Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IBM Security Guardium Is A Comprehensive Data Security Platform That Provides A Full Range of Capabilities
IBM Security Guardium Is A Comprehensive Data Security Platform That Provides A Full Range of Capabilities
Uploaded by
Tikumusu Agborbesong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesIBM Security Guardium is a comprehensive data security platform that provides capabilities like discovery and classification of sensitive data, vulnerability assessment, and data activity monitoring to protect sensitive data across databases, big data, cloud, and file systems. Guardium monitors activities like SQL errors, logins, database queries, commands, and XML execution. It uses non-invasive host-based probes to provide real-time database monitoring with minimal performance impact. Guardium helps secure data and meet compliance needs across different environments and standards.
Original Description:
Original Title
IBM Security Guardium is a comprehensive data security platform that provides a full range of capabilities
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIBM Security Guardium is a comprehensive data security platform that provides capabilities like discovery and classification of sensitive data, vulnerability assessment, and data activity monitoring to protect sensitive data across databases, big data, cloud, and file systems. Guardium monitors activities like SQL errors, logins, database queries, commands, and XML execution. It uses non-invasive host-based probes to provide real-time database monitoring with minimal performance impact. Guardium helps secure data and meet compliance needs across different environments and standards.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesIBM Security Guardium Is A Comprehensive Data Security Platform That Provides A Full Range of Capabilities
IBM Security Guardium Is A Comprehensive Data Security Platform That Provides A Full Range of Capabilities
Uploaded by
Tikumusu AgborbesongIBM Security Guardium is a comprehensive data security platform that provides capabilities like discovery and classification of sensitive data, vulnerability assessment, and data activity monitoring to protect sensitive data across databases, big data, cloud, and file systems. Guardium monitors activities like SQL errors, logins, database queries, commands, and XML execution. It uses non-invasive host-based probes to provide real-time database monitoring with minimal performance impact. Guardium helps secure data and meet compliance needs across different environments and standards.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
IBM Security Guardium is a comprehensive data security platform that provides a full range of
capabilities – from discovery and classification of sensitive data to vulnerability assessment to
data and file activity monitoring to masking, encryption, blocking, alerting and quarantining to
protect sensitive data. Guardium helps secure sensitive data across a full range of
environments – from databases to big data, cloud, file systems and more. Guardium also
provides automated analysis to quickly uncover internal and external risks to sensitive data
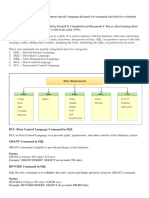
What does Guardium monitor?
SQL Errors and failed logins
DDL commands (Create/Drop/Alter Tables)
SELECT queries
DML commands (Insert, Update, Delete)
DCL commands (Grant, Revoke)
Procedural languages
XML executed by database
Returned results sets
Real-Time Database Monitoring with InfoSphere Guardium Host-based Probes (S-TAPs)
Collector
Non-invasive architecture
Outside database
Minimal performance impact (2-3)
No DBMS or application changes
Cross-DBMS solution
100 visibility including local DBA access
Enforces separation of duties
Does not rely on DBMS-resident logs that can
easily be erased by attackers, rogue insiders
Granular, real-time policies auditing
Who, what, when, how
Automated compliance reporting, sign-offs
escalations (SOX, PCI, NIST, etc.)
How are most databases audited today?
