Professional Documents
Culture Documents
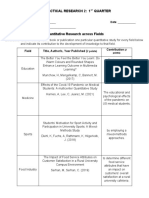
Research Design Goal How Variables Are Handled or Manipulated
Research Design Goal How Variables Are Handled or Manipulated
Uploaded by
Ram MejiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Design Goal How Variables Are Handled or Manipulated
Research Design Goal How Variables Are Handled or Manipulated
Uploaded by
Ram MejiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 1
Lesson 1: Quantitative Research Designs
Learning Task 1: Study the following parts: What I Know; What’s In; What I Need to Know; What’s New; What Is It; and
What I Have Learned. Write your answers ON YOUR PERSONAL NOTES. Check you answer using the answer key given in
your SLM.
Learning Task 2: Perform Activity 2 and 3 (What’s More)
What’s More
Activity 2. Quantitative Research Designs Summary
Directions: Using the template below, summarize the five quantitative research designs according to its goal, and its
corresponding variable manipulation.
Research Design Goal How variables are handled or
manipulated
1. Descriptive As descriptive researches are exploratory in nature, and by The variables are either
the name itself implies that descriptive researches aim to observed or surveyed
produce a “description” from observing a phenomenon as particularly giving description
it is currently happening. Primarily, it does not answer the about the descriptive research
question why/how/when questions but particularly problem. Particularly the
who/what/where. Secondly it aims to describe a population’s characteristics
characteristic of a population or phenomenon. and features are being
observed in these.
2. Correlational As what I have already learned from my grade 11 class, Variables, particularly
correlational studies determine the relationship as well as independent variables are
the strength of relationship two variables have. Thus, subjected into either an
correlational studies do not relate to causal situation but increase or decrease to know
particularly to what extent does the two variables relates its possible effect on the
to one another—if a variable increases or decreases does dependent variable—which
the other one does too? leads researchers in
concluding relationships and
strength of relationships.
3. Ex Post Facto The goal of ex post facto research design is to, like the Both independent and
module already said is measuring a cause from a pre- dependent variables in this
existing effect. Particularly it is research that has no control design are not subjected to
over the variables, but he or she seeks the variables any manipulation. As of
included—particularly answering the question why/how handling, it can be said that
does the effect happened, where did it start, when did it this research designs measures
start, who are involved and many more. the cause of an effect,
although not manipulated, it is
measure to any extent as to
how a certain effect happens.
4. Quasi-Experimental I had a hard time differentiating this one with the latter The populations are subjected
part but I already understood. Quasi-Experimental to the researcher’s choice of
research design is a research design that, of course, seeks intervention. Generally, the
an answer to the research problems—but mostly revolves respondents, subjects and
on the cause and effect among the variables. It is an participants are not subjected
experimental research design that makes and evaluates an to assignments. Particularly,
intervention among groups without actual randomization. this research designs includes
The groups created are not subjected to any assignments. treatment groups that are
Thus, it has a disadvantage of having limited answers as to subjected to treatment and
it is already given that they have groups in terms of their interventions. Populations is
commonalities but they have all experience the same sub-divided on groups,
interventions. stablished ones particularly on
a nominal scale.
5. Experimental Unlike quasi-experimental groups, experimental groups are Unlike quasi-experimental
considered as true experimental as subjects, participants again, experimental groups
and respondents are subjected to scientific process as well have treatment groups and
as assignments. In contrast with the previous design, control groups (which are not
experimental research also has groups thy could subjected to the researcher’s
manipulate and could not. People are separated to groups intervention). Thus, it can be
which can become control groups or treatment groups. concluded that experimental
Thus, the goal of the researcher is mainly to view various research manipulates not just
standpoints regarding their research problems: treatment the groups but also to the
groups are subjected to treatment and interventions while outcome of the research.
on the other hand control groups are not subjected into
these. Similarly, it aims to affect a group that comes from
the manipulation. Additionally, and lastly, random
assignment of subjects or participants into treatment and
control group is done increasing the validity of the study.
