar VarshneyNo ratings yet
- K S Patil ICETRE PaperDocument9 pagesK S Patil ICETRE PaperShruti ShahNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Seismic Response of A Full-ScaleDocument10 pagesThree-Dimensional Seismic Response of A Full-ScaleMaldi KokalariNo ratings yet
- Pushover AnalysisDocument5 pagesPushover AnalysisDigambar JadhavNo ratings yet
- 1.1. General: Seismic Performance of Steel On Different Span ArrangementsDocument7 pages1.1. General: Seismic Performance of Steel On Different Span ArrangementsChetan PatilNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Shear-Wall On Existing Irregular Building Under Seismic LoadingsDocument6 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Shear-Wall On Existing Irregular Building Under Seismic LoadingsMahhhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: Bruno Dal Lago, Milot Muhaxheri, Liberato FerraraDocument19 pagesEngineering Structures: Bruno Dal Lago, Milot Muhaxheri, Liberato FerraraMohammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument163 pagesFull ThesisRidwan Mohammed NurNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of Structures Subjected To Combined ActionDocument24 pagesPushover Analysis of Structures Subjected To Combined ActionNaman RaiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Infill Walls On Response of Multi Storey Reinforced Concrete StructureDocument5 pagesEffect of Infill Walls On Response of Multi Storey Reinforced Concrete StructurePREMALATHA JNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Radial Basis Function and Functional Back Propagation Neural Networks For Estimating Inframe Fill StabilityDocument6 pagesImplementation of Radial Basis Function and Functional Back Propagation Neural Networks For Estimating Inframe Fill Stabilitypurushothaman sinivasanNo ratings yet
- Performance Based Earthquake Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsDocument8 pagesPerformance Based Earthquake Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete BuildingsJulio Cesar ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Wcee2012 4059 Yf PDFDocument10 pagesWcee2012 4059 Yf PDFKS LeeNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Approach For Pushover Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry (Urm) StructuresDocument21 pagesAn Efficient Approach For Pushover Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry (Urm) StructuresHaris AlamNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Investigation of An 11-Story Reinforced Concrete Building's Nonlinear Dynamic BehaviorDocument6 pagesExperimental and Numerical Investigation of An 11-Story Reinforced Concrete Building's Nonlinear Dynamic BehaviorDeepak Kr GuptaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Unreinforced Masonry BuildDocument20 pagesNumerical Simulation of Unreinforced Masonry BuildLuis Wilmer Nuñez EchaccayaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Evaluation of Seismic Response of Asymmetrical Reinforced Concrete Frame BuildingsDocument6 pagesNumerical Evaluation of Seismic Response of Asymmetrical Reinforced Concrete Frame BuildingsSahar Aktham RashedNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Machine Foundation Surrounded by Diaphragm Wall Using OpenSees ProgramDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Machine Foundation Surrounded by Diaphragm Wall Using OpenSees ProgramAhMed SaMeerNo ratings yet
- Stbu 11 00022Document16 pagesStbu 11 00022Elena MiceliNo ratings yet
- Seismic Performance of AAC MasonryDocument9 pagesSeismic Performance of AAC MasonrySandip AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Analyses of Micropile PDFDocument10 pagesStatic and Dynamic Analyses of Micropile PDFjorgemalagaNo ratings yet
- Eqe 3427Document19 pagesEqe 3427Abir SenNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Multi-Storeyed Frame-Shear Wall Building Considering SSIDocument5 pagesDynamic Analysis of Multi-Storeyed Frame-Shear Wall Building Considering SSIravi kumarNo ratings yet
