Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bs Ig Notes Organization
Bs Ig Notes Organization
Uploaded by
Purple Feather InitiativesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bs Ig Notes Organization
Bs Ig Notes Organization
Uploaded by
Purple Feather InitiativesCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge IGCSE Business Studies 2.
2 Organisation and management
2.2.1 – Draw, interpret and understand simple organisational charts
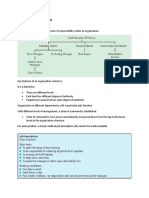
Definition of Organisation Structure
Organisation structure refers to how responsibility and authority is shared in a
business organisation.
This is often displayed in the form of an organisational chart. The 2 common
type of charts are
● Tall organisational charts – These have a long chain of command and a
small span of control
● Flat organisational charts – Short chain of command, wide span of
control
Advantages of an organisational chart
● Shows how everybody is linked together in a business
● Lines of communication are clear
● Motivational as employees can see where they belong and can plan their
career paths
Chain of Command – is how the power and authority is passed down from the
top of the organisation (managers) to lower employees
Span of Control – The number of employees working directly under a manager.
Levels of Hierarchy – Number of layers in an organisation structure
Advantages of short chain of command
● Faster communication – Communication is quicker and more accurate
since it is passed on by fewer people.
● Stronger relationship between high-level managers and employees –
This is because there are fewer levels between managers and employees.
● Each manager is responsible for more employees – This encourages
them to delegate (pass down) more work to employees.
De-layering – removing an entire row of management
2.2.2 – The role of management
Roles of managers in a business.
1. Planning
● Set goals for the future of the organisation.
● Give the business a sense of direction and purpose (e.g. we will aim to
increase sales by 10% by next year.)
2. Organising
● Organising of people and resources so that the business operates
efficiently (Managers can’t do everything, they must delegate tasks to
other employees)
3. Coordinating
● Making sure all departments are working together to achieve the overall
objectives and plans of the organisation. (e.g. Manager makes sure
marketing and operations department work together to plan for a new
product launch)
4. Commanding
● Guiding, leading and supervising of employees in the organisation.
(Managers need to make sure that employees are doing their work!)
5. Controlling
● This involves monitoring performance to ensure that objectives will be
met.
Delegation – Passing down authority and responsibility to a subordinate
(employee)
Advantages of delegation
● More time for manager to do other tasks
● More interesting and rewarding work for employee (motivational)
● Employee feels trusted (motivational)
● Trains employee to do important tasks.
2.2.3 – Leadership styles
There are 3 main leadership styles – Autocratic, democratic and laissez-faire
Autocratic – Leader is in charge and gives orders to employees
● Makes decision alone
● Everything depends on the leader
● May de-motivate employees
● May be an advantage for some businesses where decision needs to be
made quickly
Democratic – Other employees involved in decision making
● Communication between managers and employees
● Future plans are discusssed with other employees
● Motivates employees because they are involved in making decisions.
● Sharing of ideas within the business.
● Can delay decision making
Laissez-Faire – “let it be” Leader sets objectives and employees makes decision
and organise their own work.
● Can be useful when creative ideas are needed
● Highly motivational for employees as they control their own working
life
● Poor coordination and decision making
● Relies on good team work
Leadership style may be dependent on various factors. e.g.
● Type of business (creative or supply driven)
● Nature of task (requires cooperation?)
2.2.4 – Trade unions
What is a trade union?
Trade union – Group of workers who have joined together to ensure their
interest are protected.
Why join a trade union?
