Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrition Results: Trait Name Your Results Possible Outcomes
Nutrition Results: Trait Name Your Results Possible Outcomes
Uploaded by
hroooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition Results: Trait Name Your Results Possible Outcomes
Nutrition Results: Trait Name Your Results Possible Outcomes
Uploaded by
hroooCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrition Results
YOUR
TRAIT NAME POSSIBLE OUTCOMES
RESULTS
Moderate: Moderately likely to gain weight
Tendency to gain weight
A genetic tendency for higher weight gain due to Low: Less likely to gain weight
increased energy storage
High: Highly likely to gain weight
Moderate: Moderately likely to overeat
Tendency to overeat
Low: Less likely to overeat
A genetic tendency to over consume foods due to
increased craving
High: Highly likely to overeat
Moderate: Likely to overconsume high fat foods
Tendency to prefer fatty foods
A genetic tendency for lower fat taste perception and Low: Less likely to overconsume high fat foods
overconsumption of fatty foods
High: Highly likely to overconsume high fat foods
Moderate: Likely to overconsume sweet foods
Tendency to prefer sweet foods
Low: Less likely to overconsume sweet foods
A genetic tendency for lower sweet taste perception
and overconsumption of sweet foods
High: Highly likely to overconsume sweet foods
Moderate: Normal bitter vegetable preference
Tendency to prefer bitter foods
A genetic tendency for high bitter taste perception and Low: Less likely to prefer bitter vegetables
low intake of bitter vegetables
High: Likely to prefer bitter vegetables
Moderate: Likely to gain weight on high carb intake
Carbohydrate intake and weight gain
tendency Low: Less likely to gain weight on high carb
A genetic tendency for increased weight gain upon
higher carb intake High: Highly likely to gain weight on high carb intake
Moderate: Likely to gain weight on high SFA intake
Saturated fats intake and weight gain
tendency Low: Less likely to gain weight on high SFA intake
A genetic tendency for higher weight gain upon higher
sat fat intake High: Highly likely to gain weight on high SFA intake
Moderate: Likely to gain weight with high MUFA intake
Mono unsaturated fats intake and weight
gain tendency Low: Less likely to gain weight with high MUFA intake
A genetic tendency for weight gain upon higher MUFA
intake High: Highly likely to gain weight with high MUFA intake
Moderate: Likely to gain weight with high PUFA intake
Poly unsaturated fats intake and weight
gain tendency Low: Less likely to gain weight with high PUFA intake
A genetic tendency for weight gain upon higher PUFA
intake High: Highly likely to gain weight with high PUFA intake
YOUR
TRAIT NAME POSSIBLE OUTCOMES
RESULTS
Protein intake and weight loss tendency Moderate: Likely to lose weight on high protein intake
A genetic tendency for increased weight loss upon
higher protein intake High: Highly likely to lose weight on high protein intake
Moderate: Likely to regain weight after weight loss
Tendency to regain weight
A genetic tendency for rapid weight regain after a Low: Less likely to regain weight after weight loss
weight loss program
High: Highly likely to regain weight after weight loss
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin A intake
Vitamin A needs
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin A due to Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin A intake
inefficient metabolism of vitamin A
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin A intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin B12 intake
Vitamin B12 needs
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin B12 due to Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin B12 intake
inefficient metabolism of vitamin B12
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin B12 intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin B6 intake
