Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Uploaded by
supianazma zari affendiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physical Science p2 Gr12 LAST PUSHDocument119 pagesPhysical Science p2 Gr12 LAST PUSHZwavhudi100% (1)
- ? Organic ChemHack 2nd EDITION - SampleDocument17 pages? Organic ChemHack 2nd EDITION - SampleKomal83% (18)
- Natural Product Chemistry at A Glance PDFDocument147 pagesNatural Product Chemistry at A Glance PDFcoloromaneNo ratings yet
- Module 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptDocument10 pagesModule 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptYuan MasudaNo ratings yet
- Improved Synthesis of Basic Zinc AcetateDocument2 pagesImproved Synthesis of Basic Zinc Acetatejinzo88No ratings yet
- Hand Sanitizer Version 1 - 01.04.2020Document19 pagesHand Sanitizer Version 1 - 01.04.2020Heidy Roxana Lopez VelizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument102 pagesChapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsCute ni LeynesNo ratings yet
- Phenol 203Document47 pagesPhenol 203ajibolaakorede20No ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol and Ether FinalDocument33 pagesAlcohol Phenol and Ether FinalC.S. KrithikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDocument99 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition張湧浩No ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-1 Chapter-12 PDFDocument18 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-1 Chapter-12 PDFDK SainiNo ratings yet
- FenolDocument43 pagesFenolRedyNo ratings yet
- Phenols: Bio-Organic Chemistry-I BBT-202 Lecture-13Document37 pagesPhenols: Bio-Organic Chemistry-I BBT-202 Lecture-13Sate AhmadNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)Document71 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)ridwan100% (3)
- Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument17 pagesChapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiolshussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- 1288 PhenolsDocument29 pages1288 PhenolsX ThrxNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument47 pagesAcid BaseAsmZziz OoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 PhenolsDocument20 pagesChapter 21 PhenolsardanynazlimNo ratings yet
- 05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsDocument5 pages05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PhenolsDocument34 pagesPhenolsLoran Prelya TengayNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Etherskanit8713No ratings yet
- Alchol Ether Phenol NotesDocument18 pagesAlchol Ether Phenol Notesnani roshanNo ratings yet
- ChemicalIdeas13 4OHGroupDocument2 pagesChemicalIdeas13 4OHGroupOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - PhenolsDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Phenolsdr.3nonaNo ratings yet
- Alkohol Dan EterDocument27 pagesAlkohol Dan EterMery Sunardea DamanikNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 2Document4 pagesAlcohols 2Abdullah SalmainNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersDocument57 pagesCh-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersBhavishya VermaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HssliveDocument16 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HsslivemartyNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideAshli GrantNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument32 pagesPhenol SBangaloredNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and ThiolsDocument19 pagesChapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiolshanna liuNo ratings yet
- 04awater and Acid-Base SystemDocument27 pages04awater and Acid-Base SystemAtirahNo ratings yet
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 1Document35 pages11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 1Aswath SNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - WatermarkDocument44 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Watermarkasp212009No ratings yet
- Formulae For: Alcohol, Phenols and EthersDocument10 pagesFormulae For: Alcohol, Phenols and EthersSâmïr Kumar MundariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.0 Hydroxy CompoundDocument76 pagesChapter 8.0 Hydroxy CompoundChris Tai JiqianNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsDocument55 pagesAlcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsHuiru ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Phenol: A Guide For CAPE StudentsDocument11 pagesPhenol: A Guide For CAPE StudentsJordan SteeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document41 pagesChapter 8민규강No ratings yet
- PH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFDocument54 pagesPH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- PH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFDocument54 pagesPH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFZenonissya GalwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionDocument36 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionArk Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols and EthersDocument13 pagesAlcohol Phenols and EthersShivaanee SK100% (1)
- Class 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Document106 pagesClass 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Ridhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2Document18 pagesAlcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2PrakharNo ratings yet