● Improved conditions of employment
● Improved work environment
● Improved benefits
● Improved job satisfaction
● Advice/financial support
● Strenght in number (many employees will join)
Disadvantages
● Cost money to be a member
● May be forced to take action e.g. strike even if you don’t agree
You might also like
- Chapter 4 - Workforce FocusDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - Workforce FocusShaina Trish Taguiam100% (1)
- Herzberg Motivation Hygiene TheoryDocument2 pagesHerzberg Motivation Hygiene TheoryDev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eustress Distress WorksheeDocument2 pagesEustress Distress WorksheeJoe LevinneNo ratings yet
- Employee Resilience: Mehermah Shafat Hadiqa Rashid Daniyal Hasan Tabish Faisal Farrukh ImranDocument17 pagesEmployee Resilience: Mehermah Shafat Hadiqa Rashid Daniyal Hasan Tabish Faisal Farrukh ImranmehermahNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentFang QiNo ratings yet
- CH - Organisation and Management - Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCH - Organisation and Management - Summary Notescatan nabazNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - Business StudiesDocument19 pagesSection 2 - Business Studiesanaayaa chitnisNo ratings yet
- Business Section 2 Notes (Igcse)Document19 pagesBusiness Section 2 Notes (Igcse)Anushree JalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Organisation and ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Organisation and Managementtaj qaiserNo ratings yet
- Managment and Leadership (2.1)Document7 pagesManagment and Leadership (2.1)Audrey SakaueNo ratings yet
- Managment and Leadership (2.1)Document7 pagesManagment and Leadership (2.1)Iris MarekNo ratings yet
- Internal Organizationsal Environment: Functions of ManagementDocument8 pagesInternal Organizationsal Environment: Functions of Managementshantol wedderburnNo ratings yet
- Organisation and Management - Business StudiesDocument7 pagesOrganisation and Management - Business Studiesjaime.tarlieNo ratings yet
- Organistion and ManagementDocument5 pagesOrganistion and ManagementmielatmiluNo ratings yet
- Pob Section 2Document13 pagesPob Section 2Nathefa LayneNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Motivating Workers 2.1.1 - The Importance of A Well-Motivated WorkforceDocument16 pages2.1 Motivating Workers 2.1.1 - The Importance of A Well-Motivated WorkforceLisandra SantosNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-18 at 7.16.12 AMDocument65 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-18 at 7.16.12 AMgetachewgenet01No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Management StylesDocument25 pagesUnit 7 Management StylesMiguel Angel Escoto CanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Organisational Structure NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Organisational Structure NotesvotfsoulNo ratings yet
- Organization and ManagmentDocument9 pagesOrganization and ManagmentMariyam IfhamNo ratings yet
- Nature of OrganizationDocument6 pagesNature of OrganizationShahina ParvinNo ratings yet
- Internal OrganizationDocument9 pagesInternal OrganizationMelissa PattonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Essentials of ManagementDocument20 pagesChapter 3 - Essentials of ManagementloubnaNo ratings yet
- Management: - Levels of Management - Functions of Managers - Managerial Skills - Management StylesDocument15 pagesManagement: - Levels of Management - Functions of Managers - Managerial Skills - Management StylesNadeem AshrafNo ratings yet
- Organisational StructuresDocument15 pagesOrganisational Structuresdajiah greenNo ratings yet
- Organizational DesignDocument11 pagesOrganizational DesignPeter John SabasNo ratings yet
- Kiu7518 MGT 1401 Ca01Document8 pagesKiu7518 MGT 1401 Ca01Dineth CharukaNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument17 pagesOrganizingJester DavidNo ratings yet
- Planning AllDocument23 pagesPlanning AllZawad AbrarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Business StudiesDocument15 pagesUnit 2 Business StudiesSalsabila AureliaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: After Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument34 pagesObjectives: After Reading This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToCherichBNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Organization and ManagementDocument7 pagesLesson 7 - Organization and ManagementDeshanNo ratings yet
- It 32 Unit 2Document47 pagesIt 32 Unit 2shinhari332No ratings yet
- Organisation and ManagementDocument28 pagesOrganisation and Managementzena mohamedNo ratings yet
- Exam ReviewDocument87 pagesExam ReviewAdamNo ratings yet
- FMOB RESEARCH PAPER - Organising As A Function of ManagementDocument16 pagesFMOB RESEARCH PAPER - Organising As A Function of ManagementRidhiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document5 pagesChapter 7meryem berradaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Start-Ups 03600201: Lecturer-Applied Science, Diploma StudyDocument85 pagesEntrepreneurship and Start-Ups 03600201: Lecturer-Applied Science, Diploma StudySMIT CHRISTIANNo ratings yet
- 10 Unit 12 Management StylesDocument15 pages10 Unit 12 Management StylesLeena AaronNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Organisation and ManagementDocument30 pages2.2 Organisation and ManagementBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- Orma ReviewerDocument13 pagesOrma Reviewer21-50974No ratings yet
