Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measuring Poverty and Inequality: Per Capita Income
Measuring Poverty and Inequality: Per Capita Income
Uploaded by
Angela DimituiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measuring Poverty and Inequality: Per Capita Income
Measuring Poverty and Inequality: Per Capita Income
Uploaded by
Angela DimituiCopyright:
Available Formats
CH10- POVERTY AND INCOME DISTRIBUTION Climate and geography- continues to matter greatly for econ
development, alongside w/ the importance of economic and
INTRODUCTION political institutions.
2005- 25% or about 1.4 B people around the world lived in poverty
Asia- host to a majority of world’s poor: (China- 207M India- 455M) STRONG RECOMMENDATION: reintroduction of geographical
-home to more than 911 M whop struggle to meet basic food, considerations into the econometric and theoretical studies of
clothing and housing need or 66% of wold’s poor cross-country econ growth
Sustained growth in income = gap bet rich and poor has grown MEASURING POVERTY AND INEQUALITY
Poverty- broader sense, inability to access for minimal or
per capita income acceptable standard of living. But this loose definition contains
In 1960, (8 times greater) subjective notions- fact that what one needs or finds “acceptable”
Richest 20 economies ----------->------------poorest 20 countries or “minimal” is a very relative matter.
After 35 yrs of record growth In total world income, this income Poverty standards and definitions thus vary across different
differential has more than doubled. countries.
Similar trends: fruits of economic gains over the years have accrued Economic inequality- uneven distribution of income or
ONLY to a select few. expenditure
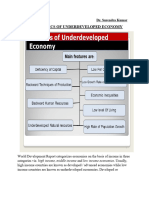
THE VARIOUS CIRCLE OF POVERTY AND INEQUALITY Income gaps- inevitable consequences of growth and
Core of all development policies (AM): development , and will correct itself in due course.
-alleviation of poverty
-minimization of economic inequality Gov’t intervention- used to avoid or at least minimize the
observed income gaps
Impact of differences is more marked in developing countries where
gov’t faces greater constraints in its ability to provide much needed Measurement of Poverty
assistance to improve the lot of their poor citizens Development economics- poverty as inability to access resources
to enjoy a minimal or acceptable standard of living.
Sacrifice required to send a child to school is substantial even tuition
charges are low. Cost of clothing transpo, books are quite high relative However, minimum needs or acceptable standards of living vary
to income levels of poor. form county to country, indiv to indiv, in accordance with CESC
(cultural, economic, social norms, expectation)
Children raised in poverty- NO peer groups or role model to instill in
them virtues of educ and human capital acquisition. HENCE, THIS DEFINITION IS NOT VERY USEFUL WHEN MEASURING
POVERTY AMD EVEN LESS SO WHEN MAKING CROSS_COUNTRY
Drugs and crime (perhaps sport)- only ways out of this low-level trap. COMPARISONS.
Perpetuation of poverty to successive generations, gap bet rich and Poverty- at subsistence level, means identifying the poor based
poor will be perpetuated and get worse - if chain will not be broken mainly on a universally accepted benchmark of PES (physiological,
economic and social) requirements for survival. (this is a standard
Is Climate a factor? - Climate theory of development approach in development economics wc works well to
Temperate climate - provides more conducive environment for econ operationalize poverty concept)
growth
Critical threshold point- minimum “acceptable income or
Almost all successful and modern industrial econ- situated in consumption ”- this def. Will vary, sometimes based on purchasing
temperate zone and colder places of the world power equivalent to buy min. Caloric intake and no more.
Heat causes more rapid rate of soil deterioration and rapid Very poor countries like India- poverty line is calculated by using
deterioration of other natural resources. estimates of expenditures required to guarantee a min.
Consumption of calories. Where caloric estimate=intake to
Warmer countries- heath of workforce is more adversely affected due maintain health and ability to work
to greater frequency of air- and water-borne infections and DISEASES
SPREAD MORE RAPIDLY. Also, working is more taxing on physical body, Wealthier countries- clothing and shelter is often added
hence, labor productivity is lower.
