Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12
CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12
Uploaded by
Andro Romano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageCellular respiration requires oxygen to produce ATP through the electron transport chain. It involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and produces a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down the products of glycolysis and generates more ATP and reduced cofactors. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the reduced cofactors to power ATP synthesis, producing the majority of ATP. Without oxygen, fermentation allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD+ through other pathways, but yields much less ATP than aerobic respiration.
Original Description:
Original Title
CN in EARTH ANF LIFE- 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCellular respiration requires oxygen to produce ATP through the electron transport chain. It involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and produces a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down the products of glycolysis and generates more ATP and reduced cofactors. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the reduced cofactors to power ATP synthesis, producing the majority of ATP. Without oxygen, fermentation allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD+ through other pathways, but yields much less ATP than aerobic respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageCN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12
CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12
Uploaded by
Andro RomanoCellular respiration requires oxygen to produce ATP through the electron transport chain. It involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose and produces a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further breaks down the products of glycolysis and generates more ATP and reduced cofactors. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the reduced cofactors to power ATP synthesis, producing the majority of ATP. Without oxygen, fermentation allows glycolysis to continue by regenerating NAD+ through other pathways, but yields much less ATP than aerobic respiration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
CONCEPT NOTE IN EARTH Anaerobic respiration is SUMMARY (DIAGRAM) OF
SCIENCE similar to aerobic respiration CELLULAR RESPIRATION
NAME: DATE: but consumes compounds Most cellular respiration
TRAND/SEC: RATING: other than O2. requires O2 to produce ATP.
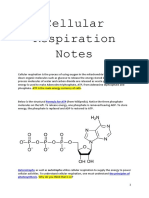
Equation of cellular respiration: Without O2, the electron
I. TOPIC: BIOENERGETICS: transport chain will cease to
UTILIZATION OF ENERGY Reactants: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 operate.
Products: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy In that case, glycolysis
II. OBJECTIVES: (ATP + heat) couples with fermentation or
1. Enumerate the stages of anaerobic respiration to
cellular respiration; The Principle of Redox Process produce ATP.
2. Identify the requirements and During cellular respiration, the fuel
products of each stage in the (such as glucose TYPES OF FERMENTATION
process of breakdown of (C6H12O6) is oxidized, and O2 is Fermentation consists of
molecules from glucose to reduced. glycolysis plus reactions that
carbon dioxide and water; Oxidation – loses electron Reduction – regenerate NAD+, which can
3. Explain the major stages of gains electron be reused by glycolysis.
cellular respiration; Two common types are
4. Discuss how ATP is used by THE STAGES OF CELLULAR alcohol fermentation and
cells; RESPIRATION lactic fermentation.
5. Describe the relationship of Harvesting of energy from glucose has In alcohol fermentation,
photosynthesis and cellular three stages: pyruvate is converted to
respiration. 1. Glycolysis is the breakdown of ethanol in two steps, with the
III. CONCEPT: glucose to pyruvate where small first releasing CO2.
amounts of ATP are produced. This Alcohol fermentation by yeast
Living cells require energy process occurs in the cytoplasm of the is used in brewing,
from outside sources. cell. winemaking, and baking.
Some animals, such as the Before the citric acid cycle In lactic acid fermentation,
chimpanzee, obtain energy by can begin, pyruvate must be pyruvate is reduced to NADH,
eating plants, and some converted to acetyl forming lactate as an end
animals feed on other Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA), product, with no release of
organisms that eat plants. which links glycolysis to the CO2.
Energy flows into an citric acid cycle. Lactic acid fermentation by
ecosystem as sunlight and 2. The Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle some fungi and bacteria is
leaves as heat. degrades pyruvate to carbon dioxide, used to make cheese and
Photosynthesis generates O2 water, ATP and reducing power in the yogurt.
and organic molecules, which form of NADH, H+. This stage happens Human muscle cells use lactic
are used in cellular in the matrix of the mitochondria. acid fermentation to generate
respiration. 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation which ATP when O2 is scarce.
