Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q2 Science 10 M3ST3
Q2 Science 10 M3ST3
Uploaded by
Leother Yee SosmenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2 Science 10 M3ST3
Q2 Science 10 M3ST3
Uploaded by
Leother Yee SosmenaCopyright:
Available Formats
JULIO LEDESMA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Science Quarter 2 – Module 3
Summative Assessment 3
Name: ______________________________ Date: ____________
Grade and Section: ______________________________________
SHADE THE CIRCLE WHICH CORRESPONDS TO THE LETTER OF THE CORRECT ANSWER.
1 (A) (B) (C) (D) 12 (A) (B) (C) (D) 23 (A) (B) (C) (D)
2 (A) (B) (C) (D) 13 (A) (B) (C) (D) 24 (A) (B) (C) (D)
3 (A) (B) (C) (D) 14 (A) (B) (C) (D) 25 (A) (B) (C) (D)
4 (A) (B) (C) (D) 15 (A) (B) (C) (D)
5 (A) (B) (C) (D) 16 (A) (B) (C) (D)
6 (A) (B) (C) (D) 17 (A) (B) (C) (D)
7 (A) (B) (C) (D) 18 (A) (B) (C) (D0029
8 (A) (B) (C) (D) 19 (A) (B) (C) (D)
9 (A) (B) (C) (D) 20 (A) (B) (C) (D)
10 (A) (B) (C) (D) 21 (A) (B) (C) (D)
11 (A) (B) (C) (D) 22 (A) (B) (C) (D)
1. What is the orientation of an image formed by a convex mirror?
a. inverted B. upright C. cannot be determined D. reduced
2. Which of the following best describes how light behaves on a smooth surface such as a mirror?
a. Upon reaching the surface, light is absorbed by the mirror.
b. Upon reaching the surface, light is transmitted by the mirror to the other side.
c. Upon reaching the surface, light is scattered in all directions.
d. Upon reaching the surface, light bounces back.
3. Which of the following describes a convex lens?
a. It has an outward curve. C. It has a flat surface.
b. It has an inward curve. D. It is thin.
4. When two plane mirrors are placed at right angles with each other, how many images will be formed?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
5. Which of the following are examples LUMINOUS objects?
I. laser II. Sun III. Moon IV. Light bulb
A. I, II, III B. I, III, IV C. II, III, IV D. I, II, IV
6. Which type of mirror forms an upright virtual image, located behind the mirror, and the same size as the object?
A. Concave mirror B. Convex mirror C. Plane mirror D. Spoon
7. Light does not need any medium to travel. This means that it can travel through .
a. water B. air C. solids D. vacuum
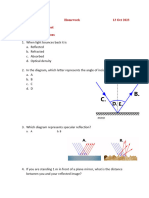
For number 8, refer to the figure on the right.
8. A stands for , while B stands for .
A. angle of reflection; angle of incidence C. angle of incidence; angle of refraction
B. angle of incidence; angle of reflection D. angle of refraction; angle of incidence
9. Which of the following correctly describe/s a real image?
I. It can be formed on a screen.
II. It is inverted with respect to the object.
III. It is formed when light rays do not actually interest after reflection, but appear to diverge from the mirror.
A. I, II B. II, III C. I, III D. I, II, III
10. An image that you can see when you look into a mirror, but does not really exist is called .
A. real image B. virtual image C. fake image D. digital image
11. Why is it difficult to see a clear image of a mountain on wavy water?
a. The water is too shallow that light can easily penetrate through it.
b. The surface of the water is rough that light is reflected in all directions.
c. The wave water absorbs the light that reaches its surface.
d. When light hits the surface of the wavy water, it is transmitted by the wavy water itself.
12. Which of the following refers to the Law of Reflection?
a. When light rays hit the surface of a mirror, it bounces back.
b. The angle of incidence is less than the angle of reflection.
c. The angle of incidence is greater than the angle of reflection.
d. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
13. What is the size of the image formed by a convex mirror?
a. Same B. Enlarged C. Reduced D. Cannot be determined
For number 14, refer to the figures on the right.
14. The figures show the two types of spherical (curved) mirrors. Which
statement is true about the figures?