Vitamin B6 needs
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin B6 due to Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin B6 intake
inefficient metabolism of vitamin B6
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin B6 intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin B9 intake
Vitamin B9 needs
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin B9 due to Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin B9 intake
inefficient metabolism of vitamin B9
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin B9 intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin D intake
Vitamin D needs
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin D due to Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin D intake
inefficient metabolism of vitamin D
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin D intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin E intake
Vitamin E needs
Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin E intake
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin E due to
inefficient metabolism of vitamin E
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin E intake
Need more: Moderately increase vitamin K intake
Vitamin K needs
Normal: Maintain normal Vitamin K intake
A genetic tendency to require more Vitamin K due to
inefficient metabolism of vitamin K
Need more: Significantly increase vitamin K intake
Need less: You may have higher calcium levels
Calcium needs
A genetic tendency to need more or less of Calcium Normal: Maintain normal Calcium intake
due to differences in metabolism of Calcium
Need more: Significantly increase Calcium intake
YOUR
TRAIT NAME POSSIBLE OUTCOMES
RESULTS
Need more: Moderately increase Copper intake
Copper needs
Normal: Maintain normal Copper intake
A genetic tendency to require more Copper due to
inefficient metabolism of Copper
Need more: Significantly increase Copper intake
Need more: Moderately increase Iron intake
Iron needs
Normal: Maintain normal Iron intake
A genetic tendency to require more Iron due to
inefficient metabolism of Iron
Need more: Significantly increase Iron intake
Need more: Moderately increase Magnesium intake
Magnesium needs
A genetic tendency to require more Magnesium due to Normal: Maintain normal Magnesium intake
inefficient metabolism of Magnesium
Need more: Significantly increase Magnesium intake
Need more: Moderately increase Phosphate intake
Phosphate needs
A genetic tendency to require more Phosphate due to Normal: Maintain normal Phosphate intake
inefficient metabolism of Phosphate
Need more: Significantly increase Phosphate intake
Need more: Moderately increase Zinc intake
Zinc needs
Normal: Maintain normal Zinc intake
A genetic tendency to require more Zinc due to
inefficient metabolism of Zinc
Need more: Significantly increase Zinc intake
Need more: Moderately increase Selenium intake
Selenium needs
A genetic tendency to require more Selenium due to Normal: Maintain normal Selenium intake
inefficient metabolism of Selenium
Need more: Significantly increase Selenium intake
Need more: Moderately increase antioxidants intake
Antioxidant needs
A genetic tendency to require more Antioxidants due Normal: Maintain normal antioxidants intake
to inefficient metabolism of Antioxidants
Need more: Significantly increase antioxidants intake
High: Likely to consume more caffeine
Caffeine consumption
Low: Likely to consume less caffeine
A genetic tendency for variation in caffeine
consumption due to difference in preference
Moderate: Likely to consume moderate amount of caffeine
Caffeine metabolism Slow: Likely to be a slow metabolizer of caffeine
A genetic tendency for variation in caffeine clearance
due to varied metabolism Fast: Likely to be a fast metabolizer of caffeine
Gluten insensitive: Unlikely to be gluten sensitive
Gluten sensitivity
A genetic tendency for variation in response to due to