- Section 2 - Internal Organisation EnvironmentDocument24 pagesSection 2 - Internal Organisation Environmentstevinfisher8No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PrintDocument15 pagesChapter 1 PrintEmebet TesemaNo ratings yet
- Hbs 201 Management PrinciplesDocument50 pagesHbs 201 Management PrinciplesTawanda MahereNo ratings yet
- Introduction ManagmentDocument175 pagesIntroduction ManagmentbarkeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Myo Min Oo: Ph.D. (New Orleans), D.Min. (Indiana), M.S.B. (Notre Dame)Document28 pagesDr. Myo Min Oo: Ph.D. (New Orleans), D.Min. (Indiana), M.S.B. (Notre Dame)Marlar ShweNo ratings yet
- What Is An Organization ?Document10 pagesWhat Is An Organization ?Juliana LawNo ratings yet
- Management AssigmentDocument10 pagesManagement AssigmentBOSS HASHMINo ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5Document5 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 5avishaNo ratings yet
- Unit ReviewDocument17 pagesUnit ReviewHuyền HạnhNo ratings yet
- Business Essentials - Chapter 2 (Additional)Document14 pagesBusiness Essentials - Chapter 2 (Additional)Lix BammoNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument33 pagesObjectivesCherichBNo ratings yet
- Management NotesDocument26 pagesManagement Notesydab gamesNo ratings yet
- Introduction MGMT NuruDocument174 pagesIntroduction MGMT NuruibsaashekaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ManagementDocument20 pagesIntroduction To ManagementAmilda StewartNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CMPMDocument31 pagesChapter 1 CMPMHerwinn Ruiz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Organisational Overview: Roles of Leader and ManagerDocument2 pagesOrganisational Overview: Roles of Leader and ManagerFasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quản trị học - C5Document13 pagesQuản trị học - C5Phuong PhanNo ratings yet
- Office Organization and Management: Submitted byDocument13 pagesOffice Organization and Management: Submitted byAnoop pratap singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- CH 2 ManDocument50 pagesCH 2 Manaryan KadamNo ratings yet
- ORGANISINGDocument74 pagesORGANISINGtypicravagerNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I Nature & Significance of Management (2+5 7-Marks)Document148 pagesChapter - I Nature & Significance of Management (2+5 7-Marks)d-fbuser-65596417No ratings yet
- Ean 102 120Document3 pagesEan 102 120Daniela BaloghováNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- Gaya Kepimpinan Kolaboratif Pengetua Dan Tahap Kepuasan Kerja Guru Sekolah Menengah KebangsaanDocument17 pagesGaya Kepimpinan Kolaboratif Pengetua Dan Tahap Kepuasan Kerja Guru Sekolah Menengah KebangsaanNOOR AZLENNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument4 pagesTheoretical FrameworkBhie JaneeNo ratings yet
- Allsec Technologies................Document49 pagesAllsec Technologies................SyamkumarDuggiralaNo ratings yet
- HRD - Bba ViDocument46 pagesHRD - Bba ViPrabhat ThakurNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase Studymariam bhatti100% (1)
- Project TopicsDocument6 pagesProject TopicssachinNo ratings yet
- Variables Influencing Employee Performance in Organization.Document10 pagesVariables Influencing Employee Performance in Organization.Moshiur Tusher75% (4)
- Estres ParentalDocument7 pagesEstres ParentalFátima PérezNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Staff Performance in Tertiary Institutions in NigeriaDocument37 pagesMotivation and Staff Performance in Tertiary Institutions in NigeriaChris Vaso100% (1)
- 34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisDocument11 pages34.factors Influencing Employee Job Satisfaction A Conceptual AnalysisJawadNo ratings yet
- Road Map To Competency MappingDocument2 pagesRoad Map To Competency Mappingfarazalam08100% (2)
- Staff Performance Appraisal FormDocument4 pagesStaff Performance Appraisal FormLoren MandaNo ratings yet
- What Is Pinoy Management TheoryDocument2 pagesWhat Is Pinoy Management Theorynorma_smith_94311786100% (3)
- Driving Performance and Retention Through Employee EngagementDocument20 pagesDriving Performance and Retention Through Employee EngagementAngela WhiteNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction ReportDocument10 pagesJob Satisfaction Reportnida haqNo ratings yet
- Linking Emotional Intelligence and Performance at WorkDocument341 pagesLinking Emotional Intelligence and Performance at WorkMarius Bertolucci100% (5)
- AIOU Assignment 1 of MED 671 CODEDocument4 pagesAIOU Assignment 1 of MED 671 CODEmuhammad naseerNo ratings yet
- Case of Jack Nelson'S ProblemDocument22 pagesCase of Jack Nelson'S ProblemDr. Harshada MulayNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesSample QuestionnaireMajidAli TvNo ratings yet
- Individual Task PI ADocument1 pageIndividual Task PI AThalya Oriza SativaNo ratings yet
- Job Characteristics ModelDocument13 pagesJob Characteristics ModelZeeshan RajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Succession ManagementDocument24 pagesChapter 8 - Succession ManagementAnish PenujuruNo ratings yet
- Session 8Document2 pagesSession 8Yến Vũ KimNo ratings yet
- Directing and MotivationDocument15 pagesDirecting and Motivationanant_lakshendraNo ratings yet
- Ema Misc FilesDocument103 pagesEma Misc Filesatiema82No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Attitude SatisfactionDocument14 pagesChapter 3 Attitude SatisfactionDuc TranAnhNo ratings yet