Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks Router
Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks Router
Uploaded by
Nishil VijayanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks Router
Star Topology: Types of Network Topologies Ethernet Local Area Networks Router
Uploaded by
Nishil VijayanCopyright:
Available Formats
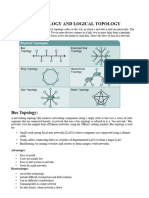
STAR TOPOLOGY
Star topology, also known as star network, is a computer network topology. It is a common
network setup where the computers and other devices on the network are connected to a central
or master computer, also known as the hub. The star topology, which is one of the types of
network topologies, got its name because the connections of the computers resemble a star. The
hub, along with the leaf nodes and the transmission lines connecting them form the topology of a
star. The star topology is used mostly in Ethernet and Local Area Networks (LAN). After
installation the star topology resembles the spokes of a bicycle wheel. The cabling segments of
the topology meet at a central connection point which is known as a router or switch. Each host
or computer is connected to the central device or hub with the help of cables that transmit data.
An extended star topology is a star network that is expanded and an additional networking device
is connected to the central or main networking device.
The active star network or star topology has an active central node which prevents problems
related to echoes created during transmissions. But in a passive central node, the initial or
originating central node should be able to bear up the echoes created during the receptions of the
transmission. There is also a delay caused due to a two way transmission. The chances of a
failure in the network is reduced when all the systems are connected to the central node. The star
topology can also be applied to a bus network. A bus network or bus topology is a central hub
which broadcasts transmissions that is received from a peripheral mode to the rest of the
peripheral modes that are connected to the network, including the central node. If there is a
failure in the transmission in any peripheral node to the originating node, then that peripheral is
isolated without affecting the rest of the system. A node consists of workstations, peripherals and
file servers that are connected directly to the network hub. The data on the star topology is
transmitted through the hub before it reaches its destination. The central hub controls all the
functions and transmissions of the networks that are connected to it. The configuration of the star
topology is done with the help of optical fiber cable, twisted pair cable or a coaxial cable. There
are many star topology advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a look at the advantages and
disadvantages of a star topology separately.
Advantages of Star Topology
A star topology has many advantages. Some of the advantages of a properly functioning star
topology are listed below;
The star topology is easy to install and wire.
The star topology gives a better performance than any other network topology as there is
no clogging of nodes. In order to communicate between any two devices only 2 links and
3 devices are involved to prevent confusion. The hub also has adequate capacity to
handle high utilization by one device, without disrupting the functioning of the other
devices.
The working of the star topology is simple to establish, understand and navigate. Any
fault in the devices connected to the central hub can be detected easily as the
malfunctioned device or link is isolated, which allows easy probing into the matter.
The faulty and defective parts of the network can be easily replaced. Till the links are
replaced, the other devices continue their normal functions without any disruptions.
Expansion of the star topology is easy as the format is very simple thus aiding the growth
of networking.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
One of the main disadvantages of the star topology is that if the central hub has some errors, then
the communication between the systems fail, as the nodes are highly dependent on the proper
functioning of the central hub. There is a limit to the number of networks that can be connected
to the hub and the performance of the entire computer network is monitored by its throughput.
The traffic of the network is also disrupted if the node that occupies a major portion in the
processing capability of the central node is faulty. The star topology is one of the costliest
network topologies and the wiring of the system is a complex process.
Advantages
Better performance: star topology prevents the passing of data packets through an
excessive number of nodes. At most, 3 devices and 2 links are involved in any
communication between any two devices. Although this topology places a huge overhead
on the central hub, with adequate capacity, the hub can handle very high utilization by
one device without affecting others.
Isolation of devices: Each device is inherently isolated by the link that connects it to the
hub. This makes the isolation of individual devices straightforward and amounts to
disconnecting each device from the others. This isolation also prevents any non-
centralized failure from affecting the network.
Benefits from centralization: As the central hub is the bottleneck, increasing its
capacity, or connecting additional devices to it, increases the size of the network very
easily. Centralization also allows the inspection of traffic through the network. This
facilitates analysis of the traffic and detection of suspicious behavior.