Activity 3. Choose the Appropriate Research Design Directions:
Determine the quantitative research design appropriate for the sample research titles. Make sure to explain your choice
into two to three sentences.
1. Relationship between Academic Stressors and Learning Preferences of Senior High School Students
Quantitative Research Design: Correlational Research Design
Explanation: Simply because it pertains or refers onto how the two variables are related: academic stressors and learning
preferences. It can be concluded along the research the relationship between these two as well as the strength of
relationship between the two of them. Additionally, one variable can either be negatively or positively correlated with
one another.
2. Reading Electronic Learning Materials as a Support for Vocabulary of Grade 1 Pupils
Quantitative Research Design: Experimental Research Design
Explanation: Primarily, I consider the electronic learning materials as treatments as well as interventions in supporting
the vocabulary of the subject given. Secondly, this research topic can be subdivide students in control groups as well as
treatment groups, particularly manipulating some students to engage in reading materials electronically.
3. Impact of the Implementation of COVID – 19 Health Protocols in Supermarkets on Consumer Behaviors
Quantitative Research Design: Descriptive Research Design
Explanation: “What are the impacts?” is the first thing I have in mind upon reading the research title. Particularly this
aims to study the population, specifically on the impacts the health protocols it brought them in a broad aspect,
physically, mentally, spiritually, emotionally, socially and environmentally. Secondly, little is known about the subject
and it is exploratory in sense as it can affect many individuals in various ways. Thus, it can make out a description after
probing onto the subject.
4. Effects of Morning Exercise on the Health Anxiety Level of Senior Citizens
Quantitative Research Design: Experimental Research Design/Quasi-Experimental Research
Explanation: In line with my question number two answer, I also can consider this as experimental research design
because senior citizens can be categorized or be put in control groups as well as treatment groups. Thus, promoting a
more valid research interpretation and answers on how morning exercises affects the certain group of subject,
participants or respondents. Similarly, basing from a research study’s delimitations we can conclude that if this occurs in
only one small area, participants could be subjected into interventions regardless of a formation of control groups.
5. Measuring the Gadgets Usage of Children at Home during COVID-19 Community Quarantine
Quantitative Research Design: Ex Post Facto Research Design
Explanation: With regards to the research title given, it can be said that it measures the gadget usage of children at
home. Ever wondered why? And also the existence of only on variable. This particular topic focuses on getting a cause of
a pre-existing effect. It measures the gadget usage of students for supporting a given effect.
6. Level of Academic Achievement of Senior High Schools in Different Learning Modalities
Quantitative Research Design: Descriptive Research Design
Explanation: Primarily, I could consider this as descriptive research simply because it asks about a population’
characteristics, a nominal feature. Secondly, it gives description as a support or outcome in learning in various learning
modalities.
7. Effects of Story Telling on Quality of Sleep of Children
Quantitative Research Design: Experimental Research Design
Explanation: This is experiment research. People particularly can sleep without story telling. Thus, this can be subjected in
giving randomization and assignments to various people. The Story Telling could serve as a treatment or intervention for
the treatment group.
Lesson 2: Sample Procedure and the Sample
Learning Task 3: Study the following parts: What I Know; What’s In; What I Need to Know; What’s New; What Is It; and
What I Have Learned. Write your answers ON YOUR PERSONAL NOTES. Check you answer using the answer key given in
your SLM.
Learning Task 4: Perform Activity 1 and 2 (What’s More)
What’s More
Activity 1. Determine the Sampling Procedure
Directions: Identify the sampling procedure used in each given situation. Write your answer on the space provided and
then explain your choice.
