Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
Uploaded by
Raymond MerisCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IB Math MYP II Summative Assessment Criteria C & D Cooking Proportions ChallengeDocument7 pagesIB Math MYP II Summative Assessment Criteria C & D Cooking Proportions ChallengeMich Castilleja100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Document12 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Raymond Meris100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Document12 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Raymond Meris100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Document9 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Document9 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- E3d CommandsDocument21 pagesE3d Commandsmih189% (9)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- IB Math I Summative Assessment Criteria D 3D ShapesDocument9 pagesIB Math I Summative Assessment Criteria D 3D ShapesMich Castilleja100% (4)
- SA Quadratic Equation. Criterion DDocument5 pagesSA Quadratic Equation. Criterion DКамиля Кокенова100% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Document5 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Raymond Meris100% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Document5 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Raymond Meris100% (1)
- G9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Document6 pagesG9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Ayuu Nur AfifahNo ratings yet
- Myp 3 Mathematics Sample Paper EOY Exam 2020 - 21 PART-2Document5 pagesMyp 3 Mathematics Sample Paper EOY Exam 2020 - 21 PART-2Anoop Sreedhar100% (2)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Document6 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Raymond Meris0% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Document6 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Raymond Meris0% (1)
- Unit 1 - Number System-1 PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Number System-1 PDFAmna Ali100% (1)
- 10MYP - Application Criterion D - TrigonometryDocument8 pages10MYP - Application Criterion D - Trigonometryvirgie100% (1)
- IB HL AA Unit 01 Patterns and SequencesDocument5 pagesIB HL AA Unit 01 Patterns and SequencesChee Wong100% (1)
- Summative Assessment Unit 1 - MYP 4Document5 pagesSummative Assessment Unit 1 - MYP 4Lorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MYP 2 - Unit PlannersDocument42 pagesMathematics MYP 2 - Unit Plannershemendu nandanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MYP 3 - Unit PlannersDocument48 pagesMathematics MYP 3 - Unit Plannershemendu nandan100% (1)
- Mathematics MYP 1 - Unit PlannersDocument40 pagesMathematics MYP 1 - Unit Plannershemendu nandanNo ratings yet
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- Ratios and Proportions JL MYP Unit/Weekly Lesson PlannerDocument8 pagesRatios and Proportions JL MYP Unit/Weekly Lesson PlannerJoel LogboNo ratings yet
- MYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryDocument12 pagesMYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryKelly OroszNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Unit Math and Language and Literature Year 3Document15 pagesInterdisciplinary Unit Math and Language and Literature Year 3api-311248365100% (1)
- Cici Yan - Bivariate Data Summative AssessmentDocument7 pagesCici Yan - Bivariate Data Summative Assessmentapi-430430225No ratings yet
- Math MYP 5 (Standard) Criteria D PDFDocument2 pagesMath MYP 5 (Standard) Criteria D PDFMeta DispiniNo ratings yet
- MYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Document27 pagesMYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Raymond MerisNo ratings yet
- MYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Document27 pagesMYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Raymond MerisNo ratings yet
- NEW IB Internal Assessment Scoring Criterion ChecklistDocument4 pagesNEW IB Internal Assessment Scoring Criterion ChecklistTeutë Domi100% (1)
- Summative Trig Test CR A - CDocument5 pagesSummative Trig Test CR A - CREYHAN HUSEYİNOVA100% (4)
- IB Mathematics SL Course OutlineDocument10 pagesIB Mathematics SL Course OutlinesaadNo ratings yet
- Maths G10e U2 - Functions GraphsDocument6 pagesMaths G10e U2 - Functions Graphsapi-429688581No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesUnit 5 - Exponential and Logarithmic Functionsapi-264152935100% (1)
- Example MYP Unit Planner Grade 9 QuadraticsDocument5 pagesExample MYP Unit Planner Grade 9 QuadraticsJamie Mitchell100% (1)
- Myp 4 Maths Unit Plan 1Document6 pagesMyp 4 Maths Unit Plan 1Joel Logbo100% (3)
