Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 viewsSheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Sheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Uploaded by
Lars vanheuverzwynThe document provides instructions for the dissection and examination of the external and internal anatomy of a sheep heart. It guides the reader to identify various external structures like the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and auricles. Upon opening the heart, it describes locating the internal chambers, including the right and left atria and ventricles, as well as the valves that separate them like the tricuspid and bicuspid valves. The document also notes anatomical features like the chordae tendineae that connect the valves to papillary muscles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pythagorean Theorem NotesDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem NotesMilla TanNo ratings yet
- Qsssa TemplateDocument2 pagesQsssa Templateapi-3290353840% (1)
- Short Stories Contain IdiomsDocument12 pagesShort Stories Contain IdiomsAnonymous jXOG0NdI6100% (2)
- Electricity Separate With AnswersDocument112 pagesElectricity Separate With AnswersMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesHuman Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyAhmad WirawanNo ratings yet
- Investigating BreathingDocument4 pagesInvestigating BreathingAal LyyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System of Invertebrates: Prepared By: Nerizza Anne Q. LozanoDocument23 pagesIntegumentary System of Invertebrates: Prepared By: Nerizza Anne Q. LozanoNerizza Anne Q. Lozano100% (1)
- Geometrical ShapesDocument31 pagesGeometrical ShapesAlanie Grace Beron Trigo100% (1)
- Y9 March 2019Document8 pagesY9 March 2019John LeeNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts Science Olympiad - Quizlet1-Geol-Bot-MinDocument7 pagesFast Facts Science Olympiad - Quizlet1-Geol-Bot-MinSanjay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Reasoning and Proof Chapter 2 PostulatesDocument19 pagesReasoning and Proof Chapter 2 PostulatesCherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Year 2 WorksheetDocument11 pagesYear 2 Worksheet434666No ratings yet
- Set 5 AnswersDocument80 pagesSet 5 AnswersThanmay ShajinNo ratings yet
- Biology B2Document14 pagesBiology B2madhujayanNo ratings yet
- NSTC 9 Sample Paper 2011 13 V1Document24 pagesNSTC 9 Sample Paper 2011 13 V1M Nisar Chishti Hassan100% (1)
- Igcse AccommodationDocument3 pagesIgcse AccommodationChr1zFX4No ratings yet
- Junior Mathematical Challenge: InstructionsDocument4 pagesJunior Mathematical Challenge: InstructionsAdd UpNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Honours Assessment Test 2015 PDFDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Honours Assessment Test 2015 PDFDennisNo ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13Document18 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13YazaanNo ratings yet
- 2005 AMC 12B SolutionsDocument9 pages2005 AMC 12B SolutionsjabagaweeNo ratings yet
- USABODocument2 pagesUSABOkcinvinciblemanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2: Year 7 Semester ExamDocument11 pagesPaper 2: Year 7 Semester ExamLee Chung100% (1)
- RespirationDocument10 pagesRespirationmohd zulkepli zakaria100% (1)
- 2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentDocument6 pages2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentvleeeeNo ratings yet
- Essentials: Week by WeekDocument9 pagesEssentials: Week by WeekRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- H. Conditional Probability (H)Document12 pagesH. Conditional Probability (H)Papia SultanaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Math Worksheet 14 - A StatisticsDocument4 pagesClass 7 Math Worksheet 14 - A StatisticsDeath SychoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Data Analysis and Statistics Practice WorksheetDocument6 pagesChapter 10 - Data Analysis and Statistics Practice WorksheetGreEdgeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11 Concept ReviewDocument31 pagesChemistry 11 Concept ReviewJames Ernest Baker-taylor100% (1)
