Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
Uploaded by
Richard EVCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- FSP 28"-2000 Psi Diverter/BOP: Diverters' Simplicity Maximizes ReliabilityDocument2 pagesFSP 28"-2000 Psi Diverter/BOP: Diverters' Simplicity Maximizes Reliabilitymehmet sait öztürkNo ratings yet
- Product Information Bulletin: Date: Bulletin Number: 1000059437-PIB Revision: 01Document7 pagesProduct Information Bulletin: Date: Bulletin Number: 1000059437-PIB Revision: 01carlosorizabaNo ratings yet
- D601000439 Man 001Document25 pagesD601000439 Man 001Riski KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Equipment FlyerDocument7 pagesEquipment FlyerCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- 15K Lightweight NOVDocument4 pages15K Lightweight NOVJuanNo ratings yet
- Hydril Blowout Preventers Ram Seal KitsDocument1 pageHydril Blowout Preventers Ram Seal KitsJIN WANGNo ratings yet
- Hydril Blowout Preventers Ram AssembliesDocument2 pagesHydril Blowout Preventers Ram AssembliesJIN WANGNo ratings yet
- Offshore Project LastDocument23 pagesOffshore Project LastchigooNo ratings yet
- Aftermarket Services: Parts Service Repair TrainingDocument12 pagesAftermarket Services: Parts Service Repair Trainingmehmet sait öztürkNo ratings yet
- Model fm4Document25 pagesModel fm4LeandroNo ratings yet
- D601005184 Man 001Document17 pagesD601005184 Man 001Riski Kurniawan100% (1)
- BPV Specification and Drawings PDFDocument4 pagesBPV Specification and Drawings PDFParag PadoleNo ratings yet
- Maintenance & Operations Manual Regan Type K Blowout PreventerDocument4 pagesMaintenance & Operations Manual Regan Type K Blowout PreventerAshok SureshNo ratings yet
- D392005428-MKT-001 6012 Bop PDFDocument2 pagesD392005428-MKT-001 6012 Bop PDFMitul PatelNo ratings yet
- M60es54 Na549y QC Man 001Document29 pagesM60es54 Na549y QC Man 001Riski Kurniawan67% (3)
- CatalogDocument424 pagesCatalogLuis David Concha CastilloNo ratings yet
- Operating and Service Manual For Hyd. Act. Series 4000,5000,6500Document24 pagesOperating and Service Manual For Hyd. Act. Series 4000,5000,6500Mehdi Norouzi100% (1)
- Field Evaluation Test Results: Cameron Information Sheet 99-006Document1 pageField Evaluation Test Results: Cameron Information Sheet 99-006Gregory StewartNo ratings yet
- FH18 35(21)英文说明书Document16 pagesFH18 35(21)英文说明书ADM MTCNo ratings yet
- PB DDM 026Document3 pagesPB DDM 026Jim SharpNo ratings yet
- VetoDocument4 pagesVetohenry christian wontumiNo ratings yet
- Trex 03168Document1 pageTrex 03168OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Cameron EB 919 Rev A1 - Bonnet Bolt Makeup ProceduresDocument7 pagesCameron EB 919 Rev A1 - Bonnet Bolt Makeup Procedureskurtis.clevelandNo ratings yet
- Blowout Preventers: Invetion Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipDocument40 pagesBlowout Preventers: Invetion Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipAhmed HajiNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Alert: 22 February 2021Document4 pagesProduct Safety Alert: 22 February 2021carlosorizabaNo ratings yet
- General Catalog 2016Document64 pagesGeneral Catalog 2016Jamal100% (1)
- Drilling BOPsDocument12 pagesDrilling BOPsSaroo MusicNo ratings yet
- Bowl Protectors and ToolsDocument2 pagesBowl Protectors and Toolsagfdgsdf100% (1)
- Contitech HP HosesDocument65 pagesContitech HP HosesRobert FlateråsNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual 1222B: Booster Cylinder Assembly EH34-BC03Document21 pagesTech Manual 1222B: Booster Cylinder Assembly EH34-BC03jose perozoNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual: 5.12", 10,000 Psi Working Pressure, Eh Series Single, Dual, Triple & Quad Combi BopDocument34 pagesTech Manual: 5.12", 10,000 Psi Working Pressure, Eh Series Single, Dual, Triple & Quad Combi BopPastor VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Coil E Coil Unit CatalogueDocument2 pagesCoil E Coil Unit CatalogueLuisNo ratings yet
- Accumulator - Yancheng RuihuaDocument26 pagesAccumulator - Yancheng RuihuaBoedi SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Stripper TOT 2.50 10M DS34 TechMan1146Document13 pagesStripper TOT 2.50 10M DS34 TechMan1146Diego OspinaNo ratings yet
- DL AnnularDocument40 pagesDL Annulara.solvevNo ratings yet
- Parker HTR ActuatorDocument22 pagesParker HTR ActuatorYorkistNo ratings yet
- 25k Bop FlyerDocument1 page25k Bop FlyersyedainahmadNo ratings yet
- Baker PDFDocument6 pagesBaker PDFanthony silvaNo ratings yet
- FMC Weco Butterfly Valve Catalog-006Document1 pageFMC Weco Butterfly Valve Catalog-006ferdy110276No ratings yet
- 1PackerSystem PackerAccessories&tools PDFDocument21 pages1PackerSystem PackerAccessories&tools PDFAnand aashishNo ratings yet
- Oilfield UnionsDocument5 pagesOilfield Unionslalberto96No ratings yet
- Uztel OrizontalDocument5 pagesUztel OrizontalDorin RaduNo ratings yet
- Cameron EB 539 D Rev D1 - Preferred Seal Orientation For Pressure Control EquipmentDocument7 pagesCameron EB 539 D Rev D1 - Preferred Seal Orientation For Pressure Control EquipmentCanrig RamdeNo ratings yet