Sample Situation Sampling Procedure Justification
1. Alex’s target population for his study are the Cluster Sampling As what have been already said, “he
employees of hotels in Mindanao. Since there randomly selected based on hotel size.”
are too many employees in these We can conclude that he first classified
establishments, he randomly selected ten the hotels based from their sizes and
hotels based on hotel size. And then he chose 10 hotels from the hotel sizes.
randomly selected employees as participants in From there, he also chose random
his study. respondents in each hotel. It can be given
that the nature of the study is for the
whole Mindanao which is a large area.
From that large locale, he then classified
the sizes of the hotel to groups and
randomly selected from these clusters
made. Finally, regardless of the unchosen
groups random sampling is done in the
selected ones. If this was a stratified
sampling equal or proportional chances
will be given.
2. Dianne wants to know if the new learning Systematic Sampling Basically, this is a systematic sampling
modalities in the first semester affects the because primarily it does not divide the
academic performance of senior high students. population into strata; and secondly,
He took all the lists of all students in her school there is no randomization done. It is a
and selected every 6th name to be part of her systematic sampling because there is a
study. form of system or pattern the teacher
uses to select students.
3. Faye wants to survey all the parents in Actuality, she has just Primarily, she can use simple random
Cagayan de Oro who opt to enroll their decided, meaning sampling with help of randomizers from
elementary children to an online class. All in all, there are no particular the online which automatically pick
there 26,000 parents. Faye decided to have 380 sampling yet. But as respondents. Secondly, stratified random
from the target population. for suggestion she sampling can be done if she would decide
could use any of the in grouping Cagayan de Oro in terms of
four sampling provinces, and proportionally pick from
procedures from this each based from population. Thirdly is
module. cluster sampling by choosing a cluster
(province) that could represent the whole
population. And lastly is the systematic
sampling, which follows a system of
patters: it can be done through
factorization and/or similar final numbers.
Activity 2. Search the design and sampling procedure.
Directions: Search on the internet for a sample research study. Identify the research design used and its sampling
procedure.
Example 1 Example 2 Example 3
Title of the Research Study Technological pedagogical Attitude of Grade 12 SHS Assessing the level of
knowledge self-efficacy and Academic Tracks Students awareness on climate
continuance intention of Towards Speaking in change and sustainable
Philippine teachers in English development among
remote education amid students of Partido State
COVID-19 crisis University, Camarines Sur,
Philippines
Research Design Correlational Research Descriptive-Correlational Descriptive Research
Design Research Design Design
Characteristics of K to 12 teachers employed Grade 12 Senior High Students of Partido State
Population in various government and School Academic Track University (PSU),
private schools in students (particularly ABM Camarines Sur, Philippines
Mindanao, Philippines and HUMSS) with the use
of the English-Speaking
Attitude Questionnaire
(ESAQ) of Sto. Tomas
National High School
Sampling Procedure Simple Random Sampling Stratified Random Stratified Random
Procedure Sampling Sampling
Sample Size 1065 47 247
Source Cahapay, M. B., & Anoba, Canceran, D. J. B., & Barreda, A. B. (2018).
J. L. D. (2021). Malenab-Temporal, C. Assessing the level of
Technological pedagogical (2018). Attitude of Grade 12 awareness on climate
knowledge self-efficacy and SHS Academic Tracks change and sustainable
continuance intention of Students towards Speaking development among
Philippine teachers in in English. Journal of students of Partido State
remote education amid English as an International University, Camarines Sur,
COVID-19 crisis. Journal of Language, 13, 219-231. Philippines. Journal of
Pedagogical Sustainability
Research, 5(3), 68-79. Education, 17.
Learning Task 5: Assignment (Collaborative), do the activity in the What I can Do for both lesson 1 and 2
Week 2
Lesson 3: Research Instrument, Validity and Reliability
Learning Task 1: Study the following parts: What I Know; What’s In; What I Need to Know; What’s New; What Is It; and
What I Have Learned. Write your answers ON YOUR PERSONAL NOTES. Check you answer using the answer key given in
your SLM.