varied sensitivity Gluten Sensitive: Increased risk of being gluten sensitive
YOUR
TRAIT NAME POSSIBLE OUTCOMES
RESULTS
Tolerant: Less likely to be lactose intolerant
Lactose intolerance
A genetic tendency for difference in response to
lactose due to varied tolerance Intolerant: Likely to be lactose intolerant
Moderate: Likely to have lower BP on low salt diet
Salt intake and blood pressure sensitivity
A genetic tendency for lower blood pressure due to Normal: Likely to slightly reduce BP on low salt diet
salt sensitivity
High: Highly likely to have lower BP on low salt diet
Riboflavin and blood pressure response Insensitive: Less likely to have lower BP on high Riboflavin intake
A genetic tendency for lower blood pressure on
increased riboflavin intake Sensitive: Highly likely to have lower BP with high Riboflavin Intake
You might also like
- Solution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)Document122 pagesSolution Manual of Modern Semiconductor Devices For Integrated Circuits (Chenming Calvin Hu)hu leo86% (7)
- Coding BreakdownDocument2 pagesCoding BreakdownAlex SouzaNo ratings yet
- CS101 Current Mid-Term Solved Papers 2022 BY M ZAMANDocument44 pagesCS101 Current Mid-Term Solved Papers 2022 BY M ZAMANNabil AhmedNo ratings yet
- My Diet Analysis PaperDocument3 pagesMy Diet Analysis PaperRyan Calhoun50% (2)
- Inspection Checklist 1 - Footing and FoundationDocument4 pagesInspection Checklist 1 - Footing and Foundationthescubatater100% (1)
- Policy - Co-2-034 Independent Double Check High Alert MedicationsDocument8 pagesPolicy - Co-2-034 Independent Double Check High Alert MedicationsTravel JunkyNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION Virginia Virg MyHeritagerawdnadata1.csvDocument26 pagesNUTRITION Virginia Virg MyHeritagerawdnadata1.csvvirginia13No ratings yet
- DIET DURING PREGNANCY AND LACTATION (Group II) (New)Document31 pagesDIET DURING PREGNANCY AND LACTATION (Group II) (New)coosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Role in Promoting Nutritional Health During Pregnancy Maternal Nutrition and Fetal Health #1Document5 pagesThe Nursing Role in Promoting Nutritional Health During Pregnancy Maternal Nutrition and Fetal Health #1Marileth JeffersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Diets in Modified CompositionDocument9 pagesChapter 3. Diets in Modified CompositionMAY JOY MARQUEZNo ratings yet
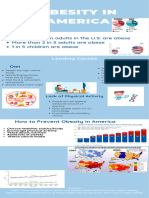
- Stop ObesityDocument28 pagesStop ObesityAhmad AkaderNo ratings yet
- Diet Therapy in ObesityDocument35 pagesDiet Therapy in ObesitySaher YasinNo ratings yet
- Nutrition-and-Diet-Therapy-Finals 11Document11 pagesNutrition-and-Diet-Therapy-Finals 11ChskNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Session 11Document6 pagesPregnancy and Lactation: Nutrition and Diet Therapy Session 11Alanis MaligatNo ratings yet
- Oh BessDocument19 pagesOh Besslola&losa farhanNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition & Breast Feeding & Complementary Feeding د نورا اطباءDocument11 pagesMalnutrition & Breast Feeding & Complementary Feeding د نورا اطباءرافت العواضيNo ratings yet
- Nutriiiiii ErrDocument9 pagesNutriiiiii ErrElleNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Throughout The LifespanDocument48 pagesNutrition Throughout The Lifespantanya merdeNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 2Document2 pagesUntitled Document 2api-748643383No ratings yet
- Booklet 4 Achieving Healthy Weight GainDocument7 pagesBooklet 4 Achieving Healthy Weight GainRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cram Sheet - 4Document1 pageNursing Cram Sheet - 4Reeya RayamajhiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 Nutrition in Pregnancy and LactationDocument27 pagesGROUP 1 Nutrition in Pregnancy and LactationKaye NaigNo ratings yet
- 1 GDHremajaMIKM20042013Document69 pages1 GDHremajaMIKM20042013Nurdin_14No ratings yet
