Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Task 7
Task 7
Uploaded by
Nesrine TitiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Task 7
Task 7
Uploaded by
Nesrine TitiCopyright:
Available Formats
The tiny and powerful transistor changed the future of electronics.
History
Following the works made on the semiconductors, the transistor was invented on December
23, 1947 by the Americans John Bardeen, William Shockley and Walter Brattain, researchers
of Bell Laboratories.
These researchers received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1956 for this invention. The
transistor is considered as a huge progress compared to the electron tube: much smaller,
lighter and more robust, working with low voltages, allowing a battery power supply, and it
works almost instantaneously once powered, unlike the electron tubes which required about
ten seconds of heating, generated a significant consumption and required a high voltage
source (several hundred volts).
several large-scale researches had been elaborated, allowing the development of more and
more diversified models of transistors, using not germanium but silicium instead.
The industrialization comes at the beginning of the 1950s, under the impulse of Norman
Krim, vice-president of Raytheon.
types
From the time of invention of the first transistor to the present day, transistors are classified
into different types depending either on their construction or their operation.
Junction transistor (BJT) Npn and pnp
Field effect transistor (FET) available in both N–Channel and P–Channel types.
Mofset available in depletion and enhancement types. Further, the depletion and
enhancement types are classified into N–Channel and P–Channel types.
Transistors are also classified depending on the functions (operations or applications) they
perform. We can find:
Small Signal Transistors
Small Switching Transistors
Power Transistors
High Frequency Transistors
Photo Transistor
Uni-Junction Transistors (UJT)
Principle
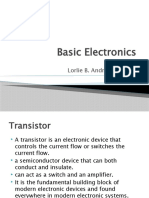
The transistor is the basic element of all electronic components starting from a small amplifier
to integrated circuits. it’s small in size and requires low energy for operation and also has low
power dissipation.
It is the meeting of two diodes, one is biased in direct and the other in reverse to ensure the
normal operation of the transistor.
It is called bipolar because the electrical conduction is achieved by the two types of charge
holders: electrons and holes. A static study is made to determine the type of type of operation
of the transistor from the position of the rest point. The dynamic study is characterized by four
parameters: the input and output impedance and the gain voltage and current gain. The values
of these quantities determine the characteristics of the transistor and consequently its
application.
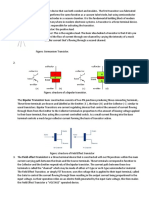
A transistor is made up of three pieces of semiconductor alternately doped "N or "P
The NPN transistor is symbolized by the outgoing emitter current and conversely for PNP
There are three operating states of a transistor:
On state
A current (modulated or fixed) on the Base (B) allows more or less current to pass
(which will also be modulated or fixed) between C and E.
Maximum saturation state (or clip)
Once it has reached its maximum, the transistor will act as a simple closed switch and will therefore
let the entire supply current to pass through it. It therefore acts as a switch.
Blocked state
If there is no current at the base (B), nothing passes through the transistor and it will act as an open
switch.
Application
As an amplifier
It can be used in long-distance communication because the intensity of the
signal obtained at the output will be high.
As switcher
Memory cards in mobile phones.