Learning Task 2: Perform Activity 3 and 4 (What’s More)
Lesson 4: Research Intervention
Learning Task 3: Study the following parts: What I Know; What’s In; What I Need to Know; What’s New; What Is It; and
What I Have Learned. Write your answers ON YOUR PERSONAL NOTES. Check you answer using the answer key given in
your SLM.
Learning Task 4: Perform Activity 1 (What’s More)
Learning Task 5: Assignment (Collaborative), do the activity in the What I can Do for both lesson 3 and 4 including the
Additional Activity
Week 3
Lesson 5: Planning Data Collection Procedure
Learning Task 1: Read and understand the discussion on Lesson 5: Planning Data Collection Procedure and answer
“What’s More”: Activity 2
Lesson 6: Planning Data Analysis
Learning Task 6: Read and understand the discussion on Lesson 6: Planning Data Analysis, then answer What’s More
Activity 3
Week 4
Lesson 7: Presenting Research Methodology
Learning Task 1: Read and understand the discussion on Lesson 7: Presenting Research Methodology
Learning Task 2: Performance Task: “What I Can Do” Written Research Methodology. Rubrics is provided in the module.
Learning Task 3: Write a SHORT REFLECTION
You might also like
- Chmsu ReviewerDocument18 pagesChmsu Reviewerrenzmacitas06100% (1)
- THE 12 Rs of OPPORTUNITY SCREENINGDocument1 pageTHE 12 Rs of OPPORTUNITY SCREENINGMaria AngelaNo ratings yet
- Maui and The Sun PowerPointDocument18 pagesMaui and The Sun PowerPointCarla Holtzhausen100% (1)
- Optimizing Energy System (Nutrition, Hydration and Relaxation) Getting Refreshed: Your Food and You Activity 1: Let'S Go, Let'S Grow, Let'S GlowDocument3 pagesOptimizing Energy System (Nutrition, Hydration and Relaxation) Getting Refreshed: Your Food and You Activity 1: Let'S Go, Let'S Grow, Let'S GlowElijshaumel ValdezNo ratings yet
- Help Me To DecideDocument3 pagesHelp Me To DecideMylene Tomas ValixNo ratings yet
- Tower DesignDocument15 pagesTower DesignKushan Dhanushka Nanayakkara100% (2)
- IRAC Formulas PDFDocument7 pagesIRAC Formulas PDFroy rebosuraNo ratings yet
- Linking Words ExercisesDocument4 pagesLinking Words ExercisesNLBekvalac100% (1)
- PRACTICAL RESEARCH Module 2 Lesson 1-3Document14 pagesPRACTICAL RESEARCH Module 2 Lesson 1-3Karla Carbonel100% (1)
- Activity 3Document1 pageActivity 3Jerome PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- WorkImmersion 2 AnswerDocument4 pagesWorkImmersion 2 AnswerHershey Caron100% (1)
- Module 3 MILDocument15 pagesModule 3 MILzenaida nombrao100% (2)
- PR2 Research DesignDocument10 pagesPR2 Research DesignMary Joy Llosa Redulla100% (1)
- You Can Do It-Homeroom GuidanceDocument3 pagesYou Can Do It-Homeroom GuidanceAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Target: Before Proceeding Further, Check How Much You Know About BusinessDocument16 pagesTarget: Before Proceeding Further, Check How Much You Know About BusinessGhilany Carillo CacdacNo ratings yet
- Media and Informationliteracy: Learning ModuleDocument7 pagesMedia and Informationliteracy: Learning Modulejudy bernusNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument2 pagesResearch DesignAndrea GomezNo ratings yet
- DRRR M4Document2 pagesDRRR M4Rhod Manalo SupresenciaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Quarter 4 - Module 6Document15 pagesPractical Research 2: Quarter 4 - Module 6Je-ann AcuNo ratings yet
- G11 SLM2 PR2 Q3 FinalDocument21 pagesG11 SLM2 PR2 Q3 FinalLouis Gerard PadayaoNo ratings yet
- 3 EyesDocument10 pages3 EyesCarmehlyn BalogbogNo ratings yet