- Experiment C: Synthesis of Frambinone by Aldol Condensation and Catalytic HydrogenationDocument6 pagesExperiment C: Synthesis of Frambinone by Aldol Condensation and Catalytic HydrogenationalinaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Ii (Och221T) : Chemical Engineering Class 2017BDocument40 pagesOrganic Chemistry Ii (Och221T) : Chemical Engineering Class 2017BSiphelele SimelaneNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Document103 pagesAcids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Zaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Top Concepts: 1. Structure of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument10 pagesClass XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Top Concepts: 1. Structure of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilDocument13 pagesHsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydrogen Bonding On Physical Properties of SubstanceDocument2 pagesEffect of Hydrogen Bonding On Physical Properties of SubstanceAhJeeNo ratings yet
- Principles Related To Practical ChemistryDocument38 pagesPrinciples Related To Practical Chemistrynandhakishore412No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDsukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol EtherDocument281 pagesAlcohol Phenol EtherRitu Raj VermaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction TableDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction TableKristineNo ratings yet
- Tema 10 IGDocument20 pagesTema 10 IGPanda Mi ÍDOLONo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Acid Base Equilibria ADRIANNENENG1 ANSWERSDocument8 pagesActivity 5 Acid Base Equilibria ADRIANNENENG1 ANSWERSadrian nenengNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - 240412 - 192907Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethers - 240412 - 192907Andrew BenjaminNo ratings yet
- ML023020618 USNRC Power Plant Engineering 2Document147 pagesML023020618 USNRC Power Plant Engineering 2MutahirrasoolNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument47 pagesAlcohols and PhenolsniyazrahimNo ratings yet
- 2endterm Inorg NotesDocument23 pages2endterm Inorg NotesLyric GrantzNo ratings yet
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDocument22 pagesCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument40 pagesQualitative AnalysisIsabelle AvellanedaNo ratings yet
- NRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsDocument10 pagesNRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsTirtha Mukerjee ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Blue and Green Photoluminescence Graphene Quantum Dots SynthesizedDocument4 pagesBlue and Green Photoluminescence Graphene Quantum Dots SynthesizedRajanikar KandikondaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesSweatNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Naming of EstersDocument6 pagesFunctional Groups: Naming of EsterspappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Acidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsDocument35 pagesAcidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsLoveena Steadman100% (1)
- CH 23 StudentDocument33 pagesCH 23 StudentRabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Acidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsDocument35 pagesLesson 14 Acidic and Basic Character of Organic Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Poly (Butylene Succinate) and Poly (ButyleneDocument9 pagesDegradation of Poly (Butylene Succinate) and Poly (Butylenetiffany charlottaNo ratings yet
- Dibal HDocument6 pagesDibal HAnthony BasantaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDocument18 pagesAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 2016Document20 pages9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 2016Hamza JunaidNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lab 1 PHC464Document8 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lab 1 PHC464beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Conversions (ORGANIC)Document8 pagesConversions (ORGANIC)Abir Dutta80% (5)
- C - Sol - Ch-26 - Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageC - Sol - Ch-26 - Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsRishi KeshNo ratings yet
- Revision Pack: (Please Keep This Pack With You)Document32 pagesRevision Pack: (Please Keep This Pack With You)Dev SenNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument20 pagesNomenclatureViejay RegNo ratings yet
- PolimerDocument12 pagesPolimerMuhammad IkramullahNo ratings yet
- Using Molecular Marker Technology in Studies On Plant Genetic DiversityDocument375 pagesUsing Molecular Marker Technology in Studies On Plant Genetic DiversitySharifAr-RaffiNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan Chemistry 2ndt YearDocument7 pagesAnnual Plan Chemistry 2ndt Yeartoruqwerty2008No ratings yet
- Goc 6002eec9ca05fDocument14 pagesGoc 6002eec9ca05fAyush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Proteins Students Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesProteins Students Lecture NoteskesheeestopaNo ratings yet
- Short NotesDocument58 pagesShort Notespriyapriyankan43No ratings yet
- Module 10 Lab: Identification of Organic CompoundsDocument5 pagesModule 10 Lab: Identification of Organic CompoundsNorab, tebmaNo ratings yet
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Uploaded by
supianazma zari affendiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Chapter 15.6 Phenol
Uploaded by
supianazma zari affendiCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING
CHAPTER OUTCOMES:
8.6: PHENOL
Compare the acidity of phenol, alcohol and water.
Explain the chemical properties of phenol with reference to :
Reaction with sodium
Reaction with sodium hydroxide
Identification tests using FeCI3 solution and bromine water.
THEORY OF ACID
Acid - compound that form
H+ ions or H3O+ ions in
BRONSTED-LOWRY THEORY aqueous solution
ARRHENIUS THEORY
Acid - proton donors
Base - proton acceptor
HA + H2O A- + H3O+
Conjugate
base
ACIDITY
ACIDITY To determine the stability of the conjugate base of an acid.