- Breast Milk: Benefits & BarriersDocument22 pagesBreast Milk: Benefits & BarriersNazia ArifNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument11 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument16 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumGracy Casaña100% (2)
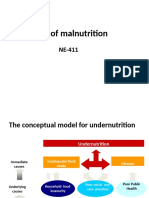
- Causes of MalnutritionDocument13 pagesCauses of MalnutritionEman ZahraNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Needs During PregnancyDocument4 pagesNutritional Needs During PregnancyFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care - Healthy PregnancyDocument19 pagesPrenatal Care - Healthy PregnancysanthanalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic DietsDocument8 pagesTherapeutic DietsmArLoN91% (11)
- Infant Nutrition 101: Amanda Mcmurray Registered Dietitian PediatricsDocument21 pagesInfant Nutrition 101: Amanda Mcmurray Registered Dietitian PediatricsxxpixiexxNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Nutrition Lec M1Document43 pagesPregnancy and Nutrition Lec M1Judea PagedpedNo ratings yet
- FAD DIETS PowerPointDocument48 pagesFAD DIETS PowerPointTechnoShindo100% (1)
- Lesson#6 - Anemias in Pregnancy & Multiple GestationDocument17 pagesLesson#6 - Anemias in Pregnancy & Multiple GestationKyle Ethan De la RiarteNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pregnancy Minidian Fasitasari Medical School of Unissula SemarangDocument33 pagesNutrition in Pregnancy Minidian Fasitasari Medical School of Unissula SemarangNorman AjxNo ratings yet
- Promotion of Nutrition Among Pregnant and Lactating MothersDocument12 pagesPromotion of Nutrition Among Pregnant and Lactating MothersGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- InfographicDocument1 pageInfographicapi-739298057No ratings yet
- NDT Lec FinalsDocument7 pagesNDT Lec Finalsnaomie manaliliNo ratings yet
- Unhealthy Foods: BurgerDocument1 pageUnhealthy Foods: BurgerDavid SaezNo ratings yet
- 09 Feb 2023Document51 pages09 Feb 2023azeem dilawarNo ratings yet
- Listening Task SheetDocument1 pageListening Task SheetMohd Syamsul Mohd SyamsulNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian DietsDocument7 pagesVegetarian DietsJuan RamirezNo ratings yet
- HOTL 3012 - Module 8 - DietaryDocument20 pagesHOTL 3012 - Module 8 - Dietaryyanchiyuan3No ratings yet
- NoakesDocument1 pageNoakesapi-357484980No ratings yet
- Activity # 3 - Santos, Aira Kristelle M.Document13 pagesActivity # 3 - Santos, Aira Kristelle M.Ai MendozaNo ratings yet
- LactationDocument11 pagesLactationWan SakinahNo ratings yet
- Nutrition IIDocument15 pagesNutrition IIMelorie MutiaNo ratings yet
- ObesityDocument11 pagesObesitysenthilkumarharishragavNo ratings yet
- Nutrition During Pregnancy and Lactation: Energy Needs Key Mineral and Vitamin NeedsDocument20 pagesNutrition During Pregnancy and Lactation: Energy Needs Key Mineral and Vitamin NeedsJIEA THERESE SIANNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION AND DIET Chap 17Document6 pagesNUTRITION AND DIET Chap 172083385No ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Lactation Nutrition and DietDocument35 pagesPregnancy and Lactation Nutrition and DietRj SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Overweight,:, & UnderweightDocument97 pagesOverweight,:, & UnderweightTajul AnshorNo ratings yet
- Meat-Free For A FiverDocument21 pagesMeat-Free For A FiverGarry DentNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Pregnancy: Dr.A.Rathna - M.S (O&G) 2 Yr PG MMC &riDocument37 pagesNutrition in Pregnancy: Dr.A.Rathna - M.S (O&G) 2 Yr PG MMC &rihaisureshNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity NewsletterDocument2 pagesChildhood Obesity Newsletterapi-357111605No ratings yet
- MODULE 8 - NCM105j JDocument8 pagesMODULE 8 - NCM105j JALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- Childhood Obesity: The Global Epidemic: Romanciuc Lilia, Doctor of Ph. in Medicine Department of PediatricsDocument55 pagesChildhood Obesity: The Global Epidemic: Romanciuc Lilia, Doctor of Ph. in Medicine Department of PediatricsusmfdocNo ratings yet
