Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-Garnet
Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-Garnet
Uploaded by
John Kerby Corral0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views14 pagesPower supplies have essential functions like changing voltage and providing stable power. They must match the needs of the device to avoid inefficiency or damage. Getting too much or too little capability could cost unnecessary money or harm devices.
Original Description:
Original Title
HOMEWORK 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPower supplies have essential functions like changing voltage and providing stable power. They must match the needs of the device to avoid inefficiency or damage. Getting too much or too little capability could cost unnecessary money or harm devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views14 pagesHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-Garnet
Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-Garnet
Uploaded by
John Kerby CorralPower supplies have essential functions like changing voltage and providing stable power. They must match the needs of the device to avoid inefficiency or damage. Getting too much or too little capability could cost unnecessary money or harm devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
HOMEWORK 1
John Kerby C. Corral
X-Garnet
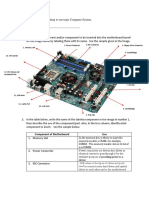
WHAT IS THE USE OF POWER SUPPLY?
Power supplies have essential functions found in all
models with additional operations added depending
on the device type. Power supplies may need to
change voltage up or down, convert power to direct
current, or regulate power for smoother outcoming
voltage. These functions will help you choose which
supply you need for your electrical needs. Getting a
device with too many features could cost you more
money than you need to spend, but if you don’t get
the features you require, you could damage the
devices you need to power.
CPU is the electronic
circuitry in a computer
that executes
instructions that make
1. CPU up a program. It is also
(Central known as a central
processor or the main
Processing processor. The CPU
Unit) chip executes the basic logic,
arithmetic, controlling
as well as input/output
(I/O) operations
specified by the
instructions in the
desktop programs.
2. RAM RAM is a kind of
computer memory that
(Random can be read and written.
Access It is mainly used to save
data and machine code.
Memory) A RAM device permits
slots data to be read or
written in nearly the
same amount of time no
matter where the data’s
physical location is in
the memory. Compared
to the direct-access
storage devices like hard
drives, CD/DVD and
magnetic tapes, RAM
media is much faster for
data reading and
writing.
3. They are the two chips
in the core logic chipset
Southbridge/n on the motherboard.
orthbridge Typically, the
southbridge implements
the slower capabilities
of the motherboard in a
northbridge/southbridg
e chipset computer
architecture.
The northbridge, also
known as host bridge or
Memory Controller Hub,
is connected directly to
the CPU via the front-
side bus (FSB). It is
responsible for tasks
requiring the highest
performance. Together
with the southbridge,
they manage
communications
between the CPU and
other motherboard
components.
4. BIOS BIOS, also called system
BIOS, PC BIOS or ROM
(Basic BIOS, is firmware that is
Input/Output used to perform
hardware initialization
System) during the booting
process; and to provide
runtime services for
operating system and
programs. The BIOS
firmware is the first
software to run when
powered on; it is re-
installed on a PC’s
system board.
5. I/O port Input/output ports are
the connections
between the CPU and
peripheral devices on a
motherboard. There are
two complementary
methods to perform
input and output
processes: memory-
mapped I/O (MMIO) and
port-mapped I/O
(PMIO). Alternatively,
you can use dedicated
I/O processors, called
channels on mainframe
computers, which
execute their own
instructions.
6. USB USB is an industry
standard that creates
(Universal specifications for
Serial Bus) connectors, cables and
protocols for
connection; power
supply (interfacing) and
communication among
computers, computer
peripherals as well as
other desktops. There
are a great many USB
hardware including
several different
connectors, of which
USB-C is the latest kind.
7. CPU slot A CPU slot, also called a
CPU socket or Processor
socket, contains one or
more mechanical
components that
provide mechanical and
electrical connections
between the PCB and a
microprocessor (CPU).
Therefore, you can
install a CPU on a
motherboard without
soldering.
8. PCI Peripheral Component
Interconnect is a local
(Peripheral computer bus for
Component connecting hardware to
a computer. It supports
Interconnect) all the functions of a
slot processor bus. PCI is
usually been called
Conventional PCI to
distinguish it from its
successor PCI Express
(PCIe, PCI-e or PCI-E).
