Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factors Affecting Intensity of A Reflection
Factors Affecting Intensity of A Reflection
Uploaded by
Naveen MeenaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors Affecting Intensity of A Reflection
Factors Affecting Intensity of A Reflection
Uploaded by
Naveen MeenaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture‐7 highlights
MM 201
Factors affecting Intensity of a reflection
Factors affecting the relative intensity of the diffraction line (of powder method) are:
o Structure factor,
o Lorentz-polarization factor (LP factor)
o Multiplicity factor,
o Temperature factor
o Absorption factor
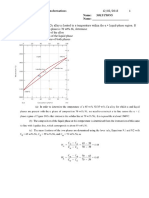
LP factor = , plot of LP factor v/s θ decreases first upto 450 and then
increases. The overall effect of this factor is to decrease the intensity of reflection at
intermediate angles compared to those in forward or backward directions.
Multiplicity factor, may be defined as the number of the different planes in a form
having the same spacing.
- as λ = 2 d sin and
- = (only for unit cell having α=β=γ=900 ; i.e. for cubic
(a=b=c), tetragonal (a=b≠c), and orthorhombic (a≠b≠c))
- So for cubic, = 6 for {100} (i.e. set of plane Ι00,0Ι0,00Ι,Ī00,0Ī0,00Ī )
= 8 for {111} (i.e. III, ΙΙĪ, ΙĪΙ, ĪΙΙ,ΙĪ Ī , ĪΙĪ, Ī ĪΙ, Ī Ī Ī )
= 12 for {110}
= 48 for{hkl} (where h≠k≠l≠0)
and for tetragonal, = 16 for{hkl} (where h≠k≠l≠0)
- An observation: Below 1200C intensity line of BaTiO3 splits into two closely
spaced line and with lowered intensity w.r.t. as it was at high temperature.
Explanation: At high temperature BaTiO3 is in cubic (a=b=c) form while below
1200C it changes to tetragonal form, where one axis is distorted (a=b<c). The
splitting of intensity line is essentially due to the introduction of new plane
spacings (d ), caused by increase in the lattice parameter, c. For example, in
the cubic cell, the (100), (010), and (001) planes all have the same spacing and
only one line is formed, called 100 line, but this line splits into two when the cell
becomes tetragonal, since now the (001) plane spacing differs from others two.
(for slightly different d , equation λ = 2 d sin is satisfied for slightly
different θ, means different position of intensity line, as λ is the same.)
And the intensity is lowered because now less number of the planes are
contributing to the intensity line.
Temperature Factor = where = (sinθ⁄λ) and B is taken as constant here.
- Thermal vibration of atom about the mean position, decreases the electron
density and results in sharp plot of atomic scattering factor, .
- Thus the intensity of a diffracted beam decreases as the temperature is raised,
and for a constant temperature, thermal vibration causes a greater decrease in
the reflected intensity at high angle than at low angles. ( one reason among
various others for low intensity at high angle)
Intensity for powder pattern lines-
+
=∣ ∣ . .