- Recommended Installation of A Bop Control SystemDocument8 pagesRecommended Installation of A Bop Control SystemHamid Reza BabaeiNo ratings yet
- Blow Out PreventorDocument6 pagesBlow Out PreventorCesar Valdivia MontañoNo ratings yet
- 12 Drilling PreventersDocument82 pages12 Drilling PreventersDavid Kusuma100% (1)
- Cameron EB 555 D Rev U2 - VBR Engineering InfoDocument6 pagesCameron EB 555 D Rev U2 - VBR Engineering InfoCanrig Ramde100% (1)
- Maintenance Schedule For Adapter Flange - 5131086 - 01Document7 pagesMaintenance Schedule For Adapter Flange - 5131086 - 01franko guddiNo ratings yet
- Claxton Riser Systems BrochureDocument12 pagesClaxton Riser Systems BrochureQingming MaNo ratings yet
- FKQ50-2 Use R ManualDocument56 pagesFKQ50-2 Use R ManualMuthia AstriNo ratings yet
- QBH Ram Bop'S: 4-1/16" 15,000 Psi WPDocument32 pagesQBH Ram Bop'S: 4-1/16" 15,000 Psi WPjuan olarte0% (1)
- D4510664815-Pib-001 1 5 in SPM Valves Rev 06 LDocument7 pagesD4510664815-Pib-001 1 5 in SPM Valves Rev 06 LEdmo VirgensNo ratings yet
- Oteco Inc. 3" Reset Relief Valve 3" LPT Inlet & Outlet Installation & Maintenance Manual PART NO. 130350Document12 pagesOteco Inc. 3" Reset Relief Valve 3" LPT Inlet & Outlet Installation & Maintenance Manual PART NO. 130350VRV.RELATORIO.AVARIA RELATORIO.AVARIANo ratings yet
- Sub-X: Wellhead & BOP GasketsDocument2 pagesSub-X: Wellhead & BOP GasketsEugene EvgerNo ratings yet
- Design of Blowout Preventer Lifting FramDocument10 pagesDesign of Blowout Preventer Lifting FramAndreansyah PratamaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Ebb N Fid5717Document7 pagesUser Manual Ebb N Fid5717Andrey GapsNo ratings yet
- 2 - Completion Pressure Control Equipment - Well Control For Well Intervention - 6619932 - 01Document94 pages2 - Completion Pressure Control Equipment - Well Control For Well Intervention - 6619932 - 01Carlos A.No ratings yet
- KSB Pump Movi ManualDocument12 pagesKSB Pump Movi ManualVenkat Dora100% (5)
- OMM and OMME Repair InstructionsDocument11 pagesOMM and OMME Repair InstructionsleonNo ratings yet
- Bap1929-100 InstallationDocument29 pagesBap1929-100 InstallationDAVID JONATHAN ALVAREZ CASTILLONo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-36-40Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-36-40Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-16-20Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-16-20Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-6-10Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-6-10Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Battery and Vessel - : For Compressor Without Cold Weather Equipments EC StandardDocument2 pagesBattery and Vessel - : For Compressor Without Cold Weather Equipments EC StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-1-5Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-1-5Richard EVNo ratings yet
- XA Series 62Document1 pageXA Series 62Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Frame and Mounts - : StandardDocument1 pageFrame and Mounts - : StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- XA Series 58 59Document2 pagesXA Series 58 59Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Oil System - : StandardDocument2 pagesOil System - : StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Bodywork - : XAS 137 StandardDocument4 pagesBodywork - : XAS 137 StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- JDN Air Hoists ProfiDocument8 pagesJDN Air Hoists ProfiRichard EVNo ratings yet
- G-SHOCK Manual 5132 PDFDocument4 pagesG-SHOCK Manual 5132 PDFRichard EV100% (1)
- T 19Document1 pageT 19Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Aramax Wedge-Band: Banded BeltDocument4 pagesAramax Wedge-Band: Banded BeltRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Ks Permaglide CatalogueDocument76 pagesKs Permaglide CatalogueSkocko SkockicNo ratings yet
- Quincy CompressorDocument112 pagesQuincy CompressorRichard EV100% (2)
- Fishing Tools PDFDocument45 pagesFishing Tools PDFRichard EV100% (1)
- Pacseal HydraulicDocument10 pagesPacseal HydraulicRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Rig Power LLCDocument12 pagesRig Power LLCRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges Stainless Steel, Safety Pattern Version, High Overpressure Safety Model 232.36/233.36, Without/with Liquid FillingDocument2 pagesBourdon Tube Pressure Gauges Stainless Steel, Safety Pattern Version, High Overpressure Safety Model 232.36/233.36, Without/with Liquid FillingRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Yoke Industrial Corp.: Company Profi LeDocument1 pageYoke Industrial Corp.: Company Profi LeRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Agitator Manual AM 001 Rev5Document37 pagesAgitator Manual AM 001 Rev5Richard EVNo ratings yet
- MAYAKIINC BusinessPlanDocument20 pagesMAYAKIINC BusinessPlanRichard EVNo ratings yet
