Professional Documents
Culture Documents
27 Regulation of Body Temperature: Check Your Progress
27 Regulation of Body Temperature: Check Your Progress
Uploaded by
steve LOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
27 Regulation of Body Temperature: Check Your Progress
27 Regulation of Body Temperature: Check Your Progress
Uploaded by
steve LCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE Biology – a modern approach 5
Suggested answers to coursebook exercises
27 Regulation of Body Temperature
Check your progress
27.1 Regulation of body temperature
True or false
1. F
2. T
3. T
4. F (1 mark each)
(Total: 4 marks)
27.2 The skin and body temperature regulation
A. Matching
1. E
2. G
3. H
4. I
5. D
6. C
7. B
8. F
9. J
10. A (1 mark each)
(Total: 10 marks)
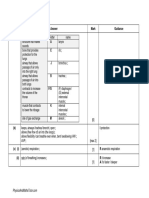
B. Fill in the blanks
When it is hot When it is cold
1. hairs (lie flat/raised) lie flat raised
2. erector muscles
relax contract
(relax/contract)
3. arterioles near the skin surface
dilate constrict
(dilate/constrict)
© 2010 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 1
HKDSE Biology – a modern approach 5
Suggested answers to coursebook exercises
4. sweating (increases/decreases) increases decreases
(1/2 mark each)
(Total: 4 marks)
27.3 Muscles and heat production
27.4 Hormonal control of body temperature
Multiple choice
1. B
2. D
3. B (1 mark each)
(Total: 3 marks)
27.5 The hypothalamus as the regulatory centre
27.6 Behavioural control of body temperature
Multiple choice
1. D
2. A
3. B
4. C (1 mark each)
(Total: 4 marks)
© 2010 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 2
HKDSE Biology – a modern approach 5
Suggested answers to coursebook exercises
Revision Exercise
Structured questions
1. (a) layer X: epidermis (1 mark)
layer Y: dermis (1 mark)
(b) Any two of the following: (2 marks)
- It provides physical protection / prevents invasion of pathogens / prevents water loss.
- It produces vitamin D.
- It provides camouflage / protective colour.
(c) Structure C contracts (1 mark)
and pulls the base of structure A which therefore becomes erect. (1 mark)
A thicker layer of air is trapped among structure A. (1 mark)
As a result, less heat is lost from the skin. (1 mark)
(d) structure D (1 mark)
When the air temperature is higher than the body temperature, the body can only lose
heat to the surroundings by the evaporation of sweat. (1 mark)
but not by radiation and conduction when it is against the temperature gradient.
(1 mark)
(Total: 11 marks)
2. (a) rate of oxygen consumption / carbon dioxide production / heat loss (1 mark)
(b) The metabolic rate increases. (1 mark)
This is because when the air temperature decreases from 30ºC to 25ºC, the rate of heat
loss from the body / skin increases. (1 mark)
Increase in metabolic rate helps maintain the body temperature constant / compensates
the increase in heat loss. (1 mark)
(c) Sweating increases (1 mark)
so that more heat can be lost from the skin by the evaporation of sweat. (1 mark)
Vasodilation occurs / Arterioles in the skin dilates (1 mark)
so that more blood flows through the capillaries near the skin surface and more heat
can be lost by conduction and radiation. (1 mark)
(d) This is because heat loss by conduction and radiation could not occur from 37ºC to
40ºC /against temperature gradient. (1 mark)
In addition, the water heat lost by the evaporation of sweat would be reduced
significantly when the relative humidity rose to 99%. (1 mark)
As a result, the body would be over-heated / enzymes in the body would be denatured.
