Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsTitle Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Title Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Uploaded by
Nikki BorcenaThe document discusses Philippine laws related to parental authority and child protection. It outlines circumstances under which parental authority may be terminated, such as death of the parent or child, adoption, or abuse. Child abuse is defined as physical, psychological, sexual abuse and neglect. The law establishes protections for children under 18 from exploitation and gives guidelines for reporting abuse. It also discusses exemption of children below 15 from criminal liability and the process for taking custody of children below the age of criminal responsibility. Finally, it outlines the composition of the Juvenile Justice and Welfare Council.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Police Report: Case No: Date: Reporting Officer: Prepared By: IncidentDocument1 pagePolice Report: Case No: Date: Reporting Officer: Prepared By: Incidentjv bhogsNo ratings yet
- Bs Criminology Obe Curriculum: St. Mary'S College of Tagum, IncDocument24 pagesBs Criminology Obe Curriculum: St. Mary'S College of Tagum, IncRichelle BenaguaNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesQuestionnaireChristopher ConleyNo ratings yet
- ARD and DUI - Questions and Answers - Adam County, PADocument3 pagesARD and DUI - Questions and Answers - Adam County, PASteve Rice LawNo ratings yet
- Sample AffidavitDocument6 pagesSample AffidavitKarNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7610Document19 pagesRepublic Act No. 7610Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610 FrancisDocument34 pagesRepublic Act 7610 FrancisFrancis Rey GayaniloNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V Crimsoc 5Document4 pagesCHAPTER V Crimsoc 5eunard.albania4No ratings yet
- Ra 7610 Report SummaryDocument6 pagesRa 7610 Report SummaryyetyetNo ratings yet
- JuvenileDocument10 pagesJuvenilecandilariafacuraNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document69 pagesRa 7610Moises MasedmanNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument23 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActMyk Rthur DavidNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (RA 7610)Document20 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (RA 7610)Motiong MpsNo ratings yet
- AGALI Policy Brief Child Protection Justice Act 10 1 11Document2 pagesAGALI Policy Brief Child Protection Justice Act 10 1 11Kate CarinóNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument19 pagesRA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActEmerald RidaoNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse - Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument33 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse - Exploitation and Discrimination ActJuan Carlos NocedalNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 - Child Abuse LawDocument11 pagesRA 7610 - Child Abuse LawCiara NavarroNo ratings yet
- R A No 7610 SummaryDocument3 pagesR A No 7610 SummaryHoney Gio100% (2)
- (RA 7610) Child AbuseDocument20 pages(RA 7610) Child AbuseNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- RA7610Document4 pagesRA7610Claudine Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Juvenile-Module-2021 - FinalDocument16 pagesJuvenile-Module-2021 - FinalMelchor MaasinNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document8 pagesRa 7610lex libertadoreNo ratings yet
- SPL Group II Part I GallegaDocument114 pagesSPL Group II Part I GallegaMARK TIMUGEN BELLANo ratings yet
- Beed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroDocument22 pagesBeed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroRosalinda Rubio SanicoNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document27 pagesRa 7610MONA LIZA JOIE URSALNo ratings yet
- Irr 9523Document9 pagesIrr 9523klariseNo ratings yet
- Laws Protecting ChildrenDocument144 pagesLaws Protecting ChildrenCristina Joy Vicente CruzNo ratings yet
- Crimso5 Juvenile-Delinquency (Reviewer)Document6 pagesCrimso5 Juvenile-Delinquency (Reviewer)tweeengtwengNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument22 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledLove-Love Jeraldine Mondia DalupinesNo ratings yet
- RA 7610-Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument13 pagesRA 7610-Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActRosa GamaroNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610 Nad JurisprudenceDocument11 pagesRepublic Act 7610 Nad JurisprudencebertobalicdangNo ratings yet
