Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aspects of The Production, Control, Regulation, Inspection, Distribution and Consumption of Commercially Grown, and Even Sometimes Home Grown, Food
Aspects of The Production, Control, Regulation, Inspection, Distribution and Consumption of Commercially Grown, and Even Sometimes Home Grown, Food
Uploaded by
Ronalyn AsunioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aspects of The Production, Control, Regulation, Inspection, Distribution and Consumption of Commercially Grown, and Even Sometimes Home Grown, Food
Aspects of The Production, Control, Regulation, Inspection, Distribution and Consumption of Commercially Grown, and Even Sometimes Home Grown, Food
Uploaded by
Ronalyn AsunioCopyright:
Available Formats
I’m Cedrick Emberador im Assigned to tackle about the definition of Global food security and
the major challenges involving to it
Food security is the measure of the availability of food and individuals' ability to access it.
According to the United Nations' Committee on World Food Security, food security is defined as
meaning that all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe,
and nutritious food that meets their food preferences and dietary needs for an active and healthy life.
The availability of food irrespective of class, gender or region is another one. There is evidence of
food security being a concern many thousands of years ago, with central authorities in ancient
China and ancient Egypt being known to release food from storage in times of famine. At the
1974 World Food Conference, the term "food security" was defined with an emphasis on supply;
food security is defined as the "availability at all times of adequate, nourishing, diverse, balanced
and moderate world food supplies of basic foodstuffs to sustain a steady expansion of food
consumption and to offset fluctuations in production and prices".[2] Later definitions added demand
and access issues to the definition. The first World Food Summit, held in 1996, stated that food
security "exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe
and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
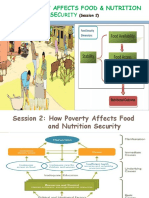
CHALLENGES TO ACHIEVE FOOD SECURITY
Food security faces a number of challenges across both production and consumption which research will
be essential to solve. Some of them are:
- Production – Food production, as the name suggests, is all about preparing food, in which raw materials
are converted into ready-made food products for human use either in the home or in the food processing
industries. slow rate of growth of food production is adversely affecting the supply of food grains.
- Consumption – Food consumption is a periodic behavior. It is triggered at various moments of
the day by a number of converging factors. As eating progresses, inhibitory influences of many
origins develop and finally bring the meal to an end. increasing consumption and wastages are
putting pressures on food grains stocks
- Distribution – Food distribution is the process where a general population is supplied with
food. bottlenecks pose threats to its availability even in normal times
- Politics – Food politics is a term which encompasses not only food policy and legislation, but all
aspects of the production, control, regulation, inspection, distribution and consumption of
commercially grown, and even sometimes home grown, food.
You might also like
- Soitany Dairy Self Help Group ProposalDocument17 pagesSoitany Dairy Self Help Group ProposalPhilip JumaNo ratings yet
- 4 5861665975673294635Document17 pages4 5861665975673294635Asnake YohanisNo ratings yet
- Report Global Food SecurityDocument3 pagesReport Global Food SecurityK8Y KattNo ratings yet
- Food Security: Meaning and ImportanceDocument4 pagesFood Security: Meaning and ImportanceNitish Thakur100% (1)
- Lesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENTDocument31 pagesLesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENTyamizenaku04No ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument25 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMelanie JulianesNo ratings yet
- FNS eDocument71 pagesFNS eRaaz The ghostNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument11 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMarjorie O. Malinao100% (1)
- Food SecurityDocument6 pagesFood SecurityRiya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument22 pagesFood SecurityKuber JaishiNo ratings yet
- Food System Sustainability and Food SecuDocument10 pagesFood System Sustainability and Food Secu8mb8sgsc2bNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument15 pagesGlobal Food SecurityRyan Chalimeg100% (1)