- The Atomic SublimeDocument28 pagesThe Atomic SublimeMarco BellanoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Bidang Kemampuan Suplai (Scope of Supply) Untuk Pengadaan BarangDocument6 pagesDaftar Bidang Kemampuan Suplai (Scope of Supply) Untuk Pengadaan BarangAdhiezNo ratings yet
- Engagementletter - Business Closure20Document4 pagesEngagementletter - Business Closure20Dv AccountingNo ratings yet
- 12f-601-Midterm Machine LearningDocument21 pages12f-601-Midterm Machine Learningale mekeNo ratings yet
- Soundoff Led Flasher ManualDocument2 pagesSoundoff Led Flasher ManualDaniel BonillaNo ratings yet
- E.G. Admin - UserDocument2 pagesE.G. Admin - UserdavidakpaluNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Visual Studio IDE With FeaturesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Visual Studio IDE With FeaturesriponcseNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover OptimizationDocument35 pagesFDD LTE Handover OptimizationmunzewNo ratings yet
- S.H.A.R.D Rev 2Document21 pagesS.H.A.R.D Rev 2Hassaan tahirNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall Types, and Instance Parameters: 1. Start Revit 2020Document36 pagesCurtain Wall Types, and Instance Parameters: 1. Start Revit 2020Jasmina HajdukovicNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things and SecurityDocument9 pagesInternet of Things and SecurityNareshNo ratings yet
- CA51013 - ACTIVITY 1 (Group Work)Document2 pagesCA51013 - ACTIVITY 1 (Group Work)Elaine AntonioNo ratings yet
- 12ABM - Group 6 (TSSBTE)Document2 pages12ABM - Group 6 (TSSBTE)Kimberly ValdezNo ratings yet
- AVIC-X1R Installation Manual en de IT ES FI GRDocument181 pagesAVIC-X1R Installation Manual en de IT ES FI GRMartin Czuba OlsenNo ratings yet
- PetroChem EnggDocument90 pagesPetroChem EnggSampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Big Book of Windows HacksDocument8 pagesBig Book of Windows HacksRendy Adam FarhanNo ratings yet
- ActivityGuide ConfigDocument176 pagesActivityGuide Configrajeshgr9063No ratings yet
- BS en 10111 - 2008Document16 pagesBS en 10111 - 2008Артем ТитовNo ratings yet
- Alex Stancu - WiFi Mesh Optimization For Bucharest City CenterDocument62 pagesAlex Stancu - WiFi Mesh Optimization For Bucharest City CenterRazvan MaziluNo ratings yet
- E Starco Steel Elevator BucketDocument1 pageE Starco Steel Elevator BucketAhmed SadekNo ratings yet
- Do You Know How Map - HashMap Works Internally in Java - Part 1 PDFDocument1 pageDo You Know How Map - HashMap Works Internally in Java - Part 1 PDFYaegar WainNo ratings yet
- 101景觀台解謎遊戲憑證Document3 pages101景觀台解謎遊戲憑證Bing Zhang WangNo ratings yet
- Global Business Intelligence: An Integrated Business Intelligence Solution Across GT Nexus Trade and LogisticsDocument1 pageGlobal Business Intelligence: An Integrated Business Intelligence Solution Across GT Nexus Trade and LogisticsMageshNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Contact Center Express Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 9.0Document50 pagesCisco Unified Contact Center Express Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 9.0Mohammed alhimyariNo ratings yet
- RWTP GB Mne Msa 000151Document90 pagesRWTP GB Mne Msa 000151slayerzzz22No ratings yet
- Risk Management by Protiviti X MentorKartDocument14 pagesRisk Management by Protiviti X MentorKartShubam VermaNo ratings yet
- Flotation Equipment Selection - OutotecDocument13 pagesFlotation Equipment Selection - Outoteclouza8No ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbineDocument19 pagesHydraulic Turbinesami almjanNo ratings yet
- MTL101:: Tutorial 3:: Linear AlgebraDocument2 pagesMTL101:: Tutorial 3:: Linear AlgebraKuldeep MalNo ratings yet
- JS - Zoom Parents GuideDocument2 pagesJS - Zoom Parents GuideNoman KulachiNo ratings yet
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
Uploaded by
Richard EVOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
SL Manual Lock 13 58 Shaffer Ram Bop Page-11-15
Uploaded by
Richard EVCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 2
Operation
Section 2
Operation
2.1 Inspection • checking for external hydraulic leaks while
The inspection process includes the activities listed below. pressure testing.
1. Thoroughly clean the SL Manual Lock Blowout Note
Preventer (BOP) before installation (see Appen- Cleaning, inspection and testing of the
dix A). SL BOP immediately after completion
of drilling operations reduces installa-
2. Clean and inspect the sealing surface of the ring tion time on the next well (see Section
groove for minor pits and scratches. Remove these 3.16).
with emery cloth. If there is excessive damage,
call a Shaffer service representative.
2.2 Installation Instructions
3. Clean and inspect studs and nuts (see Appendix
A). Replace any that are damaged. 1. Ensure that the BOP is installed right-side-up.
• Some models have “Top” or “This Side Up” cast
4. Ensure the correct size rams are in each cavity. into the BOP housing.
The part number is stamped into the block of
• Some models have lifting lugs above the mud
each ram.
flange outlets (see Figure 2-1).