9. AGP AGP was designed as a
high-speed point-to-
(Accelerated point channel for
Graphics connecting a video card
(graphics card) to a
Port) slot computer system.
Primarily, it was used to
assist in the acceleration
of 3D computer
graphics. AGP is
originally designed to be
a descendant of the PCI
series of connections for
video cards. Yet, it was
replaced by the PCIe
slots.
10. ISA ISA is the 16-bit
(Industry internal bus of IMB
PC/AT and similar
Standard computers that are
Architecture) based on Intel
slot 80286 and its
immediate
successors during
the 1980s. It was
backward
compatible with the
8-bit bus of the
8088-based IBM PC
largely.
There once was an
attempt to extend
ISA into a 32-bit
bus, called
Extended Industry
Standard
Architecture
(EISA). The attempt
wasn’t very
successful and the
EISA was largely
replaced by the
later VESA Local
Bus and the PCI
bus.
11. Parallel A parallel port is a
port kind of interface for
attaching
peripherals on
desktops. The
name of this kind
of port is derived
from the way the
data is sent. That
is, the parallel
ports send multiple
bits of data at the
same time. Serial
interfaces, on the
contrary, send bits
one data at once.
To achieve parallel
data transfer, there
are multiple data
lines in the parallel
port cables. The
parallel port cable
is larger than the
cable of a
contemporary
serial port, which
only has one data
line within.
12. FDC FDC is a special-
(Floppy-Disk purpose chip and
associated disk
Controller) controller circuitry.
It controls and
directs reading
from and writing to
a computer’s
floppy disk drive
(FDD).
13. IDE The devices used
(Integrated for connecting IDE,
Ethernet, FireWire,
Drive USB and other
Electronics) systems can be
controller called host adapter.
So, the IDE
controller refers to
the host adapter. A
host adapter, also
called a host
controller or a host
bus adapter (HBA),
connects a
computer (acting
as the host system)
to other network
and storage
devices.
14. CMOS CMOS battery, also
(Complement called memory
battery, clock
ary Metal- battery or real-time
oxide- clock (RTC), is
semiconducto generally a CR2032
lithium coin cell.
r) battery The lifespan of the
CMOS battery is
estimated to be
three years when
the power supply
unit (PSU) is
unplugged or
switch off.
15. Power A power supply
supply provides the
necessary
connector electrical power to
let the computer to
work. It takes
standard 110-Volt
AC (Alternative
Current) power to
DC (Direct Current)
power of 12 Volt, 5
Volt, 3.3 Volt, etc.
16. Mouse All computers have
and keyboard a keyboard port
connected directly
ports to the
motherboard.
There are two types
of connectors. The
oldest one is a
special DIN
(Deutsches Institut
für Normung)
connector while the
newest one is the
mini DIN PS/2-style
connector. Many
PCs use the PS/2-
style connectors
for both keyboard
and mouse; and
the connectors are
marked clearly for
different usage.
17. DIP (Dual A DIP switch is a
In-line manual electric
switch packaged
Package) with others in a
switch standard dual in-
line package. The
term may refer to
an individual
switch or the whole
unit. The DIP
switch is designed
to be used on a
printed circuit
board
(motherboard)
together with other
electronic
motherboard
components. It is
usually used to
customize the
behavior of an
electronic device
for specific
situations.
18. Jumper A jumper is a short
length of conductor
that is used to
close, open or
bypass part of an
electronic circuit.
Typically, jumpers
are used to set up
or configure
printed circuit
boards like the
motherboard.
19. Heat A heat sink is a
sink/heatsink passive heat
exchanger that
(cooling transfers the heat
system) generated by parts
of motherboard
into a fluid medium
like liquid or air.
The fluid medium
will dissipate away
from the device.
Thus, the
temperature of the
device is kept
within a tolerable
range. On the
motherboard, the
heatsink is usually
used to cool CPU,
GPU (graphics
processing unit),
chipsets and RAM
modules.
20. Clock A clock generator
generator is an electronic
oscillator (circuit)
that produces a
clock signal for
usage in
synchronizing a
circuit’s operation.
The clock signal
ranges between
high and low
frequencies, thus
creating a
metronome for the
coordination of
actions.