- Learner Notes 0411Document14 pagesLearner Notes 0411Mohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Food Security: A PrimerDocument4 pagesFood Security: A PrimerjournalNo ratings yet
- Farm LawDocument14 pagesFarm LawDEEPALI KATIYARNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument11 pagesFood SecurityJanedyl Mando Salvador100% (1)
- Global Food SecurityDocument34 pagesGlobal Food SecurityAnnie Rose Argañoza OpongNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument6 pagesFood SecurityYukta PatilNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Food InsecurityDocument10 pagesModule 6 Food InsecurityNizea Camille Navarro JavierNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument2 pagesFood SecurityZahid GujjarNo ratings yet
- PPH 324 Lecture 1Document5 pagesPPH 324 Lecture 1KendiNo ratings yet
- Contemp ExpalinDocument8 pagesContemp ExpalinEka MagsigayNo ratings yet
- Concept of Food SecurityDocument5 pagesConcept of Food SecurityDrSanjay Rastogi0% (1)
- Tuaia. Taranikai (S11235078)Document2 pagesTuaia. Taranikai (S11235078)ft8d7kfvyqNo ratings yet
- Food SectDocument8 pagesFood SectKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- FINAL REPORT Food SecurityDocument23 pagesFINAL REPORT Food SecurityAbinash KansalNo ratings yet
- World Food SecurityDocument2 pagesWorld Food SecurityAireen Jade BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument7 pagesGlobal Food SecurityBERNARD CALZARNo ratings yet
- Food Security: Pillars, Determinants and Factors Affecting ItDocument12 pagesFood Security: Pillars, Determinants and Factors Affecting ItHasibullah AsadiNo ratings yet
- Food Security: Hunger StarvationDocument15 pagesFood Security: Hunger StarvationhanumanthaiahgowdaNo ratings yet
- Gender, Food Security and MigrationDocument33 pagesGender, Food Security and MigrationPrabina JoshiNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecuirtyDocument9 pagesGlobal Food SecuirtyAichelle Ann BersabeNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument5 pagesFood SecurityNoor AfizahNo ratings yet
- Global SustainabilityDocument21 pagesGlobal Sustainabilityramszlai100% (1)
- 7 Local and Global InitiativesDocument10 pages7 Local and Global Initiativesdyz2nybk8zNo ratings yet
- Shahid Hussain Raja Independent Consultant-Public Policy: WWW - Sanoconsultants.co - UkDocument28 pagesShahid Hussain Raja Independent Consultant-Public Policy: WWW - Sanoconsultants.co - UkshaziadurraniNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument5 pagesGlobal Food SecurityArianne Marie Omo100% (1)
- Conworld FINALSDocument9 pagesConworld FINALSLary Lou VenturaNo ratings yet
- FAO Introduction To FSDocument3 pagesFAO Introduction To FSBin LiuNo ratings yet
- Food Safety FAO PaperDocument2 pagesFood Safety FAO PaperKathiravan GopalanNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Global Food SecurityDocument12 pagesGroup 5 Global Food SecuritySean Kenneth RosarosoNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL FOOD SECURITY By. Oñate, Richard Q.Document4 pagesGLOBAL FOOD SECURITY By. Oñate, Richard Q.Richard Queman Oñate100% (1)
- Food SecurityDocument6 pagesFood SecurityPascual SalasNo ratings yet
- Food InsecurityDocument4 pagesFood InsecurityElisa WintaNo ratings yet
- Chaifetz, Jagger - 2014 - 40 Years of Dialogue On Food Sovereignty A Review and A Look AheadDocument7 pagesChaifetz, Jagger - 2014 - 40 Years of Dialogue On Food Sovereignty A Review and A Look AheadFabian Garcia CifuentesNo ratings yet
- An Assignmennt On Food SecurityDocument16 pagesAn Assignmennt On Food SecuritySamira RahmanNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument6 pagesGlobal Food SecurityKassandra Bravo SagunNo ratings yet
- Food Insecurity Duration: 6 HoursDocument13 pagesFood Insecurity Duration: 6 HoursLeila Mae L. InfanteNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument20 pagesGlobal Food SecurityGenshin ImpactAccNo ratings yet
- Lecture II Food and Nutrition SecurityDocument24 pagesLecture II Food and Nutrition SecurityJorge Mario Al IINo ratings yet
- Food Security Final ReportDocument28 pagesFood Security Final ReportAqsa SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7Daroo D.TNo ratings yet
- GRP 7 - Food SecurityDocument59 pagesGRP 7 - Food SecurityOrangeIsLemon100% (1)
- Global Food SecurityDocument13 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMiguel Gabriel OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument39 pagesFood Securitycpaloma664No ratings yet
- Environmental Studies.: End Hunger and Achieve Food SecurityDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Studies.: End Hunger and Achieve Food SecurityRishita JalanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food SafetyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Food SafetyENJOY YOUR MUSICNo ratings yet