You might also like
- Explain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesExplain The Working of Fet With Neat Diagram and Relevant Characteristics. Indicate Each Region of The CharacteristicsS Dispiser100% (1)
- Transistor Unit 2Document5 pagesTransistor Unit 2DINESH SINGH100% (1)
- Transistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?Document7 pagesTransistor As Led Flasher: What Is A Transistor?study buddyNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Transistor DefinitionDocument30 pagesTransistors: Transistor DefinitionLaxman BabuNo ratings yet
- Transistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPDocument5 pagesTransistor: How Does It Work - NPN & PNPadeelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument2 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorAravind VinasNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument11 pagesBJTVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2Document16 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2leon saifullahNo ratings yet
- BEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendDocument5 pagesBEC Notes Lecture 11 by Ur Engineering FriendsupNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument25 pagesTransistorAdnan Hyder SoomroNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransistorDocument5 pagesWhat Is A TransistorSOMOSCONo ratings yet
- Module3 TransistorsDocument21 pagesModule3 Transistorsgreensun_auwrciScribdDBNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TransistorsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Transistorsdivya jessiNo ratings yet
- Asked By: Tony Whelan: Who Invented The Transistor? How Do Transistors Work?Document3 pagesAsked By: Tony Whelan: Who Invented The Transistor? How Do Transistors Work?samuelNo ratings yet
- NextechDocument15 pagesNextechNEXTECH ElectroicsNo ratings yet
- Transistor: by P.Sai SrivathsaDocument15 pagesTransistor: by P.Sai Srivathsak.saikumarNo ratings yet
- LT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Document5 pagesLT3A - 06 - Ayu Novita Anggraeni - English Script Topic 4 (AC Transistor)Ayu Novita AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- BJT PresentationDocument24 pagesBJT PresentationzakireceNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentBethelhem AshenafiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXDocument17 pagesElectronic Assignment Final 2.2 LNXleon saifullahNo ratings yet
- Adisa MujakDocument19 pagesAdisa MujakAmraSmajlovicNo ratings yet
- Electronics Presentation (Arish)Document7 pagesElectronics Presentation (Arish)Asif SheikhNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesThe Bipolar TransistorMohammed MushfiqurNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transistors and Their WorkingDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Transistors and Their WorkingVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Transistors: DiscussionDocument9 pagesTopic 3 Transistors: DiscussionEnitsuj Eam EugarbalNo ratings yet
- NPN TransistorDocument1 pageNPN TransistorsphinxNo ratings yet
- L1-Introduction To TransistorsDocument15 pagesL1-Introduction To TransistorsSadikielNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument3 pagesTransistorsSohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- LM II TransistorDocument53 pagesLM II TransistorMa. Fe TabbuNo ratings yet
- Example of TransistorsDocument12 pagesExample of TransistorslathageethaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument35 pagesSemiconductor DevicesRacknarockNo ratings yet
- TRANSISTORDocument60 pagesTRANSISTORNaty SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsDocument4 pagesBasic Electronics Final Project: Submitted by Group Members Submitted To Date of Submission Grade/ PointsMahnam Nasir Nasir NaeemNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument15 pagesTransistorTêrrã MäûttNo ratings yet
- Chương 4 - EnglishDocument26 pagesChương 4 - Englishquan leNo ratings yet
- BJT ConstructionDocument3 pagesBJT ConstructionRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronics I CH 3 BJT Lecture 1 W3L3Document14 pagesElectronics I CH 3 BJT Lecture 1 W3L3ladikapubg6420No ratings yet
- Transistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Document8 pagesTransistor: Name: Gita Setyani Putri Class: LT 3E Number: 12Fariz Aditya PutraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3bjt. Presentation of Lositomonique A. Bsece 2cDocument14 pagesChapter 3bjt. Presentation of Lositomonique A. Bsece 2cNathaniel BarnidoNo ratings yet
- Practical 6Document11 pagesPractical 6Purva PatelNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument25 pagesAbebeAnteneh AbebeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Modul 3Document10 pagesJurnal Modul 3Dasiah RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Introduction BJTDocument3 pages2.1 Introduction BJTlizhi0007No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorSummer WangNo ratings yet
- L4 Basic-ElectronicsDocument16 pagesL4 Basic-Electronicstheo dominic silvosaNo ratings yet