Anything that stabilizes the conjugate base makes the acid more acidic.
The higher the stability of the conjugate base the higher the acidity.
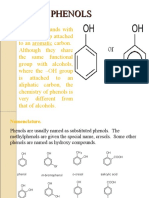
COMPARISON OF ACIDITY
R – OH < Water <
Aliphatic alcohol Phenol
Acidity increases
Alcohols, water and phenols are classified as weak acid.
- THEY ARE ACID & act as proton donor in aqueous solution.
Compounds pKa Ka
Ethanol 16 1x10-16
Water 14 1x10-14
Phenol 10 1x10-10
ALIPHATIC ALCOHOL, R-OH
CHAPTER 8.0:HYDROXY COMPOUNDS_ sem 2 2018/2019_ aef Page 1
Alkyl, R
Aliphatic alcohol (R-OH) are less acidic than water due to presence of electron donating
group,EDG (alkyl)
The electron donating group,EDG will increase the density of negative charge on the
-
Arrange theatom
oxygen makingbelow
compound the R-O ion less
according to stable (destabilizes)
increasing acidity compare to hydroxide ion(OH-)
R OH + H2 O R O
-
+ H3 O
+
Compounds pKa Ka
H O 2 + H2 O OH
-
+ H3 O
+
Ethanol 16 1x10-16
-
R-O ion less stable because the negative charge is localized only on the oxygen
atom of alkoxideWater
ion 14 1x10-14
Examples of EDG (Acidity decrease with presence of EDG)
Alkyl (R) Phenol 10 1x10-10
Hydroxyl (OH)
Amino (NH2)
If ALCOHOL attach with electron withdrawing group, EWG, it will stabilize the
ions & increase acidity
Examples of EWG (Acidity increase with presence of EWG)
Halogen, X Carbonyl, C=O
Carboxyl, COOH
PHENOL
Phenol is the most acidic because the phenoxide ion is stable.
The acidity of phenol is due to the delocalisation of the negative charge on
oxygen atom of the phenoxide ion onto the benzene ring which causes
the ion to be stabilized by the resonance effect
EXAMPLE
RESONANCE STRUCTURES
CHAPTER 8.0:HYDROXY COMPOUNDS_ sem 2 2018/2019_ aef Page 2
Arrange the compound below according to increasing acidity
EXERCISE
CHAPTER 8.0:HYDROXY COMPOUNDS_ sem 2 2018/2019_ aef Page 3
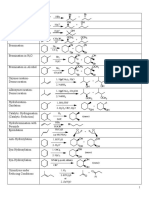
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF PHENOL
CHEMICAL REACTIONS IDENTIFICATION TESTS
CHAPTER 8.0:HYDROXY COMPOUNDS_ sem 2 2018/2019_ aef Page 4
1. REACTION WITH Na 1. USING FeCl3
Observation: Purple complex formed
2. REACTION WITH NaOH
2. BROMINE WATER
Observation: Reddish brown colour of
bromine decolourised and white precipitate
formed
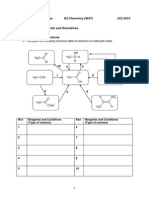
EXERCISES
1. Suggest a chemical test to differentiate the following pairs of compounds
a. Phenol from benzyl alcohol
Name of Test
Reagent
Chemical Reaction &
Observation
2. . The structural formula of X is shown below :
Suggest a chemical test to differentiate the following pairs of compounds
b. 1,2-ethanediol and phenol
c.