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Str. Factor LP factor multiplicity temp. factor
factor
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Manual Sonatest 250sDocument110 pagesManual Sonatest 250sEnrique TaviraNo ratings yet
- Nano Chemistry Notes - B. E I Year-1Document17 pagesNano Chemistry Notes - B. E I Year-1Varshini Rajkumar100% (16)
- Intensity Bragg ReflnDocument34 pagesIntensity Bragg ReflnNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Reciprocal Lattice (Contd..) : 9 HighlightsDocument2 pagesThe Reciprocal Lattice (Contd..) : 9 HighlightsNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lec 10Document2 pagesLec 10Naveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document1 pageLec 3Naveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Si STD XRDDocument2 pagesSi STD XRDNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact and Life Cycle Assessment of MaterialsDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Impact and Life Cycle Assessment of MaterialsNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 (ch1 - Introduction)Document30 pagesLecture1 (ch1 - Introduction)Naveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 (ch2 - Atomic Structure)Document67 pagesLecture2 (ch2 - Atomic Structure)Naveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- The Royal SocietyDocument19 pagesThe Royal SocietyNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Phase TransformationsDocument2 pagesTutorial - Phase TransformationsNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Phase Transformations 2 - SolutionsDocument2 pagesTutorial - Phase Transformations 2 - SolutionsNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Materials SelectionDocument3 pagesTutorial - Materials SelectionNaveen MeenaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry MidtermDocument3 pagesInorganic Chemistry MidtermGerick Dave Monencillo VenderNo ratings yet
- 411 IR WavenosDocument2 pages411 IR WavenosIsraa SalmanNo ratings yet
- L14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDocument3 pagesL14Q1 - Lesson 14 - PHY112 Courseware - BuX - BRAC UniversityDipto MahmudNo ratings yet
- Solution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Document14 pagesSolution Padhai Ak Mazza Notes 2023Prabhat JhaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Alternator Synchronisig by 8085mycroprocessorDocument20 pagesAutomatic Alternator Synchronisig by 8085mycroprocessorSHYAMAL PARIANo ratings yet
- GRL+Prosp - EDocument2 pagesGRL+Prosp - Ethoma111sNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetOMARNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 (W6)Document6 pagesGeneral Physics 1 (W6)Kim SeungminNo ratings yet
- Welded Connections - Problems: Mr. P. JAGADESH., M.E., M.B.A., (PH.D)Document33 pagesWelded Connections - Problems: Mr. P. JAGADESH., M.E., M.B.A., (PH.D)Dsryfxsr100% (1)
- b&c18pzb46 8Document1 pageb&c18pzb46 8Jesus Ruy SanchezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideDocument146 pagesClinical Ultrasound A How-To GuideNacko Stavreski67% (3)
- 3M Locating and Marking SystemDocument12 pages3M Locating and Marking SystemYohanes Dimas PriambodhoNo ratings yet
- Velocity Time Graphs PDFDocument42 pagesVelocity Time Graphs PDFAk R71No ratings yet
- Electronegativity WorksheetDocument1 pageElectronegativity Worksheetandrea3246No ratings yet
- Astm C348Document6 pagesAstm C348katieNo ratings yet
- Customer Approval Specification: Digital PDP Division, LG Electronics IncDocument37 pagesCustomer Approval Specification: Digital PDP Division, LG Electronics InccaseysamNo ratings yet
- Flex& Spur OutletDocument9 pagesFlex& Spur OutletTehran KhanNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Methods For Calculating Transmission Line Conductor 1979 PDFDocument19 pagesA Survey of Methods For Calculating Transmission Line Conductor 1979 PDFAbraham MaravíNo ratings yet
- Improper IntegralsDocument41 pagesImproper Integrals220112034No ratings yet
- Effect of Friction Pendulum Bearing Properties On Behaviour of BuildingsDocument20 pagesEffect of Friction Pendulum Bearing Properties On Behaviour of BuildingsJuan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cbse Board 10march Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper With Solutions 2023Document19 pagesCbse Board 10march Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper With Solutions 2023harshsharma1513No ratings yet
- The Bushing Group Product SpectrumDocument4 pagesThe Bushing Group Product SpectrumCLAVOT100% (1)
- Chapter6 - THEORY AND APPLICATION OF MODAL MODEL ANALYSISDocument35 pagesChapter6 - THEORY AND APPLICATION OF MODAL MODEL ANALYSISVo Duy KhanhNo ratings yet
- To Study The Variations of Current Flowing in A C...Document2 pagesTo Study The Variations of Current Flowing in A C...K U P RNo ratings yet
- BS en 1052-1 (1999)Document12 pagesBS en 1052-1 (1999)fizaNo ratings yet
- ch11 Lecture DzyubenkoDocument26 pagesch11 Lecture DzyubenkoRyan NegadNo ratings yet
- Lines PlanDocument23 pagesLines PlanhaeiriNo ratings yet
- CFSEI Shear Wall Design GuideDocument45 pagesCFSEI Shear Wall Design GuideDaniel AielloNo ratings yet