A B
A. Figure A is a concave mirror and forms a real image while figure B is a convex mirror and forms a virtual image.
B. Figure A is a concave mirror and forms a virtual image while figure B is a convex mirror and forms a real image.
C. Figure A is a convex mirror and forms a real image while figure B is a concave mirror and forms a virtual image.
D. Figure A is a convex mirror and forms a virtual image while figure B is a concave mirror and forms a real image.
15. What is a focal length?
a. The distance from an image to the object.
b. The distance from the focal point to the vertex.
c. The distance from the center of the sphere to the image.
d. The distance from the vertex to the center of curvature.
16. Which of the following refers to the concave lens?
a. The lens which merges the light rays at a particular point, that travels through it.
b. The lens which disperses the light rays around, that hits the lenses.
c. The lens which merges the light rays and disperses it back to the opposite side of the lens.
d. The lens which disperses the light rays around and merges it back to the opposite side of the lens.
17. Which type of mirror is shown here?
A. Concave mirror B. Convex mirror
C. Plane mirror D. curved mirror
18. Which of the following is the speed of light?
A. 3 x 108 m/s B. 3 x 107 m/s C. 3 x 106 m/s D. 3 x 105 m/S
19. Which of the following is/are the characteristics of a virtual image formed by a curved mirror?
I. It can be formed on a screen.
II. Light rays actually meet after reflection.
III. It is erect with respect to the object.
A. I B. II C. III D. I, II, III
20. In a concave mirror, when the object is placed beyond the center of curvature, the image formed will be located
_.
A. at C B. between C and F C. beyond C D. cannot be determined
21. What will happen to the number of images when the angle between the two plane mirrors is decreased?
A. also increases B. decreases C. stays the same D. cannot be determined
22. Which of the following is NOT one characteristic of an image formed by a plane mirror?
a. Image is real. C. Same orientation as the object.
b. Same size as the object. D. Same distance from the mirror as the object.
23. What type of image is formed when an object is placed at the focus in front of a concave mirror?
a. real B. virtual C. no image is formed D. cannot be determined
24. Which lens is used to correct myopia?
a. concave lens C. both concave and convex
b. convex lens D. none of the two types of lenses can correct myopia.
25. When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image will be located _.
a. between C and F B. beyond C C. at C D. No image is formed
Answer Key (Summative Assessment Q2M3 – Science 10)
1. C
2. D
3. A
4. C
5. D
6. C
7. D
8. B
9. A
10. B
11. B
12. D
13. C
14. A
15. B
16. B
17. B
18. A
19. C
20. B
21. A
22. A
23. C
24. A
25. C
You might also like
- Lesson Plan in Science 10 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10 2nd QuarterJenevev82% (22)
- Questions On Mirrors and LensesDocument29 pagesQuestions On Mirrors and LensesKamal Naser100% (2)
- Q2, WEEK-7-S10FE-IIg-50 - 51Document19 pagesQ2, WEEK-7-S10FE-IIg-50 - 51CRISTINE MAE AREVALONo ratings yet
- SUm Test 3 2nd QDocument1 pageSUm Test 3 2nd QJamaica MamburaoNo ratings yet
- Optics QuizDocument5 pagesOptics QuizJhun Dimate FerreroNo ratings yet
- PPSB-CLASS X-Physics-Refraction Through LensDocument8 pagesPPSB-CLASS X-Physics-Refraction Through LensKrishna Agarwal [PRIMUS]No ratings yet
- Arihant Science Class Test-Class-X (MCQ)Document4 pagesArihant Science Class Test-Class-X (MCQ)Hadron ClassesNo ratings yet
- Mirror (Assessment)Document3 pagesMirror (Assessment)Jhun Dimate FerreroNo ratings yet
- Light Revision Class 10Document34 pagesLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Final Na ToDocument5 pages2nd Quarter Exam Final Na ToMerlyn Mendoza100% (1)
- FilipinoDocument6 pagesFilipinosalvoabegail56No ratings yet
- Reflection (Homework) SAS Grade 11Document6 pagesReflection (Homework) SAS Grade 11merry glorNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Second 2Document3 pagesGrade 10 Second 2Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Second Periodical TestDocument6 pagesScience 10 Second Periodical TestMarl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Direction: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of PaperDocument1 pageDirection: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer. Write Your Answer On A Separate Sheet of Paperjoy grace jaraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice TestDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Testchristy angelie mojado67% (3)