- Trends Q2 Module 3: Business Law (Colegio San Agustin - Makati)Document34 pagesTrends Q2 Module 3: Business Law (Colegio San Agustin - Makati)elbemzkie 75100% (1)
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Sheet in Practical Research 2Document10 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Sheet in Practical Research 2Darlene Mae VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyJohn Kenneth BeaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 121Document2 pagesPractical Research 121Ericka Rivera Santos100% (1)
- Eapp Module 4Document29 pagesEapp Module 4Reign ManeseNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Q2, Module1Document6 pagesEmpowerment Q2, Module1Heeseung Lee100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheets Physical ScienceDocument17 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Physical ScienceMichelle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Module 3Document15 pagesPhilosophy Module 3Youngmi NaNo ratings yet
- (21 Century) Module 3: Insta Poem by Rupi Kaur Tittle: Rupi Kaur MESSAGE: The Message of The Story Is To Love Our Family andDocument3 pages(21 Century) Module 3: Insta Poem by Rupi Kaur Tittle: Rupi Kaur MESSAGE: The Message of The Story Is To Love Our Family andJhorrielle Miles CarnateNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4Document9 pagesEntrepreneurship: Quarter 3 Week 4michelleNo ratings yet
- Las Shs Physci Melc 5 q2 Week-2Document7 pagesLas Shs Physci Melc 5 q2 Week-2Lorenz Mondia YansonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document37 pagesPractical Research 2: Quarter 1 - Module 1bernadette domoloanNo ratings yet
- DRR Week 1 - 2Document15 pagesDRR Week 1 - 2Aleli Joy Profugo Dalisay100% (1)
- ECONOMICSDocument2 pagesECONOMICSSuzui MasudaNo ratings yet
- Case - Study ItangDocument1 pageCase - Study ItangRheny Bondoc100% (5)
- What's New: Fatima Almira M. Ibba Stem 12 Practical Research2Document13 pagesWhat's New: Fatima Almira M. Ibba Stem 12 Practical Research2Krisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Quantitative Research DesignDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Quantitative Research DesignViernes, Alesxandra DennisseNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 Week 2 ModulesDocument13 pagesHope 3 Week 2 ModulesPearl Arianne Moncada MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative TestDocument12 pagesSecond Quarter Summative TestBonna MaeNo ratings yet
- Active Video Games Helps Some Kids Get Active by Jennifer WarnerDocument2 pagesActive Video Games Helps Some Kids Get Active by Jennifer WarnerAdexentrix WPNo ratings yet
- Practical Research IiDocument5 pagesPractical Research IiRisel WandalenNo ratings yet
- Describe The Activity Based On The Following: Walking Around For 5 Minutes Brisk Walking For 4 Minutes 3-Minute Jump JacksDocument4 pagesDescribe The Activity Based On The Following: Walking Around For 5 Minutes Brisk Walking For 4 Minutes 3-Minute Jump JacksJeremiah Se-engNo ratings yet
- Philosopy Module 2, Grade 12 BezosDocument10 pagesPhilosopy Module 2, Grade 12 Bezosadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Technology: Department of EducationDocument16 pagesMedia and Information Technology: Department of EducationSenior High E-ClassNo ratings yet
- Francisco, Ma. Thea Victoria P.: Complete The Chart With The Information Needed. Write Your Answers On Your Answer SheetDocument3 pagesFrancisco, Ma. Thea Victoria P.: Complete The Chart With The Information Needed. Write Your Answers On Your Answer SheetThea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Shs PR 2 Module 5 Final Revision Applied Sabio RoldanDocument24 pagesShs PR 2 Module 5 Final Revision Applied Sabio RoldanMarissa UrnosNo ratings yet