Cells use chemical energy includes electron transport chain and
stored in organic molecules to chemiosmosis generates high amounts Guide Questions
regenerate ATP, which of ATP, because it is powered by redox 1. How can we utilize energy or
powers work. reactions. This stage occurs in the make it something useful?
Cellular Respiration is a process of inner membrane of the mitochondria. 2. Explain the Krebs cycle
releasing energy stored in sugar in the Oxidative phosphorylation 3. What are the stages of
presence of oxygen. accounts for almost 90% of cellular respiration? State and
Cellular respiration includes the ATP generated by cellular explain.
both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
respiration but is often used to For each molecule of glucose
refer to aerobic respiration. degraded to CO2 and water
Aerobic respiration consumes by respiration, the cell makes
organic molecules and O2 up to 32 molecules of ATP.
and yields ATP
You might also like
- Ebook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument32 pagesEbook Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9Th Edition Taylor Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtristandoyledtnpkozbgj100% (16)
- Cellular Respiration Doodle NotesDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Doodle NotesGrace WalkerNo ratings yet
- 03 - Metabolisme Protein - MonogastrikDocument25 pages03 - Metabolisme Protein - MonogastrikHerni Bustam100% (1)
- Biology RespirationDocument20 pagesBiology Respirationhafizah_90100% (2)
- Lesson 2 Group 1Document7 pagesLesson 2 Group 1Zyreine MenoriasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 ScienceDocument4 pagesWeek 7 ScienceKaru GreyNo ratings yet
- CellRespi 2Document21 pagesCellRespi 2Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular RespirationMohammedNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration - 1 THDocument12 pagesCellular - Respiration - 1 THarin.mekan1985No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy: Chapter ObjectivesDocument12 pagesHow Cells Harvest Chemical Energy: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadDocument9 pagesBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 13th Edition Starr Solutions Manual DownloadGraham Hissem100% (24)
- BIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Document39 pagesBIO20 Cell Resp Teacher Notes 2020Shariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis CR WKS KEY 28dnwi2Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis CR WKS KEY 28dnwi2Raye Shyn AsiloNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument6 pagesRespiration in Plants-NotesAnirudh KhannaNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration:: Write The Equation For Respiration One Time in Your Notes (To Learn It-Write 10x)Document36 pagesCellular Respiration:: Write The Equation For Respiration One Time in Your Notes (To Learn It-Write 10x)Clark GabutenNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 8 and 9Document31 pagesBiology CH 8 and 9Ann QuiranteNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument49 pagesCellular RespirationJohn Paul RoaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23Document13 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 - Respiration in Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNo ratings yet
- Activity Modeling Cell RespirationDocument3 pagesActivity Modeling Cell RespirationWendy RatliffNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- 8 3Document22 pages8 3lianneNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonDocument6 pagesLesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonMarielle RamosNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesCampbell Biology Concepts and Connections 9th Edition Taylor Solutions Manualkevinrodriguezcnytfpaskx100% (26)
- Chapter 5 Cellular Respiration and FermentationDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Cellular Respiration and Fermentationbm-3272No ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Periodic Term III NotesDocument22 pagesPeriodic Term III Notessm2524363No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Basic Features of Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Basic Features of Photosynthesis and RespirationangelNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesCellular RespirationJunjun GwapoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology PracDocument6 pagesBiotechnology PracNathan ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationDocument2 pagesC6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1Document50 pagesQuarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1champimiloNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDocument13 pagesJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Group1Document53 pagesCellular Respiration Group1Erline Suzette GabrielNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsHafiz HussainNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration and FermentationDocument18 pagesAnaerobic Respiration and