Simplicity: This topology is easy to understand, establish, and navigate. Its simplicity
obviates the need for complex routing or message passing protocols. Also, as noted
earlier, the isolation and centralization it allows simplify fault detection, as each link or
device can be probed individually.
Easy to install and wire.
Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
[edit] Disadvantages
High dependence of the system on the functioning of the central hub
Failure of the central hub renders the network inoperable
The performance and scalability of the network depends on the capabilities of the hub
Network size is limited by the number of connections that can be made to the hub
Other nodes may see a performance drop if traffic to another node occupies a significant
portion of the central node's processing capability or throughput.
Wiring up of the system can be very expensive.
BUS
Advantages:
Failure of one of the station does not affect others.
Good compromise over the other two topologies as it allows relatively high rate of data
tansmittion.
Well suited for temporary networks that must be set up in a hurry.
Easy to implement and extend.
Disadvantage:
Require a network to detect when two nodes are transmitting at the same time.
Does not cope well with heavy traffic rates
Difficult to administer/troubleshoot.
Limited cable length and number of stations.
A cable brake can disable the entire network; no redundancy.
Maintenance cost may be higher in the long run.
Performance degrade as additional computers are added.
Advantages
Easy to implement and extend.
Easy to install.
Well-suited for temporary or small networks not requiring high speeds (quick setup), resulting in
faster networks.
Cheaper than other topologies (But in recent years has became less important due to devices
like a switch)
Cost effective; only a single cable is used.
Easy identification of cable faults.
Reduced weight due to fewer wires.
[edit] Disadvantages
Limited cable length and number of stations.
If there is a problem with the cable, the entire network breaks down.
Maintenance costs may be higher in the long run.
Performance degrades as additional computers are added or on heavy traffic (shared
bandwidth).
Proper termination is required (loop must be in closed path).
Significant Capacitive Load (each bus transaction must be able to stretch to most distant link).
It works best with limited number of nodes.
Commonly has a slower data transfer rate than other topologies.
Only one packet can remain on the bus during one clock pulse.
You might also like
- BeneHeart D6 Service Manual V8.0 enDocument168 pagesBeneHeart D6 Service Manual V8.0 en77robert71% (7)
- Cell Phone Jammer DataDocument3 pagesCell Phone Jammer DataGrzesiek DobrowolskiNo ratings yet
- R. G. Meadows (Auth.) - Electrical Communications - Theory, Worked Examples and Problems-Macmillan Education UK (1976)Document186 pagesR. G. Meadows (Auth.) - Electrical Communications - Theory, Worked Examples and Problems-Macmillan Education UK (1976)Laz GsodfjxNo ratings yet
- Bus TopologyDocument6 pagesBus Topologylea_eazeNo ratings yet
- Group Number:-3: Team Mates NamesDocument41 pagesGroup Number:-3: Team Mates NamesManish GautamNo ratings yet
- Star Topology LabDocument3 pagesStar Topology LabBint e Farooq100% (1)
- Network Topologies: and Its TypesDocument19 pagesNetwork Topologies: and Its TypesJeff Clifford LuyahanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3 3api-236083981No ratings yet
- Holiday HomeworkDocument22 pagesHoliday Homeworkh2462915No ratings yet
- Physical Topology and Logical TopologyDocument3 pagesPhysical Topology and Logical TopologyNO NameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04Document3 pagesLecture 04Rabeeah ZakiNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 pagesNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNo ratings yet
- Network Systems & Protocols: Task 1Document12 pagesNetwork Systems & Protocols: Task 1qwerty2711No ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument22 pagesComputer Projecth2462915No ratings yet