- Al Agha 2021Document10 pagesAl Agha 2021Qorry OktaliaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Assessment Using Pushover Analysis An Overview by Saurabh PednekarDocument7 pagesSeismic Assessment Using Pushover Analysis An Overview by Saurabh PednekarSaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: Yang Lu, Iman Hajirasouliha, Alec M. MarshallDocument14 pagesEngineering Structures: Yang Lu, Iman Hajirasouliha, Alec M. MarshallMahdi AbdeddaimNo ratings yet
- Pushover Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Structures by Fiber Finite Element MethodDocument24 pagesPushover Analysis of Unreinforced Masonry Structures by Fiber Finite Element MethodAndrei ANo ratings yet
- Seismic Behavior of Nonseismically Detailed Interior Beam-Wide Column Joints-Part II: Theoretical Comparisons and Analytical StudiesDocument10 pagesSeismic Behavior of Nonseismically Detailed Interior Beam-Wide Column Joints-Part II: Theoretical Comparisons and Analytical StudiesPaul KohanNo ratings yet
- Bi Layer Diaphragm Walls Structural andDocument8 pagesBi Layer Diaphragm Walls Structural andLuthfi NNo ratings yet
- Modal Pushover-Based Scaling of Two Components of Ground Motion Records For Nonlinear RHA of BuildingsDocument7 pagesModal Pushover-Based Scaling of Two Components of Ground Motion Records For Nonlinear RHA of Buildingsmajid heidariNo ratings yet
- ComparisonDocument5 pagesComparisonPraveen ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Response of Reinforced Frame Structure With Soft Stories at Different FloorsDocument34 pagesSeismic Response of Reinforced Frame Structure With Soft Stories at Different FloorsAkshay UphadeNo ratings yet
- NemaliDeepika KSaiSantosh 206Document10 pagesNemaliDeepika KSaiSantosh 206Aya KhalifaNo ratings yet
- Large-Scale Shaking Table Test On Tall Buildings With Viscous Dampers Considering Pile-Soil-Structure InteractionDocument14 pagesLarge-Scale Shaking Table Test On Tall Buildings With Viscous Dampers Considering Pile-Soil-Structure InteractionVladekNo ratings yet
- Thesis ProposalDocument3 pagesThesis ProposalRamesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Literature Review & ObjectiveDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Literature Review & ObjectivevanshajNo ratings yet
- Simplified Frame Model For Capacity Assessment of Masonry BuildingsDocument4 pagesSimplified Frame Model For Capacity Assessment of Masonry Buildingssingh.dipendra9749No ratings yet
- Performance Based Seismic Design by Capacity Spectrum MethodDocument14 pagesPerformance Based Seismic Design by Capacity Spectrum MethodNeenuskNo ratings yet
- 14 Finite Element and Equivalent Frame Analysis of Masonry Façade - Having An Arched Opening Anish Lakhera 3542Document6 pages14 Finite Element and Equivalent Frame Analysis of Masonry Façade - Having An Arched Opening Anish Lakhera 3542Andrei ANo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures 31 (2009) 999-1009Document11 pagesEngineering Structures 31 (2009) 999-1009rpatel5509No ratings yet
- Study On The Concentration of Moment at PDFDocument7 pagesStudy On The Concentration of Moment at PDFZAKROUNNo ratings yet
- Parative Study On Seismic Performance of Flat Slab and Conventional SlabDocument6 pagesParative Study On Seismic Performance of Flat Slab and Conventional Slabaji raNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0141029610002786 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0141029610002786 MainTheyCalledMe ZafNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0267726122004286 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0267726122004286 MainMert GőkdoğanNo ratings yet
- Studying and Analyzing The Seismic Performance of Concrete MomentResisting Frame BuildingsCivilEngDocument21 pagesStudying and Analyzing The Seismic Performance of Concrete MomentResisting Frame BuildingsCivilEngdaniel ticonaNo ratings yet
- Fem Analysis of Anchored Sheet Pile Quay Wall: A Case Study On The Failure of Wq-7 Berth of Visakhapatnam PortDocument7 pagesFem Analysis of Anchored Sheet Pile Quay Wall: A Case Study On The Failure of Wq-7 Berth of Visakhapatnam Portbasum matNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Seismic Response of Soft-Storey Infilled FramesDocument25 pagesEvaluation of Seismic Response of Soft-Storey Infilled FramesMadhav PurohitNo ratings yet
- 39 42, Tesma110, IjeastDocument4 pages39 42, Tesma110, IjeastYirga BezabehNo ratings yet