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument2 pagesCirculatory System ActivityA. ZNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 3CD Exam Calc Free 2011 PDFDocument12 pagesMathematics 3CD Exam Calc Free 2011 PDFTejajjjNo ratings yet
- 2016 AMO Paper and SolutionsDocument23 pages2016 AMO Paper and SolutionsCareen S AlicawayNo ratings yet
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Matrix AlgebraDocument22 pagesMatrix AlgebraDeeDz Sophisticated-FantabulousNo ratings yet
- Answers bk1 2 Weebly Y9Document25 pagesAnswers bk1 2 Weebly Y9api-287224366100% (1)
- Area of Composite Shapes Activity SheetDocument3 pagesArea of Composite Shapes Activity SheetgayatriNo ratings yet
- 02 03 StretchesDocument5 pages02 03 StretchesGladys TanNo ratings yet
- 2011 P5 Math SA1 MGSDocument28 pages2011 P5 Math SA1 MGSBakialetchumy TanasikaranNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Power and Expon Laws ReviewDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Power and Expon Laws Reviewmichael.delaney8541100% (1)
- Physics 2 Guidebook PDFDocument485 pagesPhysics 2 Guidebook PDFErica Gale Joseph100% (1)
- Math-Epol338 Course Notes - Mathematics Curriculum StudyDocument105 pagesMath-Epol338 Course Notes - Mathematics Curriculum StudyBlair SmithNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument10 pagesPolygonCherry CurryNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 2008 Trial Exam 1Document24 pagesBiology Unit 3 2008 Trial Exam 1Vy PhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Quantitative Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument78 pagesLesson 5 - Quantitative Analysis and Interpretation of Dataojs99784No ratings yet
- This Question Paper Consists of 26 Questions. Answer All Questions. The Usage of Calculator Is Not AllowedDocument6 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 26 Questions. Answer All Questions. The Usage of Calculator Is Not AllowedNeserajan_Subr_7555No ratings yet
- Batdangthuc DDTHDocument40 pagesBatdangthuc DDTHTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- Points of Concurrency WS-1Document5 pagesPoints of Concurrency WS-1eebobNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Questions ARC 2006Document28 pagesBiology HSC Questions ARC 2006timeflies23No ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaDocument10 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaSefLRho0% (1)
- Work Mixture DistanceDocument7 pagesWork Mixture DistanceJerry LicayanNo ratings yet
- 2016 KS2 Mathematics Mark SchemesDocument28 pages2016 KS2 Mathematics Mark SchemesmayNo ratings yet
- Geometry Final ReviewDocument12 pagesGeometry Final Reviewblue butterflyNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Year 9 - Simultaneous Equations QuizDocument3 pagesYear 9 - Simultaneous Equations QuizMathKeysNo ratings yet
- Notes 1.1 - Points, Lines, PlanesDocument6 pagesNotes 1.1 - Points, Lines, PlanesSusie GreenNo ratings yet
- EST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Document16 pagesEST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Hazem ShehabNo ratings yet
- Sheep Heart DissectionDocument3 pagesSheep Heart DissectionMorgan DanielsNo ratings yet
- Aoi M - LAB - Heart DissectionDocument5 pagesAoi M - LAB - Heart Dissections25123No ratings yet
- pig-heart-dissection-lab-hand-out-Document7 pagespig-heart-dissection-lab-hand-out-Macarena Arechavaleta JaniniNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection: Background InformationDocument9 pagesHeart Dissection: Background Informationapi-482694849No ratings yet
- Pig Heart DissectionDocument6 pagesPig Heart DissectionNathalia Uhna BalboaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument10 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-253942549No ratings yet
- Sargassumfish ReproductionDocument3 pagesSargassumfish ReproductionBinu VargheseNo ratings yet