5. Thoroughly clean and oil the inside of the SL BOP • On all models and on models without stampings
(see Appendix A). or lugs:
3 Externally, the side outlets for the choke and
2 . 1 . 1 Condition of BOP is Unknown kill lines are below the rams
If the condition of the BOP is unknown, e.g., stored 3 Internally, the skids in the ram
for some length of time or has not been maintained compartments are below the rams, and ram
on a scheduled maintenance program, perform a three- sealing seats are located in the top of the
month maintenance check as described in Section 3.5. ram cavity.
A three-month maintenance check includes:
• visually inspecting and thoroughly greasing the
inside of the BOP
• performing a field wellbore pressure test as
described in Section 3.8
• performing an hydraulic pressure test as
described in Section 3.9
• operating the manual locks as described in
Section 2.5
2 . 1 . 2 BOP Maintained on a Scheduled
Maintenance Program
If the BOP has been properly maintained (scheduled
maintenance program), a monthly maintenance check
(see Section 3.4) is all that is required. A monthly
maintenance check includes:
• performing a field wellbore pressure test per
Section 3.8, and
Lifting Lug
Figure 2-1
Lifting Lug Location
October, 1994 2-1
Section 2
Operation
Warning
If the BOP is installed upside-down,
it will not contain wellbore pressure.
2. Lift the SL Manual Lock BOP according to the
instructions below.
• On models with lifting lugs cast into the body,
the BOP is lifted by wrapping a chain or cable
of sufficient strength around the lug (see Figure
2-2).
• On models without lifting lugs, place a strap Figure 2-2
or chain around the door flat as close to the Lifting the SL Manual Lock BOP
body as possible. Lift the BOP by attaching this With Lifting Lugs
chain to the lifting cable or chain (see Figure
2-3).
Caution
Do not lift the BOP by the cylinders. This
will damage the cylinders, piston assem-
bly and/or the ram shaft and prevent
the BOP from working correctly.
Note
Use a chain or cable capable of lifting
the weight of the BOP.
Figure 2-3
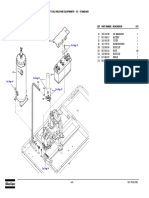
3. Flanged and studded connections are made up
Lifting the SL Manual Lock BOP
according to the instructions below (see Figure
Without Lifting Lugs
2-4).
• Install the ring gasket. See API Ring Gaskets
parts list, Table 4-24 for the proper part 4. Connect the side flanges as in step 3 above.
number.
5. Hub connections are made up in the following
• Install the BOP on the mating flange.
manner (see Figure 2-6).
• Lubricate the stud threads and nut faces with
• Install the ring gasket. See Table 2-2 or Table
grease specified in API BUL SA2: Thread
2-3 for the correct gasket. See Table 4-24 for
Compounds.
the proper part number.
• Install the studs and/or nuts. See Tables 4-25
• Install the BOP on the mating flange.
and 4-26 for the proper part number.
• Clean and lubricate the raised surface of the
Caution hub, the internal surfaces of the hub clamp,
Use extreme care during the removal and the stud threads, and nut faces with the grease
installation of studs and nuts. Inspect specified in API BUL 5A2: Thread Compounds.
the threads of the studs and the stud • When assembling the clamp joint, tighten the
hole for damage such as deformation, studs alternately from one side to the other.
stripping or burns. Do not overtorque • Maintain the same distance between the two
studs when installing in studded flange. clamp halves.
Use specified lubricants. Do not use
Loctite or similar compounds. • Table 2-2 lists standard API clamp sizes for SL
Manual Lock BOP with stud size, wrench size
• Tighten all nuts uniformly in a diametrically (across the nut flats), and recommended
staggered pattern as shown in Figure 2-5. See torques.
Table 2-1 for proper torque specifications.
2-2 October, 1994
Section 2
Operation
Flanged
Studded
Studded
Figure 2-4
End Connections Flanged
Table 2-1
Recommended 6BX-Flange Bolt Torque*
Torque
Bolt Size ft-lb N-m
3
/4 "–10 UNC 200 271.2
7
/8"–9 UNC 325 440.6
1"–8 UNC 475 644.0
1
1 /8"–8 UNC 600 813.5
13/8"–8 UNC 1200 1627.0
11/2"–8 UNC 1400 1898.2
15/8"–8 UNC 1700 2304.9
13/4"–8 UNC 2040 2765.9
7
1 /8"–8 UNC 3220 4365.7
Figure 2-5
2"–8 UNC 3850 5219.9
Flanged Bolting Sequence
1
2 /4"–8 UNC 5250 7130.0
21/2"–8 UNC 7250 9860.0
* Torque values are satisfactory for both Standard and H2S studs.
Reference API specification 6A, Table 2-1 shows torque values
arrived at by using new commercial stud bolts and nuts, well-
lubricated at the threads and nut faces with API thread compound
API Bul. 5A2: Thread Compounds. This produces a stress of
52,500 psi 362.0 MPa in the bolting.