- Sci Quarterly Assessment 10Document6 pagesSci Quarterly Assessment 10Christian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Sci Collab TayoDocument22 pagesSci Collab TayoJullie Ann AcuninNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- Optics PacketDocument24 pagesOptics Packetjayen romaNo ratings yet
- Light - Worksheet 2 SCDocument7 pagesLight - Worksheet 2 SC。无名。。No ratings yet
- Science Practice Test: Grade: 6 Total Marks: 20 Time: 30 MinsDocument6 pagesScience Practice Test: Grade: 6 Total Marks: 20 Time: 30 MinsNimisha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- PDF&Rendition 1 13Document5 pagesPDF&Rendition 1 13rishikajn4795No ratings yet
- Pre Assessment Test (Refraction in Lenses and Mirrors)Document21 pagesPre Assessment Test (Refraction in Lenses and Mirrors)Kenneth Roy Matuguina100% (1)
- X Physics PracticeDocument6 pagesX Physics PracticeJeena RajNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THDocument5 pagesLight - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THhiranyakshivNo ratings yet
- Weekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Document4 pagesWeekly TEst 20th Sep 2021Sarvesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document9 pagesModule 6chef curryNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test Scie 10Document7 pages2nd Periodical Test Scie 10JOEL JACOBNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsDocument3 pagesPhysics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Part-I - Reflection Part-A - Level-I - (Theory) : Single Answer CorrectDocument27 pagesRay Optics Part-I - Reflection Part-A - Level-I - (Theory) : Single Answer CorrectAkanshNo ratings yet
- Light MCQs PadhleDocument19 pagesLight MCQs Padhlesinghatharva2367No ratings yet
- Mirror Assessment1Document2 pagesMirror Assessment1Ihopdu Doirqvr50% (2)
- 2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Document13 pages2nd QUARTER EXAM SCIENCE 10Manuela Kassandra Soriao Tribiana0% (1)
- Science 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Document8 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Joy Valerie AricayosNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document5 pagesLight-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024yashasvisharma sharmaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Surat Revision Worksheet Subject: Physics Class: X Maximum Marks: 20Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Surat Revision Worksheet Subject: Physics Class: X Maximum Marks: 20Deb Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- Light-Mirrors and Lens WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight-Mirrors and Lens WorksheetTharunaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors Summative TestDocument2 pagesMirrors Summative Testjimmy100% (1)
- Second Periodic Test Grade10Document5 pagesSecond Periodic Test Grade10Marl Rina EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- g10-2nd Quarter Exam Science 10Document4 pagesg10-2nd Quarter Exam Science 10Kier Black100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter Science 10 - NewDocument12 pages2nd Quarter Science 10 - NewJOEL JACOBNo ratings yet
- Light - MCQDocument9 pagesLight - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 2nd PeriodicalDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 2nd PeriodicalKa KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- Concave and Convex Mirror ExerciseDocument5 pagesConcave and Convex Mirror ExerciseĐặng Thái Nhật100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter Summative TestDocument3 pages2nd Quarter Summative TestMiriam UbiÑa MabborangNo ratings yet
- EoT 1Document2 pagesEoT 1ak dNo ratings yet
- Class X PhyDocument4 pagesClass X PhyNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgCggT71E HfapMy80vxxTqharAWqAcja6twdvl URhy6t0 ScCDOkJGyvlde6kUrDINqpSjaytLmlh-u3pLtCciXv7SpOr5fu2MqbePk9ZlRajNRfSzw3jJEjhM99W - 1GMx TyACrLQ-0CDocument5 pagesACFrOgCggT71E HfapMy80vxxTqharAWqAcja6twdvl URhy6t0 ScCDOkJGyvlde6kUrDINqpSjaytLmlh-u3pLtCciXv7SpOr5fu2MqbePk9ZlRajNRfSzw3jJEjhM99W - 1GMx TyACrLQ-0CAltaf Hussain ShaikNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 pagesGeometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamedNo ratings yet