Reliance on native audit logs within DBMS
Lacks visibility and granularity
Privileged users difficult to monitor
Tracing the real user of application is
difficult
Level of audit detail is insufficient
Inefficient and costly
Impacts database performance
Large log files provide little value
Different methods for each DB type
No segregation of duties
DBAs manage monitoring system
Privileged users can bypass the system
Audit trail is unsecured
The Compliance Mandate
DDL Data Definition Language (aka schema
changes) DML Data Manipulation Language (data
value changes) DCL Data Control Language
Database Activity Monitoring Three Key Business Drivers
Prevent data breaches
Mitigate external and internal threats
Ensure data integrity
Prevent unauthorized changes to sensitive data
Reduce cost of compliance
Automate and centralize controls
Across DBMS platforms and applications
Across SOX, PCI, SAS70,
Simplify processes
You might also like
- Security Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesFrom EverandSecurity Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Amazon Quicksight UserDocument359 pagesAmazon Quicksight Userspanda3j3No ratings yet
- 2018-11 FS9100 DatasheetDocument3 pages2018-11 FS9100 DatasheetNguyen Van HaiNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Database Compliance With Real-Time Database Monitoring, Security & AuditingDocument39 pagesEnsuring Database Compliance With Real-Time Database Monitoring, Security & AuditingmohitsportNo ratings yet
- 7 0 Guardium BrochureDocument6 pages7 0 Guardium BrochureNaveen KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- CC-DBMS Security080305Document4 pagesCC-DBMS Security080305Mohamed Hassan Mohamed 171-15-9224No ratings yet
- DB Audit: For Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Sybase ASE, Sybase ASA, and IBM DB2Document5 pagesDB Audit: For Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Sybase ASE, Sybase ASA, and IBM DB2almari76No ratings yet
- 8 Steps To Holistic Database SecurityDocument6 pages8 Steps To Holistic Database SecurityelazarineNo ratings yet
- Key and Advantages of DBMSDocument2 pagesKey and Advantages of DBMSJulianna DomingoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Database Access Manager and Dynamic Data MaskingDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Database Access Manager and Dynamic Data Maskingoluyinkaa14No ratings yet
- DG Platform Technical Overview WPDocument17 pagesDG Platform Technical Overview WPcoba cobaNo ratings yet
- Bit 420 Cat 1 and 2 Gs180289bsitDocument24 pagesBit 420 Cat 1 and 2 Gs180289bsitMERCY-JEDIDIAH-BELOVED OF JEHOVAH Nungari mukuruNo ratings yet
- MySql IT Security DocumentDocument11 pagesMySql IT Security DocumentNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- SIEMDocument13 pagesSIEMDavie NgangaNo ratings yet
- Digital Guardian Network Data Loss Prevention: Protect Sensitive Data On The Move To Support Regulatory ComplianceDocument2 pagesDigital Guardian Network Data Loss Prevention: Protect Sensitive Data On The Move To Support Regulatory Compliancevinay kNo ratings yet
- AbhiDocument9 pagesAbhiAbhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Mod 2Document101 pagesMod 2MUSLIMA MBA21-23No ratings yet
- Database SecurityDocument19 pagesDatabase SecurityAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Database Security UsecasesDocument8 pagesDatabase Security UsecasesMarcia MéndezNo ratings yet
- Database SecurityDocument19 pagesDatabase SecurityShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Report 2Document11 pagesReport 2kbbhadran7No ratings yet
- It's Your Data - Are You Sure It's Safe?: Team Mag 5Document14 pagesIt's Your Data - Are You Sure It's Safe?: Team Mag 5Sami Lo'o Lo'oNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument25 pagesDatabase Management Systemsabhinavgupta2010No ratings yet
- Data Loss Prevention For Endpoint enDocument3 pagesData Loss Prevention For Endpoint enMostafaEl-sayedNo ratings yet