- Haki Crack SeminarDocument62 pagesHaki Crack SeminarBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- CV. BassamDocument1 pageCV. BassamBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- Third Lecture Sight DistanceDocument11 pagesThird Lecture Sight DistanceBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- 00 1commandDocument56 pages00 1commandBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- LEE F 26-1 TYL İntibak Formu - ENGDocument2 pagesLEE F 26-1 TYL İntibak Formu - ENGBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- Bassam Wazir Bdaiwi BdaiwiDocument1 pageBassam Wazir Bdaiwi BdaiwiBassam WazirNo ratings yet
- Bassam Wazir Bdaiwi Bdaiwi (203724113)Document25 pagesBassam Wazir Bdaiwi Bdaiwi (203724113)Bassam WazirNo ratings yet
- A Fluid Mechanics Approach To The Labyrinth Seal Leakage ProblemDocument10 pagesA Fluid Mechanics Approach To The Labyrinth Seal Leakage ProblemandersonbritoNo ratings yet
- Temporary Sound Barrier System From Natural Fiber 2023 Materials Today ProDocument12 pagesTemporary Sound Barrier System From Natural Fiber 2023 Materials Today Prodeepali boradeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Bouyancy ForceDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 Bouyancy ForceSyamim HamizanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - II - Fundamental of 1-D Compressible FlowDocument92 pagesChapter - II - Fundamental of 1-D Compressible FlowshmyeNo ratings yet
- Targeting With Modified Equinoctial Orbital ElementsDocument4 pagesTargeting With Modified Equinoctial Orbital ElementsAnonymous REw1YIq4q7No ratings yet
- 10th Physics HB-1Document4 pages10th Physics HB-1Adeel adeelahmedNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Remoulded Shear Strength of Offshore Clays and Application To Pipeline-Soil and Riser-Soil InteractionDocument45 pagesEvaluation of The Remoulded Shear Strength of Offshore Clays and Application To Pipeline-Soil and Riser-Soil Interactionmarius_onoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 5Document54 pagesQuarter 2 Week 5rixzylicoqui.salcedoNo ratings yet
- CH 12 AaDocument9 pagesCH 12 Aafastidious_5No ratings yet
- Roba - DS: Your Reliable PartnerDocument80 pagesRoba - DS: Your Reliable PartnerFelySaezNo ratings yet
- TEST-6: Sub: Fluid Mechanics Module: 63-66Document2 pagesTEST-6: Sub: Fluid Mechanics Module: 63-66jhacademyhydNo ratings yet
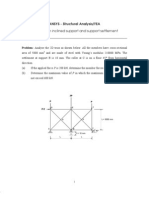
- MAK3172-3B Ex.2-Inclined Support TrussDocument7 pagesMAK3172-3B Ex.2-Inclined Support TrussHaydar SarpNo ratings yet
- Wave Maker Design and PreformanceDocument76 pagesWave Maker Design and PreformanceMohammed GamalNo ratings yet
- Recycled Miniature Car Equipped With CD Tape Wheels and Rubber BandDocument6 pagesRecycled Miniature Car Equipped With CD Tape Wheels and Rubber BandEdmark LuspeNo ratings yet
- NotchesDocument3 pagesNotchesnithansaNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Axially Loaded Concrete-Filled Circular Fiber-Reinforced Polymer TubesDocument10 pagesBehavior of Axially Loaded Concrete-Filled Circular Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Tubesflaco_astrozaNo ratings yet
- A4Document1 pageA4Kris CunninghamNo ratings yet
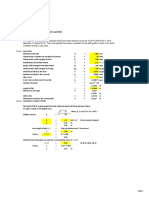
- 13920-COLUMN DESIGN ExcelDocument7 pages13920-COLUMN DESIGN Excelyedida viswanadhNo ratings yet
- HT Exp-3 Natural ConvectionDocument6 pagesHT Exp-3 Natural ConvectionRaj PratyushNo ratings yet
- Geodesic Analysis SampleDocument22 pagesGeodesic Analysis SampleSeaShell_6No ratings yet
- Deck Plate Check at Upper Deck: Proj No Calc No X Deck Plating CheckDocument2 pagesDeck Plate Check at Upper Deck: Proj No Calc No X Deck Plating Checkhk089No ratings yet
- How To Determine Motor CapacityDocument5 pagesHow To Determine Motor CapacityTushar MangratiNo ratings yet
- ProMax PipeDocument23 pagesProMax PipechenguofuNo ratings yet
- Brass AnnealingDocument11 pagesBrass AnnealingChristos KalavrytinosNo ratings yet
- Physics HSSC 1 Paper II-4Document16 pagesPhysics HSSC 1 Paper II-4Qudsia AbrarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Basic - KeypointsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Basic - KeypointsAjmal SheriffNo ratings yet