Name of Test
Reagent
Chemical Reaction &
Observation
Draw structural formula of product form when X reacts with :
a. Sodium
b. Aqueous sodium hydroxide
c. Phosphorus pentachloride
d. Propanoic acid refluxed with traces of concentrated sulfuric acid
CHAPTER 8.0:HYDROXY COMPOUNDS_ sem 2 2018/2019_ aef Page 5
You might also like
- Physical Science p2 Gr12 LAST PUSHDocument119 pagesPhysical Science p2 Gr12 LAST PUSHZwavhudi100% (1)
- ? Organic ChemHack 2nd EDITION - SampleDocument17 pages? Organic ChemHack 2nd EDITION - SampleKomal83% (18)
- Natural Product Chemistry at A Glance PDFDocument147 pagesNatural Product Chemistry at A Glance PDFcoloromaneNo ratings yet
- Module 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptDocument10 pagesModule 9a Buffer Preparation and Hydrolysis of Salts ConceptYuan MasudaNo ratings yet
- Improved Synthesis of Basic Zinc AcetateDocument2 pagesImproved Synthesis of Basic Zinc Acetatejinzo88No ratings yet
- Hand Sanitizer Version 1 - 01.04.2020Document19 pagesHand Sanitizer Version 1 - 01.04.2020Heidy Roxana Lopez VelizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument102 pagesChapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsCute ni LeynesNo ratings yet
- Phenol 203Document47 pagesPhenol 203ajibolaakorede20No ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol and Ether FinalDocument33 pagesAlcohol Phenol and Ether FinalC.S. KrithikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 EditionDocument99 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 9 Edition張湧浩No ratings yet
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-1 Chapter-12 PDFDocument18 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-4 Level-1 Chapter-12 PDFDK SainiNo ratings yet
- FenolDocument43 pagesFenolRedyNo ratings yet
- Phenols: Bio-Organic Chemistry-I BBT-202 Lecture-13Document37 pagesPhenols: Bio-Organic Chemistry-I BBT-202 Lecture-13Sate AhmadNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)Document71 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydroxy Compound)ridwan100% (3)
- Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and ThiolsDocument17 pagesChapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Thiolshussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- 1288 PhenolsDocument29 pages1288 PhenolsX ThrxNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument47 pagesAcid BaseAsmZziz OoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 PhenolsDocument20 pagesChapter 21 PhenolsardanynazlimNo ratings yet
- 05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsDocument5 pages05a Qualitative Analysis For Organic CompoundsReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PhenolsDocument34 pagesPhenolsLoran Prelya TengayNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Etherskanit8713No ratings yet
- Alchol Ether Phenol NotesDocument18 pagesAlchol Ether Phenol Notesnani roshanNo ratings yet
- ChemicalIdeas13 4OHGroupDocument2 pagesChemicalIdeas13 4OHGroupOCRChemistrySaltersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - PhenolsDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Phenolsdr.3nonaNo ratings yet
- Alkohol Dan EterDocument27 pagesAlkohol Dan EterMery Sunardea DamanikNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 2Document4 pagesAlcohols 2Abdullah SalmainNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersDocument57 pagesCh-11 Part-2 Alcohols, Phenols ðersBhavishya VermaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HssliveDocument16 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Anil HsslivemartyNo ratings yet
- Cape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideDocument10 pagesCape Chemistry Unit Ii Module I Alcohols and Phenol and Alkenes Worksheet and Revision GuideAshli GrantNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument32 pagesPhenol SBangaloredNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Phenols and EthersDocument16 pagesAlcohols-Phenols and EthersTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and ThiolsDocument19 pagesChapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiolshanna liuNo ratings yet
- 04awater and Acid-Base SystemDocument27 pages04awater and Acid-Base SystemAtirahNo ratings yet
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 1Document35 pages11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethers 1Aswath SNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - WatermarkDocument44 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Watermarkasp212009No ratings yet
- Formulae For: Alcohol, Phenols and EthersDocument10 pagesFormulae For: Alcohol, Phenols and EthersSâmïr Kumar MundariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8.0 Hydroxy CompoundDocument76 pagesChapter 8.0 Hydroxy CompoundChris Tai JiqianNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsDocument55 pagesAlcohol, Esters and Carboxylic AcidsHuiru ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Phenol: A Guide For CAPE StudentsDocument11 pagesPhenol: A Guide For CAPE StudentsJordan SteeleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document41 pagesChapter 8민규강No ratings yet
- PH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFDocument54 pagesPH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- PH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFDocument54 pagesPH and Acid-Base Reactions PDFZenonissya GalwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionDocument36 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Based On Mcmurry'S Organic Chemistry, 7 EditionArk Olfato ParojinogNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols and EthersDocument13 pagesAlcohol Phenols and EthersShivaanee SK100% (1)