- Fbi Recommendation To Stop Ransomware AttacksDocument16 pagesFbi Recommendation To Stop Ransomware AttacksToding SampurnaNo ratings yet
- Cyb 403Document17 pagesCyb 403yormie2019No ratings yet
- DS SecureSphere DAM and DBF - Mar2018Document2 pagesDS SecureSphere DAM and DBF - Mar2018jennykenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II NewwDocument3 pagesChapter II NewwCHARLES REBOLLOSNo ratings yet
- DBMS ReportDocument24 pagesDBMS ReportNishchal GondNo ratings yet
- Dbprotect: Ensure Your Sensitive Data Is Secure and Your Compliance Requirements Are AchievedDocument6 pagesDbprotect: Ensure Your Sensitive Data Is Secure and Your Compliance Requirements Are AchievedRachid RachNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Architecture Risk AssessmDocument244 pagesCyber Security Architecture Risk AssessmSatya SmartyNo ratings yet
- Database Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaDocument11 pagesDatabase Security: Under Authorization of DR - SalwaKhaled AdelNo ratings yet
- Data Security Best PracticesDocument20 pagesData Security Best Practiceshim2000himNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document26 pagesUnit 5raxit.janiNo ratings yet
- EDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1Document29 pagesEDIT 3101 - Database Management System - Lecture 1sichingadavies84No ratings yet
- 03.database Design ConceptsDocument45 pages03.database Design ConceptsJanaka SampathNo ratings yet
- PC4 - GROUP 7 - Database Management SoftwareDocument2 pagesPC4 - GROUP 7 - Database Management SoftwarepotatootamoooNo ratings yet
- Eh Unit 3Document15 pagesEh Unit 3tixove1190No ratings yet
- DBMS Chapter-1Document30 pagesDBMS Chapter-1aiden.atz78No ratings yet
- Database SecurityDocument16 pagesDatabase SecurityTiruneh SimachewNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Introduction To Database ManagementDocument14 pages4.3 Introduction To Database ManagementppghoshinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Database Management SystemDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 - Database Management SystemMiriam B BennieNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Assignment 2Document2 pagesUnit 6 Assignment 2DKnott86No ratings yet
- Chapter 16 IT Controls Part II Security and AccessDocument41 pagesChapter 16 IT Controls Part II Security and AccessGazelem Zeryne AgootNo ratings yet
- NormalizationDocument14 pagesNormalizationkundan9ydvNo ratings yet
- Guardium Data Encryption Data SheetDocument8 pagesGuardium Data Encryption Data Sheetcentangdua11No ratings yet
- Lecture 3- DBMS FunctionsDocument48 pagesLecture 3- DBMS FunctionsMercy ChinyukuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document29 pagesLecture 3ABDUL QUDOOSNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab UniversityDocument30 pagesDatabase Management System: Dr. Neha Gulati University Business School Panjab UniversityNavneet Nanda100% (1)
- SSH CryptoAuditor 20120725 2Document10 pagesSSH CryptoAuditor 20120725 2JohnNo ratings yet
- Structured Data Manager DsDocument8 pagesStructured Data Manager DsRockey ZapNo ratings yet
- Forcepoint ONE CASB DatasheetDocument6 pagesForcepoint ONE CASB DatasheetP BarreraNo ratings yet
- Database Security Mechanisms and ImplementationsDocument6 pagesDatabase Security Mechanisms and Implementationsguru_maheshNo ratings yet
- Self Study 9.1Document15 pagesSelf Study 9.1rasindugamlath9No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Database Security 2Document18 pagesUnit 5 Database Security 2varun821026No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - ObjectivesFIZA SAIFNo ratings yet
- CipherTrust Data Security Platform DsDocument22 pagesCipherTrust Data Security Platform DstomektrNo ratings yet
- DataSunrise InfoDocument2 pagesDataSunrise Infomahesh malveNo ratings yet
- MIS 6050 RevisionDocument2 pagesMIS 6050 RevisionwilberNo ratings yet