FermentationSean Nixter BallestraNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson l44Document48 pagesScience Daily Lesson l44Audie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- PHMP Topic 2Document8 pagesPHMP Topic 2yhcaesthetic proNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsDocument7 pages3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsJanine Abiegale PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument29 pagesRespiration in PlantsJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerDocument2 pagesMid-Term Review Sheet John FarmerJohn FarmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 RespirationDocument5 pagesChapter 12 RespirationKai TongNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument36 pagesCellular RespirationWillow ItchiroNo ratings yet
- GB 1 NotesDocument10 pagesGB 1 Notesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 8.1 Cellular RespirationDocument7 pagesMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 8.1 Cellular Respirationapi-455371000No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- Bio Lesson 21 RespiDocument48 pagesBio Lesson 21 RespiChlzy ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cellular RespirationDocument25 pagesSummary of Cellular RespirationHeric ValdemoroNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and PhotorespirationDocument29 pagesRespiration and PhotorespirationThảo UyênNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Tennis Ball LabDocument5 pagesAnaerobic Tennis Ball Labapi-30432692050% (2)
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 2Document14 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 2Saroja Veeresh100% (2)
- B.sc. (H) Biochemistry 3rd Semester 2019Document17 pagesB.sc. (H) Biochemistry 3rd Semester 2019bhartikumari121003No ratings yet
- Grade 9-ScienceDocument4 pagesGrade 9-ScienceMark Anthony Telan PitogoNo ratings yet
- Sas 9Document14 pagesSas 9Reizel GaasNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - GizmoCellEnergySE A & BDocument5 pagesKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - GizmoCellEnergySE A & BALEXA CADENANo ratings yet
- Ba400 Hasil PemeriksaanDocument55 pagesBa400 Hasil PemeriksaanLabor PrimaNo ratings yet
- WHLP Gen Bio 2 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesWHLP Gen Bio 2 2nd QuarterSir JoshNo ratings yet
- Exam Bio-Organic Chemistry (8S140) Thursday November 23, 2008 14.00-17.00 H This Exam Consists of 7 Questions. Explain Your Answers Clearly. Answers May Be Given in English or DutchDocument5 pagesExam Bio-Organic Chemistry (8S140) Thursday November 23, 2008 14.00-17.00 H This Exam Consists of 7 Questions. Explain Your Answers Clearly. Answers May Be Given in English or DutchSergeyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - WikipediaDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis - Wikipediaمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument11 pagesChapter 7 - Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and Protistsyudi prakasaNo ratings yet
- Question PapersDocument3 pagesQuestion PapersAbdullah TegginmaniNo ratings yet
- By: DR Elfatih Yagoub AliDocument24 pagesBy: DR Elfatih Yagoub AliAbdulrhManNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Si Worksheet 10Document5 pagesAnswer Key Si Worksheet 10Jersey BarquillaNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument2 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayGianneCarloGomedNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Model Question PaperDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Model Question PaperRAMSUREMAN PATEL20% (5)
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDocument1 pageGlycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism & ReapirationDocument9 pagesCellular Metabolism & ReapirationAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.2 PhotosynthesisPamela MalihanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 LipidsDocument43 pagesChapter 21 Lipidsdaoud sarrawyNo ratings yet
- Liver Metabolism: Liver Is The Chief Metabolic Organ of Our BodyDocument123 pagesLiver Metabolism: Liver Is The Chief Metabolic Organ of Our Bodymex Gbrekorkos100% (1)
- Carbohydrate, Protein and Lipid Metabolism-B.NDocument77 pagesCarbohydrate, Protein and Lipid Metabolism-B.NBusy worldNo ratings yet
- The Emerging Role and Targetability of The TCA Cycle in Cancer Metabolism PDFDocument22 pagesThe Emerging Role and Targetability of The TCA Cycle in Cancer Metabolism PDFMilagros Levano SanchezNo ratings yet
- Testbank Chapter 10Document44 pagesTestbank Chapter 10Fiona SimeonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMDocument20 pagesReviewer For General Biology (Mitosis, Meiosis, Etc.) : Grade 11 STEMYanni SerenoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism All LecturesDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism All Lecturesmizare29gNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Classifieds Final 2023 (2) 2Document11 pagesUnit 5 Classifieds Final 2023 (2) 2MNRNo ratings yet