- Merritt Morning Market 2773 - Sept 28Document2 pagesMerritt Morning Market 2773 - Sept 28Kim LeclairNo ratings yet
- Appendix Working With Young Campers Giraffes - Cant - DanceDocument2 pagesAppendix Working With Young Campers Giraffes - Cant - DanceCorey SandersNo ratings yet
- Useless FactsDocument6 pagesUseless FactshawkeyeNo ratings yet
- Maternal Inheritence: (Ii) Coiling of Snail Shells (Limnaea Peregra)Document10 pagesMaternal Inheritence: (Ii) Coiling of Snail Shells (Limnaea Peregra)Kartik MishraNo ratings yet
- Show Me How To SurviveDocument19 pagesShow Me How To SurviveWeldon Owen Publishing100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakayunyhafitryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 FertilizationDocument18 pagesLecture 04 FertilizationBry RafNo ratings yet
- DACP OrderDocument5 pagesDACP OrderSohan PalNo ratings yet
- Learned BehaviourDocument19 pagesLearned Behaviourapi-176402481No ratings yet
- German Pinscher: 1 DescriptionDocument4 pagesGerman Pinscher: 1 DescriptiondescataNo ratings yet
- Musical Instrument of IsraelDocument18 pagesMusical Instrument of IsraelJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Anthology: Something Exploded in The KitchenDocument38 pagesAnthology: Something Exploded in The KitchendaphnehoNo ratings yet
- Golden Retriever Contract Non BindingDocument5 pagesGolden Retriever Contract Non BindingxdbubblieygumNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Competency-Based Learning Material: CBLM On Date Developed: Issued By: Developed byDocument92 pagesParts of A Competency-Based Learning Material: CBLM On Date Developed: Issued By: Developed byRocz RocoNo ratings yet
- Surgery Examination - 3-4 (Question Cases) (Eng)Document45 pagesSurgery Examination - 3-4 (Question Cases) (Eng)Aiman TymerNo ratings yet
- Akashay Rokade CompliantDocument4 pagesAkashay Rokade Compliantsubhash hulyalkarNo ratings yet
- Animal - Plant Classification MCQDocument9 pagesAnimal - Plant Classification MCQAnjana LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Perumal Santhanam, Ajima Begum, Perumal Pachiappan - Basic and Applied Phytoplankton Biology-Springer Singapore (2019) PDFDocument337 pagesPerumal Santhanam, Ajima Begum, Perumal Pachiappan - Basic and Applied Phytoplankton Biology-Springer Singapore (2019) PDFJherson Agurto SocolaNo ratings yet
- Literacy Prop Box - ZookeeperDocument3 pagesLiteracy Prop Box - Zookeeperapi-338550244No ratings yet
- Pigs - Basic Housing Requirements For PigsDocument7 pagesPigs - Basic Housing Requirements For PigsBukhosi Buks MhlangaNo ratings yet
- PHẦN 12 ĐẠI TỪDocument5 pagesPHẦN 12 ĐẠI TỪNguyen Viet LovesUlisNo ratings yet
- English 5 - Q4 PTDocument8 pagesEnglish 5 - Q4 PTShaina DaquilNo ratings yet
- Sectoral Finals - Grade 1 - 2014Document26 pagesSectoral Finals - Grade 1 - 2014Judah Lazaga0% (1)
- Grade 6 - Quiz BeeDocument68 pagesGrade 6 - Quiz BeeALYSSA MAE DAPADAPNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Chapter 1 Anatomical Regions (Chapter 1)Document33 pagesAnatomy Chapter 1 Anatomical Regions (Chapter 1)Fidaa Jaafrah100% (2)
- Platero y Yo - Juan Ramón JiménezDocument42 pagesPlatero y Yo - Juan Ramón JiménezYêu Văn HọcNo ratings yet
Sheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Sheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Uploaded by
Lars vanheuverzwyn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views3 pagesThe document provides instructions for the dissection and examination of the external and internal anatomy of a sheep heart. It guides the reader to identify various external structures like the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and auricles. Upon opening the heart, it describes locating the internal chambers, including the right and left atria and ventricles, as well as the valves that separate them like the tricuspid and bicuspid valves. The document also notes anatomical features like the chordae tendineae that connect the valves to papillary muscles.