(1 mark)
(Total: 11 marks)
© 2010 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 3
HKDSE Biology – a modern approach 5
Suggested answers to coursebook exercises
3. (a) Both the rate of sweating and rate of blood flow through capillaries (1 mark)
increased after exercise. (1 mark)
(b) The body temperature increased (1 mark)
because muscle contractions produced a lot of heat during exercise. (1 mark)
(c) As the body temperature increased during exercise, sweating increased, so that more
heat could be lost from the skin by evaporation of sweat. (1 mark)
Moreover, the rate of blood flow through capillaries also increased so that more heat
could be lost from the skin by radiation and conduction. (1 mark)
The combined effect canceled out the increased heat production during exercise
(1 mark)
so as to restore the body temperature to normal / prevent over-heating. (1 mark)
(d) Hairs would lie flat on the skin. (1 mark)
This change contributes to temperature regulation by reducing the thickness of air
trapped between hairs (1 mark)
so as to promote heat loss by radiation and conduction. (1 mark)
(Total: 11 marks)
© 2010 Aristo Educational Press Ltd. 4
You might also like
- Statement of Purpose HarvardPersonalNEW1Document3 pagesStatement of Purpose HarvardPersonalNEW1Johnson IdowuNo ratings yet
- Ans EP 5 eDocument21 pagesAns EP 5 eToto lstNo ratings yet
- 28 Regulation of Gas Content in Blood: Check Your ProgressDocument5 pages28 Regulation of Gas Content in Blood: Check Your Progresssteve LNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 1 MSDocument8 pagesHomeostasis 1 MSNana Barnett QuaicooNo ratings yet
- Aristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersDocument9 pagesAristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersyanaaNo ratings yet
- CB - Ans12e - Transport of Substances in HumansDocument5 pagesCB - Ans12e - Transport of Substances in HumanschemNo ratings yet
- Schema Set 2Document5 pagesSchema Set 2Hanisah RazaliNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Paper 3 June 99Document3 pagesMark Scheme Paper 3 June 99Abdo AbdalatifNo ratings yet
- CB - Ans04e - Movement of Substances Across MembraneDocument5 pagesCB - Ans04e - Movement of Substances Across Membranesteve LNo ratings yet
- CB - Ans04e - Movement of Substances Across MembraneDocument5 pagesCB - Ans04e - Movement of Substances Across Membranesteve LNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRDocument16 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Biology (4BI1) Paper 2BRilovefettuccine100% (2)
- Specimen 2019 (IAL) MS - Unit 6 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument6 pagesSpecimen 2019 (IAL) MS - Unit 6 Edexcel Biology A-LevelTiffanyNo ratings yet
- 1 B 2 and 3 Only (1) (1) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019Document3 pages1 B 2 and 3 Only (1) (1) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019salmaNo ratings yet
- AQA Trilogy Unit 4.4 Bioenergetics - AnswersDocument3 pagesAQA Trilogy Unit 4.4 Bioenergetics - AnswersAzwa ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Free Mock Test (Prime Testing Service - PTS©)Document20 pagesFree Mock Test (Prime Testing Service - PTS©)kuldeeplohana89No ratings yet
- Heat Energy Transfer MsDocument5 pagesHeat Energy Transfer Msneena qureshiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans 1 MSDocument6 pagesGas Exchange in Humans 1 MSKatlego MedupeNo ratings yet
- ARMY PUBLIC SCHOOL PATIALA P.A - 1 (2021-22) CLASS-X SCIENCE TIME - 1hr M.M - 40 (Preview) Microsoft FormsDocument13 pagesARMY PUBLIC SCHOOL PATIALA P.A - 1 (2021-22) CLASS-X SCIENCE TIME - 1hr M.M - 40 (Preview) Microsoft FormsAkshay KumarNo ratings yet
- Dev Bio 6 MS PDFDocument8 pagesDev Bio 6 MS PDFVenant HakizimanaNo ratings yet
- EM - Sci - G11 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018Document20 pagesEM - Sci - G11 - T3 - I, II PP Ans - 2018Hashini VihangaNo ratings yet
- Gcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology SUMMER 2011Document21 pagesGcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology SUMMER 2011sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To 2014-15 S5 Biology Final ExaminationDocument3 pagesSuggested Answers To 2014-15 S5 Biology Final ExaminationDietzem WongNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Lungs MSDocument3 pagesUnit 1 The Lungs MSHassanIsmailNo ratings yet