- Ntse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Document9 pagesNtse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Science 10newwwwwDocument10 pages2nd Quarter Exam Science 10newwwwwPrudencio GolezNo ratings yet
- Open Book Test - OpticsDocument9 pagesOpen Book Test - OpticsGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Physics Final ExamDocument4 pagesPhysics Final ExamMilkias BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Optics QuestionsDocument2 pagesOptics QuestionsUnidentified PersonNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction PDFDocument5 pagesReflection & Refraction PDFSushri Sangeeta MohantyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentNeeraj PuniaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science BookletDocument66 pagesClass 8 Science BookletHimanshu TalwarNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Paper Class 9 ST - Jhons High SchoolDocument4 pagesPhysics Question Paper Class 9 ST - Jhons High Schoolsultanamubarak09No ratings yet
- Ray Opitics Disha PDFDocument4 pagesRay Opitics Disha PDFRaman GoyalNo ratings yet
- 31-C-2 Science (086) Marking Scheme Comptt 2020Document12 pages31-C-2 Science (086) Marking Scheme Comptt 2020cryptosingh69No ratings yet
- Curved Mirror - Detaileed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesCurved Mirror - Detaileed Lesson PlanLory Dacumos Gonzalo100% (1)
- Asm 18667Document7 pagesAsm 18667sharmaa9212705357No ratings yet
- State The Laws of ReflectionDocument2 pagesState The Laws of ReflectionSuman DasNo ratings yet
- 9 RayopticsDocument8 pages9 RayopticsViredra Vikash C MNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet 2 (Light)Document24 pagesRevision Sheet 2 (Light)Somaya HussienNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsSagnik MajumderNo ratings yet
- R. John Williams - The Buddha in The MachineDocument367 pagesR. John Williams - The Buddha in The MachineR John WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Model Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationDocument22 pagesModel Question Solution Made By: Krishna Shah Group 'A': Answer ExplanationKrishna ShahNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 NumericalsDocument10 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 NumericalsAthar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 5 6325658594104575425Document142 pages5 6325658594104575425david royNo ratings yet
- Activity 1,2,3,4,5,6Document8 pagesActivity 1,2,3,4,5,6Crazy ShortzNo ratings yet
- Fiit Jee Aits Full TestDocument21 pagesFiit Jee Aits Full TestsindhwanimohitNo ratings yet
- Light (Mirrors and Lenses)Document19 pagesLight (Mirrors and Lenses)allijah gwyneth dalesNo ratings yet
- Physics LightDocument107 pagesPhysics LightBlessing TshumaNo ratings yet
- Final Revision MCQ 2023 PDFDocument6 pagesFinal Revision MCQ 2023 PDFReuben DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-xii-10-Concave Mirror (Normal Incidence, U-V, Graph) - SignedDocument4 pagesHsslive-xii-10-Concave Mirror (Normal Incidence, U-V, Graph) - SignedAryan PanwarNo ratings yet
- Class Test 10 (RRH)Document3 pagesClass Test 10 (RRH)Jeevanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- MCQs - LightDocument9 pagesMCQs - Lightdeepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Definition Menaning PhysicsDocument14 pagesDefinition Menaning PhysicsIEyra ShaHeraNo ratings yet
- Lens and Mirror School Lab Manual by Junior ScientistDocument41 pagesLens and Mirror School Lab Manual by Junior ScientistGopi Chand100% (1)
- Grade-X - Physics - Experiment-Focal LengthDocument5 pagesGrade-X - Physics - Experiment-Focal LengthOP GAMERZNo ratings yet
- Laws of ReflectionDocument4 pagesLaws of ReflectionAreefa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class Ten All DiagramsDocument42 pagesCbse Class Ten All Diagramssharikamb2008100% (1)
- NTSE Stage I (SAT) Mock TestDocument14 pagesNTSE Stage I (SAT) Mock TestSocialscience4u.blogspot.com100% (1)
- Grade 10 - Lab ManualDocument10 pagesGrade 10 - Lab ManualMoghanNo ratings yet