You might also like
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- All Kali Linux CommandsDocument20 pagesAll Kali Linux Commandsanbarasu100% (1)
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetDocument13 pagesHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralNo ratings yet
- Give All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipDocument7 pagesGive All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipjanNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument6 pagesMotherboardj9694052No ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsRige Mae MuescoNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDocument12 pagesComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Information Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpDocument16 pagesInformation Technology Assignment:: Motherboard Write-UpJuline AsmeryNo ratings yet
- Acronym of Computer System PDFDocument10 pagesAcronym of Computer System PDFJether Pactol TeroNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskDocument5 pagesMotherboard Components of A Desktop Computer: CPU RAM CD DVD Hard DiskRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNo ratings yet
- Kurt PogiDocument2 pagesKurt PogiKurt KenNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Document10 pagesMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaNo ratings yet
- 4 MotherboardDocument4 pages4 MotherboardJaynard Paul ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- ITcomDocument3 pagesITcomRodel Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- AMAY AND PACULBA Function 2Document2 pagesAMAY AND PACULBA Function 2Kurt KenNo ratings yet
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Document5 pagesTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresNo ratings yet
- Assignment CS by ABRARDocument9 pagesAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioNo ratings yet
- Academic Year: 2018-19 Semester: IV Class / Branch: SE IT Subject: Microprocessor Programming LabDocument6 pagesAcademic Year: 2018-19 Semester: IV Class / Branch: SE IT Subject: Microprocessor Programming LabKaustubh SawantNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Submitted By:-Nisha .R. NairDocument5 pagesMotherboard: Submitted By:-Nisha .R. NairNisha NairNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument12 pagesClass NotesHeart WeyganNo ratings yet
- ITC Lec 3Document31 pagesITC Lec 3josephNo ratings yet
- CSS Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesCSS Lesson Planirene cadizNo ratings yet
- Power PointDocument33 pagesPower PointJames LopezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - IO BusesDocument70 pagesLecture 8 - IO BusesHydie CruzNo ratings yet
- System Unit and Internal Components, Ports at The Back of System UnitDocument5 pagesSystem Unit and Internal Components, Ports at The Back of System UnitArt Dollosa100% (3)
- 1.assemble Computer HardwareDocument18 pages1.assemble Computer HardwareallyzamoiraNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument5 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionnominnanaaespasolNo ratings yet
- Basic Notes 2Document6 pagesBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- A++ Note For SECE by TamiratDocument60 pagesA++ Note For SECE by TamiratHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDocument10 pagesThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument15 pagesMotherboardDragoon GamingNo ratings yet
- Chipset PC Motherboard Southbridge Sandy Bridge: Northbridge (Computing)Document6 pagesChipset PC Motherboard Southbridge Sandy Bridge: Northbridge (Computing)risky_asNo ratings yet
- ICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFDocument5 pagesICCS 2 Converted Word To PDFElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- Components of System UnitDocument8 pagesComponents of System Unitroger_embalsado331988% (16)
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDocument11 pagesLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardraze techNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven BED ITEd3342Document8 pagesChapter Seven BED ITEd3342Nardos TesemaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardDocument6 pagesParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument5 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemIssan VillaruelNo ratings yet
- The Motherboard and It'S ComponentsDocument12 pagesThe Motherboard and It'S ComponentsVanessaNo ratings yet