- (Ans) ch7 Gaseous Exchange in HumansDocument6 pages(Ans) ch7 Gaseous Exchange in HumansCharlene MakNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Bot Study-Package-5 Set-1 Chapter-19 PDFDocument28 pagesCLS Aipmt-15-16 XIII Bot Study-Package-5 Set-1 Chapter-19 PDFvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Vumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Document6 pagesVumbi Marking Guide of Biology A Level Carrefour Umurezi 2023-2024-1Theogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Answers For Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Document24 pagesLife Sciences Answers For Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Anathiey Certified Jnr.No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007Document17 pagesMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007hasimahazitNo ratings yet
- AS Kinetics MSDocument21 pagesAS Kinetics MSvintu pvNo ratings yet
- 4bi1 2b Rms 20220825 PDFDocument21 pages4bi1 2b Rms 20220825 PDFNyabenda FideleNo ratings yet
- Science Paper I IieDocument15 pagesScience Paper I Iiegaindu ggvNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument17 pagesMark SchemequsaielnoorNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-AND-HEALTH-SCIENCES-THEORY-AND-PRACTICAL-EXAMINATION-S2 (1)Document16 pagesBIOLOGY-AND-HEALTH-SCIENCES-THEORY-AND-PRACTICAL-EXAMINATION-S2 (1)JEAN Fred ISHIMWENo ratings yet
- Thermal Worksheet MSDocument6 pagesThermal Worksheet MSshookookie 101No ratings yet
- Lec 12Document15 pagesLec 12sojib35390No ratings yet
- Natural SC Gr9 2012 QP EngDocument14 pagesNatural SC Gr9 2012 QP EngHabibannie Tamano0% (1)
- 4.2 Respiration MSDocument11 pages4.2 Respiration MSliufanjing07No ratings yet
- 19.4-Nitrogen-and-fertilisers-MS-IGCSE-CIE-Chemistry-Extended-theory-paperDocument5 pages19.4-Nitrogen-and-fertilisers-MS-IGCSE-CIE-Chemistry-Extended-theory-paperSamson YauNo ratings yet
- F.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesF.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam Answersjonas hoNo ratings yet
- 2223 Term 1 Pre-Assessment Unit 1-3Document17 pages2223 Term 1 Pre-Assessment Unit 1-37E10 Cheuk Kiu Ivana HENo ratings yet
- 26 Regulation of Water Content: Check Your ProgressDocument5 pages26 Regulation of Water Content: Check Your Progresssteve LNo ratings yet
- Thyolo Chemistry 1 Marking KeyDocument6 pagesThyolo Chemistry 1 Marking KeykamwendopeacefxNo ratings yet
- Questions and ProblemsDocument6 pagesQuestions and ProblemsRie CabigonNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Total Marks 25 STD 8 Subject: Science. Time: 1 Hrs Q1. Fill in The Blanks (5 Marks)Document11 pagesQuestion Paper Total Marks 25 STD 8 Subject: Science. Time: 1 Hrs Q1. Fill in The Blanks (5 Marks)Alefiya HKNo ratings yet
- 34 Use of Microorganisms: Check Your ProgressDocument4 pages34 Use of Microorganisms: Check Your Progresssteve LNo ratings yet
- Wbi13 01 Rms 20240307Document15 pagesWbi13 01 Rms 20240307Mohamed Karam100% (1)
- Additional Sample Assessment Material Sport Unit 1 Marking GridDocument14 pagesAdditional Sample Assessment Material Sport Unit 1 Marking Gridalyssafitzgerald2007No ratings yet
- 9 Recalls: Special Topics Dr. Lozada & VilchesDocument5 pages9 Recalls: Special Topics Dr. Lozada & VilchesMark Joseph PalicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction: Evolution and The Foundations of BiologyDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction: Evolution and The Foundations of Biologyjack nodiNo ratings yet
- Cape CHM 2006 MsDocument4 pagesCape CHM 2006 MsChavi RamloganNo ratings yet
- Raus IAS Prelims 2024 Test 23Document29 pagesRaus IAS Prelims 2024 Test 23shub56jainNo ratings yet
- Nabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursDocument10 pagesNabista Jet 3: 231/1 Biology Theory Paper 1 March/April 2019 Time: 2 HoursCecilia KhaombiNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument19 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernardNo ratings yet
- Resource - 231121 215449Document7 pagesResource - 231121 215449jemwazvibzNo ratings yet
- Third Term Biology TestDocument9 pagesThird Term Biology TestTheogene NTEGEREJIMANANo ratings yet
- CGP L1 Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesCGP L1 Mark SchemeBeverleyNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme - Rate of Reaction WSDocument2 pagesMarking Scheme - Rate of Reaction WSSiyaNo ratings yet
- XI Biology Sample PapersDocument6 pagesXI Biology Sample Papersprem TNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Thermodynamics: I. Conservation of EnergyDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Thermodynamics: I. Conservation of EnergyCarlos RamosNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- 22-23 F3CS GR 2.1Document1 page22-23 F3CS GR 2.1steve LNo ratings yet
- Conv ExamDocument1 pageConv Examsteve LNo ratings yet
- 22-23 F1BCDGR 3.XDocument6 pages22-23 F1BCDGR 3.Xsteve LNo ratings yet