Clamp
Hub
Figure 2-6
Hubbed Connections
October, 1994 2-3
Section 2
Operation
Table 2-2
Recommended Bolt Torque* for API Clamp Connectors
Working Pressure Hub Size Clamp Torque Ring Wrench Size
psi (bar) in. (mm) Number Bolt Size ft-lb N-m Gasket Across Flats
10,000 (690) 211/4" (539.7) 15A 43/4"–8UN-2B 37,745 51,175 RX73 7 1/ 4" (184.15 mm)
3 1
18 /4" (476.2) 14A 4 /2"–8UN-2A 32,078 43,492 RX69 6 7/ 8" (174.62 mm)
163/4" (425.4) 13A 37/8"–8UN-2A 20,236 27,436 RX65 5 15/ 16" (150.81 mm)
5 1
13 /8" (346.0) 12A 3 /4"–8UN-2A 11,865 16,087 RX57 5" (127.00 mm)
11" (279.4) 11A 23/4"–SUN-2A 7,099 9,625 RX53 4 1/ 4" (107.95 mm)
5,000 (345) 163/4" (425.4) 10A 31/4"–8UN-2A 11,865 16,087 RX65 5" (127.00 mm)
5
13 /8" (346.0) 9A 37/8"–8UN-2A 6,182 8,382 RX57 4 5/ 8" (117.47 mm)
* Torques calculated to produce stress of 40,000 psi (276 MPa) in bolt when thread and nut bearing surfaces are well-lubricated
with API 5A2 thread compound. Use of other compounds without proper change in torque can result in: (1) overstressing clamp
and bolt or (2) insufficient preload on connection. (API Specification 6A, Table 2.7A)
Table 2-3
Recommended Bolt Torque* for Non-Standard Clamp Connectors
Working Pressure Hub Size Clamp Torque Ring Wrench Size
psi (bar) in. (mm) Number Bolt Size ft-lb N-m Gasket Across Flats
15,000 (1,034) 135/8" (346.0) 28 2 3 / 4"–8N 9,700 13,151 BX-159 4 1/ 4" (107.95 mm)
1
11" (279.4) 15 2 / 2"–8N 7,250 9,830 BX-158 3 7/8" (98.42 mm)
10,000 (690) 211/4" (539.7) 26 3"–8N 12,600 17,083 BX-166 4 5/ 8" (117.47 mm)
3 3
18 /4" (476.2) 27 2 / 4"–8N 9,700 13,151 BX-164 4 1/ 4" (107.95 mm)
163/4" (425.4) 28 2 3 / 4"–8N 9,700 13,151 BX-162 4 1/ 4" (107.95 mm)
5 1
13 /8" (346.0) 15 2 / 2"–8N 7,250 9,830 BX-159 3 7/8" (98.42 mm)
11" (279.4) 22 2 1 / 4"–8N 5,250 7,118 BX-158 3 1/2" (88.90 mm)
3 1
5,000 (345) 16 /4" (425.4) 19 2 /2 "–SN 7,250 9,830 BX-162 3 7/8" (98.42 mm)
5 1
13 /8" (346.0) 13 2 /4 "–SN 5,250 7,118 BX-160 3 1/2" (88.90 mm)
3,000 (207) 135/8" (346.0) 11 2 1 / 4"–8N 5,250 7,118 RX-57 3 1/2" (88.90 mm)
* Torques calculated to produce stress of 40,000 psi (276 MPa) in bolt when thread and nut bearing surfaces are well-lubricated
with API 5A2 thread compound. Use of other compounds without proper change in torque can result in: (1) overstressing clamp
and bolt or (2) insufficient preload on connection. (API Specification 6A, Table 2.7A)
• Table 2-3 lists non-standard clamp sizes for one opening port and one closing port
SL Manual Lock BOP with stud size, wrench is to be used.
size (across the nut flats), and recommended A gauge and valve should be included
torques. in the opening and closing hydraulic
lines to the BOP. This will facilitate test-
6. Connect the hydraulic lines from the BOP clos- ing procedures (see Figure 2-8).
ing unit to the “Open” and “Close” ports of the
BOP. Make sure all connections are clean and
tight. Each set of rams requires one opening and 7. A universal joint and handwheel are furnished
one closing line (see Figures 2-7 and 2-8). for each locking shaft. Handwheel extensions are
cut from standard weight 2" (50.80 mm) pipe
Note furnished by the customer.
Two opening and two closing hydraulic
ports are clearly marked on the back Fabricate a handwheel extension for each lock-
(hinge) side of the BOP (see Figure 2-7). ing shaft. Attach a handwheel to one end of each
The extra hydraulic ports are provided extension. Attach a universal joint to the other
to facilitate hydraulic hookup and only end of each handwheel extension (see Figure 2-
9).
2-4 October, 1994
Section 2
Operation
U-Joint Handwheel
Assembly
Standard Weight
2" Pipe
(Customer Supplied)
Figure 2-7
Opening and Closing Hydraulic Ports
Gauge Closing
Hydraulic
Valve
Line Figure 2-9
Manual Lock Handwheel Assembly
Note
When closing the rams manually the
open hydraulic line must be vented to
prevent a hydraulic lock.
2 . 3 . 1 Hydraulic Operation
Opening Opening and closing hydraulic pressure is applied as
Hydraulic shown in Figure 2-10.