- Special Laws 1Document6 pagesSpecial Laws 1bg009090No ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610Document11 pagesRepublic Act 7610Vaness MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Juvenile For MidtermDocument62 pagesLecture in Juvenile For MidtermMarlon CainongNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Republic Act 7610Document31 pagesGroup 1 - Republic Act 7610Sopi May Sun QueNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 - Anti-Child Abuse LawDocument15 pagesRA 7610 - Anti-Child Abuse LawAnonymous KgPX1oCfrNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse Relevant LawsDocument23 pagesChild Abuse Relevant LawsMaxim CadornaNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument12 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress Assembledprettyppink1987No ratings yet
- De CASTRO RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument36 pagesDe CASTRO RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActAnonymous PjHuK2kLNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument11 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledisttyNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document33 pagesRa 7610Noel Christopher G. Belleza100% (1)
- Other Special Penal LawsDocument47 pagesOther Special Penal LawsMa Jean Baluyo CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Salient Features of RA 7610 The Special Protection of Children Against Child AbuseDocument59 pagesLesson 5 Salient Features of RA 7610 The Special Protection of Children Against Child AbuseodangojohnheronNo ratings yet
- Ra 9344Document1 pageRa 9344thedoodlbotNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (Republic Act No. 7610, 17 June 1992)Document5 pagesSummary of The Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (Republic Act No. 7610, 17 June 1992)Grandeur P. G. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- An Act Providing For Stronger Deterrence and Special Protection Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination, and For Other PurposesDocument19 pagesAn Act Providing For Stronger Deterrence and Special Protection Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination, and For Other PurposesgirlNo ratings yet
- Anti-Child Abuse Law (R.a. 7610)Document15 pagesAnti-Child Abuse Law (R.a. 7610)Victoria Beltran SubaranNo ratings yet
- The Child and Youth Welfare Code RA7610Document18 pagesThe Child and Youth Welfare Code RA7610Rabhak Khal-Hadjj100% (24)
- Childrens ActDocument7 pagesChildrens ActDarlene GubantesNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument65 pagesRepublic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActkaiaceegeesNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document12 pagesRa 7610Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document10 pagesRa 7610Eliselda LegaspiNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument13 pagesRA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActKai RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Article Ititle, Policy, Principles and Definitions of TermsDocument12 pagesArticle Ititle, Policy, Principles and Definitions of TermsNelson OponNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument37 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledMa Janelli Erika AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument9 pagesRepublic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActmongNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Justice and Welfare Act of 2006Document21 pagesJuvenile Justice and Welfare Act of 2006sam cadleyNo ratings yet
- Child Protection: Executive Order No. 53Document7 pagesChild Protection: Executive Order No. 53Joana Samputon100% (1)
- Child Abuse LawDocument32 pagesChild Abuse LawPrincess MagpatocNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document17 pagesRa 7610RhoddickMagrataNo ratings yet
- What You Need to Know When Your Child Is Admitted to a Psychiatric FacilityFrom EverandWhat You Need to Know When Your Child Is Admitted to a Psychiatric FacilityNo ratings yet