- 22-23 F1BCDGR +Document3 pages22-23 F1BCDGR +steve LNo ratings yet
- 23-24 F1BCDGR 2.2Document3 pages23-24 F1BCDGR 2.2steve LNo ratings yet
- 23-24 - F1BCDGR - 1.X (Key)Document4 pages23-24 - F1BCDGR - 1.X (Key)steve LNo ratings yet
- 23-24 - F1BCDGR - 2.1 (Key)Document3 pages23-24 - F1BCDGR - 2.1 (Key)steve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent Quiz U14-13 Final eDocument3 pagesScicent Quiz U14-13 Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent Quiz U14-9 Final eDocument4 pagesScicent Quiz U14-9 Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent Quiz U14-10 Final R eDocument3 pagesScicent Quiz U14-10 Final R esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent Quiz U14-12 Final eDocument3 pagesScicent Quiz U14-12 Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent Quiz U14-11 Final eDocument3 pagesScicent Quiz U14-11 Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U3 1-2 SetA Final eDocument6 pagesScicent SQ U3 1-2 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 1 SetA Final eDocument5 pagesScicent SQ U2 1 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Beta 2 MicroglobulinDocument6 pagesBeta 2 MicroglobulinMohamed FaizalNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction - WikipediaDocument36 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction - Wikipedia93428ZEFHDNo ratings yet
- Jof 07 00844 v2Document11 pagesJof 07 00844 v2Sonia HernándezNo ratings yet
- Definition and Sources of DrugsDocument29 pagesDefinition and Sources of DrugsSAHILA SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- Aw1435@txstate - Edu: Amanda Wilson #594648 Bio 2450 Genetics Dr. N. Martin Amanda SchultzDocument12 pagesAw1435@txstate - Edu: Amanda Wilson #594648 Bio 2450 Genetics Dr. N. Martin Amanda Schultzaw1435No ratings yet
- READING 3.: Reading Section of Toefl Online CourseDocument3 pagesREADING 3.: Reading Section of Toefl Online CourseArdina Nur PramudhitaNo ratings yet
- Nerve Cells and Insect Behavior - Kenneth D. Roeder, 1967Document264 pagesNerve Cells and Insect Behavior - Kenneth D. Roeder, 1967S R100% (1)
- Hec Course PDFDocument3 pagesHec Course PDFDr-Rehan Zafar ParachaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology Activity 3 PDFDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Activity 3 PDFjack alkhabazNo ratings yet
- 1 The Definition of ProbioticsDocument11 pages1 The Definition of ProbioticsMohd Shuaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Three Different Filters and Two Methods For Recovering Viruses From Drinking WaterDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Three Different Filters and Two Methods For Recovering Viruses From Drinking WaterAzlyn SyafikahNo ratings yet
- Leukocytes or White Blood Cells (WBC)Document22 pagesLeukocytes or White Blood Cells (WBC)Md Atikur AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFDocument69 pagesChapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFdarren100% (2)
- 8th Sem SyllabusDocument32 pages8th Sem SyllabusDRx Ijajul HussainNo ratings yet
- Contractia MuscularaDocument33 pagesContractia MuscularaIulia JalbaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 - Actividad 3 PhysioexDocument4 pagesEjercicio 1 - Actividad 3 PhysioexMayra MarroquinNo ratings yet
- Quiz Fungi With AnswerDocument8 pagesQuiz Fungi With AnswerLek SanprasertNo ratings yet
- Turner SyndromeDocument4 pagesTurner SyndromeKylalerrsssNo ratings yet
- Dna Denaturation and RenaturationDocument2 pagesDna Denaturation and RenaturationSoumyaranjan PatiNo ratings yet
- KVL Wefvrb: Wøzxq Aa VQDocument21 pagesKVL Wefvrb: Wøzxq Aa VQHasin IsraqNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Document47 pages02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Actualización de Inmunoterapia en CáncerDocument13 pagesActualización de Inmunoterapia en CáncerAli BelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 33Document16 pagesChapter 33Shfici AdanNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument2 pagesGenetic EngineeringMinal KantNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 - Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument28 pagesCOVID-19 - Diagnosis - UpToDateTerang MelialaNo ratings yet
- Methods To Study HistologyDocument26 pagesMethods To Study HistologyDMNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Humans: Discover Biology G.C.E. 'N' Level Science: Textbook AnswersDocument2 pagesRespiration in Humans: Discover Biology G.C.E. 'N' Level Science: Textbook AnswersShyam PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Cdsco Stem CellDocument84 pagesCdsco Stem CellKIITAA FANINo ratings yet