Original Description:
Original Title
Copy of Heart Dissection
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for the dissection and examination of the external and internal anatomy of a sheep heart. It guides the reader to identify various external structures like the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and auricles. Upon opening the heart, it describes locating the internal chambers, including the right and left atria and ventricles, as well as the valves that separate them like the tricuspid and bicuspid valves. The document also notes anatomical features like the chordae tendineae that connect the valves to papillary muscles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views3 pagesSheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Sheep Heart Dissection: External Anatomy
Uploaded by
Lars vanheuverzwynThe document provides instructions for the dissection and examination of the external and internal anatomy of a sheep heart. It guides the reader to identify various external structures like the pulmonary trunk, aorta, and auricles. Upon opening the heart, it describes locating the internal chambers, including the right and left atria and ventricles, as well as the valves that separate them like the tricuspid and bicuspid valves. The document also notes anatomical features like the chordae tendineae that connect the valves to papillary muscles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
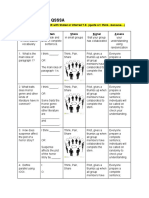
Name ___________________________________ Hour_________
Sheep Heart Dissection
External Anatomy
1. Identify the right and left sides of the heart. Look closely
and on one side you will see a diagonal line of blood vessels
that divide the heart, this line is called the interventricular
sulcus. The half that includes all of the apex (pointed end) of
the heart is the left side.
2. Locate the coronary arteries and veins that are on the
surface of the heart.
3.. Find the flaps of dark tissue on the top of the heart. These
ear-like flaps are called auricles.
4. The front-most vessel is the pulmonary trunk. Place a
probe or pencil in this vessel to mark its place.
5. Just behind the pulmonary trunk is the aorta. Depending
on how the heart was removed, you might also see a branch
of the aorta called the brachiocephalic artery. Place a pencil
or probe in the aorta to mark its place.
6. Turn the heart so that you are looking at its dorsal
side (the back of the heart.) Find the large opening at
the top of the heart next to the right auricle. This is
the superior vena cava. Place a pencil in this vessel,
you may also use your finger to feel the inside of
the right atrium.
7. Locate another opening on the backside of the heart
on the left side. This is the pulmonary vein. You can
feel the inside of the right atrium by probing this
opening with your finger. Place a pencil in
the pulmonary vein opening.
Checkpoint: Make sure you know the location of each
of the following before continuing to the internal
anatomy of the heart:
superior vena cava inferior vena cava aorta
pulmonary artery pulmonary veins
left atrium and ventricle right atrium and ventricle
auricle apex coronary arteries & veins interventricular sulcus
8. Visually (or use diagrams) to indicate which vessels connect to which chambers:
Pulmonary artery to the ______________________________
Pulmonary vein to the _______________________________
www.biologycorner.com
Aorta to the ______________________________________
Superior vena cava to the ____________________________
Dissection: Internal Anatomy
1. Use a scalpel to make an incision in the heart at the superior vena cava. The
incision should follow the line of the right side of the heart so that you can open
just the right side and see the right atrium, the right ventricle, and
the tricuspid valve between them. Alternatively, you can make a single cut
that bisects the heart into the front and back halves.
2. The chordae tendineae, also called the "heartstrings" can be found attached to
the thin flaps of the tricuspid. They are anchored to the wall of the heart at
the papillary muscle.
3. Make a similar incision on the left side of the heart to expose the left
atrium, left ventricle, and the bicuspid (mitral) valve. You will also be able to see
the chordae tendineae and the papillary muscle on this side of the heart.
5. Insert a probe into the aorta and observe where the probe exits the heart. You
may even be able to find the small aortic semilunar valve at the place where the
aorta connects to the heart. This valve does not have chordae tendineae and was
likely broken when you identified the aorta in the first part of this activity.
** Compare the heart of the sheep to human hearts by viewing various heart models in the
room.