- BK1 CH3 Vocab P43Document2 pagesBK1 CH3 Vocab P43عبد الحميد حورانيNo ratings yet
- All About Obesity !!: Sify HR Sify India All Mon, 28 Mar 2022, 12:42 PM Oledata - MsoDocument3 pagesAll About Obesity !!: Sify HR Sify India All Mon, 28 Mar 2022, 12:42 PM Oledata - MsoAnil Chaudhary 1627980No ratings yet
- Gizi Kesehatan MasyarakatDocument40 pagesGizi Kesehatan Masyarakatdfghjk lkjhgNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Vegan Bodybuilding Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide For Bodybuilders And Athletes To Build A Perfect Body With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Vegan Bodybuilding Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide For Bodybuilders And Athletes To Build A Perfect Body With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- HOW TO BE A SLIM & RADIANT VEGAN: Achieve a Slim Body, All-Day Energy & Glow with a Plant-Based LifestyleFrom EverandHOW TO BE A SLIM & RADIANT VEGAN: Achieve a Slim Body, All-Day Energy & Glow with a Plant-Based LifestyleNo ratings yet
- Layout of NykaaDocument12 pagesLayout of Nykaayogesh DivechaNo ratings yet
- Push Button Typical WiringDocument12 pagesPush Button Typical Wiringstrob1974No ratings yet
- Modern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesModern Business Statistics With Microsoft Office Excel 4Th Edition Anderson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFjerryholdengewmqtspaj100% (11)
- Porter's Five Forces Model of Competition-1Document14 pagesPorter's Five Forces Model of Competition-1Kanika RustagiNo ratings yet
- MC III Exp User ManualDocument136 pagesMC III Exp User ManualJamesStenhouse100% (1)
- Oct-Chapter 1&2 - Practical ResearchDocument16 pagesOct-Chapter 1&2 - Practical ResearchJaimee Mojica TaligonNo ratings yet
- Psycosocial Activities Day 3Document40 pagesPsycosocial Activities Day 3John Briane CapiliNo ratings yet
- Judicial Review CSGDocument13 pagesJudicial Review CSGSushmaNo ratings yet
- Sooceal ProjectDocument40 pagesSooceal ProjectSushil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument233 pagesPDFtuNo ratings yet
- PH.D - Synopsis - M. Praveen KumarDocument12 pagesPH.D - Synopsis - M. Praveen KumaralexabcdxyzNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research NotesDocument8 pagesQualitative Research NotesAnanta SinhaNo ratings yet
- 09-Humble Homemade Hifi - PhleaDocument4 pages09-Humble Homemade Hifi - Phleajns0110No ratings yet
- In Company 3.0 Intermediate in Action Video Worksheet - Scenario Worksheet CDocument2 pagesIn Company 3.0 Intermediate in Action Video Worksheet - Scenario Worksheet CAma GavNo ratings yet
- SNS NotesDocument26 pagesSNS NotesyslnjuNo ratings yet
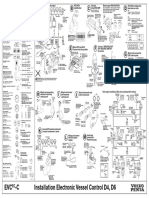
- D C A B: Installation Electronic Vessel Control D4, D6 EVC - CDocument2 pagesD C A B: Installation Electronic Vessel Control D4, D6 EVC - Csivan_sg1800No ratings yet
- Community Capstone Health Policy PaperDocument17 pagesCommunity Capstone Health Policy Paperapi-417446716No ratings yet
- Product Characteristics and ClassificationsDocument3 pagesProduct Characteristics and Classificationstsega-alemNo ratings yet
- 2014 Table Clinic InstructionsDocument19 pages2014 Table Clinic InstructionsMaria Mercedes LeivaNo ratings yet
- Gas Bill AprilDocument4 pagesGas Bill AprilMozhie OicangiNo ratings yet
- ASTM D2041 aashto T209 ефект процент битума PDFDocument4 pagesASTM D2041 aashto T209 ефект процент битума PDFanon_711474514No ratings yet
- Lu PDFDocument34 pagesLu PDFAlexanderNo ratings yet
- Fesco Online BillDocument2 pagesFesco Online BillFaisal NaveedNo ratings yet
- MorphingDocument16 pagesMorphingSahil BansalNo ratings yet
- Is It Time For You To Say 'I Do' by Rommel N. AngaraDocument1 pageIs It Time For You To Say 'I Do' by Rommel N. AngaraWell-loved Essays100% (2)