- GE 3 Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Global Food SecurityDocument20 pagesGE 3 Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Global Food Securityjuliet maeNo ratings yet
- FP Lecture 2-4 2020Document15 pagesFP Lecture 2-4 2020Richard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Equity in Food SecurityDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Equity in Food SecurityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Gastronomic Guardians : Safeguarding Food Safety at Home and BeyondFrom EverandGastronomic Guardians : Safeguarding Food Safety at Home and BeyondNo ratings yet
- WWF Strategic Plan 2014-2018Document30 pagesWWF Strategic Plan 2014-2018Anisa Hapsari KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- Ok - Helen Sebastian Final2Document72 pagesOk - Helen Sebastian Final2Lhen Gui Sebastian100% (1)
- BOOKLETISEF2020 EnglishVersionRevDocument138 pagesBOOKLETISEF2020 EnglishVersionRevLucky AristioNo ratings yet
- UDAYAN-BD ProfileDocument8 pagesUDAYAN-BD ProfileUDAYAN - BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Final Community Partnership ResourceDocument7 pagesFinal Community Partnership Resourceapi-315848490No ratings yet
- Indian Social and Political Environment Reflection-2: House On Fire-India's Ecological Security UnderminedDocument3 pagesIndian Social and Political Environment Reflection-2: House On Fire-India's Ecological Security UnderminedAnirban ChandraNo ratings yet
- MA Thesis - Ethiopian Civil Service University (Final) PDFDocument83 pagesMA Thesis - Ethiopian Civil Service University (Final) PDFAnonymous MH8HHb8zat98% (44)
- Gmo Socratic Seminar 2019Document6 pagesGmo Socratic Seminar 2019api-448144386No ratings yet
- Rice News 12march2022Document82 pagesRice News 12march2022Mujahid AliNo ratings yet
- QA - Webinar 27.05.2020Document18 pagesQA - Webinar 27.05.2020Dana AfengerNo ratings yet
- University of Gondar College of Natural and Computational Sciences Department of BiologyDocument76 pagesUniversity of Gondar College of Natural and Computational Sciences Department of BiologyDawit BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs For CSS 2023Document152 pagesCurrent Affairs For CSS 2023Shah Fahad SepahNo ratings yet
- Ge 102 Contemporary World Module 2Document14 pagesGe 102 Contemporary World Module 2Selene Acosta100% (1)
- JEMAD Vol 7 No 2 Maghirang 1Document12 pagesJEMAD Vol 7 No 2 Maghirang 1FrancisNo ratings yet
- Results from the Strategic Assessment of International Rice Research Priorities: comparing the potential of rice technologies to make a difference for the poor, the food insecure and the environment in AsiaDocument41 pagesResults from the Strategic Assessment of International Rice Research Priorities: comparing the potential of rice technologies to make a difference for the poor, the food insecure and the environment in Asiairri_social_sciencesNo ratings yet
- World Food ProblemsDocument4 pagesWorld Food ProblemsAyushi pandeyNo ratings yet
- DESALEGN FINAL THESISs PDFDocument79 pagesDESALEGN FINAL THESISs PDFDesalegn KusaNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument7 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMizraim EmuslanNo ratings yet
- Primary Sources GLFDocument25 pagesPrimary Sources GLFcraterrbNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2017Document24 pagesAnnual Report 2017John Glenn SpaceNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances and Opportunities in Sustainable Food Supply Chain A Model Oriented ReviewDocument24 pagesRecent Advances and Opportunities in Sustainable Food Supply Chain A Model Oriented ReviewdhivirajNo ratings yet
- Ahme Paper RevisedDocument54 pagesAhme Paper Revisedkassahun meseleNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ExamDocument3 pagesContemporary ExamKaye TanNo ratings yet
- TWW SNAP Congressional Delegation LetterDocument4 pagesTWW SNAP Congressional Delegation LetterGovernor Tom Wolf100% (1)
- Herder-Farmer Conflicts in South East Nigeria: Assessing The DangersDocument8 pagesHerder-Farmer Conflicts in South East Nigeria: Assessing The DangersThe Wilson CenterNo ratings yet
- E&Y Report Reefer TransportDocument20 pagesE&Y Report Reefer TransportashisbhuniyaNo ratings yet
- Mun Position Paper IdeasDocument2 pagesMun Position Paper Ideaseunyoung parkNo ratings yet
- Cooperatives and The Sustainable Development GoalsDocument18 pagesCooperatives and The Sustainable Development GoalsJeanette LampitocNo ratings yet
- Ghana - Rural BankDocument53 pagesGhana - Rural BankNeerajNo ratings yet