No uniform standard in determining poverty line,there is difficulty
Geographical tropics countries- nearly all poor to make accurate comparisons of poverty across countries or
Mid and higher latitudes- high income countries within countries
You might also like
- Date Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceDocument2 pagesDate Narration Chq./Ref - No. Value DT Withdrawal Amt. Deposit Amt. Closing BalanceArshiya Ayaz UmerNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Chapter 10Document3 pagesEconomic Development Chapter 10Ara Mae WañaNo ratings yet
- Problems of PoliciesDocument2 pagesProblems of PoliciesAirah Jane TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6Document5 pagesChapter 5 & 6Cyrus ArmamentoNo ratings yet
- Cyclical Poverty: Context ConstitutesDocument4 pagesCyclical Poverty: Context ConstitutesstrangerNo ratings yet
- Issues in The Third World PoiticsDocument6 pagesIssues in The Third World PoiticsOsman BayNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Subject:-Poverty Course Code:-GED 3606 Course Title:-Introduction To Sociology Submission Date:-5.09.2020Document6 pagesAssignment: Subject:-Poverty Course Code:-GED 3606 Course Title:-Introduction To Sociology Submission Date:-5.09.2020Afrid ArafNo ratings yet
- Handouts Econ Final 1Document4 pagesHandouts Econ Final 1Lilian FredelucesNo ratings yet
- SSE 108 Module 3Document20 pagesSSE 108 Module 3solomonmaisabel03No ratings yet
- Ray Chapter8 PovertyDocument46 pagesRay Chapter8 PovertyPhoulLitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3Peter John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 3 Characteristics of Transitional SocietiesDocument10 pages3 Characteristics of Transitional SocietiesSteve mungenduNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentMA. REGINA MAI COMIANo ratings yet
- Presentation PovertyDocument19 pagesPresentation Povertydr.willfred a. tacsuan90% (10)
- Final 1.1 Poverty and Income DistributionDocument19 pagesFinal 1.1 Poverty and Income Distributionjayson deeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Poverty and InequalityDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Poverty and InequalityHyuna KimNo ratings yet
- Summary Development Economics LecturesDocument32 pagesSummary Development Economics LecturesGishaNo ratings yet
- Development PresentationDocument33 pagesDevelopment PresentationKisten NallanNo ratings yet
- Summary Week 11Document3 pagesSummary Week 11gabriela2299No ratings yet
- Unit 7 POVERTY - INEQUALITY 2021Document11 pagesUnit 7 POVERTY - INEQUALITY 2021Riron CassandraNo ratings yet
- 5 - Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentDocument17 pages5 - Poverty, Inequality, and DevelopmentJesie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Govman Lesson 4Document9 pagesGovman Lesson 4Airah Jane TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi FinalDocument28 pagesUnit Vi FinalCatrina Joanna AmonsotNo ratings yet
- What Is Economic InclusionDocument6 pagesWhat Is Economic InclusionromainNo ratings yet
- Long Matrix Reformatted From Manifesto 16 AprilDocument18 pagesLong Matrix Reformatted From Manifesto 16 AprilAnonymous mvGv6v4QNo ratings yet
- Poverty in Equality and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesPoverty in Equality and DevelopmentASA PRATAMANo ratings yet
- Poverty Is A Global Issue!Document5 pagesPoverty Is A Global Issue!rex rexNo ratings yet
- Consuemr Demographics Week 4Document2 pagesConsuemr Demographics Week 4RoseNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Poverty Definition, Measurement, and AnalysisDocument15 pagesAppendix 1 Poverty Definition, Measurement, and Analysisanon_663315313No ratings yet
- Inequality, Poverty and DevelopmentDocument38 pagesInequality, Poverty and DevelopmentCresenciano MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 9 - Chapters 9 and 10: ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT - Finals (Summer)Document5 pagesQUIZ 9 - Chapters 9 and 10: ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT - Finals (Summer)sofiaNo ratings yet