Label the Heart
1. _________suprerior vena cave___________________
2. __________briochiocephalic trunk__________________
3. ___________left common carotid artery_________________
4. ____________left subclavian artery________________
5. _____________aorta_______________
6. _____________pulmonary artery_______________
7. _____________right atrium_______________
8. _____________pulmonary valve_______________
9. _____________left atrium_______________
10. ____________right ventricle_______________
11. ____________tricuspid_______________
12. ____________left ventricle_______________
13. ____________aortic valve_______________
14. What muscles attach to the chordae tendineae to hold the valves
in place? __________papillary muscles________________
15. What are the flaps on the front of the atria called?
_________superior vena cava_________________
16. If you place a probe in the aorta, into what chamber will it exit? _the right atrium_________________________
17. The superior and inferior vena cava enter into what chamber of the heart? ________left
atrium__________________
www.biologycorner.com
18. The large vessel on the front of the heart that lies in front of the aorta is the ______pulmonary trunk__________
19. What are the tendons that connect the valves to the muscles ? ________chordae tendineae __________________
20. What is another name for the bicuspid valve? ________mitral valve__________________
(Larger version of heart for overhead projector)
www.biologycorner.com
You might also like
- Pythagorean Theorem NotesDocument2 pagesPythagorean Theorem NotesMilla TanNo ratings yet
- Qsssa TemplateDocument2 pagesQsssa Templateapi-3290353840% (1)
- Short Stories Contain IdiomsDocument12 pagesShort Stories Contain IdiomsAnonymous jXOG0NdI6100% (2)
- Electricity Separate With AnswersDocument112 pagesElectricity Separate With AnswersMitra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesHuman Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyAhmad WirawanNo ratings yet
- Investigating BreathingDocument4 pagesInvestigating BreathingAal LyyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System of Invertebrates: Prepared By: Nerizza Anne Q. LozanoDocument23 pagesIntegumentary System of Invertebrates: Prepared By: Nerizza Anne Q. LozanoNerizza Anne Q. Lozano100% (1)
- Geometrical ShapesDocument31 pagesGeometrical ShapesAlanie Grace Beron Trigo100% (1)
- Y9 March 2019Document8 pagesY9 March 2019John LeeNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts Science Olympiad - Quizlet1-Geol-Bot-MinDocument7 pagesFast Facts Science Olympiad - Quizlet1-Geol-Bot-MinSanjay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Reasoning and Proof Chapter 2 PostulatesDocument19 pagesReasoning and Proof Chapter 2 PostulatesCherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Year 2 WorksheetDocument11 pagesYear 2 Worksheet434666No ratings yet
- Set 5 AnswersDocument80 pagesSet 5 AnswersThanmay ShajinNo ratings yet
- Biology B2Document14 pagesBiology B2madhujayanNo ratings yet
- NSTC 9 Sample Paper 2011 13 V1Document24 pagesNSTC 9 Sample Paper 2011 13 V1M Nisar Chishti Hassan100% (1)
- Igcse AccommodationDocument3 pagesIgcse AccommodationChr1zFX4No ratings yet
- Junior Mathematical Challenge: InstructionsDocument4 pagesJunior Mathematical Challenge: InstructionsAdd UpNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Honours Assessment Test 2015 PDFDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Honours Assessment Test 2015 PDFDennisNo ratings yet
- AP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13Document18 pagesAP Phys1 Momentum AP Style Free Response Questions 2019-11-13YazaanNo ratings yet
- 2005 AMC 12B SolutionsDocument9 pages2005 AMC 12B SolutionsjabagaweeNo ratings yet
- USABODocument2 pagesUSABOkcinvinciblemanNo ratings yet
- Paper 2: Year 7 Semester ExamDocument11 pagesPaper 2: Year 7 Semester ExamLee Chung100% (1)
- RespirationDocument10 pagesRespirationmohd zulkepli zakaria100% (1)