- LEGALDocument13 pagesLEGALNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- 1987 Constitution (Art.13 18Document92 pages1987 Constitution (Art.13 18Nikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Sss and Gsis LawDocument61 pagesSss and Gsis LawNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Casio - Preferred Online Shopping PlatformDocument42 pagesCasio - Preferred Online Shopping PlatformNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects in Education: Discussant: Ana Rose C. GranadiDocument24 pagesLegal Aspects in Education: Discussant: Ana Rose C. GranadiNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- The Preferred Online Shopping Platform of Psba, Manila Students During The Time of Pandemic 2021Document22 pagesThe Preferred Online Shopping Platform of Psba, Manila Students During The Time of Pandemic 2021Nikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- The Birth of A Filipino National Consciousness: Cirilo Gazzingan, Iii Bsce - Ii Saint Paul University PhilippinesDocument74 pagesThe Birth of A Filipino National Consciousness: Cirilo Gazzingan, Iii Bsce - Ii Saint Paul University PhilippinesNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Strike Barangay RondaDocument3 pagesStrike Barangay Rondabacoor cps opnNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Inquiry, Investigation and TrialDocument2 pagesDifferentiate Inquiry, Investigation and TrialZeeshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hao vs. PeopleDocument16 pagesHao vs. PeopleMrln VloriaNo ratings yet
- Cancellation of BailsDocument21 pagesCancellation of BailsAditi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines, Willie Amaguin, Gildo Amaguin and Celso Amaguin, Willie Amaguin and Gildo AmaguinDocument11 pagesPeople of The Philippines, Willie Amaguin, Gildo Amaguin and Celso Amaguin, Willie Amaguin and Gildo AmaguinAndrei Anne PalomarNo ratings yet
- PDF People Vs Anonuevo CompressDocument1 pagePDF People Vs Anonuevo CompressEFGNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards CasesDocument84 pagesLabor Standards CasesAldrinmarkquintanaNo ratings yet
- Dungo v. People G.R. No. 209464Document2 pagesDungo v. People G.R. No. 209464Joycee Armillo50% (2)
- Next Legal Steps - PP vs. Tim Cansas XXXDocument6 pagesNext Legal Steps - PP vs. Tim Cansas XXXArchie MuyrongNo ratings yet
- AFTER OPNS DISTRICT BUTING For SPDDocument3 pagesAFTER OPNS DISTRICT BUTING For SPDGideon Tangan Ines Jr.No ratings yet
- Answer Key Criminal Law - IiDocument4 pagesAnswer Key Criminal Law - IiLalit AhakeNo ratings yet
- Consipracy As Tort UPSC Law OPtional Mains ConceptsDocument4 pagesConsipracy As Tort UPSC Law OPtional Mains ConceptsaskshubhangivermaNo ratings yet
- Maine Bullying DataDocument26 pagesMaine Bullying DataZach BlanchardNo ratings yet
- Taena Mo Part 2Document148 pagesTaena Mo Part 2Bea Czarina NavarroNo ratings yet
- Notes - Penal Laws On Sexual HarassmentDocument2 pagesNotes - Penal Laws On Sexual HarassmentStephen TesalonaNo ratings yet
- People vs. Jaime Jose, Et - Al., G.R. No. L-28232, Feb. 6, 1971Document26 pagesPeople vs. Jaime Jose, Et - Al., G.R. No. L-28232, Feb. 6, 1971Ivan ArchilleNo ratings yet
- Elements of Crime Index CardsDocument142 pagesElements of Crime Index CardsJea Co100% (1)
- Indian Law Institute: Online Assignment-III On Cyber CrimesDocument5 pagesIndian Law Institute: Online Assignment-III On Cyber CrimesDeepanshu ShakargayeNo ratings yet
- Buyers IndictmentDocument49 pagesBuyers IndictmentHayley PetersonNo ratings yet
- DPC ProjectDocument13 pagesDPC ProjectTaraChandraChouhanNo ratings yet
- Titles AND RUBRICS of Research Paper BA LLB IX SEMESTERDocument5 pagesTitles AND RUBRICS of Research Paper BA LLB IX SEMESTERSumit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jose Antonio Leviste V CADocument1 pageJose Antonio Leviste V CAAbby PerezNo ratings yet
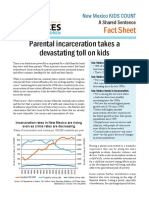
- NM Incarceration FactsheetDocument2 pagesNM Incarceration FactsheetNew Mexico Political ReportNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Animal Abuse To Violence and Other Forms of Antisocial BehaviorDocument13 pagesThe Relationship of Animal Abuse To Violence and Other Forms of Antisocial BehaviorLyn JonesNo ratings yet
- People Vs Ah ChongDocument1 pagePeople Vs Ah ChongCholong Adik Sayo HabangbuhayNo ratings yet
Title Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Title Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Uploaded by
Nikki Borcena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesThe document discusses Philippine laws related to parental authority and child protection. It outlines circumstances under which parental authority may be terminated, such as death of the parent or child, adoption, or abuse. Child abuse is defined as physical, psychological, sexual abuse and neglect. The law establishes protections for children under 18 from exploitation and gives guidelines for reporting abuse. It also discusses exemption of children below 15 from criminal liability and the process for taking custody of children below the age of criminal responsibility. Finally, it outlines the composition of the Juvenile Justice and Welfare Council.