- TopologyDocument11 pagesTopologyAdilet KenesovNo ratings yet
- Network Topology: Presented by Susanta MaharanaDocument18 pagesNetwork Topology: Presented by Susanta Maharanasanyasi mahakhudNo ratings yet
- What Is Topology or Network Topology?Document25 pagesWhat Is Topology or Network Topology?Mimi Rubia AvilaNo ratings yet
- Topology StarDocument3 pagesTopology StarSyafiq FauziNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Network TypologiesDocument6 pagesDifference Between Network Typologiesشمیم نازNo ratings yet
- Star TopologyDocument7 pagesStar TopologyadelenyamhuriNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Network Technology: M.S Raza MohamedDocument8 pagesNetwork Technology: M.S Raza Mohamedrazamohamed1No ratings yet
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathNo ratings yet
- Net 101Document24 pagesNet 101Ed JullezaNo ratings yet
- Network Topology 1Document10 pagesNetwork Topology 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- A Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and ResourceDocument7 pagesA Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and Resource2nablsNo ratings yet
- CN - Assignment2Document14 pagesCN - Assignment2WhatsApp statusNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture FileDocument49 pagesComputer Architecture FileFunsuk VangduNo ratings yet
- Topology Networks g10Document6 pagesTopology Networks g10Julie BinwagNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument10 pagesNetwork Topologyvickroid007No ratings yet
- What Is Network TopologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Network TopologyGoldy BatraNo ratings yet
- Network Topology in Modern NetworkingDocument5 pagesNetwork Topology in Modern NetworkingkksancyNo ratings yet
- MemunaDocument6 pagesMemunajallohadrahNo ratings yet
- 173462129-Atikur Rahman PDFDocument3 pages173462129-Atikur Rahman PDFAtikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologiesraidenNo ratings yet
- DCC NotesDocument15 pagesDCC NotesOm SutarNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument6 pagesNetwork TopologiesTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Basic NetworkingDocument8 pagesBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaNo ratings yet
- 89492NW TopologiesDocument25 pages89492NW TopologiesAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument10 pagesNetwork TopologyLegese TusseNo ratings yet
- Bus Topology: Carrier Sense Multiple Access BusDocument9 pagesBus Topology: Carrier Sense Multiple Access Busbassy10No ratings yet
- TopologyDocument2 pagesTopologyMuhammad OwaisNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogNo ratings yet
- Advantages of A Linear Bus TopologyDocument5 pagesAdvantages of A Linear Bus Topologynirav4042No ratings yet
- 02 TopologyDocument4 pages02 TopologyHailay HadushNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesNetwork Topology DiagramSatvik SalatNo ratings yet
- HCSI35 Assignment Network TopologiesDocument10 pagesHCSI35 Assignment Network TopologiesDonNo ratings yet
- Topology: Chapter - 5Document12 pagesTopology: Chapter - 5RoopaNo ratings yet
- Networking Is The Practice of Connecting Multiple Devices and Computers Together in Order To Share Resources and Communicate With Each OtherDocument3 pagesNetworking Is The Practice of Connecting Multiple Devices and Computers Together in Order To Share Resources and Communicate With Each Othermumo dannNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Computer ActivityDocument28 pagesClass 10 Computer ActivityAshmita ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies GalizaDocument7 pagesNetwork Topologies GalizaGabriel GalizaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Types of Topologies 1487157223 247536Document9 pagesPresentation Types of Topologies 1487157223 247536Priyam TripathiNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument17 pagesNetwork TopologyAanchal AhirwarNo ratings yet