- MIL Q4 Module-10 Version-4Document20 pagesMIL Q4 Module-10 Version-4Myka Shanelle MabaelNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet: Grade 12 - MODULE 1: Self-Analysis: A Step To My ImprovementDocument3 pagesActivity Sheet: Grade 12 - MODULE 1: Self-Analysis: A Step To My ImprovementFonzy Rone100% (1)
- Lesseon 2: Methods of Philosophizing 2.1: Knowledge and TruthDocument4 pagesLesseon 2: Methods of Philosophizing 2.1: Knowledge and TruthAlex Abonales Dumandan100% (1)
- Academic Language Includes Language Used in Textbooks, in Classrooms, On TestsDocument10 pagesAcademic Language Includes Language Used in Textbooks, in Classrooms, On TestsAster JadeNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document2 pagesActivity 1Roland Mark Dumaliang0% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet in 3is (Inquiries, Investigation, Immersion)Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in 3is (Inquiries, Investigation, Immersion)Roselyn Relacion LucidoNo ratings yet
- Application (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingDocument2 pagesApplication (The Road Trip) Using The Road Trip Signs Write Your Answer On The FollowingPam Maglalang SolanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Chapter 5-2Document38 pagesLesson 2 Chapter 5-2RHEA GENIONo ratings yet
- Compilation of Answers in 4th Quarter HUM CREATIVE WRITING and MODULE 9&10 (HUM 113)Document18 pagesCompilation of Answers in 4th Quarter HUM CREATIVE WRITING and MODULE 9&10 (HUM 113)Black PinkNo ratings yet
- Adm Philo Module-3Document6 pagesAdm Philo Module-3Ellegor Eam Gayol (girl palpak)No ratings yet
- Your Guide in Decision-Making The Way You Did ItDocument6 pagesYour Guide in Decision-Making The Way You Did It45Villa, Shadrac12STEMANo ratings yet
- Brgy. San Roque, Biliran, Biliran: Name: Mejarito, Angelica L. Grade and Section: 12 HERACLES-STEMDocument3 pagesBrgy. San Roque, Biliran, Biliran: Name: Mejarito, Angelica L. Grade and Section: 12 HERACLES-STEMPrincess Mejarito MahilomNo ratings yet
- Naive Nancy, Selfish Sam, and Fair-Minded FranDocument5 pagesNaive Nancy, Selfish Sam, and Fair-Minded FranJoan Conje Bonagua50% (2)
- PR2-Q1 - WS - Quantitative Research Across FieldsDocument3 pagesPR2-Q1 - WS - Quantitative Research Across FieldsEmmanuel Buenaventura PardoNo ratings yet
- Entrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskDocument2 pagesEntrepneurship Module 3 Performance TaskIvanah Mae Guaro Aclo100% (1)
- 5 Signed Off - EntrepreneurshipG12 - Mod5 - 7 - Ps Marketing - Branding - v3Document30 pages5 Signed Off - EntrepreneurshipG12 - Mod5 - 7 - Ps Marketing - Branding - v3Nicole Peña TercianoNo ratings yet
- 18POA01013 Tabbasam Murtaza 837Document16 pages18POA01013 Tabbasam Murtaza 837Mian Muhammad Haseeb AshrafNo ratings yet
- Physical Education and Health Week 9-10, Quarter 1, Module 4Document2 pagesPhysical Education and Health Week 9-10, Quarter 1, Module 4Ram MejiaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Week 9, Quarter 1, MODULE 5: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergDocument4 pagesPersonal Development Week 9, Quarter 1, MODULE 5: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergRam MejiaNo ratings yet