Figure 2-8 Line
2 . 3 . 2 Operating Pressure
Recommended Hydraulic Line Hookup
Under normal operating conditions, 1,500 psi (103
bar) hydraulic pressure is recommended. This oper-
Note ating pressure will close any model SL Ram BOP with
its rated wellbore pressure, except the 11" (279.4 mm)
Handwheel extensions can be tack and 135/8" (346 mm) 15,000 psi (1,034 bar) models.
welded or pinned to the universal joints Both the 11" (279.4 mm) and 135/8" (346 mm) 15,000
and handwheels. psi (1,034 bar) models are operated at 1,500 psi (103
bar) with wellbore pressure of 10,000 psi (690 bar)
8. Perform a field wellbore pressure test (see Sec- or less.
tion 3.8). For wellbore pressure greater than 10,000 psi (690
bar), the regulator must be bypassed to apply full ac-
2.3 Operation cumulator pressure up to 3,000 psi (207 bar). Regu-
The rams can be hydraulically closed and manually locked, lated pressure up to 2,500 psi (172 bar) can be used.
or, should hydraulic pressure fail, the rams can be manu- At a working pressure of 15,000 psi (1,034 bar), a
ally closed and locked. However, the rams cannot be manu- minimum of 2,200 psi (151 bar) closing pressure is
ally opened.
October, 1994 2-5
You might also like
- FSP 28"-2000 Psi Diverter/BOP: Diverters' Simplicity Maximizes ReliabilityDocument2 pagesFSP 28"-2000 Psi Diverter/BOP: Diverters' Simplicity Maximizes Reliabilitymehmet sait öztürkNo ratings yet
- Product Information Bulletin: Date: Bulletin Number: 1000059437-PIB Revision: 01Document7 pagesProduct Information Bulletin: Date: Bulletin Number: 1000059437-PIB Revision: 01carlosorizabaNo ratings yet
- D601000439 Man 001Document25 pagesD601000439 Man 001Riski KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Equipment FlyerDocument7 pagesEquipment FlyerCatalin StoicescuNo ratings yet
- 15K Lightweight NOVDocument4 pages15K Lightweight NOVJuanNo ratings yet
- Hydril Blowout Preventers Ram Seal KitsDocument1 pageHydril Blowout Preventers Ram Seal KitsJIN WANGNo ratings yet
- Hydril Blowout Preventers Ram AssembliesDocument2 pagesHydril Blowout Preventers Ram AssembliesJIN WANGNo ratings yet
- Offshore Project LastDocument23 pagesOffshore Project LastchigooNo ratings yet
- Aftermarket Services: Parts Service Repair TrainingDocument12 pagesAftermarket Services: Parts Service Repair Trainingmehmet sait öztürkNo ratings yet
- Model fm4Document25 pagesModel fm4LeandroNo ratings yet
- D601005184 Man 001Document17 pagesD601005184 Man 001Riski Kurniawan100% (1)
- BPV Specification and Drawings PDFDocument4 pagesBPV Specification and Drawings PDFParag PadoleNo ratings yet
- Maintenance & Operations Manual Regan Type K Blowout PreventerDocument4 pagesMaintenance & Operations Manual Regan Type K Blowout PreventerAshok SureshNo ratings yet
- D392005428-MKT-001 6012 Bop PDFDocument2 pagesD392005428-MKT-001 6012 Bop PDFMitul PatelNo ratings yet
- M60es54 Na549y QC Man 001Document29 pagesM60es54 Na549y QC Man 001Riski Kurniawan67% (3)
- CatalogDocument424 pagesCatalogLuis David Concha CastilloNo ratings yet
- Operating and Service Manual For Hyd. Act. Series 4000,5000,6500Document24 pagesOperating and Service Manual For Hyd. Act. Series 4000,5000,6500Mehdi Norouzi100% (1)
- Field Evaluation Test Results: Cameron Information Sheet 99-006Document1 pageField Evaluation Test Results: Cameron Information Sheet 99-006Gregory StewartNo ratings yet
- FH18 35(21)英文说明书Document16 pagesFH18 35(21)英文说明书ADM MTCNo ratings yet
- PB DDM 026Document3 pagesPB DDM 026Jim SharpNo ratings yet
- VetoDocument4 pagesVetohenry christian wontumiNo ratings yet
- Trex 03168Document1 pageTrex 03168OSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Cameron EB 919 Rev A1 - Bonnet Bolt Makeup ProceduresDocument7 pagesCameron EB 919 Rev A1 - Bonnet Bolt Makeup Procedureskurtis.clevelandNo ratings yet
- Blowout Preventers: Invetion Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipDocument40 pagesBlowout Preventers: Invetion Unique Design & Extraordinary CraftsmanshipAhmed HajiNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Alert: 22 February 2021Document4 pagesProduct Safety Alert: 22 February 2021carlosorizabaNo ratings yet
- General Catalog 2016Document64 pagesGeneral Catalog 2016Jamal100% (1)
- Drilling BOPsDocument12 pagesDrilling BOPsSaroo MusicNo ratings yet
- Bowl Protectors and ToolsDocument2 pagesBowl Protectors and Toolsagfdgsdf100% (1)
- Contitech HP HosesDocument65 pagesContitech HP HosesRobert FlateråsNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual 1222B: Booster Cylinder Assembly EH34-BC03Document21 pagesTech Manual 1222B: Booster Cylinder Assembly EH34-BC03jose perozoNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual: 5.12", 10,000 Psi Working Pressure, Eh Series Single, Dual, Triple & Quad Combi BopDocument34 pagesTech Manual: 5.12", 10,000 Psi Working Pressure, Eh Series Single, Dual, Triple & Quad Combi BopPastor VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Coil E Coil Unit CatalogueDocument2 pagesCoil E Coil Unit CatalogueLuisNo ratings yet