Original Description:
Original Title
RA 7610, RA 9344,
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses Philippine laws related to parental authority and child protection. It outlines circumstances under which parental authority may be terminated, such as death of the parent or child, adoption, or abuse. Child abuse is defined as physical, psychological, sexual abuse and neglect. The law establishes protections for children under 18 from exploitation and gives guidelines for reporting abuse. It also discusses exemption of children below 15 from criminal liability and the process for taking custody of children below the age of criminal responsibility. Finally, it outlines the composition of the Juvenile Justice and Welfare Council.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views3 pagesTitle Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Title Ix:Parental Authority (Family Code of The Philippines)
Uploaded by
Nikki BorcenaThe document discusses Philippine laws related to parental authority and child protection. It outlines circumstances under which parental authority may be terminated, such as death of the parent or child, adoption, or abuse. Child abuse is defined as physical, psychological, sexual abuse and neglect. The law establishes protections for children under 18 from exploitation and gives guidelines for reporting abuse. It also discusses exemption of children below 15 from criminal liability and the process for taking custody of children below the age of criminal responsibility. Finally, it outlines the composition of the Juvenile Justice and Welfare Council.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
TITLE IX:PARENTAL AUTHORITY (FAMILY CODE OF THE PHILIPPINES)
CHAPTER 5: Suspension or Termination of Parental Authority
Article 228
- Parental Authority terminates permanently:
(1) Upon the death of the parents;
(2) Upon the death of the Child; or
(3) Upon emancipation of the Child.
Article 229
- Unless subsequently revived by a final judgement, parental authority also
terminate;
(1) Upon adaption of the Child;
(2) Upon appointment of a general guardian;
(3) Upon judicial declaration of abandonment of the child in case filed for the
purpose;
(4) Upon the final judgement of a competent court divesting the party concerned
of parental authority; or
(5) Upon judicial declaration of absence
or incapacity of the person exercising parental authority.
Article 230
- Parental Authority iis suspended upon conviction of the parent or the person
exercising the same of a crime which carries with it the penalty civil interdiction.
Article 231
- The court in an action filed for the purpose or in a related case may also
suspend parental authority of the parent or the person exercising the same:
1) Treats the child with excessive harshness
or cruelty;
(2) Gives the child corrupting orders, counsel or example;
(3) Compels the child to beg; or
(4) Subjects the child or allows him to be subjected to acts of lasciviousness.
Article 232
- If the person exercising the Parental Authority has subjected the child or allowed him
to be subjected to sexual abuse, such person shall be permanently deprived by the
court of such authority.
Article 233
- The person exercising substitute parental authority shall have the same authority over
the person of the child as parents.
- In no case shall the school administrator, teacher or individual engaged in child care
and exercising special parental authority, inflict corporal punishment upon the child.
Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and
Discrimination Act (RA 7610)
Who are considered Children?
• Children - persons below 18 years of age or those over but are unable to to fully
take care of themselves or protect themselves from abuse, neglect, cruelty,
exploitation or discrimination because of a physical or mental disability or
condition.
What is the Rationale of RA 7610?
To give protection to persons below 18 years of age or those over but are
unable to fully take care of themselves or protect themselves from abuse, cruelty and
exploitation.
Offenses Against Children under RA 7610
1. Child Prostitution and other sexual abuse
2. Attempt to commit child prostitution
3. Child Trafficking
4. Attempt to commit child trafficking
5. Child pornography and indecent shows and publication
6. Other Acts of Neglect, Abuse, Cruelty or Exploitation and Other Conditions
Prejudicial to the Child’s Development
Other Acts of Abuse
Any person who shall keep or have in his company a minor, twelve 12 years or under or
who is 10 years or more his junior in any public or private place, hotel, motel, beer joint,
discotheque, cabaret, pension, house, sauna or massage parlor, beach and or other
tourist resort or similar places.
Any person who shall use, coerce, force or intimidate a street child or any other child to:
Beg or use begging as means of living
Act as conduit or middleman in drug trafficking or pushing
Conduct any illegal activities
Physical Abuse
The inflicting of physical injury upon a child. This may include, burning, hitting,
punching, shaking, kicking, beating, or otherwise harming a child. The parent or
caretaker may not have intended to hurt the child, the injury is not an accident. It may,
however, been the result of over-discipline or physical punishment that is inappropriate
to the child’s age.
Psychological/Emotional Abuse
• also known as: verbal abuse, mental abuse, andpsychological maltreatment
• Includes acts or the failures to act by parents or caretakers that have caused or
could cause, serious behavioral, cognitive, emotional, or mental disorders
• Constantly blaming or putting down a child; excessive yelling, shaming
Neglect
• the withdrawal of or failure to provide a child with the basic necessities for
physical growth and development. This can include inappropriate clothing for
the weather, unhealthy food or no food at all, lack of supervision, denial of
medical care to a sick or injured child or denial of love and affection.