- Econ ReviewerDocument8 pagesEcon Reviewerkimalysa68No ratings yet
- Topic 4. Poverty and InequalityDocument7 pagesTopic 4. Poverty and InequalityAnita BoboNo ratings yet
- Yecondev - Module 5Document4 pagesYecondev - Module 5wktxlsrkfNo ratings yet
- CSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Document5 pagesCSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Muhammad Gulraiz Muhammad GulraizNo ratings yet
- POVERTYDocument8 pagesPOVERTYSai KothuruNo ratings yet
- Poverty in Pakistan: (National School of Public Policy)Document19 pagesPoverty in Pakistan: (National School of Public Policy)Salman ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Topic 2. Poverty and InequalityDocument9 pagesTopic 2. Poverty and Inequalityraimefaye seduconNo ratings yet
- CSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Document4 pagesCSS Essay Poverty Alleviation - Complete Solved Essay (CSS Exams 2005)Touseef AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Picture in Brief: Diana CarneyDocument3 pagesThe Picture in Brief: Diana CarneypmanikNo ratings yet
- Eco 631 Spring 2020 LW 7 PDFDocument12 pagesEco 631 Spring 2020 LW 7 PDFTawhid QurisheNo ratings yet
- 10 Reducing Inequality Jan15 DigitalDocument20 pages10 Reducing Inequality Jan15 DigitalJulio JiménezNo ratings yet
- Aligarh Muslim University: Sociology-III Topic-Concept of PovertyDocument10 pagesAligarh Muslim University: Sociology-III Topic-Concept of PovertyHarendra TeotiaNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev Chapter 5Document6 pagesEcon Dev Chapter 5Feizhen Mae RodelasNo ratings yet
- Wealth Extreme Poverty Absolute Poverty Basic Human Needs Clean and Fresh Water Relative PovertyDocument6 pagesWealth Extreme Poverty Absolute Poverty Basic Human Needs Clean and Fresh Water Relative Povertykatak kembungNo ratings yet
- Section A & B - Overall SummaryDocument9 pagesSection A & B - Overall SummaryEriane Mae C. SamaneNo ratings yet
- Social Science - Povery and Food IncesurityDocument45 pagesSocial Science - Povery and Food IncesurityErfan TanhaeiNo ratings yet
- ISSUE BRIEF Ending Poverty by 2030Document5 pagesISSUE BRIEF Ending Poverty by 2030AKHIL H KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Economic DevelopmentDocument25 pagesReviewer in Economic DevelopmentFeane LamasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-1Document52 pagesLecture 3-1adejobiolajide04No ratings yet
- Economics For Public Policy: Teaching Session 11 Michaelmas Term 2018Document28 pagesEconomics For Public Policy: Teaching Session 11 Michaelmas Term 2018Nando RivarolaNo ratings yet
- Goal 1 - Fast FactsDocument2 pagesGoal 1 - Fast Factsj.sheng0517No ratings yet
- IED and Policies Underdevelopement CountriesDocument4 pagesIED and Policies Underdevelopement Countriesnaveenram994453No ratings yet
- Environmental and DevelopmentDocument64 pagesEnvironmental and DevelopmentMekonnin BersisaNo ratings yet
- Shibam EcoDocument28 pagesShibam EcoShibam GhoshNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument51 pagesUntitledDAILY EXPRESSNo ratings yet
- POVERTY1 PPPDocument19 pagesPOVERTY1 PPPpratyushvishwastrangerNo ratings yet
- Economic Development 31 December 2017Document149 pagesEconomic Development 31 December 2017ZIA UD DINNo ratings yet
- Dev Economics MPI IntroDocument1 pageDev Economics MPI IntroMohd. RahilNo ratings yet
- Summary: The End of Poverty: Review and Analysis of Jeffrey D. Sachs's BookFrom EverandSummary: The End of Poverty: Review and Analysis of Jeffrey D. Sachs's BookNo ratings yet
- Inv Receivable: Upper and Lower Limits As Clue WordsDocument1 pageInv Receivable: Upper and Lower Limits As Clue WordsAngela DimituiNo ratings yet