- RDBMS An IntroductionDocument84 pagesRDBMS An Introductionkonda Sasi Snehith reddyNo ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- AZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500From EverandAZURE AZ 500 STUDY GUIDE-1: Microsoft Certified Associate Azure Security Engineer: Exam-AZ 500No ratings yet
- Database Upgrade 11.2.0.4 ScreenshotsDocument49 pagesDatabase Upgrade 11.2.0.4 ScreenshotsTikumusu AgborbesongNo ratings yet
- Senior Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsDocument37 pagesSenior Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsTikumusu Agborbesong100% (2)
- IBM Guardium - Administration and PerformanceDocument36 pagesIBM Guardium - Administration and PerformanceTikumusu AgborbesongNo ratings yet
- Database Activity MonitoringDocument83 pagesDatabase Activity MonitoringTikumusu AgborbesongNo ratings yet
- About Raffle DrawDocument36 pagesAbout Raffle DrawAdeyeye davidNo ratings yet
- Cassandra IntroductionDocument99 pagesCassandra IntroductionNikhil ErandeNo ratings yet
- Intel Performance Maximizer V1.0.3 User GuideDocument26 pagesIntel Performance Maximizer V1.0.3 User GuidezerotacetNo ratings yet
- Two Phase CommitDocument10 pagesTwo Phase Commitshailajawesley023No ratings yet
- 63232838956Document2 pages63232838956tarikuabraham22No ratings yet
- Apple Inc Thesis StatementDocument4 pagesApple Inc Thesis Statementafkollnsw100% (2)
- Case Study ReportDocument6 pagesCase Study ReportSamir KhatriNo ratings yet
- مصطلحات امن المعلوماتDocument21 pagesمصطلحات امن المعلوماتmohammedNo ratings yet
- BBVS - Blockchain Based Voting SystemDocument6 pagesBBVS - Blockchain Based Voting SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- TikTok For Musicians 101 - United StatesDocument5 pagesTikTok For Musicians 101 - United StatesSara MasonNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide For BridgeDocument5 pagesQuick Start Guide For BridgeCyber BellaaNo ratings yet
- Statys Ul: Static Transfer SwitchDocument63 pagesStatys Ul: Static Transfer SwitchFikre shameboNo ratings yet
- By:-Abhishek PasrichaDocument27 pagesBy:-Abhishek PasrichaSatheessh KonthalaNo ratings yet
- Pi Workshop Installation InstructionsDocument3 pagesPi Workshop Installation InstructionsDBNo ratings yet
- DeepikaUpadhyay ResumeDocument2 pagesDeepikaUpadhyay Resumekanishk vohraNo ratings yet
- Cti 2500 Quick Start - Installation Guide: Purpose of This DocumentDocument7 pagesCti 2500 Quick Start - Installation Guide: Purpose of This DocumentMartin BonuccelliNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: Leica Viva TS11Document4 pagesDatasheet: Leica Viva TS11Fahrizal RizalNo ratings yet
- C Data Structure PracticeDocument507 pagesC Data Structure Practicedivyam singhNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Threat DetectionsDocument18 pagesCybersecurity Threat DetectionsZachary CurtisNo ratings yet
- Installing PSCAD X4 PDFDocument61 pagesInstalling PSCAD X4 PDFEduardo GaliciaNo ratings yet
- How Do You Add Atom - Link With Rel - Self - To An Rss Document - Stack OverflowDocument4 pagesHow Do You Add Atom - Link With Rel - Self - To An Rss Document - Stack OverflowabeerNo ratings yet
- Mohamed EldesokyDocument2 pagesMohamed Eldesokymohamed EldesokyNo ratings yet
- FTG UI Mod - V2.1 - ManualDocument5 pagesFTG UI Mod - V2.1 - ManualSimone NardoNo ratings yet
- DSI Guide - Python List MethodsDocument16 pagesDSI Guide - Python List MethodsDr CashNo ratings yet
- Office Automation Tools II Unit 1Document24 pagesOffice Automation Tools II Unit 1Khalid AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Extract The .Msi FilesDocument2 pagesExtract The .Msi FilesvladimirNo ratings yet
- Distributed SQL: The Architecture Behind Mariadb Xpand: April 2021Document19 pagesDistributed SQL: The Architecture Behind Mariadb Xpand: April 2021IvyNo ratings yet
- Message Passing ArchitectureDocument32 pagesMessage Passing ArchitectureMøÑïkå ShàrmåNo ratings yet