Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.0 Dryers (Drying)
5.0 Dryers (Drying)
Uploaded by
Renneil De Pablo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views18 pagesThe document discusses different types of dryers used in industrial processes and key concepts related to moisture removal. It describes common dryer types like rotary, tower, hearth, centrifugal, and tray dryers. It also defines important moisture-related terms like hygroscopic materials, bone dry weight, regain, and moisture content. Several equations are provided for calculating values like moisture removed, heat supplied, dryer efficiency, and properties at different dryer process points.
Original Description:
Dryers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of dryers used in industrial processes and key concepts related to moisture removal. It describes common dryer types like rotary, tower, hearth, centrifugal, and tray dryers. It also defines important moisture-related terms like hygroscopic materials, bone dry weight, regain, and moisture content. Several equations are provided for calculating values like moisture removed, heat supplied, dryer efficiency, and properties at different dryer process points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views18 pages5.0 Dryers (Drying)
5.0 Dryers (Drying)
Uploaded by
Renneil De PabloThe document discusses different types of dryers used in industrial processes and key concepts related to moisture removal. It describes common dryer types like rotary, tower, hearth, centrifugal, and tray dryers. It also defines important moisture-related terms like hygroscopic materials, bone dry weight, regain, and moisture content. Several equations are provided for calculating values like moisture removed, heat supplied, dryer efficiency, and properties at different dryer process points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 18
MLM 2021
Is the removal of relatively small
amount of water or other liquid
from the solid material.
▪ Rotary Dryer – is the most
commonly used dryer which
consists of a rotating cylinder
inside which the materials
flow while getting in contact
with the hot gases; the
cylinder is tilted at a slight
angle and fitted with lifting
flights. Rotary dryer is used
for copra, sand and wood
chips.
▪Tower Dryer – consists of a
vertical shaft in which the
wet feed is introduced at
the top and falls downward
over baffles while coming
in contact with the hot air
which rises and exhausts at
the top. Tower dryer is used
for palay, wheat and grains.
▪Hearth Dryer – is a
type of dryer in which
the material to be dried
is supported on a floor
through which the hot
gases pass. Hearth
dryer is used for copra,
coal and enamel wares.
▪Centrifugal Dryer –
consists of a centrifuge
revolving at high speed
causing the separation,
by centrifugal force, of
the water from the
material. Centrifugal
dryer is used for drying
fertilizer, salt and sugar.
▪Tray Dryer – consists
of trays, carrying the
materials to be dried,
placed in a
compartment or
moving conveyor.
Tray dryer is used for
ipil-ipil leaves and
grains.
▪Infrared Ray Dryer –
consists of infrared
lamps in which the
rays are directed to the
articles to be dried.
Infrared ray dryer is
used for drying
painted articles like
cars.
▪ Hygroscopic Materials are
substances which are
particularly variable in the
moisture content which they
can posses at different
times.
▪ Bone Dry Weight (BDW) or dry weight is the final constant weight reached by a
hygroscopic substance after being dried out.
▪ Regain is the hygroscopic moisture content of a substance expressed as a
percentage of the bone-dry weight of the material.
Regain = weight of moisture
Bone-dry weight
▪ Moisture Content is expressed as a percentage of the gross weight of the body,
and may refer to both hygroscopic and purely surface moisture.
Moisture Content = weight of moisture
Gross weight
Gross Weight = Bone-dry weight + weight of moisture
▪ Moisture removed from materials = moisture absorbed by air
= ma (w3 – w2)
= m4 – m5
▪ Bone-dry weight of wet feed = Bone-dry weight of dried product
BDW4 = BDW5
▪ Heat Supplied in Heater = ma (h2 – h1)
▪ Efficiency of dryer = Heat absorbed by materials
Heat supplied
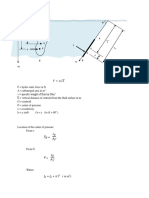
Given: Solution:
m = 10kg G.W. = Moisture Content + BDw 1
BDw = 8.5 kg
Regain = 20% For Moisture Content
Moisture content = Regain (BDw)
Moisture content = (0.20)(8.5kg)
Required:
Moisture content = 1.7 kg
Wt. of product per kg of
orig. mat. = ?
From 1
G.W. = 1.7 kg + 8.5 kg
G.W. = 10.2 kg
For weight of product per kg of original material = G.W / m
Wt. of product per kg of orig. mat. = 1.02 kg
Solution:
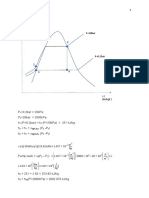
At point 1
For w1 & h1
w1 = 0.622 Pv
Pt – Pv
Given: Required:
Pv = RH Psat = (1)(10.098 kPa) = 10.098 kPa
m = 800 kg/hr At point 2 a) Mw before heating
w1 = 0.622 (10.098)
tdb = 106°C b) Mw when discharge
At point 1 101.325 – 10.098
c) Mew
RH = 100% w1 = 0.0688
d) RH3
tdb = 46°C At point 3 h1 = Cp t + w hg
e) tdp3
Psat = 10.098 kPa tdb = 61°C hg @ 46°C = 2585 kJ/kg
f) u3
h1 = (1.0062)(46)+(0.0688)(2585)
g) V2
h1 = 224.13 kJ/kg
At point 3
Passed through an adiabatic dryer
h2 = h3 = 291.41 kJ/kg
At point 2 For w3
When passing through heater h3 = Cp t + w hg
w1 = w2 = 0.0688 w3 = h3 – Cpt
h2 = Cp t + w hg hg
hg @ 106°C = 2685.4 kJ/kg hg @ 61°C = 2611.3 kJ/kg
h2 = (1.0062)(106)+(0.0688)(2685.4) w3 = 291.41 – (1.0062)(61)
2611.3
h2 = 291.41 kJ/kg
w3 = 0.0881
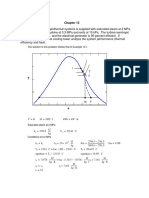
For c (Mew)
Mew = m (w3 – w2) = 800 (0.0881 – 0.0688)
Mew = 15.44 kg/hr
For a (mw1) For b (mw3)
For d (RH3)
w = mw / ma w = mw / ma
RH3 = Pv / Psat 1
mw1 = w1 ma mw3 = w3 ma
Psat @ 61°C = 20.881kPa
mw1 = (0.0688)(800 kg/hr) mw3 = (0.0881)(800 kg/hr)
For Pv
mw1 = 55.04 kg/hr mw3 = 70.48 kg/hr
Pv = w Pt = (0.0881)(101.325)
w + 0.622 0.0881 + 0.622
Pv = 12.57 kPa
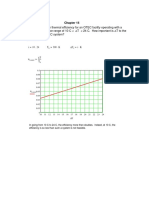
Solving for x = tdp3
50 – x = 12.349 – 12.57
x – 51 12.57 – 12.975
50 – x = 0.546
From 1 For e (tdp3)
x – 51
RH3 = 12.57 / 20.881 Pv3 = Pdp3 = 12.57 kPa
50 – x = 0.546 (x – 51)
RH3 = 0.6020 = 60.20% From Steam Table
50 – x = 0.546x – 27.83
Using interpolation
50 + 27.83 = 0.546x + x
50 12.349
77.83 = 1.546x
x 12.57
x = 50.34 °C = tdp3
51 12.975
For Pv
Pv = w Pt = (0.0688)(101.325)
w + 0.622 0.0688 + 0.622
Pv = 10.09 kPa
For f (u3) For g (V2)
From 3
u = RH (Pt – Psat) m =V / v
v = (0.287)(106+273)
Pt – Pv V = mv 2
101.325 – 10.09
u = (0.6020)(101.325 – 20.881)
v = 1.19 m³/kg
101.325 – 12.57 For v
From 2
u3 = 0.5456 = 54.56% v = Ra T 3
V = (800kg/hr)(1.19 m³/kg)(1hr/3600s)
Pt – Pv
V2 = 0.264m³/sec.
You might also like
- Full Download Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test BankDocument21 pagesFull Download Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test Bankisaaccastrole100% (28)
- MS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDocument6 pagesMS - Worthy of It All - Key of A & GDianne HorarioNo ratings yet
- Psych Exercise02 SolutionsDocument9 pagesPsych Exercise02 Solutionsjasson ponce100% (3)
- Assignment 1 Evaporation CCB 31202 55221120125Document11 pagesAssignment 1 Evaporation CCB 31202 55221120125Surendra Louis Dupuis NaikerNo ratings yet
- The Easter PageantDocument7 pagesThe Easter PageantPastor JeanneNo ratings yet
- Meneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Document19 pagesMeneses, Keziah F.: Cop T T T T T T Where: T T T Cop COP 1.4696 1.47Eriane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Highway Development and Planning PDFDocument59 pagesHighway Development and Planning PDFjun junNo ratings yet
- Design of Stuctures For The Mining Industry - Part 3 - Comementary On SANS 10208-2005 PDFDocument135 pagesDesign of Stuctures For The Mining Industry - Part 3 - Comementary On SANS 10208-2005 PDFNhlakanipho NkwanyanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Introduction To GrindingDocument5 pagesChapter1 Introduction To GrindingSwati GautamNo ratings yet
- 15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHDocument17 pages15.1 250 KG/H of Air Saturated at 2°C Is Mixed With 50 KG/H of Air at 35°C and 80% RHNathan EscobalNo ratings yet
- Pantoja HW1Document30 pagesPantoja HW1Reyes Kirby SamoyNo ratings yet
- 15.docx 1 1Document21 pages15.docx 1 1Nathan EscobalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Document9 pages2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Pryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Hvac Lab 3Document24 pagesHvac Lab 3Crystian Kobee EmpeynadoNo ratings yet
- Heating and Humidifying: M M M M Air T TDocument10 pagesHeating and Humidifying: M M M M Air T TmarkNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #2Document5 pagesTutorial #2Hafizh Renanto AkhmadNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicallyDocument21 pagesThermodynamicallySunde PascuaNo ratings yet
- MEC 4105 Test Marking GuideDocument4 pagesMEC 4105 Test Marking GuideBirimumaso DavidNo ratings yet
- P at 49° C=11.7465Kpa P Ø P Ω1= Kg KgDocument9 pagesP at 49° C=11.7465Kpa P Ø P Ω1= Kg KgBensoyNo ratings yet
- Edr 3 Prob 4Document7 pagesEdr 3 Prob 4Arfel Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- ME 22 (Industrial Plant Engineering) : Capitol UniversityDocument14 pagesME 22 (Industrial Plant Engineering) : Capitol UniversityBensoyNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Activity No. 3: Q KJ Min T T COPDocument4 pagesModule 7: Activity No. 3: Q KJ Min T T COPLeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1 CompressDocument20 pagesThermodynamics 1 Compressjlss jpNo ratings yet
- Combustion Eng'g ProblemsDocument16 pagesCombustion Eng'g ProblemsRogelyn JosolNo ratings yet
- Hematra Cooling TowerDocument4 pagesHematra Cooling Towerjc CincoNo ratings yet
- Sheet (1&2) ThermoDocument17 pagesSheet (1&2) ThermoAhmed A. TaimaNo ratings yet
- Higher Temperature Reservor, T Heat Engine Low Temperature Reservor, TDocument16 pagesHigher Temperature Reservor, T Heat Engine Low Temperature Reservor, THào Văn TríNo ratings yet
- Psychometric Properties and ProcessesDocument40 pagesPsychometric Properties and ProcessesUser140035No ratings yet
- Exercises Problem 3 Refrigeration - PascualDocument4 pagesExercises Problem 3 Refrigeration - PascualJef PascualNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument62 pagesChapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamicsamna insyirahNo ratings yet
- Blower PowerDocument8 pagesBlower PowerRaffy Luna100% (1)
- Solutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 11: November 29, 2000 J. MurthyDocument8 pagesSolutions To Extra Problems in Chapter 11: November 29, 2000 J. Murthycobalt boronNo ratings yet
- Extra Sol11Document8 pagesExtra Sol11Ahmed NasrNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Energi Pada Beberapa Volume AturDocument35 pagesPersamaan Energi Pada Beberapa Volume AturHONOR clothNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Cooling TowersDocument16 pages4.0 Cooling TowersRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers and Air DryersDocument21 pagesCooling Towers and Air DryersVince Harrison BalfermosoNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document22 pagesCH 09hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- Solution P1-GeothermalDocument7 pagesSolution P1-GeothermalJeffrey SerranoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAntonio AdorzaNo ratings yet
- Q2 SolutionDocument2 pagesQ2 SolutionSam StideNo ratings yet
- ch13 PDFDocument6 pagesch13 PDFAkash ThummarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No 1pdfpdf PDF FreeDocument87 pagesProblem Set No 1pdfpdf PDF FreeMaria Perez100% (1)
- ch14 PDFDocument8 pagesch14 PDFAkash ThummarNo ratings yet
- Coolingtowerdryer 140208204949 Phpapp02 PDFDocument22 pagesCoolingtowerdryer 140208204949 Phpapp02 PDFJel SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Given/Illustration:: Food Drying Problem Set (Laboratory Exercise)Document3 pagesGiven/Illustration:: Food Drying Problem Set (Laboratory Exercise)Ronin GoraNo ratings yet
- Given/Illustration:: Food Drying Problem Set (Laboratory Exercise)Document3 pagesGiven/Illustration:: Food Drying Problem Set (Laboratory Exercise)Ronin GoraNo ratings yet
- Nerpan Bismillahbarua5 Hal 21Document55 pagesNerpan Bismillahbarua5 Hal 21Roni SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture9: Moist Air: Psychrometric ChartDocument3 pagesLecture9: Moist Air: Psychrometric ChartHoàng Long Nguyễn BùiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 SolutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 SolutionscarolNo ratings yet
- Cycles Revision SolutionsDocument11 pagesCycles Revision SolutionsLayla JhNo ratings yet
- ES12 CH 05Document15 pagesES12 CH 05Daniel MwangangiNo ratings yet
- SARMIENTO Exercises Problem 2 Ref and Air ConDocument4 pagesSARMIENTO Exercises Problem 2 Ref and Air ConLeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- SARMIENTO Exercises Problem 2 Ref and Air ConDocument4 pagesSARMIENTO Exercises Problem 2 Ref and Air ConLeyzer MalumayNo ratings yet
- Sac Char If IcationDocument7 pagesSac Char If IcationCarol WeiNo ratings yet
- At 2.5 Mpa 2803.1 6.2575 at 50 Kpa 340.49 1.0910 2305.4 6.2575 0.000103 Sol'N: 280.31Kj /KG Solving For H: + 6.2575 1.0910+X (6.5029)Document22 pagesAt 2.5 Mpa 2803.1 6.2575 at 50 Kpa 340.49 1.0910 2305.4 6.2575 0.000103 Sol'N: 280.31Kj /KG Solving For H: + 6.2575 1.0910+X (6.5029)Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- Chapter 3 (B) Energy Balance: 3.9 AssumptionsDocument21 pagesChapter 3 (B) Energy Balance: 3.9 Assumptionssaur1No ratings yet
- 3 (A) Thermodynamics RelationsDocument6 pages3 (A) Thermodynamics Relationsananda narayananNo ratings yet
- Design Option 3Document9 pagesDesign Option 3무제untitledNo ratings yet
- Analisis PerhitunganDocument7 pagesAnalisis PerhitunganMuhammad Aditiya CandraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Energy Balance April 10 2017.v2Document31 pagesChapter 5 Energy Balance April 10 2017.v2kennethmsorianoNo ratings yet
- Exhaust-System 2Document4 pagesExhaust-System 2Aramae DagamiNo ratings yet
- Bab Iv Analisa Data Dan Pembahasan: 4.1 Perhitungan Efisiensi BoilerDocument3 pagesBab Iv Analisa Data Dan Pembahasan: 4.1 Perhitungan Efisiensi Boilerrizki hsbNo ratings yet
- Quiz4 by PassDocument3 pagesQuiz4 by PassAllaine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Psychrometry With Sample ProblemsDocument21 pages2.0 Psychrometry With Sample ProblemsRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Intro To Aircon (Properties of Moist Air) With Sample ProblemDocument10 pages1.0 Intro To Aircon (Properties of Moist Air) With Sample ProblemRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Cooling Load CalculationDocument29 pages3.0 Cooling Load CalculationRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Cooling TowersDocument16 pages4.0 Cooling TowersRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Registration: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityDocument2 pagesCertificate of Registration: Don Honorio Ventura State UniversityRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Incline HydroDocument13 pagesIncline HydroRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument9 pagesHydrostaticsRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Course: FLUID MECH 313 Fluid Statics: P Pressure, N/M F Force, N, Lb. A Area, MDocument16 pagesCourse: FLUID MECH 313 Fluid Statics: P Pressure, N/M F Force, N, Lb. A Area, MRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Properties of LiquidDocument18 pagesFundamental Properties of LiquidRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheDocument12 pagesCompressors: Isothermal - This Model Assumes That TheRenneil De PabloNo ratings yet
- Two Stage CompressorDocument7 pagesTwo Stage CompressorRenneil De Pablo100% (2)
- Learnenglish Podcasts Elementary 02 10 Support PackDocument19 pagesLearnenglish Podcasts Elementary 02 10 Support PackWilliams NiñoNo ratings yet
- BodorPro-T Laser Cutting Control SystemDocument29 pagesBodorPro-T Laser Cutting Control SystemFredy CabrejoNo ratings yet
- Elements of The StateDocument59 pagesElements of The StateJoselito DemeterioNo ratings yet
- EN 【工业事业部】制药行业MES解决方案V1.0Document37 pagesEN 【工业事业部】制药行业MES解决方案V1.0Zamstars SocialNo ratings yet
- Boiling and CondensationDocument16 pagesBoiling and CondensationJunnaid NissarNo ratings yet
- Story of Siachen-1Document28 pagesStory of Siachen-1Henish KananiNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Pharmacy: Concepts For Alzheimer's Disease Drug DevelopmentDocument4 pagesInternational Journal of Pharmacy: Concepts For Alzheimer's Disease Drug DevelopmentIndra HedarNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lab ExercisesDocument5 pagesMicroprocessor Lab ExercisesnaveenparthiNo ratings yet
- Huawei MA5600TDocument48 pagesHuawei MA5600TChangDong SunNo ratings yet
- Color 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5: DegradadoDocument4 pagesColor 1 Color 2 Color 3 Color 4 Color 5: DegradadoVentura ArgotaNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Definition of Bending Radius and Pullback Force in HDD Operations Danilo Machado L. Da Silva, Marcos V. Rodrigues, Asle Venås Antonio Roberto de MedeirosDocument8 pagesMethodology For Definition of Bending Radius and Pullback Force in HDD Operations Danilo Machado L. Da Silva, Marcos V. Rodrigues, Asle Venås Antonio Roberto de MedeirosMAHESH CHAND100% (1)
- Glastonbury Town Council - FinalReportandRecommendationsfromGlastonburys5GAdvisoryCommitteePRINTDocument115 pagesGlastonbury Town Council - FinalReportandRecommendationsfromGlastonburys5GAdvisoryCommitteePRINTJessica Learmond-CriquiNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Community Forest Management in Madagascar: Is There A Free Lunch? - 2007Document97 pagesThe Economics of Community Forest Management in Madagascar: Is There A Free Lunch? - 2007HayZara MadagascarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0272884211004202 Main PDFMario Misael Machado LòpezNo ratings yet
- Square Portal FrameDocument8 pagesSquare Portal FramenabilaNo ratings yet
- GC4000+ Auto Super Charge Station User Manual-V1.3 EN202107151155Document14 pagesGC4000+ Auto Super Charge Station User Manual-V1.3 EN202107151155lyfar.markNo ratings yet
- AI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoDocument9 pagesAI Tech Agency - by SlidesgoSULOCHNA KUJURNo ratings yet
- Cirrus 5 Oxygen Concentrator Manual: Important: Make Sure You Read and Understand All of The InformationDocument21 pagesCirrus 5 Oxygen Concentrator Manual: Important: Make Sure You Read and Understand All of The Informationmario pulido benitezNo ratings yet
- Optimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDocument9 pagesOptimasi Daya Dan Torsi Pada Motor 4 Tak Dengan MoDanaNo ratings yet
- Design of Rigid Pavement CC Road With M25Document5 pagesDesign of Rigid Pavement CC Road With M25pravincs_007No ratings yet
- Food Chain Forest Ecosystem P1Document21 pagesFood Chain Forest Ecosystem P1Allen GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Pages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFDocument1 pagePages From WRC - 452 - 2000 - , - Recommended - Practices PDFabhisheks5987No ratings yet
- 1365-1370-Oucip905 Ijetsr PDFDocument6 pages1365-1370-Oucip905 Ijetsr PDFYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Clase 06 Tornillos de PotenciaDocument25 pagesClase 06 Tornillos de PotenciajuancitoNo ratings yet