- Class 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Document106 pagesClass 12 - Alcohols Phenols Ethers-1Ridhi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2Document18 pagesAlcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2PrakharNo ratings yet
- Experiment C: Synthesis of Frambinone by Aldol Condensation and Catalytic HydrogenationDocument6 pagesExperiment C: Synthesis of Frambinone by Aldol Condensation and Catalytic HydrogenationalinaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Ii (Och221T) : Chemical Engineering Class 2017BDocument40 pagesOrganic Chemistry Ii (Och221T) : Chemical Engineering Class 2017BSiphelele SimelaneNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Document103 pagesAcids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Zaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- Class XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Top Concepts: 1. Structure of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument10 pagesClass XII Chemistry Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Top Concepts: 1. Structure of Alcohols, Phenols and EthersPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilDocument13 pagesHsslive Xii CH 7 Alcohols AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydrogen Bonding On Physical Properties of SubstanceDocument2 pagesEffect of Hydrogen Bonding On Physical Properties of SubstanceAhJeeNo ratings yet
- Principles Related To Practical ChemistryDocument38 pagesPrinciples Related To Practical Chemistrynandhakishore412No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 7 Alcohols RESTOREDsukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenol EtherDocument281 pagesAlcohol Phenol EtherRitu Raj VermaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction TableDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction TableKristineNo ratings yet
- Tema 10 IGDocument20 pagesTema 10 IGPanda Mi ÍDOLONo ratings yet
- Activity 5 Acid Base Equilibria ADRIANNENENG1 ANSWERSDocument8 pagesActivity 5 Acid Base Equilibria ADRIANNENENG1 ANSWERSadrian nenengNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers - 240412 - 192907Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethers - 240412 - 192907Andrew BenjaminNo ratings yet
- ML023020618 USNRC Power Plant Engineering 2Document147 pagesML023020618 USNRC Power Plant Engineering 2MutahirrasoolNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument47 pagesAlcohols and PhenolsniyazrahimNo ratings yet
- 2endterm Inorg NotesDocument23 pages2endterm Inorg NotesLyric GrantzNo ratings yet
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDocument22 pagesCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- Qualitative AnalysisDocument40 pagesQualitative AnalysisIsabelle AvellanedaNo ratings yet
- NRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsDocument10 pagesNRC - Chem - M15 - ChemSimplified - Acidity of Carboxylic AcidsTirtha Mukerjee ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Blue and Green Photoluminescence Graphene Quantum Dots SynthesizedDocument4 pagesBlue and Green Photoluminescence Graphene Quantum Dots SynthesizedRajanikar KandikondaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument24 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesSweatNo ratings yet
- Functional Groups: Naming of EstersDocument6 pagesFunctional Groups: Naming of EsterspappadakunduNo ratings yet
- Acidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsDocument35 pagesAcidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsLoveena Steadman100% (1)
- CH 23 StudentDocument33 pagesCH 23 StudentRabin ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Acidic and Basic Character of Organic CompoundsDocument35 pagesLesson 14 Acidic and Basic Character of Organic Compoundsdela2No ratings yet
- Proteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesProteins: A Protein Is A Naturally Occurring, Unbranched Polymer in Which The Monomer Units Are Amino Acidsdarleen joy dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Degradation of Poly (Butylene Succinate) and Poly (ButyleneDocument9 pagesDegradation of Poly (Butylene Succinate) and Poly (Butylenetiffany charlottaNo ratings yet
- Dibal HDocument6 pagesDibal HAnthony BasantaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDocument18 pagesAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 2016Document20 pages9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 2016Hamza JunaidNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lab 1 PHC464Document8 pagesPharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Lab 1 PHC464beyonduckNo ratings yet
- Conversions (ORGANIC)Document8 pagesConversions (ORGANIC)Abir Dutta80% (5)
- C - Sol - Ch-26 - Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument1 pageC - Sol - Ch-26 - Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsRishi KeshNo ratings yet
- Revision Pack: (Please Keep This Pack With You)Document32 pagesRevision Pack: (Please Keep This Pack With You)Dev SenNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument20 pagesNomenclatureViejay RegNo ratings yet
- PolimerDocument12 pagesPolimerMuhammad IkramullahNo ratings yet
- Using Molecular Marker Technology in Studies On Plant Genetic DiversityDocument375 pagesUsing Molecular Marker Technology in Studies On Plant Genetic DiversitySharifAr-RaffiNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan Chemistry 2ndt YearDocument7 pagesAnnual Plan Chemistry 2ndt Yeartoruqwerty2008No ratings yet
- Goc 6002eec9ca05fDocument14 pagesGoc 6002eec9ca05fAyush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Proteins Students Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesProteins Students Lecture NoteskesheeestopaNo ratings yet
- Short NotesDocument58 pagesShort Notespriyapriyankan43No ratings yet
- Module 10 Lab: Identification of Organic CompoundsDocument5 pagesModule 10 Lab: Identification of Organic CompoundsNorab, tebmaNo ratings yet