- MYP 3 Math Unit Planner - Linear FunctionsDocument4 pagesMYP 3 Math Unit Planner - Linear FunctionsKelly Orosz0% (1)
- Maths G10e U1Document10 pagesMaths G10e U1api-429688581No ratings yet
- MYP2 RatesDocument6 pagesMYP2 RatesYomna SherifNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Radical FunctionsDocument4 pagesUnit 4 - Radical Functionsapi-264152935No ratings yet
- MYP Unit Plan No.1 - MYP 2Document3 pagesMYP Unit Plan No.1 - MYP 2Priyanka SairamNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Rational FunctionsDocument2 pagesUnit 6 - Rational Functionsapi-264152935No ratings yet
- Myp-4 HHWDocument14 pagesMyp-4 HHWRia ChopraNo ratings yet
- NEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 Linear RelationshipsDocument7 pagesNEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 Linear RelationshipsAmos D'Shalom Irush100% (1)
- Adv Algebra Unit 1Document6 pagesAdv Algebra Unit 1api-264152935No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Analysis & Approaches: Unit QuestionDocument4 pagesMathematics: Analysis & Approaches: Unit QuestionLorraine Sabbagh100% (2)
- MYP 3 Task Sheet 24 1Document6 pagesMYP 3 Task Sheet 24 1synix0% (1)
- Criterion C and D 2 Grade 9 StandardDocument6 pagesCriterion C and D 2 Grade 9 StandardClayton HalimNo ratings yet
- Formative Unit1 G6 2022-23Document4 pagesFormative Unit1 G6 2022-23AineeNo ratings yet
- DP2 - Math AA HL - Trigonometry 1Document14 pagesDP2 - Math AA HL - Trigonometry 1mahesh tendulkarNo ratings yet
- IB HL AA Unit 03 Complex NumbersDocument6 pagesIB HL AA Unit 03 Complex NumbersLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- SL Math OutlineDocument7 pagesSL Math Outlinedadajee420No ratings yet
- Myp 1 Math Criterion OnlineDocument5 pagesMyp 1 Math Criterion Onlineapi-242287187No ratings yet
- IB Math MYP III Summative Assessment Criteria A EquationsDocument3 pagesIB Math MYP III Summative Assessment Criteria A EquationsMich Castilleja100% (2)
- Criterion D Tunnel ExplorationDocument6 pagesCriterion D Tunnel Explorationyossifwaleed611No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Applications & Interpretations: Unit QuestionDocument3 pagesMathematics: Applications & Interpretations: Unit QuestionLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathematics HL/SL Exploration Marking Criteria: A: CommunicationDocument3 pagesIb Mathematics HL/SL Exploration Marking Criteria: A: CommunicationBhavye GuptaNo ratings yet
- IB SL AA Unit 10 From Approximation To Generalization IntegrationDocument6 pagesIB SL AA Unit 10 From Approximation To Generalization IntegrationLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetDocument17 pagesMYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetridhimaNo ratings yet
- NEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 TrigonometryDocument6 pagesNEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 TrigonometryLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerDocument6 pagesMYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerMona AhmedNo ratings yet
- Form Representation, Justification Fairness and Development: Accessing Equal OpportunitiesDocument6 pagesForm Representation, Justification Fairness and Development: Accessing Equal OpportunitieskolawoleNo ratings yet
- Unit Planner - DataManagement - Y16Document5 pagesUnit Planner - DataManagement - Y16Deema El MasriNo ratings yet
- Myp Math Extended Unit 02Document6 pagesMyp Math Extended Unit 02vato otavNo ratings yet
- Unit - Planner - Bivariate - Data Y35Document6 pagesUnit - Planner - Bivariate - Data Y35moukoddim sadikouNo ratings yet
- Elastic and Inelastic CollisionsDocument11 pagesElastic and Inelastic CollisionsFatehNo ratings yet
- Predictors of Trachomatous Trichiasis Surgery OutcomeDocument13 pagesPredictors of Trachomatous Trichiasis Surgery OutcomeRania ENo ratings yet
- 169 Functional EquationsDocument83 pages169 Functional Equationshungchng100% (5)
- Effect of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Image & Loyalty Intention: A Study of Cosmetic ProductDocument13 pagesEffect of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Image & Loyalty Intention: A Study of Cosmetic ProductSagar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- AssDocument8 pagesAssEngr. Sohaib JamalNo ratings yet
- Empty Cores in Airline MarketsDocument17 pagesEmpty Cores in Airline MarketsW.J. ZondagNo ratings yet