- Accumulator - Yancheng RuihuaDocument26 pagesAccumulator - Yancheng RuihuaBoedi SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Stripper TOT 2.50 10M DS34 TechMan1146Document13 pagesStripper TOT 2.50 10M DS34 TechMan1146Diego OspinaNo ratings yet
- DL AnnularDocument40 pagesDL Annulara.solvevNo ratings yet
- Parker HTR ActuatorDocument22 pagesParker HTR ActuatorYorkistNo ratings yet
- 25k Bop FlyerDocument1 page25k Bop FlyersyedainahmadNo ratings yet
- Baker PDFDocument6 pagesBaker PDFanthony silvaNo ratings yet
- FMC Weco Butterfly Valve Catalog-006Document1 pageFMC Weco Butterfly Valve Catalog-006ferdy110276No ratings yet
- 1PackerSystem PackerAccessories&tools PDFDocument21 pages1PackerSystem PackerAccessories&tools PDFAnand aashishNo ratings yet
- Oilfield UnionsDocument5 pagesOilfield Unionslalberto96No ratings yet
- Uztel OrizontalDocument5 pagesUztel OrizontalDorin RaduNo ratings yet
- Cameron EB 539 D Rev D1 - Preferred Seal Orientation For Pressure Control EquipmentDocument7 pagesCameron EB 539 D Rev D1 - Preferred Seal Orientation For Pressure Control EquipmentCanrig RamdeNo ratings yet
- Recommended Installation of A Bop Control SystemDocument8 pagesRecommended Installation of A Bop Control SystemHamid Reza BabaeiNo ratings yet
- Blow Out PreventorDocument6 pagesBlow Out PreventorCesar Valdivia MontañoNo ratings yet
- 12 Drilling PreventersDocument82 pages12 Drilling PreventersDavid Kusuma100% (1)
- Cameron EB 555 D Rev U2 - VBR Engineering InfoDocument6 pagesCameron EB 555 D Rev U2 - VBR Engineering InfoCanrig Ramde100% (1)
- Maintenance Schedule For Adapter Flange - 5131086 - 01Document7 pagesMaintenance Schedule For Adapter Flange - 5131086 - 01franko guddiNo ratings yet
- Claxton Riser Systems BrochureDocument12 pagesClaxton Riser Systems BrochureQingming MaNo ratings yet
- FKQ50-2 Use R ManualDocument56 pagesFKQ50-2 Use R ManualMuthia AstriNo ratings yet
- QBH Ram Bop'S: 4-1/16" 15,000 Psi WPDocument32 pagesQBH Ram Bop'S: 4-1/16" 15,000 Psi WPjuan olarte0% (1)
- D4510664815-Pib-001 1 5 in SPM Valves Rev 06 LDocument7 pagesD4510664815-Pib-001 1 5 in SPM Valves Rev 06 LEdmo VirgensNo ratings yet
- Oteco Inc. 3" Reset Relief Valve 3" LPT Inlet & Outlet Installation & Maintenance Manual PART NO. 130350Document12 pagesOteco Inc. 3" Reset Relief Valve 3" LPT Inlet & Outlet Installation & Maintenance Manual PART NO. 130350VRV.RELATORIO.AVARIA RELATORIO.AVARIANo ratings yet
- Sub-X: Wellhead & BOP GasketsDocument2 pagesSub-X: Wellhead & BOP GasketsEugene EvgerNo ratings yet
- Design of Blowout Preventer Lifting FramDocument10 pagesDesign of Blowout Preventer Lifting FramAndreansyah PratamaNo ratings yet
- User Manual Ebb N Fid5717Document7 pagesUser Manual Ebb N Fid5717Andrey GapsNo ratings yet
- 2 - Completion Pressure Control Equipment - Well Control For Well Intervention - 6619932 - 01Document94 pages2 - Completion Pressure Control Equipment - Well Control For Well Intervention - 6619932 - 01Carlos A.No ratings yet
- KSB Pump Movi ManualDocument12 pagesKSB Pump Movi ManualVenkat Dora100% (5)
- OMM and OMME Repair InstructionsDocument11 pagesOMM and OMME Repair InstructionsleonNo ratings yet
- Bap1929-100 InstallationDocument29 pagesBap1929-100 InstallationDAVID JONATHAN ALVAREZ CASTILLONo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-21-25Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-36-40Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-36-40Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-16-20Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-16-20Richard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-6-10Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-6-10Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Battery and Vessel - : For Compressor Without Cold Weather Equipments EC StandardDocument2 pagesBattery and Vessel - : For Compressor Without Cold Weather Equipments EC StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- SL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-1-5Document5 pagesSL Manual Lock 13 58 SHAFFER RAM BOP Page-1-5Richard EVNo ratings yet
- XA Series 62Document1 pageXA Series 62Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Frame and Mounts - : StandardDocument1 pageFrame and Mounts - : StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- XA Series 58 59Document2 pagesXA Series 58 59Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Oil System - : StandardDocument2 pagesOil System - : StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Bodywork - : XAS 137 StandardDocument4 pagesBodywork - : XAS 137 StandardRichard EVNo ratings yet
- JDN Air Hoists ProfiDocument8 pagesJDN Air Hoists ProfiRichard EVNo ratings yet
- G-SHOCK Manual 5132 PDFDocument4 pagesG-SHOCK Manual 5132 PDFRichard EV100% (1)