- Economic Development in Asia Chapter 10 - Poverty & Income DistributionDocument45 pagesEconomic Development in Asia Chapter 10 - Poverty & Income DistributionAngela DimituiNo ratings yet
- Study Guide LawDocument2 pagesStudy Guide LawAngela DimituiNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Laws in PHDocument5 pagesAgricultural Laws in PHAngela DimituiNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev - CH2,4,5,6Document7 pagesEcon Dev - CH2,4,5,6Angela DimituiNo ratings yet
- Happy Hours Apparels Aug 20, 2021Document2 pagesHappy Hours Apparels Aug 20, 2021Noman AwanNo ratings yet
- KH21029 00 RC DD FF103Document1 pageKH21029 00 RC DD FF103AHMED TAHERNo ratings yet
- Materials Management: Submitted To-Mrs. Shaveta Chugh Submitted by - Barbie Gaba 5716Document13 pagesMaterials Management: Submitted To-Mrs. Shaveta Chugh Submitted by - Barbie Gaba 5716Barbie GabaNo ratings yet
- Part I: Theory of AccountsDocument6 pagesPart I: Theory of AccountsJanna Mari FriasNo ratings yet
- Political EconomyDocument7 pagesPolitical Economysofia bertoliniNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC416 Course HandoutDocument12 pagesMba ZC416 Course HandoutareanNo ratings yet
- QA - RBA CLOSURE AUDIT-đã XoayDocument7 pagesQA - RBA CLOSURE AUDIT-đã XoayQuỳnh VõNo ratings yet
- Stainless-Steel-Tubes-Pipes-Profiles 2462Document20 pagesStainless-Steel-Tubes-Pipes-Profiles 2462Grcic NamenskaNo ratings yet
- S&P 500 Index Fund ComparisonDocument3 pagesS&P 500 Index Fund Comparisonstevenacarpenter50% (2)
- FACILITIES & SERVICE PROVIDERS Annex A - Form CM 2JA DILG-SGLGDocument4 pagesFACILITIES & SERVICE PROVIDERS Annex A - Form CM 2JA DILG-SGLGEKEIKO PAOLA SADANGNo ratings yet
- Book1 Group Act5110Document9 pagesBook1 Group Act5110SAMNo ratings yet
- Afshan Hamid 468 P (45-64)Document20 pagesAfshan Hamid 468 P (45-64)International Journal of Management Research and Emerging SciencesNo ratings yet
- Japfa Comfeed India PVT LTDDocument2 pagesJapfa Comfeed India PVT LTDNaresh GanugulaNo ratings yet
- ACC107 MOD10&11 IllustrationsDocument8 pagesACC107 MOD10&11 IllustrationsDanah EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Most Important Question For Mid Term ExamDocument16 pagesMost Important Question For Mid Term ExamDiwakar giriNo ratings yet
- Refractory LitratureDocument43 pagesRefractory LitratureSiddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Target 2024 by Eco BabaDocument101 pagesTarget 2024 by Eco BabaAritra DasNo ratings yet
- Analisis Rasio Keuangan - PT Blue BirdDocument8 pagesAnalisis Rasio Keuangan - PT Blue BirdAzis HailyNo ratings yet
- Social Accounting ModelsDocument19 pagesSocial Accounting ModelsSabrina Supti100% (1)
- Stock Valuation at Ragan Engines CH 9Document2 pagesStock Valuation at Ragan Engines CH 9Maxim Kapin50% (2)
- International Financial ManagementDocument18 pagesInternational Financial ManagementDestarata Hamarsan MustafaNo ratings yet
- The Economist January 24 2015 PDFDocument84 pagesThe Economist January 24 2015 PDFMaria Fernanda SantiNo ratings yet
- 1.HOTEL DAN RESTORAN-OKUPASI 25 JAN 2019 - CompressedDocument71 pages1.HOTEL DAN RESTORAN-OKUPASI 25 JAN 2019 - CompressedMarcia RikumahuNo ratings yet
- Book Review Vijay Joshi. India's Long Road: The Search For ProsperityDocument6 pagesBook Review Vijay Joshi. India's Long Road: The Search For ProsperityVikram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earned Value AnalysisDocument4 pagesEarned Value AnalysisSathiyagirinathanNo ratings yet
- Denr Protest Sobretodo Marcelo 2Document3 pagesDenr Protest Sobretodo Marcelo 2Meralu PagueNo ratings yet
- DLTA Annual Report 2014Document154 pagesDLTA Annual Report 2014Lea Wigiarti33% (3)
- Lily S Villamil Vs Sps. ErguizaDocument2 pagesLily S Villamil Vs Sps. Erguizakristel jane caldoza100% (2)
- Glamox - GMO Onshore Catalouge2017Document26 pagesGlamox - GMO Onshore Catalouge2017Enling GohNo ratings yet