- Aptitude GoodDocument139 pagesAptitude GoodrupeshkumarinfoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8: Quarter 2 - Module 3A, Graph of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesDocument15 pagesMathematics 8: Quarter 2 - Module 3A, Graph of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesKai VrixtoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Spring 2010 CS507-Information Systems: OrganizationDocument46 pagesMidterm Examination Spring 2010 CS507-Information Systems: Organizationpiyara222No ratings yet
- Sum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonDocument15 pagesSum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonMaricel Balbuena100% (1)
- Mbe2036 1Document43 pagesMbe2036 1WylieNo ratings yet
- Pumps Rotordynamics PDFDocument16 pagesPumps Rotordynamics PDFDiego PugaNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On The Aims and Objectives of Teaching MathematicsDocument8 pagesBrief Notes On The Aims and Objectives of Teaching MathematicsRafiqueAbdullahParhiarNo ratings yet
- Udaydaa1 7Document75 pagesUdaydaa1 7uday bariNo ratings yet
- Final LitNum 8 Lesson Plans-1-1Document109 pagesFinal LitNum 8 Lesson Plans-1-1UhNo ratings yet
- Direct Drive Systems With Transverse Flux Reluctance MotorsDocument8 pagesDirect Drive Systems With Transverse Flux Reluctance Motorsarnika33No ratings yet
- Programming Logic and Design: Ninth EditionDocument49 pagesProgramming Logic and Design: Ninth EditionBry CamelNo ratings yet
- Ee6401 em - I PDFDocument143 pagesEe6401 em - I PDFTuhin techNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2013 SyllabusDocument8 pagesJEE Advanced 2013 SyllabusPragnesh ParekhNo ratings yet
- DLL Math G4 Q2 W3Document6 pagesDLL Math G4 Q2 W3Daniel MingoyNo ratings yet
- Present Worth AnalysisDocument27 pagesPresent Worth AnalysisMclyn Jeszarre JaymeNo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach To Performance-Based Design of RC Frame BuildingsDocument10 pagesA Unified Approach To Performance-Based Design of RC Frame BuildingsSuman BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- A Method of Thirdtypart Logistics Providers Selection and TransporntationDocument4 pagesA Method of Thirdtypart Logistics Providers Selection and TransporntationthanhthoaktNo ratings yet
- CoventorWare TutorialDocument41 pagesCoventorWare TutorialforceofconstructionNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Practice ProblemsDocument28 pagesUnit 3 Practice ProblemsSheyla GuallpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gear Drive-3Document41 pagesChapter 2 Gear Drive-3Abaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- Panel Data Analysis Sunita AroraDocument28 pagesPanel Data Analysis Sunita Aroralukgv,h100% (1)
- Comparison of The Seismic Design Code For Buildings of Nepal With The Chinese, European and American Seismic Design CodesDocument5 pagesComparison of The Seismic Design Code For Buildings of Nepal With The Chinese, European and American Seismic Design CodesRupesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance: An ExampleDocument32 pagesRepeated Measures Analysis of Variance: An Examplegore_11No ratings yet
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
Uploaded by
Raymond MerisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
IB MYP Mathematics (Standard) Unit Plan - Grade 9
Uploaded by
Raymond MerisCopyright:
Available Formats
Teacher(s) Antonio Hadap; Raymond Meris Subject group and discipline Mathematics (Standard)
Unit title A whole range of things MYP year MYP 4 (Grade 9) Unit duration (hrs) 26 hours
Inquiry: Establishing the purpose of the unit
Key concept Related concept(s) Global context
Relationships Rerpesentation Globalizaiton and Sustainability
Quantity
Statement of inquiry
How quanitites are represented can help to establish underlying relationship and trends in a population.
Inquiry questions
Factual— What are the different types of data? How are the different measures of central tendency calculated?
Conceptual— How do measures of dispersion help you describe data? How do different represenations help you compare data sets?
Debatable— Should we ignore results that aren’t typical? How do individuals stand out in a crowd?
Middle Years Programme Unit planner 1
Objectives Summative assessment
Outline of summative assessment task(s) including assessment criteria: Relationship between summative
assessment task(s) and statement
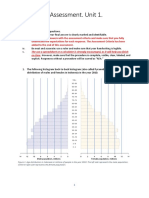
Objective C. Communicating Task 1: Problem Solving Questions taken from MYP Mathematics: A Concept-based approach
of inquiry:
4&5 Standard by Oxford University Press (pages 94 to 95)
iii. move between different forms
of mathematical representation Sample Questions:
SOI: How quanitites are
represented can help to establish
underlying relationship and trends
in a population.