- Week 9, Quarter 1: Empowerment TechnologyDocument2 pagesWeek 9, Quarter 1: Empowerment TechnologyRam MejiaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Week 8-9, Quarter 1, Module 6: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Week 8-9, Quarter 1, Module 6: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergRam MejiaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Week 9, Quarter 1, Module 5: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergDocument4 pagesOral Communication in Context Week 9, Quarter 1, Module 5: Jhay-Ram Batarina Mejia Stem 12-HeisenbergRam MejiaNo ratings yet
- Q2W3-4 - General BiologyDocument4 pagesQ2W3-4 - General BiologyRam MejiaNo ratings yet
- Q2W5-6 - General BiologyDocument2 pagesQ2W5-6 - General BiologyRam Mejia100% (1)
- Ask A Question Create A Poll: Why Is The Number "13" Considered An "Unlucky" Number?Document28 pagesAsk A Question Create A Poll: Why Is The Number "13" Considered An "Unlucky" Number?Andres TugguinNo ratings yet
- Failure of Rolling Contact BearingsDocument21 pagesFailure of Rolling Contact BearingsLuis NunesNo ratings yet
- Excipient PT FinalDocument14 pagesExcipient PT FinalPreeti Wavikar-Panhale100% (1)
- OlatheNorth DaMo Aff 01 - Washburn Rural Round 2Document25 pagesOlatheNorth DaMo Aff 01 - Washburn Rural Round 2EmronNo ratings yet
- Project Based Learning And: Authentic AssessmentDocument52 pagesProject Based Learning And: Authentic Assessmentnancie8No ratings yet
- Design ThinkingDocument24 pagesDesign Thinkingapi-302717277No ratings yet
- Grade: 10E ROOM: 212 Homeroom Adviser: John Paolo FernandezDocument1 pageGrade: 10E ROOM: 212 Homeroom Adviser: John Paolo FernandezRangga NarindraNo ratings yet
- Materials Handling: in ConstructionDocument41 pagesMaterials Handling: in ConstructionSatya NaiduNo ratings yet
- 21CLD Learning Activity Cover SheetDocument9 pages21CLD Learning Activity Cover SheetMariana VoloshynNo ratings yet
- Corey-Fuchs ReactionDocument1 pageCorey-Fuchs ReactionWinzy KatzeNo ratings yet
- Crowell Smart Goal 18-19Document2 pagesCrowell Smart Goal 18-19api-335321754No ratings yet
- 11 19 2125-02-00be Eht Rts and Cts ProcedureDocument17 pages11 19 2125-02-00be Eht Rts and Cts ProcedureDalaPaulaNo ratings yet
- Number Theory and Public Key Cryptography: SyllabusDocument26 pagesNumber Theory and Public Key Cryptography: SyllabusGeethanjali KotaruNo ratings yet
- InfosyspdfDocument30 pagesInfosyspdfBrinda BMNo ratings yet
- Sample CV For Purchase ManagerDocument3 pagesSample CV For Purchase ManagerVijay Kumar100% (1)
- Deped Copy: Fit Me RightDocument6 pagesDeped Copy: Fit Me RightHazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Figure Skating Spirals in CompetitionDocument2 pagesFigure Skating Spirals in CompetitionAlexandra PurcaroiuNo ratings yet
- CDP Proposal KavarattiDocument11 pagesCDP Proposal KavarattiShivansh Singh GautamNo ratings yet
- EssenceDocument79 pagesEssencePranshu SahasrabuddheNo ratings yet
- Practical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab ManualDocument12 pagesPractical - 4: CS341 Artificial Intelligence Lab Manual18DCS074 MANN PATELNo ratings yet
- EXP10 Synthesis of P BromoanilineDocument6 pagesEXP10 Synthesis of P Bromoanilinemonish cNo ratings yet
- KUH-1 Catalogue CDocument6 pagesKUH-1 Catalogue CEli MalanoNo ratings yet
- The Way of The Worl1Document1 pageThe Way of The Worl1Maria Olivia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Formal Theme WritingDocument2 pagesRubrics For Formal Theme WritingJudith Fetalver100% (8)
- Fso RF - Out RXRDocument11 pagesFso RF - Out RXRRF_RAJANo ratings yet
- SDP 3G SR Telok Air Tawar 2Document41 pagesSDP 3G SR Telok Air Tawar 2kltowerNo ratings yet