Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Design Standards
Structural Design Standards
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- End Bearing PileDocument1 pageEnd Bearing PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distress TypesDocument1 pageDistress TypesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionDocument1 pageRigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Jointed Plain Concrete PavementDocument1 pageJointed Plain Concrete PavementSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Fiction PileDocument1 pageFiction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distoration of Pavement SlabDocument1 pageDistoration of Pavement SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Compaction PileDocument1 pageCompaction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Piles Based On FunctionDocument1 pagePiles Based On FunctionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Classification of PilesDocument1 pageClassification of PilesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cause of Common Distresses PDFDocument1 pageCause of Common Distresses PDFSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Flexure TestDocument1 pageFlexure TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument1 pageCreepSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- 6-Ways Concrete BaseDocument1 page6-Ways Concrete BaseSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- MarkingDocument1 pageMarkingSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Measurements of WorkabilityDocument1 pageMeasurements of WorkabilitySrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity TestDocument1 pageUltrasonic Pulse Velocity TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting FailuresDocument1 pageFactors Affecting FailuresSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Precast LidsDocument1 pagePrecast LidsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Document1 pageBitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rectangualr Portal CulvertsDocument1 pageRectangualr Portal CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ribbed Skew Haunch CulvertsDocument1 pageRibbed Skew Haunch CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cationic TypeDocument1 pageCationic TypeSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- I. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenDocument1 pageI. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- JACKING Box CulvertsDocument1 pageJACKING Box CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ComponetsDocument1 pageManhole ComponetsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ConfigurationsDocument1 pageManhole ConfigurationsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Maximun Fill HeightsDocument1 pageMaximun Fill HeightsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Culverts BasesDocument1 pageCulverts BasesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Mid Girder SectionDocument1 pageMid Girder SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
Structural Design Standards
Structural Design Standards
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Design Standards
Structural Design Standards
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruCopyright:
Available Formats
WSA_NCRPB_FR FOGZB_Vol VA-1 (15 Jul 10)
3. Pavement Design
81. Considering the sub grade soil CBR of 8% and design traffic as given in Table 5-6, the
new flexible pavement thicknesses obtained for a design life period of 15 years as per IRC
37 works out as under in Table 5-7.
Table 5-7: Proposed Design of Flexible Pavement for a Design Life Period of 15 Years
Road section Pavement Design Thickness (mm) for Design Subgrade CBR 8%
Design Trafic GSB WMM DBM BC Total
Approach roads to 20 200 250 85 40 575
flyover structure
Adjacent roads of flyover 15 200 250 75 40 565
structure
Note: Above the existing road surface adjacent to flyover, flexible overlay of 40mm BC +75mm
DBM is proposed.
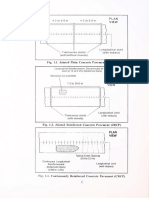
Figure 5-1: Typical Cross Section showing layers of Pavement Composition
BC + DBM
WMM
GSB
SUB GRADE, CBR 8%
4. Structural Design Standards
82. The design methodology is mainly devised from the method of construction proposed to
be adopted. Considering the intensity of daily traffic taking this route which warrants
speedy completion of the whole work, pre- cast construction method is adopted. The post
tensioned girders shall be casted in the yard and transported to the site and thus ensuring
minimum time for construction. Designs have been done for transfer and service stages.
83. Loading Standards. The structural system is designed for loadings as per IRC 6: 2000. The
basic loadings considered are:
• Dead load constituting of self weight of structural members
• Superimposed dead load constituting of weight of wearing coat, crash barrier and
median
• Live load constituting of loads due to 4 lanes of IRC Class A vehicles or 2 lanes of
IRC class 70R vehicles whichever produces the worst effect
• Wind load as applicable to the site based on the height
28
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- End Bearing PileDocument1 pageEnd Bearing PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distress TypesDocument1 pageDistress TypesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionDocument1 pageRigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Jointed Plain Concrete PavementDocument1 pageJointed Plain Concrete PavementSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Fiction PileDocument1 pageFiction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distoration of Pavement SlabDocument1 pageDistoration of Pavement SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Compaction PileDocument1 pageCompaction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Piles Based On FunctionDocument1 pagePiles Based On FunctionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Classification of PilesDocument1 pageClassification of PilesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cause of Common Distresses PDFDocument1 pageCause of Common Distresses PDFSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Flexure TestDocument1 pageFlexure TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument1 pageCreepSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- 6-Ways Concrete BaseDocument1 page6-Ways Concrete BaseSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- MarkingDocument1 pageMarkingSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Measurements of WorkabilityDocument1 pageMeasurements of WorkabilitySrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity TestDocument1 pageUltrasonic Pulse Velocity TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting FailuresDocument1 pageFactors Affecting FailuresSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Precast LidsDocument1 pagePrecast LidsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Document1 pageBitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rectangualr Portal CulvertsDocument1 pageRectangualr Portal CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ribbed Skew Haunch CulvertsDocument1 pageRibbed Skew Haunch CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cationic TypeDocument1 pageCationic TypeSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- I. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenDocument1 pageI. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- JACKING Box CulvertsDocument1 pageJACKING Box CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ComponetsDocument1 pageManhole ComponetsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ConfigurationsDocument1 pageManhole ConfigurationsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Maximun Fill HeightsDocument1 pageMaximun Fill HeightsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Culverts BasesDocument1 pageCulverts BasesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Mid Girder SectionDocument1 pageMid Girder SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet