Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 - PA - ESP (Electronic Stability Control)
03 - PA - ESP (Electronic Stability Control)
Uploaded by
Kang PujidarmoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 - PA - ESP (Electronic Stability Control)
03 - PA - ESP (Electronic Stability Control)
Uploaded by
Kang PujidarmoCopyright:
Available Formats
ESP
1. Introduction
2. System Control
Copyright by Hyundai Motor Company. All rights reserved.
ESP
To know the system components of ESP system.
Objectives To understand the system interface and the difference with the previous
version.
ESP essentially consists of three assemblies: the sensors, the electronic control unit and actuators.
Sensors measure the position of the steering wheel, the pressure in the brake master cylinder, the yaw
velocity (‘yaw rate’) and the acceleration transverse to the vehicle (lateral acceleration). This makes it
possible to compare the driver’s intention with the momentary vehicle behavior so that, in the event of
interfering deviations with adverse affect on driving safety, the electronic control unit can initiate
appropriate corrective action.
ESP not only checks the driver’s steering wheel inputs and compares them with the vehicle’s actual
behavior, but also whether the driver’s input and the actual direction of travel coincide.
Technical Service Training Center
2
ESP
1. Introduction
1.1 General
ESP (Electronic Stability Control) system for PA has been developed by MANDO and the MGH-40
version has been applied. Comparing the existing MGH-25 (for JM, TUCSON) version, almost control
logic and components are the same except additional logic of ROP (Roll Over Prevention).
The following table in the slide is for the variation of MGH model which have been applied in Hyundai
ABS/TCS and ESP system. .
Item MGH 10 MGH 20 MGH 25 MGH 40
Model
Application LC, XD, SM GK, FC JM EN, TQ, PA
1999 (ABS) 2003 (ABS)
MP year 2001 (TCS) Aug. 2006 (ESP)
2000 (TCS) 2004 (ESP)
LFC + MSC +PBA LFC + MSC + PBA
+ MIRC + MIRC + ROP
LFC: Linear flow control ROP: Roll over
Key Points On-Off valve control
MSC: Motor speed control prevention (not for
PBA: Panic brake assist PA)
MIRC: Modified
independent rear control
In case of MGH-25 version for JM, there was an independent pressure sensor for PBA control which
was located in the bottom of master cylinder. But in MGH-40 version, the pressure sensor has been
built inside of ESP control module as same as one for BOSCH 8 version in NF, CM or TG.
Also the output signal of yaw rate & lateral G-sensor for JM was transferred to ESP control module by
serial line, but in PA, the sensor has a CAN communication interface with ESP control module in order to
guarantee more reliable performance and stable control due to faster communication speed. Be sure
that this is another CAN interface which has to be identified with the external CAN bus for Powertrain.
Technical Service Training Center
3
ESP
1.2 System components
- MGH 40 components
ABS ESP
HECU
Assembly
Wheel speed
sensor
Yaw & lateral
-
G-sensor
Pressure Built in HECU
-
sensor
Steering
-
angle sensor
Technical Service Training Center
4
ESP
2. System control
2.1 MIRC (Modified Independent Rear Control)
(1) MGH-20: Select low control
Independent control Select low control
(Uneven braking force) (Equal braking force)
(2) MGH-25, MGH-40: MIRC (Modified Independent Rear Control)
It is for considering the different road condition between left and right rear wheel in order to utilize the
frictional (grip) force on the road. So it controls independently control for both rear wheels depending
on the locking tendency. However there is a limitation for the braking pressure difference for the
vehicle safety and stable control, it is limited by 20bar or less.
Master Pres.
Pres Rise Pres Rise
Limitation Limitation
P_r1
P_r2
Gain in Braking
Performance
Technical Service Training Center
5
ESP
2.2 Inputs & Outputs
Inputs Outputs
WSS (4EA) Motor pump
SAS, HECM Valves
Yaw rate & Warning lamp
Lateral G-sensor, Function lamp
Pressure sensor, CAN interface
Brake switch, (Diagnosis with scan
ESP OFF switch tool,
ABS active signal...)
2.3 Wheel speed sensor
Receiving and analyzing this signal, HECM will calculate the Front
vehicle speed and decide the wheel is being locked or not.
- Type: Active type (Digital waveform)
- Power supply: 12V
- Air gap: 0.2~2.0mm
- Working temp.: -40~150
- Frequency: 1~2,500Hz
- Possible to detect 0km/h
- Reduced size by 40~50% than magnetic type
- Not sensitive to the noise and air gap.
Rear
Be sure that the rear wheel speed sensor is integrated into the
wheel hub so that required to replace the wheel hub assembly in
order to replace the rear wheel speed sensor. (same structure like
TB)
Technical Service Training Center
6
ESP
Output Waveform
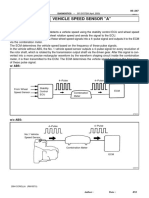
2.4 Yaw rate & lateral G-sensor
It is located on the bottom of passenger seat and it detects the yaw
rate of the vehicle in order to calculate the target yaw rate. G-sensor
detects the vehicle slip amount toward lateral direction to compensate
the sensed yaw rate which was detected by Yaw sensor.
- Power supply: 6.5~18V
- Signal output: CAN interface Front of the vehicle
- G sensor : -1.5~1.5g
- Yaw sensor: -75~75°/sec
2.5 Steering angle sensor
There are two types of steering angle sensor for ESP system. One is a relative angle type and the
other one is absolute angle type. In case of later one, it is necessary to calibrate the zero angle
(neutral position) whenever replace the sensor or remove it.
- Type: Relative angle type (Same as one for JM)
- Signal output: Serial wiring ST1
- Resolution: 2 °or less
- Measuring ability: over 1,500° /sec
ST2
ST N
Technical Service Training Center
7
ESP
2.6 Pressure sensor
To control PBA (Panic Brake Assist), HECM will refer
this signal to decide the operation and this sensor is
being installed inside control module as same as one
for ‘Bosch 8’ of NF, TG and CM. (Not possible to
replace the sensor)
- Operating voltage: 5±0.25V
- Max. pressure to measure: 200bar
2.7 Warning lamps
(1) ABS warning lamp
- This lamp turns on for 3 seconds after IG on; it turns off immediately if there is no ABS system
error.
- It turns on if any DTC is memorized.
- It turns on while the communication with the scanner.
- It turns on if the HECM connector is removed.
- ABS is not operated when this lamp is on.
(2) EBD warning lamp
- This lamp turns on for 3 seconds after IG on; it turns off immediately if there is no EBD system
error.
- It turns on if the parking brake is engaged.
- It turns on when the brake oil is not sufficient.
- It turns on while the communication with the scanner.
- It turns on if the HECM connector is removed.
- EBD is not operated when this lamp is on.
- It turns on when the solenoid valve failure, wheel speed sensor failure (more than two), HECM
failure, High voltage error and valve relay failure.
(3) ESP OFF warning lamp
- This lamp turns on for 3 seconds after IG on; it turns off immediately if there is no ESP system
error.
- It turns on if any DTC is memorized.
- It turns on while the communication with the scanner.
- Whenever ESP OFF switch is selected, this lamp turns on.
(4) ESP lamp
- This lamp turns on for 3 seconds after IG on; it turns off immediately if there is no ESP system
error and it blinks with the frequency of 2Hz while ESP operation.