- Processors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsDocument5 pagesProcessors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsAnonymous ZzYOKUcONo ratings yet
- Component of A System Unit - Desktop PCDocument8 pagesComponent of A System Unit - Desktop PCRoger EmbalsadoNo ratings yet
- Ports and CablesDocument6 pagesPorts and CablesAlfredo DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris (1) KhafliHolisNo ratings yet
- PC Hardware NotesDocument7 pagesPC Hardware NotesyelhankaNo ratings yet
- North BridgeDocument4 pagesNorth Bridgejhunlhyn100% (2)
- Elegant Architecture Portfolio by SlidesgoDocument38 pagesElegant Architecture Portfolio by SlidesgoMark Ivan AbrizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1nashwah mahomedNo ratings yet
- Computer System Parts of MotherboardDocument28 pagesComputer System Parts of MotherboardJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- Wa0010.Document3 pagesWa0010.amanray2604No ratings yet
- Basics of Compter SystemsDocument23 pagesBasics of Compter SystemsYogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- Motherboard ElementsDocument2 pagesMotherboard ElementsMithz SuneNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual/ Operator'S Guide: MANUAL NUMBER 006-05392-0001 Revision 1 July, 2003Document40 pagesMaintenance Manual/ Operator'S Guide: MANUAL NUMBER 006-05392-0001 Revision 1 July, 2003GusNo ratings yet
- PC HP G35aDocument51 pagesPC HP G35aJoseNo ratings yet
- Tidal Tutorial Guide-WindowsDocument210 pagesTidal Tutorial Guide-Windowsbinoypj100% (1)
- Cryptography With CertificatesDocument5 pagesCryptography With CertificatesramtulsipurNo ratings yet
- CCM User ManagementDocument15 pagesCCM User Managementmfavot44No ratings yet
- Getting Started With TLM-2.0 - Part2Document5 pagesGetting Started With TLM-2.0 - Part2Frankie LiuNo ratings yet
- Selenium NotesDocument15 pagesSelenium NotesVishnu MohanNo ratings yet
- Heuristic Ladder: Hadoop - Big Data Analytics CourseDocument5 pagesHeuristic Ladder: Hadoop - Big Data Analytics CoursebinoyNo ratings yet
- Experiment-5: Addressing Modes, CALL, RET, XLAT, Stack, ArraysDocument27 pagesExperiment-5: Addressing Modes, CALL, RET, XLAT, Stack, ArraysAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- AZ 900 Questions - Part 11Document4 pagesAZ 900 Questions - Part 11Nguyen Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- Spring Webflow ReferenceDocument99 pagesSpring Webflow ReferencenyellutlaNo ratings yet
- Juniper Switch - EX4300Document13 pagesJuniper Switch - EX4300kalarivathukkalNo ratings yet
- FileDocument41 pagesFileblackmamba etti jeanNo ratings yet
- Automating Administration With Windows Powershell®Document5 pagesAutomating Administration With Windows Powershell®Alok SharmaNo ratings yet
- 0 0 Filtertrie IntermediateDocument52 pages0 0 Filtertrie IntermediateakunkelasdNo ratings yet
- MAXTOR D740X 6L - User ManualDocument2 pagesMAXTOR D740X 6L - User ManualTinNo ratings yet
- RK 40Document2 pagesRK 40groovey9040No ratings yet
- Embedded Os Case Study: TinyosDocument45 pagesEmbedded Os Case Study: TinyosAditya ChimankarNo ratings yet
- IT FundamentalsDocument3 pagesIT FundamentalsCharles Ryan MontecinaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft: Exam Questions AZ-220Document8 pagesMicrosoft: Exam Questions AZ-220IamSajid JatoiNo ratings yet
- Gui Programming: Session 1 Introduction To Gui Design Lecturer: Luke Raeside, PHDDocument38 pagesGui Programming: Session 1 Introduction To Gui Design Lecturer: Luke Raeside, PHDFlaviusMihesanNo ratings yet
- Instruction Bulletin: Communication OptionDocument64 pagesInstruction Bulletin: Communication OptionLuis Henrique NovakNo ratings yet
- Huawei g735-l03 v100r001c25b263 Upgrade Guideline v1.0Document7 pagesHuawei g735-l03 v100r001c25b263 Upgrade Guideline v1.0SantiagoArmandoNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document39 pagesCH 3api-3777076No ratings yet
- Diptamoy's ResumeDocument1 pageDiptamoy's ResumeDiptamoy SinhaNo ratings yet
- Teal Grey Blue Trendy Retro Digitalism Creative PresentationDocument19 pagesTeal Grey Blue Trendy Retro Digitalism Creative PresentationJustineSabandalNo ratings yet
- jffs2 PDFDocument12 pagesjffs2 PDFKartikNo ratings yet
- McAfee SIEM Collector Installation and Configuration v1 2Document19 pagesMcAfee SIEM Collector Installation and Configuration v1 2hemant shekhawatNo ratings yet
- NimitDocument42 pagesNimitAnirudh Singh BhandariNo ratings yet