- 2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentDocument6 pages2011 Year 9 Science Acid Base AssessmentvleeeeNo ratings yet
- Essentials: Week by WeekDocument9 pagesEssentials: Week by WeekRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- H. Conditional Probability (H)Document12 pagesH. Conditional Probability (H)Papia SultanaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Math Worksheet 14 - A StatisticsDocument4 pagesClass 7 Math Worksheet 14 - A StatisticsDeath SychoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Data Analysis and Statistics Practice WorksheetDocument6 pagesChapter 10 - Data Analysis and Statistics Practice WorksheetGreEdgeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11 Concept ReviewDocument31 pagesChemistry 11 Concept ReviewJames Ernest Baker-taylor100% (1)
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument2 pagesCirculatory System ActivityA. ZNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 3CD Exam Calc Free 2011 PDFDocument12 pagesMathematics 3CD Exam Calc Free 2011 PDFTejajjjNo ratings yet
- 2016 AMO Paper and SolutionsDocument23 pages2016 AMO Paper and SolutionsCareen S AlicawayNo ratings yet
- Lec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesLec-21,22,23 - Circulatory SystemAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Matrix AlgebraDocument22 pagesMatrix AlgebraDeeDz Sophisticated-FantabulousNo ratings yet
- Answers bk1 2 Weebly Y9Document25 pagesAnswers bk1 2 Weebly Y9api-287224366100% (1)
- Area of Composite Shapes Activity SheetDocument3 pagesArea of Composite Shapes Activity SheetgayatriNo ratings yet
- 02 03 StretchesDocument5 pages02 03 StretchesGladys TanNo ratings yet
- 2011 P5 Math SA1 MGSDocument28 pages2011 P5 Math SA1 MGSBakialetchumy TanasikaranNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Power and Expon Laws ReviewDocument2 pagesUnit 2 Power and Expon Laws Reviewmichael.delaney8541100% (1)
- Physics 2 Guidebook PDFDocument485 pagesPhysics 2 Guidebook PDFErica Gale Joseph100% (1)
- Math-Epol338 Course Notes - Mathematics Curriculum StudyDocument105 pagesMath-Epol338 Course Notes - Mathematics Curriculum StudyBlair SmithNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument10 pagesPolygonCherry CurryNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 2008 Trial Exam 1Document24 pagesBiology Unit 3 2008 Trial Exam 1Vy PhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Quantitative Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocument78 pagesLesson 5 - Quantitative Analysis and Interpretation of Dataojs99784No ratings yet
- This Question Paper Consists of 26 Questions. Answer All Questions. The Usage of Calculator Is Not AllowedDocument6 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 26 Questions. Answer All Questions. The Usage of Calculator Is Not AllowedNeserajan_Subr_7555No ratings yet
- Batdangthuc DDTHDocument40 pagesBatdangthuc DDTHTuyếnĐặng100% (1)
- Points of Concurrency WS-1Document5 pagesPoints of Concurrency WS-1eebobNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Questions ARC 2006Document28 pagesBiology HSC Questions ARC 2006timeflies23No ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaDocument10 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On Genetics of BacteriaSefLRho0% (1)
- Work Mixture DistanceDocument7 pagesWork Mixture DistanceJerry LicayanNo ratings yet
- 2016 KS2 Mathematics Mark SchemesDocument28 pages2016 KS2 Mathematics Mark SchemesmayNo ratings yet
- Geometry Final ReviewDocument12 pagesGeometry Final Reviewblue butterflyNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Study GuideDocument1 pageHuman Body Systems Study Guideapi-261172766No ratings yet
- Year 9 - Simultaneous Equations QuizDocument3 pagesYear 9 - Simultaneous Equations QuizMathKeysNo ratings yet
- Notes 1.1 - Points, Lines, PlanesDocument6 pagesNotes 1.1 - Points, Lines, PlanesSusie GreenNo ratings yet
- EST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Document16 pagesEST II - Math Level 1 - December 2020Hazem ShehabNo ratings yet