Reporting
• A person who learns of facts or circumstances that gives rise to the belief that a
child has suffered abuse may report the same, either orally or in writing, to the
Department, Police or any other law enforcement agency or to the BCPC.
R.A. 10630, amending R.A. 9344
“An Act Strengthening the Juvenile Justice System in the Philippines”
Child Exempt from Criminal Responsibility
A child fifteen (15) years of age or under at the time of the commission of the
offense.
A child is deemed to be fifteen (15) years of age on the day of the fifteenth
anniversary of his/her birthdate.
A child above fifteen (15) years but below eighteen (18) years of age.
Such child shall be subjected to an intervention program. But, if he/she acted with
discernment, he/she shall be subjected to appropriate proceedings.
Note: Exemption from criminal liability does not include
exemption from civil liability
Process for taking into custody child below the age of criminal responsibility
Composition of the Juvenile Justice and Welfare Council (JJWC)
representatives of the following or departments or agencies, whose ranks shall not be
lower than director:
1) Department of Justice (DOJ)
2) Department of Social Welfare and Development (DSWD)
3) Council for the Welfare of Children (CWC)
4) Department of Education (DepEd)
5) Department of the Interior and Local Government (DILG)
6) Commission on Human Rights (CHR)
7) National Youth Commission (NYC)
8) Two (2) representatives from NGOs, designated by the Secretary of Social
Welfare and Development, selected based on the criteria established by the
Council
9) Department of Health (DOH)
10)One(1) representative each from the Leagues of Provinces, Cities,
Municipalities, and Barangays
You might also like
- Police Report: Case No: Date: Reporting Officer: Prepared By: IncidentDocument1 pagePolice Report: Case No: Date: Reporting Officer: Prepared By: Incidentjv bhogsNo ratings yet
- Bs Criminology Obe Curriculum: St. Mary'S College of Tagum, IncDocument24 pagesBs Criminology Obe Curriculum: St. Mary'S College of Tagum, IncRichelle BenaguaNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesQuestionnaireChristopher ConleyNo ratings yet
- ARD and DUI - Questions and Answers - Adam County, PADocument3 pagesARD and DUI - Questions and Answers - Adam County, PASteve Rice LawNo ratings yet
- Sample AffidavitDocument6 pagesSample AffidavitKarNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 7610Document19 pagesRepublic Act No. 7610Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610 FrancisDocument34 pagesRepublic Act 7610 FrancisFrancis Rey GayaniloNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER V Crimsoc 5Document4 pagesCHAPTER V Crimsoc 5eunard.albania4No ratings yet
- Ra 7610 Report SummaryDocument6 pagesRa 7610 Report SummaryyetyetNo ratings yet
- JuvenileDocument10 pagesJuvenilecandilariafacuraNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document69 pagesRa 7610Moises MasedmanNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument23 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActMyk Rthur DavidNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (RA 7610)Document20 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (RA 7610)Motiong MpsNo ratings yet
- AGALI Policy Brief Child Protection Justice Act 10 1 11Document2 pagesAGALI Policy Brief Child Protection Justice Act 10 1 11Kate CarinóNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument19 pagesRA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActEmerald RidaoNo ratings yet
- Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse - Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument33 pagesSpecial Protection of Children Against Child Abuse - Exploitation and Discrimination ActJuan Carlos NocedalNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 - Child Abuse LawDocument11 pagesRA 7610 - Child Abuse LawCiara NavarroNo ratings yet
- R A No 7610 SummaryDocument3 pagesR A No 7610 SummaryHoney Gio100% (2)
- (RA 7610) Child AbuseDocument20 pages(RA 7610) Child AbuseNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- RA7610Document4 pagesRA7610Claudine Ann ManaloNo ratings yet
- Juvenile-Module-2021 - FinalDocument16 pagesJuvenile-Module-2021 - FinalMelchor MaasinNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document8 pagesRa 7610lex libertadoreNo ratings yet
- SPL Group II Part I GallegaDocument114 pagesSPL Group II Part I GallegaMARK TIMUGEN BELLANo ratings yet
- Beed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroDocument22 pagesBeed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroRosalinda Rubio SanicoNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document27 pagesRa 7610MONA LIZA JOIE URSALNo ratings yet