- CN LAB FileDocument58 pagesCN LAB FileHEERAJNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument10 pagesTopologyAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Toplogys1Document9 pagesComputer Networks Toplogys1ammapetNo ratings yet
- Networking AssignmentDocument15 pagesNetworking AssignmentabcdNo ratings yet
- Bus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally UseDocument4 pagesBus Topology: Topology. Organizations Using This Type of Topology Will Generally Usehadi fASIALNo ratings yet
- Practical 1Document24 pagesPractical 1harishpillai1994No ratings yet
- TopologiesDocument5 pagesTopologiesapi-311676328No ratings yet
- Star Based Bus TopologyDocument5 pagesStar Based Bus TopologyGautamkrishna ChintaNo ratings yet
- Network Topology - Computer System ServicingDocument39 pagesNetwork Topology - Computer System ServicingVhon Xander [Personal Channel]No ratings yet
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingFrom EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Circuit ComponentsDocument48 pagesBasic Electronic Circuit ComponentsMinh LeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Exam 6Document5 pagesPeriodic Exam 6Inah RamosNo ratings yet
- Understanding LVDS For Digital Test Systems: Publish Date: Jul 27, 2012Document5 pagesUnderstanding LVDS For Digital Test Systems: Publish Date: Jul 27, 2012RinaldyNo ratings yet
- MagicSoft Playout Help PDFDocument29 pagesMagicSoft Playout Help PDFamourNo ratings yet
- Report EC101Document15 pagesReport EC101Rohan HaveriNo ratings yet
- Instruction Level ParallelismDocument2 pagesInstruction Level ParallelismRam1028No ratings yet
- Scope & Topics: ISSN: 2249 - 0175 (Online) 2249 - 2682 (Print)Document2 pagesScope & Topics: ISSN: 2249 - 0175 (Online) 2249 - 2682 (Print)ijansjournalNo ratings yet
- Display 7 SegmentosDocument1 pageDisplay 7 SegmentosrobertoNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: VS-606V7 SeriesDocument166 pagesInstruction Manual: VS-606V7 Seriesmax_ingNo ratings yet
- ntmd4n03r2 DDocument10 pagesntmd4n03r2 DKyaw ThuNo ratings yet
- Design of A Substrate Integrated WaveguideDocument3 pagesDesign of A Substrate Integrated WaveguideAlgerian AissaouiNo ratings yet
- RT8206 PDFDocument26 pagesRT8206 PDFgersonrlopesNo ratings yet
- Bazooka W2DU 1Document5 pagesBazooka W2DU 1ChasNo ratings yet
- CV338H-X42 Schematic DiagramDocument21 pagesCV338H-X42 Schematic Diagramnelson100% (2)
- Ip Over DMDWDocument19 pagesIp Over DMDWammezzNo ratings yet
- Panasonic PC Programming ManualDocument854 pagesPanasonic PC Programming ManualPenta GuardNo ratings yet
- Chap - 05-Digital Hardware ImplementationDocument20 pagesChap - 05-Digital Hardware Implementationcharbelkhalil05No ratings yet
- DSP Lab 10Document17 pagesDSP Lab 10Mo RoseNo ratings yet
- Peregrine AML STC KT74Document184 pagesPeregrine AML STC KT74AeromechanixNo ratings yet
- EE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduDocument32 pagesEE 466/586 VLSI Design: School of EECS Washington State University Pande@eecs - Wsu.eduPhạm Đức ThuậnNo ratings yet
- Katalog Kostek ETKA VWDocument22 pagesKatalog Kostek ETKA VWGregor KomNo ratings yet
- Comba Odi 065R17M18JJ G PDFDocument4 pagesComba Odi 065R17M18JJ G PDFMario RojasNo ratings yet
- FARUM POLAND - Versions of The ECGDocument1 pageFARUM POLAND - Versions of The ECGMarin R.No ratings yet
- InTech-Autonomous Inspection Robot For Power Transmission Lines Maintenance While Operating On The Overhead Ground WiresDocument6 pagesInTech-Autonomous Inspection Robot For Power Transmission Lines Maintenance While Operating On The Overhead Ground WireslucasmqsNo ratings yet
- Chapter One1Document29 pagesChapter One1مسلم محمودNo ratings yet
- Txw102 PC ArchitectureDocument62 pagesTxw102 PC ArchitectureRaulE.GarciaSorianoNo ratings yet
- Bcp-Bcpwe-1550-Yzb-Cw Series High-Pobcpwer 1550Nm Fiber Amplifier Manual With Pon PortDocument6 pagesBcp-Bcpwe-1550-Yzb-Cw Series High-Pobcpwer 1550Nm Fiber Amplifier Manual With Pon PortAntonio ChambergoNo ratings yet