- Sheep Heart DissectionDocument3 pagesSheep Heart DissectionMorgan DanielsNo ratings yet
- Aoi M - LAB - Heart DissectionDocument5 pagesAoi M - LAB - Heart Dissections25123No ratings yet
- pig-heart-dissection-lab-hand-out-Document7 pagespig-heart-dissection-lab-hand-out-Macarena Arechavaleta JaniniNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection: Background InformationDocument9 pagesHeart Dissection: Background Informationapi-482694849No ratings yet
- Pig Heart DissectionDocument6 pagesPig Heart DissectionNathalia Uhna BalboaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument10 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-253942549No ratings yet
- Sargassumfish ReproductionDocument3 pagesSargassumfish ReproductionBinu VargheseNo ratings yet
- Merritt Morning Market 2773 - Sept 28Document2 pagesMerritt Morning Market 2773 - Sept 28Kim LeclairNo ratings yet
- Appendix Working With Young Campers Giraffes - Cant - DanceDocument2 pagesAppendix Working With Young Campers Giraffes - Cant - DanceCorey SandersNo ratings yet
- Useless FactsDocument6 pagesUseless FactshawkeyeNo ratings yet
- Maternal Inheritence: (Ii) Coiling of Snail Shells (Limnaea Peregra)Document10 pagesMaternal Inheritence: (Ii) Coiling of Snail Shells (Limnaea Peregra)Kartik MishraNo ratings yet
- Show Me How To SurviveDocument19 pagesShow Me How To SurviveWeldon Owen Publishing100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakayunyhafitryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 FertilizationDocument18 pagesLecture 04 FertilizationBry RafNo ratings yet
- DACP OrderDocument5 pagesDACP OrderSohan PalNo ratings yet
- Learned BehaviourDocument19 pagesLearned Behaviourapi-176402481No ratings yet
- German Pinscher: 1 DescriptionDocument4 pagesGerman Pinscher: 1 DescriptiondescataNo ratings yet
- Musical Instrument of IsraelDocument18 pagesMusical Instrument of IsraelJulia OhNo ratings yet
- Anthology: Something Exploded in The KitchenDocument38 pagesAnthology: Something Exploded in The KitchendaphnehoNo ratings yet
- Golden Retriever Contract Non BindingDocument5 pagesGolden Retriever Contract Non BindingxdbubblieygumNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Competency-Based Learning Material: CBLM On Date Developed: Issued By: Developed byDocument92 pagesParts of A Competency-Based Learning Material: CBLM On Date Developed: Issued By: Developed byRocz RocoNo ratings yet
- Surgery Examination - 3-4 (Question Cases) (Eng)Document45 pagesSurgery Examination - 3-4 (Question Cases) (Eng)Aiman TymerNo ratings yet
- Akashay Rokade CompliantDocument4 pagesAkashay Rokade Compliantsubhash hulyalkarNo ratings yet
- Animal - Plant Classification MCQDocument9 pagesAnimal - Plant Classification MCQAnjana LiyanageNo ratings yet
- Perumal Santhanam, Ajima Begum, Perumal Pachiappan - Basic and Applied Phytoplankton Biology-Springer Singapore (2019) PDFDocument337 pagesPerumal Santhanam, Ajima Begum, Perumal Pachiappan - Basic and Applied Phytoplankton Biology-Springer Singapore (2019) PDFJherson Agurto SocolaNo ratings yet
- Literacy Prop Box - ZookeeperDocument3 pagesLiteracy Prop Box - Zookeeperapi-338550244No ratings yet
- Pigs - Basic Housing Requirements For PigsDocument7 pagesPigs - Basic Housing Requirements For PigsBukhosi Buks MhlangaNo ratings yet
- PHẦN 12 ĐẠI TỪDocument5 pagesPHẦN 12 ĐẠI TỪNguyen Viet LovesUlisNo ratings yet
- English 5 - Q4 PTDocument8 pagesEnglish 5 - Q4 PTShaina DaquilNo ratings yet
- Sectoral Finals - Grade 1 - 2014Document26 pagesSectoral Finals - Grade 1 - 2014Judah Lazaga0% (1)
- Grade 6 - Quiz BeeDocument68 pagesGrade 6 - Quiz BeeALYSSA MAE DAPADAPNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Chapter 1 Anatomical Regions (Chapter 1)Document33 pagesAnatomy Chapter 1 Anatomical Regions (Chapter 1)Fidaa Jaafrah100% (2)
- Platero y Yo - Juan Ramón JiménezDocument42 pagesPlatero y Yo - Juan Ramón JiménezYêu Văn HọcNo ratings yet