- Irr 9523Document9 pagesIrr 9523klariseNo ratings yet
- Laws Protecting ChildrenDocument144 pagesLaws Protecting ChildrenCristina Joy Vicente CruzNo ratings yet
- Crimso5 Juvenile-Delinquency (Reviewer)Document6 pagesCrimso5 Juvenile-Delinquency (Reviewer)tweeengtwengNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument22 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledLove-Love Jeraldine Mondia DalupinesNo ratings yet
- RA 7610-Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument13 pagesRA 7610-Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActRosa GamaroNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610 Nad JurisprudenceDocument11 pagesRepublic Act 7610 Nad JurisprudencebertobalicdangNo ratings yet
- Special Laws 1Document6 pagesSpecial Laws 1bg009090No ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610Document11 pagesRepublic Act 7610Vaness MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Juvenile For MidtermDocument62 pagesLecture in Juvenile For MidtermMarlon CainongNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Republic Act 7610Document31 pagesGroup 1 - Republic Act 7610Sopi May Sun QueNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 - Anti-Child Abuse LawDocument15 pagesRA 7610 - Anti-Child Abuse LawAnonymous KgPX1oCfrNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse Relevant LawsDocument23 pagesChild Abuse Relevant LawsMaxim CadornaNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument12 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress Assembledprettyppink1987No ratings yet
- De CASTRO RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument36 pagesDe CASTRO RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActAnonymous PjHuK2kLNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument11 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledisttyNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document33 pagesRa 7610Noel Christopher G. Belleza100% (1)
- Other Special Penal LawsDocument47 pagesOther Special Penal LawsMa Jean Baluyo CastanedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Salient Features of RA 7610 The Special Protection of Children Against Child AbuseDocument59 pagesLesson 5 Salient Features of RA 7610 The Special Protection of Children Against Child AbuseodangojohnheronNo ratings yet
- Ra 9344Document1 pageRa 9344thedoodlbotNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (Republic Act No. 7610, 17 June 1992)Document5 pagesSummary of The Special Protection of Children Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination Act (Republic Act No. 7610, 17 June 1992)Grandeur P. G. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- An Act Providing For Stronger Deterrence and Special Protection Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination, and For Other PurposesDocument19 pagesAn Act Providing For Stronger Deterrence and Special Protection Against Child Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination, and For Other PurposesgirlNo ratings yet
- Anti-Child Abuse Law (R.a. 7610)Document15 pagesAnti-Child Abuse Law (R.a. 7610)Victoria Beltran SubaranNo ratings yet
- The Child and Youth Welfare Code RA7610Document18 pagesThe Child and Youth Welfare Code RA7610Rabhak Khal-Hadjj100% (24)
- Childrens ActDocument7 pagesChildrens ActDarlene GubantesNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument65 pagesRepublic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActkaiaceegeesNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document12 pagesRa 7610Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document10 pagesRa 7610Eliselda LegaspiNo ratings yet
- RA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument13 pagesRA 7610 Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActKai RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Article Ititle, Policy, Principles and Definitions of TermsDocument12 pagesArticle Ititle, Policy, Principles and Definitions of TermsNelson OponNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument37 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledMa Janelli Erika AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActDocument9 pagesRepublic Act 7610: Special Protection of Children Against Abuse, Exploitation and Discrimination ActmongNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Justice and Welfare Act of 2006Document21 pagesJuvenile Justice and Welfare Act of 2006sam cadleyNo ratings yet
- Child Protection: Executive Order No. 53Document7 pagesChild Protection: Executive Order No. 53Joana Samputon100% (1)