In this tasks, students will be
changing the representation of the
data from tables to stem-and-leaf
diagrams, and to box-and-whisker
diagram. These are examples of
moving between different froms of
representations and how it can
establish relationships and trends.
Objective A: Knowing and Unit Test SOI: How quanitites are
Middle Years Programme Unit planner 2
Understanding represented can help to establish
underlying relationship and trends
i. solve problems correctly in a
in a population.
variety of contexts
In this unit test, students will be
ii. apply the selected mathematics
working with different quantities
successfully when solving
and explore the relationships
problems
among quantities in order to
identify trends in a population
Objective D: Applying G: Your goal is to show how quanitities can be represented and how can these help to establish SOI: How quanitites are
mathematics in real-world underlying relationships and trends ina population. represented can help to establish
contexts underlying relationship and trends
R: Your role is a statistician that is working for a census in a small town to identify trends in their
in a population.
i. identify relevant elements of birth and mortality rates
authentic real-life situations GRASPS authenthic assessment,
A: Your audience are the policy makers who will make decisions in health care and education
students will carry out an
ii. select appropriate systems based on the result of the birth and mortality trends in their city.
investigation into one city of their
mathematical strategies when
S: You have to select a city and from that research their birth rates from 1975 to 2005. Use choice that will allow them to
solving authentic real-life
relevant statistical tools such as measures of central tendency and measures of dispersion in explore how representation of
situations
order to analyse your data. Afterwards, you have to think of a suitable method of visually different statistical quantities can
iii. apply the selected displaying your results. The same thing has to be done with mortality trends. determine trends in a population.
mathematical strategies The statistical report that the
P: The product is a statistical report that contains important statistical information with regard to students will create will also
successfully to reach a solution
the city you are investigating, as well as a forecast of trends in the population based on investigate how relationships
statistical results. among quantities may be
S: Your output will be evaluated using Objective D: Applying mathematics in real-world contexts represented and used to make
strands i, ii, and iii. forecasts or deductions about a
population.
Approaches to learning (ATL)
In order for students to solve problems correctly in a variety of contexts, and apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving problems, students must practise
observing carefully in order to recognize problems and applying skills and knowledge in unfamiliar situations. (ATL Category: Thinking, ATL Cluster: Critical-thinking skills,
Transfer skills)
In order for students to move between different forms of mathematical representation, students must interpret data. (ATL Category: Thinking, ATL Cluster: Critical-thinking
skills)
In order for students to apply mathematics in real-world contexts (strands i, ii, and iii), students must practise observing carefully in order to recognize problems. (ATL
Middle Years Programme Unit planner 3
Category: Thinking, ATL Cluster: Critical-thinking skills)
Action: Teaching and learning through inquiry
Content Learning process
Categorizing data Learning experiences and teaching strategies Formative Assessment Differentiation
Constructing stem-and-
leaf diagrams
Students work in pairs and groups through the Exit slips (Students answer questions on a The activities are scaffolded so that
Calculating quartiles, the activities provided by the teacher. Investigation slip of paper before they exit the class, students. The teacher can provide
range, and the activities found on the textbook will be used to providing feedback to the teacher on their additional support where necessary and/or
interquartile range promote inquiry-based learning. Direct instruction level of understanding.) pair students so that a stronger student
will take place on concepts and skills that students can help one who may struggle.
Giving a five-point
may need to review.
summary of a set of data
Discussions with students as they hand in
Constructing box-and- their investigation. Checking of their work The teacher may continue to provide
whisker diagrams Students will watch the teacher model how to as they complete practice exercises guidance to those who need it while those
solve problems in statistics. Afterwards students leading up to the investigation. who learn more quickly can begin practice
Identifying outliers
will be given practice problem sets for them to try. earlier or work with
Comparing distributions They will then move on to practice. Should further supplemental/enrichment problems.
examples or guidance be needed, the teacher will Student presentations of their work and
Finding the mean, provide another problem to model how to solve. feedback will be given depending on the
median, mode, and The teacher will guideand give feedback to the work presented by the students.
ragne students as they engage in independent learning.