Technical Service Training Center
8
ESP
2.8 MGH40 ABS wiring diagram
Technical Service Training Center
9
ESP
2.9 MGH40 ESP wiring diagram
Technical Service Training Center
10
You might also like
- W211 SBC PDFDocument68 pagesW211 SBC PDFRusshs Hour100% (5)
- Nissan 1B2Document104 pagesNissan 1B2Nhàn Nguyễn Thanh100% (3)
- Nissan PDFDocument108 pagesNissan PDFHoa Thanh Phong100% (7)
- Thesis (Ademola Temitayo)Document69 pagesThesis (Ademola Temitayo)Emmanuel Solomon100% (3)
- Mercedes-Benz Sensotronic Brake Control (SBC)Document53 pagesMercedes-Benz Sensotronic Brake Control (SBC)kshep100% (18)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15From EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15No ratings yet
- From Module 5 Topic3: Stage 1 / and Section BDocument49 pagesFrom Module 5 Topic3: Stage 1 / and Section BAhmed Mahmoud100% (1)
- Lovato Engine and Gen Controllers PDFDocument10 pagesLovato Engine and Gen Controllers PDFMariano Macchi100% (1)
- (MITSUBISHI) Manual de Taller Mitsubishi Montero 2002Document21 pages(MITSUBISHI) Manual de Taller Mitsubishi Montero 2002wnsdNo ratings yet
- 318 HO SBC Presentation Version (WJB) 09-30-02Document59 pages318 HO SBC Presentation Version (WJB) 09-30-02arkhom1No ratings yet
- 1.2 - Various Information (Aug 2013) v1Document3 pages1.2 - Various Information (Aug 2013) v1Valeriy DomashenkoNo ratings yet
- GrecogiordanoDocument28 pagesGrecogiordanomilitarudNo ratings yet
- 0 - Various Information-AbbrevationsDocument2 pages0 - Various Information-AbbrevationsioanNo ratings yet
- 219 Ho SBC (WJB) 9-30-02Document36 pages219 Ho SBC (WJB) 9-30-02arkhom1No ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Stability Control (Mitsubishi SC) : Click On The Applicable Bookmark To Selected The Required Model YearDocument21 pagesMitsubishi Stability Control (Mitsubishi SC) : Click On The Applicable Bookmark To Selected The Required Model YearPerla LeticiaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Body Electrical SystemDocument95 pagesToyota Body Electrical SystemNyhcnawNo ratings yet
- Product Information.: Technical Training. F01/F02 LCI InfotainmentDocument30 pagesProduct Information.: Technical Training. F01/F02 LCI InfotainmentmunkarobertNo ratings yet
- PF6TC - Electrical Control SystemDocument137 pagesPF6TC - Electrical Control Systemanggie100% (1)
- Am EscDocument4 pagesAm EscEdin raul Yalle rafaelNo ratings yet
- Mercedes WDB2110262A762236 2023-09-11021315PMDocument4 pagesMercedes WDB2110262A762236 2023-09-11021315PMMian AhmerNo ratings yet
- Brake Control System (Abs With Ebd, Brake Assist, TRC and VSC) 1. GeneralDocument23 pagesBrake Control System (Abs With Ebd, Brake Assist, TRC and VSC) 1. GeneralconnermcleodNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: GS 33P03K10-31EDocument6 pagesGeneral Specifications: GS 33P03K10-31EmbidNo ratings yet
- 35C Traction Control, Active Stability Control SystemDocument23 pages35C Traction Control, Active Stability Control Systemmanh100% (1)
- 6 SMDocument15 pages6 SMEnrique Arevalo LeyvaNo ratings yet
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- f7z 8162 Villamos Tengely SzoftverDocument12 pagesf7z 8162 Villamos Tengely SzoftverrezakaihaniNo ratings yet
- 520L0908 - Systems&Applications SD - AB - Aug-2005 - REVDocument8 pages520L0908 - Systems&Applications SD - AB - Aug-2005 - REVMHS teamNo ratings yet
- Belimo VRP-M STP Technische BrochureDocument36 pagesBelimo VRP-M STP Technische BrochureAdrianSebastianDarmansyahNo ratings yet
- Mazda (DTC) 983640268400 20100109065430Document2 pagesMazda (DTC) 983640268400 20100109065430Yankho NalimaNo ratings yet