- Child Abuse LawDocument32 pagesChild Abuse LawPrincess MagpatocNo ratings yet
- Ra 7610Document17 pagesRa 7610RhoddickMagrataNo ratings yet
- What You Need to Know When Your Child Is Admitted to a Psychiatric FacilityFrom EverandWhat You Need to Know When Your Child Is Admitted to a Psychiatric FacilityNo ratings yet
- LEGALDocument13 pagesLEGALNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- 1987 Constitution (Art.13 18Document92 pages1987 Constitution (Art.13 18Nikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Sss and Gsis LawDocument61 pagesSss and Gsis LawNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Casio - Preferred Online Shopping PlatformDocument42 pagesCasio - Preferred Online Shopping PlatformNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Legal Aspects in Education: Discussant: Ana Rose C. GranadiDocument24 pagesLegal Aspects in Education: Discussant: Ana Rose C. GranadiNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- The Preferred Online Shopping Platform of Psba, Manila Students During The Time of Pandemic 2021Document22 pagesThe Preferred Online Shopping Platform of Psba, Manila Students During The Time of Pandemic 2021Nikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- The Birth of A Filipino National Consciousness: Cirilo Gazzingan, Iii Bsce - Ii Saint Paul University PhilippinesDocument74 pagesThe Birth of A Filipino National Consciousness: Cirilo Gazzingan, Iii Bsce - Ii Saint Paul University PhilippinesNikki BorcenaNo ratings yet
- Strike Barangay RondaDocument3 pagesStrike Barangay Rondabacoor cps opnNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Inquiry, Investigation and TrialDocument2 pagesDifferentiate Inquiry, Investigation and TrialZeeshan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hao vs. PeopleDocument16 pagesHao vs. PeopleMrln VloriaNo ratings yet
- Cancellation of BailsDocument21 pagesCancellation of BailsAditi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines, Willie Amaguin, Gildo Amaguin and Celso Amaguin, Willie Amaguin and Gildo AmaguinDocument11 pagesPeople of The Philippines, Willie Amaguin, Gildo Amaguin and Celso Amaguin, Willie Amaguin and Gildo AmaguinAndrei Anne PalomarNo ratings yet
- PDF People Vs Anonuevo CompressDocument1 pagePDF People Vs Anonuevo CompressEFGNo ratings yet
- Labor Standards CasesDocument84 pagesLabor Standards CasesAldrinmarkquintanaNo ratings yet
- Dungo v. People G.R. No. 209464Document2 pagesDungo v. People G.R. No. 209464Joycee Armillo50% (2)
- Next Legal Steps - PP vs. Tim Cansas XXXDocument6 pagesNext Legal Steps - PP vs. Tim Cansas XXXArchie MuyrongNo ratings yet
- AFTER OPNS DISTRICT BUTING For SPDDocument3 pagesAFTER OPNS DISTRICT BUTING For SPDGideon Tangan Ines Jr.No ratings yet
- Answer Key Criminal Law - IiDocument4 pagesAnswer Key Criminal Law - IiLalit AhakeNo ratings yet
- Consipracy As Tort UPSC Law OPtional Mains ConceptsDocument4 pagesConsipracy As Tort UPSC Law OPtional Mains ConceptsaskshubhangivermaNo ratings yet
- Maine Bullying DataDocument26 pagesMaine Bullying DataZach BlanchardNo ratings yet
- Taena Mo Part 2Document148 pagesTaena Mo Part 2Bea Czarina NavarroNo ratings yet
- Notes - Penal Laws On Sexual HarassmentDocument2 pagesNotes - Penal Laws On Sexual HarassmentStephen TesalonaNo ratings yet
- People vs. Jaime Jose, Et - Al., G.R. No. L-28232, Feb. 6, 1971Document26 pagesPeople vs. Jaime Jose, Et - Al., G.R. No. L-28232, Feb. 6, 1971Ivan ArchilleNo ratings yet
- Elements of Crime Index CardsDocument142 pagesElements of Crime Index CardsJea Co100% (1)
- Indian Law Institute: Online Assignment-III On Cyber CrimesDocument5 pagesIndian Law Institute: Online Assignment-III On Cyber CrimesDeepanshu ShakargayeNo ratings yet
- Buyers IndictmentDocument49 pagesBuyers IndictmentHayley PetersonNo ratings yet
- DPC ProjectDocument13 pagesDPC ProjectTaraChandraChouhanNo ratings yet
- Titles AND RUBRICS of Research Paper BA LLB IX SEMESTERDocument5 pagesTitles AND RUBRICS of Research Paper BA LLB IX SEMESTERSumit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jose Antonio Leviste V CADocument1 pageJose Antonio Leviste V CAAbby PerezNo ratings yet
- NM Incarceration FactsheetDocument2 pagesNM Incarceration FactsheetNew Mexico Political ReportNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Animal Abuse To Violence and Other Forms of Antisocial BehaviorDocument13 pagesThe Relationship of Animal Abuse To Violence and Other Forms of Antisocial BehaviorLyn JonesNo ratings yet
- People Vs Ah ChongDocument1 pagePeople Vs Ah ChongCholong Adik Sayo HabangbuhayNo ratings yet