Representing grouped Guided practice: In pairs, students will work on
data in cumulative exercises supplied by the teacher.
frequency curve
Finding five-point
summary
Constructing and
interpreting frequency
and relative frequency
histograms with equal
and unequal widths
Resources
Middle Years Programme Unit planner 4
Graphic Diplay Calculators
MYP by Concept 4&5 (Standard) by Harrison et al. (Oxford University Press)
Reflection: Considering the planning, process and impact of the inquiry
Prior to teaching the unit During teaching After teaching the unit
The pre-existing knowledge and skills of the students I realized that some students are stuck on
should be identified. investigation activities. Probably because their prior-
knowledge about statistics is lacking. We reviewed
some basic concepts first. Some scaffolds were also
given. I found this to be a good strategy in helping
students successfully finish their investigation
activity.
Middle Years Programme Unit planner 5
You might also like
- IB Math MYP II Summative Assessment Criteria C & D Cooking Proportions ChallengeDocument7 pagesIB Math MYP II Summative Assessment Criteria C & D Cooking Proportions ChallengeMich Castilleja100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Document12 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Raymond Meris100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Document12 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches Subject Outline 2021Raymond Meris100% (3)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Document9 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Document9 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Probability (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- E3d CommandsDocument21 pagesE3d Commandsmih189% (9)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis Unit Plan - Number and Alegbra (Core SL-HL)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- IB Math I Summative Assessment Criteria D 3D ShapesDocument9 pagesIB Math I Summative Assessment Criteria D 3D ShapesMich Castilleja100% (4)
- SA Quadratic Equation. Criterion DDocument5 pagesSA Quadratic Equation. Criterion DКамиля Кокенова100% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Document5 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Raymond Meris100% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Document5 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 7Raymond Meris100% (1)
- G9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Document6 pagesG9 U1 Math MYP Unit Planner 20182019Ayuu Nur AfifahNo ratings yet
- Myp 3 Mathematics Sample Paper EOY Exam 2020 - 21 PART-2Document5 pagesMyp 3 Mathematics Sample Paper EOY Exam 2020 - 21 PART-2Anoop Sreedhar100% (2)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Document6 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Raymond Meris0% (1)
- IB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Document6 pagesIB MYP Mathematics Unit Plan - Grade 8Raymond Meris0% (1)
- Unit 1 - Number System-1 PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 1 - Number System-1 PDFAmna Ali100% (1)
- 10MYP - Application Criterion D - TrigonometryDocument8 pages10MYP - Application Criterion D - Trigonometryvirgie100% (1)
- IB HL AA Unit 01 Patterns and SequencesDocument5 pagesIB HL AA Unit 01 Patterns and SequencesChee Wong100% (1)
- Summative Assessment Unit 1 - MYP 4Document5 pagesSummative Assessment Unit 1 - MYP 4Lorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MYP 2 - Unit PlannersDocument42 pagesMathematics MYP 2 - Unit Plannershemendu nandanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics MYP 3 - Unit PlannersDocument48 pagesMathematics MYP 3 - Unit Plannershemendu nandan100% (1)
- Mathematics MYP 1 - Unit PlannersDocument40 pagesMathematics MYP 1 - Unit Plannershemendu nandanNo ratings yet
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- DP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Document8 pagesDP Math Analysis and Approaches SL Unit Plan Functions (Part 1)Raymond Meris100% (2)
- Ratios and Proportions JL MYP Unit/Weekly Lesson PlannerDocument8 pagesRatios and Proportions JL MYP Unit/Weekly Lesson PlannerJoel LogboNo ratings yet
- MYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryDocument12 pagesMYP3 Math Unit Planner - GeometryKelly OroszNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Unit Math and Language and Literature Year 3Document15 pagesInterdisciplinary Unit Math and Language and Literature Year 3api-311248365100% (1)