- T 19Document1 pageT 19Richard EVNo ratings yet
- Aramax Wedge-Band: Banded BeltDocument4 pagesAramax Wedge-Band: Banded BeltRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Ks Permaglide CatalogueDocument76 pagesKs Permaglide CatalogueSkocko SkockicNo ratings yet
- Quincy CompressorDocument112 pagesQuincy CompressorRichard EV100% (2)
- Fishing Tools PDFDocument45 pagesFishing Tools PDFRichard EV100% (1)
- Pacseal HydraulicDocument10 pagesPacseal HydraulicRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Rig Power LLCDocument12 pagesRig Power LLCRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges Stainless Steel, Safety Pattern Version, High Overpressure Safety Model 232.36/233.36, Without/with Liquid FillingDocument2 pagesBourdon Tube Pressure Gauges Stainless Steel, Safety Pattern Version, High Overpressure Safety Model 232.36/233.36, Without/with Liquid FillingRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Yoke Industrial Corp.: Company Profi LeDocument1 pageYoke Industrial Corp.: Company Profi LeRichard EVNo ratings yet
- Agitator Manual AM 001 Rev5Document37 pagesAgitator Manual AM 001 Rev5Richard EVNo ratings yet
- MAYAKIINC BusinessPlanDocument20 pagesMAYAKIINC BusinessPlanRichard EVNo ratings yet
- The Atomic SublimeDocument28 pagesThe Atomic SublimeMarco BellanoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Bidang Kemampuan Suplai (Scope of Supply) Untuk Pengadaan BarangDocument6 pagesDaftar Bidang Kemampuan Suplai (Scope of Supply) Untuk Pengadaan BarangAdhiezNo ratings yet
- Engagementletter - Business Closure20Document4 pagesEngagementletter - Business Closure20Dv AccountingNo ratings yet
- 12f-601-Midterm Machine LearningDocument21 pages12f-601-Midterm Machine Learningale mekeNo ratings yet
- Soundoff Led Flasher ManualDocument2 pagesSoundoff Led Flasher ManualDaniel BonillaNo ratings yet
- E.G. Admin - UserDocument2 pagesE.G. Admin - UserdavidakpaluNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Visual Studio IDE With FeaturesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Visual Studio IDE With FeaturesriponcseNo ratings yet
- FDD LTE Handover OptimizationDocument35 pagesFDD LTE Handover OptimizationmunzewNo ratings yet
- S.H.A.R.D Rev 2Document21 pagesS.H.A.R.D Rev 2Hassaan tahirNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall Types, and Instance Parameters: 1. Start Revit 2020Document36 pagesCurtain Wall Types, and Instance Parameters: 1. Start Revit 2020Jasmina HajdukovicNo ratings yet
- Internet of Things and SecurityDocument9 pagesInternet of Things and SecurityNareshNo ratings yet
- CA51013 - ACTIVITY 1 (Group Work)Document2 pagesCA51013 - ACTIVITY 1 (Group Work)Elaine AntonioNo ratings yet
- 12ABM - Group 6 (TSSBTE)Document2 pages12ABM - Group 6 (TSSBTE)Kimberly ValdezNo ratings yet
- AVIC-X1R Installation Manual en de IT ES FI GRDocument181 pagesAVIC-X1R Installation Manual en de IT ES FI GRMartin Czuba OlsenNo ratings yet
- PetroChem EnggDocument90 pagesPetroChem EnggSampathkumar MtechNo ratings yet
- Big Book of Windows HacksDocument8 pagesBig Book of Windows HacksRendy Adam FarhanNo ratings yet
- ActivityGuide ConfigDocument176 pagesActivityGuide Configrajeshgr9063No ratings yet
- BS en 10111 - 2008Document16 pagesBS en 10111 - 2008Артем ТитовNo ratings yet
- Alex Stancu - WiFi Mesh Optimization For Bucharest City CenterDocument62 pagesAlex Stancu - WiFi Mesh Optimization For Bucharest City CenterRazvan MaziluNo ratings yet
- E Starco Steel Elevator BucketDocument1 pageE Starco Steel Elevator BucketAhmed SadekNo ratings yet
- Do You Know How Map - HashMap Works Internally in Java - Part 1 PDFDocument1 pageDo You Know How Map - HashMap Works Internally in Java - Part 1 PDFYaegar WainNo ratings yet
- 101景觀台解謎遊戲憑證Document3 pages101景觀台解謎遊戲憑證Bing Zhang WangNo ratings yet
- Global Business Intelligence: An Integrated Business Intelligence Solution Across GT Nexus Trade and LogisticsDocument1 pageGlobal Business Intelligence: An Integrated Business Intelligence Solution Across GT Nexus Trade and LogisticsMageshNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Contact Center Express Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 9.0Document50 pagesCisco Unified Contact Center Express Installation and Upgrade Guide, Release 9.0Mohammed alhimyariNo ratings yet
- RWTP GB Mne Msa 000151Document90 pagesRWTP GB Mne Msa 000151slayerzzz22No ratings yet
- Risk Management by Protiviti X MentorKartDocument14 pagesRisk Management by Protiviti X MentorKartShubam VermaNo ratings yet
- Flotation Equipment Selection - OutotecDocument13 pagesFlotation Equipment Selection - Outoteclouza8No ratings yet
- Hydraulic TurbineDocument19 pagesHydraulic Turbinesami almjanNo ratings yet
- MTL101:: Tutorial 3:: Linear AlgebraDocument2 pagesMTL101:: Tutorial 3:: Linear AlgebraKuldeep MalNo ratings yet
- JS - Zoom Parents GuideDocument2 pagesJS - Zoom Parents GuideNoman KulachiNo ratings yet