- Brakes Description and OperationDocument17 pagesBrakes Description and Operationlilianadiaz.201074No ratings yet
- Engine Control System (Jan2015)Document26 pagesEngine Control System (Jan2015)A.i. StergianosNo ratings yet
- 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS: Powertrain Control Module (PCM)Document12 pages2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS 2008 Hyundai Santa Fe GLS: Powertrain Control Module (PCM)Manolo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mercedes-Benz VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC REPORT - WDD1760011J147109 - 2024033110716Document6 pagesMercedes-Benz VEHICLE DIAGNOSTIC REPORT - WDD1760011J147109 - 2024033110716Nidhameddine Ben AyedNo ratings yet
- Overview of Mechatronics Overview of MechatronicsDocument65 pagesOverview of Mechatronics Overview of Mechatronicsdoan luc100% (3)
- Specification: Unit Description Specification Remark ABS ESPDocument22 pagesSpecification: Unit Description Specification Remark ABS ESPmanualNo ratings yet
- FANUC Series 16i 18i 21i-TBMB FANUC Series 16i18i21i-TBMB Safety Function at Opening Protection Door (Safe Spindle Stop Function)Document9 pagesFANUC Series 16i 18i 21i-TBMB FANUC Series 16i18i21i-TBMB Safety Function at Opening Protection Door (Safe Spindle Stop Function)mahdi elmay0% (1)
- Adaptive Damper SystemDocument37 pagesAdaptive Damper Systemwilder0l0pezNo ratings yet
- Eps Manual NissanDocument8 pagesEps Manual Nissanjoiler pajueloNo ratings yet
- GS PT500 E 3rd PDFDocument7 pagesGS PT500 E 3rd PDFvipin2511100% (1)
- GS PT500 E 3rd PDFDocument7 pagesGS PT500 E 3rd PDFHemraj Singh Rautela100% (1)
- 17 Engine and Enmission ControlDocument2 pages17 Engine and Enmission ControlRodolphe AzarNo ratings yet
- Control+system New ModelDocument136 pagesControl+system New ModelTimkenNo ratings yet
- Electronic Braking Control ModuleDocument10 pagesElectronic Braking Control ModuleHanumantha ContiNo ratings yet
- TM Ga800sw 064Document28 pagesTM Ga800sw 064physicudoNo ratings yet
- Simovert Master Drives Simovert FC Simovert FCDocument10 pagesSimovert Master Drives Simovert FC Simovert FCMuhammad TaufikNo ratings yet
- DTC P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor "A": Circuit DescriptionDocument4 pagesDTC P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor "A": Circuit Descriptionjeremih alhegnNo ratings yet
- 03 - TPMS Sensores de RuedasDocument28 pages03 - TPMS Sensores de RuedasjoseNo ratings yet
- Cj1W-Ad/Da/Mad: Consistent Microsecond Throughput: Models With Direct Conversion Join The LineupDocument14 pagesCj1W-Ad/Da/Mad: Consistent Microsecond Throughput: Models With Direct Conversion Join The LineupXulescuNo ratings yet
- GS33J15C10 01enDocument9 pagesGS33J15C10 01enMayankNo ratings yet
- XK8 CATS SuspensionDocument6 pagesXK8 CATS Suspensionjuha_teuvonnen100% (1)
- Av00 0074enDocument8 pagesAv00 0074enbayursanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Stability Program Starting Model Year 1996Document25 pagesElectronic Stability Program Starting Model Year 1996Ozgean SeitomerNo ratings yet
- Belimo VRP-M Vav 4 1 enDocument36 pagesBelimo VRP-M Vav 4 1 enNenad MutavdzicNo ratings yet
- PEUGEOT 307 407 607 806 807 406 306 106 107 FaultCodes 0587 PDFDocument1 pagePEUGEOT 307 407 607 806 807 406 306 106 107 FaultCodes 0587 PDFIoan NovacNo ratings yet
- Chevrolet Opel Vauxhall Asm X 1024 59b25b521723dddcc6daea72Document34 pagesChevrolet Opel Vauxhall Asm X 1024 59b25b521723dddcc6daea72manutecNo ratings yet
- Electronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesFrom EverandElectronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Nissan-Infinity VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)From EverandAutomotive Electronic Diagnostics (Course 2)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Electronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Honda Acura vehiclesFrom EverandElectronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Honda Acura vehiclesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Toyota & Lexus VehiclesFrom EverandElectronic Automotive Transmission Troubleshooter Toyota & Lexus VehiclesNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2021-WhatsApp-008617663081468Document100 pagesCatalog 2021-WhatsApp-008617663081468justino cantaNo ratings yet
- E-Catalog Bardahl 2021Document3 pagesE-Catalog Bardahl 2021Fernando J NainggolanNo ratings yet
- 02 Suspension-Mazda TrainingDocument38 pages02 Suspension-Mazda TrainingHoàng Ngọc DươngNo ratings yet
- Som 10.1 P - Air Compressor PMS Feb 2022Document1 pageSom 10.1 P - Air Compressor PMS Feb 2022Amit BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Intersections Transportation EngineeringDocument38 pagesLecture 4 Intersections Transportation EngineeringIftikhar MughalNo ratings yet
- 13173/KANCHANJUNGA Sleeper Class (SL)Document2 pages13173/KANCHANJUNGA Sleeper Class (SL)NITESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Man Made DisasterDocument31 pagesMan Made Disastersam 1No ratings yet
- Kia Seltos Next Gen Brochure DesktopDocument9 pagesKia Seltos Next Gen Brochure DesktopGillNo ratings yet
- Lide H16Document901 pagesLide H16Николай МозговNo ratings yet
- MOTORDocument2 pagesMOTORernesto.zuniga.enaNo ratings yet
- Ford Cd4e Atsg Automatic Transmission Service GroupDocument120 pagesFord Cd4e Atsg Automatic Transmission Service Groupmferrari1976No ratings yet
- Cargo Crew - 3Document78 pagesCargo Crew - 3Osman Mert AtabayNo ratings yet
- Duhai Toll PlazaDocument34 pagesDuhai Toll PlazaVikas DixitNo ratings yet
- 2021 Michelin Maintenance GuideDocument176 pages2021 Michelin Maintenance Guidejorge daza100% (2)
- Bill of LadingDocument5 pagesBill of LadingVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Airbus A350 XWBDocument14 pagesAirbus A350 XWBstiveNo ratings yet
- CS/CS/CS/HB 1301: Department of TransportationDocument39 pagesCS/CS/CS/HB 1301: Department of TransportationBrandon HoganNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Montero Sport ChallengerDocument1 pageMitsubishi Montero Sport ChallengerFabricio VillacisNo ratings yet
- History of TransportationDocument14 pagesHistory of TransportationRAYMOND CALSADANo ratings yet
- Harga Suku Cadang Sepeda Motor HondaDocument8 pagesHarga Suku Cadang Sepeda Motor HondaFeistNo ratings yet
- Hostel PDFDocument1 pageHostel PDFsagar jadhavNo ratings yet
- 120 MM Mortars: Mortar SystemsDocument2 pages120 MM Mortars: Mortar Systemscbcfy7mfNo ratings yet
- Proforma 1 19308Document2 pagesProforma 1 19308raul ramirezNo ratings yet
- Decko - Training Matrix - Civil WorkDocument5 pagesDecko - Training Matrix - Civil Workmichael. wfpinternNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Plan Checklist: Project DetailsDocument10 pagesConstruction Management Plan Checklist: Project DetailsTariq JamalNo ratings yet
- International TradeDocument16 pagesInternational TradeAndraina Andrianarivelo100% (1)
- SUPER 1900-3i: Highway ClassDocument22 pagesSUPER 1900-3i: Highway ClassТракия Билд0% (2)
- D2.2 SWOT AnalysisDocument16 pagesD2.2 SWOT AnalysisPALACIOS HERRERA JORGE LUISNo ratings yet