- Ewp 5Document12 pagesEwp 5Aakansha PaunikarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3AdsbymeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Module 1Document26 pagesElectronic Devices Module 1Nick WonkaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument3 pagesBipolar TransistorAndrei Josef NizaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Transistors: Presented byDocument19 pagesPresentation On Transistors: Presented byMonith ElyonNo ratings yet
- RB6802B35Document25 pagesRB6802B35MishtiNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesAnalog Electronics Viva Questions2K19/EC/005 AASTIKNo ratings yet
- Bilj Ti T It Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) (BJT) : Sub Title: Transistor Characteristics Transistor CharacteristicsDocument21 pagesBilj Ti T It Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) (BJT) : Sub Title: Transistor Characteristics Transistor CharacteristicsKrisna Adji SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Transistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiDocument15 pagesTransistors Question and Answers Doc by PranghiPRANGHI80% (10)
- BM - Physics 2Document36 pagesBM - Physics 2Rishabh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Topic 1) Transistors: Marks 24: IntroductionDocument24 pagesTopic 1) Transistors: Marks 24: IntroductionSudershan Dolli100% (1)
- TransistorsDocument44 pagesTransistorsramil.bocaNo ratings yet
- Task 03Document4 pagesTask 03Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Task 08Document2 pagesTask 08Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Video: Two Strangers Who Meet Five Times' LinkDocument8 pagesVideo: Two Strangers Who Meet Five Times' LinkNesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Task 04 AstronomyDocument2 pagesTask 04 AstronomyNesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Y&R July 05 2016Document14 pagesY&R July 05 2016Nesrine TitiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: NPN Switching TransistorDocument8 pagesData Sheet: NPN Switching TransistorJoao JesusNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - HK md7133h 7759585Document10 pagesDatasheet - HK md7133h 7759585suriantoNo ratings yet
- Project File OF Physics: Logic Gates Combination For A Given Truth TableDocument28 pagesProject File OF Physics: Logic Gates Combination For A Given Truth Tableritesh chauhanNo ratings yet
- Ee212 Lab 4Document8 pagesEe212 Lab 4Hilda SiaNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument28 pagesMOSFETBck SreedharNo ratings yet
- Iot Based SriprasannaaDocument23 pagesIot Based Sriprasannaasriprasannaa pNo ratings yet
- LF356, LF398, LM135, LM358: Application Note 292 Applications of The LM3524 Pulse-Width-ModulatorDocument8 pagesLF356, LF398, LM135, LM358: Application Note 292 Applications of The LM3524 Pulse-Width-ModulatorM Usman RiazNo ratings yet
- Ece 56 Sem 17Document85 pagesEce 56 Sem 17Chaithra LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 30f124 330v 220a Canal NDocument7 pagesMosfet 30f124 330v 220a Canal NEdisson Alarcon MoraNo ratings yet
- CSD Syllabus StructureDocument174 pagesCSD Syllabus StructureTaqi ShahNo ratings yet
- Standards 22 Nanometers Technology Backgrounder PDFDocument2 pagesStandards 22 Nanometers Technology Backgrounder PDFajith.ganesh2420No ratings yet
- KDL-40R455A, Sony TV Service Manual-77704 PDFDocument40 pagesKDL-40R455A, Sony TV Service Manual-77704 PDFcesar meriño100% (3)
- Low Noise Power Amplifier Circuit Design For 5Ghz To 6 GHZDocument4 pagesLow Noise Power Amplifier Circuit Design For 5Ghz To 6 GHZisma8070% (1)
- Sem3 EE EEEDocument12 pagesSem3 EE EEEGpc JaisalmerNo ratings yet
- GATE 2009 ECE Question PaperDocument16 pagesGATE 2009 ECE Question PaperLamont Wright100% (1)
- 16 FDocument10 pages16 Fbebeto90No ratings yet
- Power Supply Design Notes Zener Diode Voltage Regulator - Power Electronics News 1632736156073Document9 pagesPower Supply Design Notes Zener Diode Voltage Regulator - Power Electronics News 1632736156073Brian KoechNo ratings yet
- Micro Electronics CicuitsDocument4 pagesMicro Electronics Cicuitsbalajibs203285No ratings yet
- Amplifier Classes ExplainedDocument8 pagesAmplifier Classes ExplainedAehtsham Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Short Channel Effects and ScalingDocument23 pagesShort Channel Effects and ScalingskarthikpriyaNo ratings yet
- Zvn3320astz PDFDocument96 pagesZvn3320astz PDFyako1511No ratings yet
- Gcse Tech Support 4937Document58 pagesGcse Tech Support 4937AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 2n3866 SeriesDocument3 pages2n3866 Seriessas999333No ratings yet
- Night Security LightDocument30 pagesNight Security LightCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- Ec8252 SyllabusDocument1 pageEc8252 SyllabusSarika AyyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Optocoupler Design GuideDocument69 pagesOptocoupler Design Guidescribd_20_emmanuelfaure100% (1)
- Syllabus-BSc Electronics PDFDocument199 pagesSyllabus-BSc Electronics PDFJacob AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Mbs Public School: Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesMbs Public School: Physics ProjectSwaraj PatelNo ratings yet
- RA33H1516M1Document8 pagesRA33H1516M1Napo BereNo ratings yet
- Nano ComputersDocument37 pagesNano Computersrajashekarpula100% (2)