- Cici Yan - Bivariate Data Summative AssessmentDocument7 pagesCici Yan - Bivariate Data Summative Assessmentapi-430430225No ratings yet
- Math MYP 5 (Standard) Criteria D PDFDocument2 pagesMath MYP 5 (Standard) Criteria D PDFMeta DispiniNo ratings yet
- MYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Document27 pagesMYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Raymond MerisNo ratings yet
- MYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Document27 pagesMYP Mathematics - Subject Group Overview SGO 2021-2022 (Updated)Raymond MerisNo ratings yet
- NEW IB Internal Assessment Scoring Criterion ChecklistDocument4 pagesNEW IB Internal Assessment Scoring Criterion ChecklistTeutë Domi100% (1)
- Summative Trig Test CR A - CDocument5 pagesSummative Trig Test CR A - CREYHAN HUSEYİNOVA100% (4)
- IB Mathematics SL Course OutlineDocument10 pagesIB Mathematics SL Course OutlinesaadNo ratings yet
- Maths G10e U2 - Functions GraphsDocument6 pagesMaths G10e U2 - Functions Graphsapi-429688581No ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Exponential and Logarithmic FunctionsDocument3 pagesUnit 5 - Exponential and Logarithmic Functionsapi-264152935100% (1)
- Example MYP Unit Planner Grade 9 QuadraticsDocument5 pagesExample MYP Unit Planner Grade 9 QuadraticsJamie Mitchell100% (1)
- Myp 4 Maths Unit Plan 1Document6 pagesMyp 4 Maths Unit Plan 1Joel Logbo100% (3)
- MYP 3 Math Unit Planner - Linear FunctionsDocument4 pagesMYP 3 Math Unit Planner - Linear FunctionsKelly Orosz0% (1)
- Maths G10e U1Document10 pagesMaths G10e U1api-429688581No ratings yet
- MYP2 RatesDocument6 pagesMYP2 RatesYomna SherifNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Radical FunctionsDocument4 pagesUnit 4 - Radical Functionsapi-264152935No ratings yet
- MYP Unit Plan No.1 - MYP 2Document3 pagesMYP Unit Plan No.1 - MYP 2Priyanka SairamNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Rational FunctionsDocument2 pagesUnit 6 - Rational Functionsapi-264152935No ratings yet
- Myp-4 HHWDocument14 pagesMyp-4 HHWRia ChopraNo ratings yet
- NEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 Linear RelationshipsDocument7 pagesNEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 Linear RelationshipsAmos D'Shalom Irush100% (1)
- Adv Algebra Unit 1Document6 pagesAdv Algebra Unit 1api-264152935No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Analysis & Approaches: Unit QuestionDocument4 pagesMathematics: Analysis & Approaches: Unit QuestionLorraine Sabbagh100% (2)
- MYP 3 Task Sheet 24 1Document6 pagesMYP 3 Task Sheet 24 1synix0% (1)
- Criterion C and D 2 Grade 9 StandardDocument6 pagesCriterion C and D 2 Grade 9 StandardClayton HalimNo ratings yet
- Formative Unit1 G6 2022-23Document4 pagesFormative Unit1 G6 2022-23AineeNo ratings yet
- DP2 - Math AA HL - Trigonometry 1Document14 pagesDP2 - Math AA HL - Trigonometry 1mahesh tendulkarNo ratings yet
- IB HL AA Unit 03 Complex NumbersDocument6 pagesIB HL AA Unit 03 Complex NumbersLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- SL Math OutlineDocument7 pagesSL Math Outlinedadajee420No ratings yet
- Myp 1 Math Criterion OnlineDocument5 pagesMyp 1 Math Criterion Onlineapi-242287187No ratings yet
- IB Math MYP III Summative Assessment Criteria A EquationsDocument3 pagesIB Math MYP III Summative Assessment Criteria A EquationsMich Castilleja100% (2)
- Criterion D Tunnel ExplorationDocument6 pagesCriterion D Tunnel Explorationyossifwaleed611No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Applications & Interpretations: Unit QuestionDocument3 pagesMathematics: Applications & Interpretations: Unit QuestionLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathematics HL/SL Exploration Marking Criteria: A: CommunicationDocument3 pagesIb Mathematics HL/SL Exploration Marking Criteria: A: CommunicationBhavye GuptaNo ratings yet
- IB SL AA Unit 10 From Approximation To Generalization IntegrationDocument6 pagesIB SL AA Unit 10 From Approximation To Generalization IntegrationLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetDocument17 pagesMYP 5 - Looping Back Revision SheetridhimaNo ratings yet
- NEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 TrigonometryDocument6 pagesNEXT CHAPTER MYP UP 9 TrigonometryLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerDocument6 pagesMYP 5 (Math-Unit 1) PlannerMona AhmedNo ratings yet
- Form Representation, Justification Fairness and Development: Accessing Equal OpportunitiesDocument6 pagesForm Representation, Justification Fairness and Development: Accessing Equal OpportunitieskolawoleNo ratings yet
- Unit Planner - DataManagement - Y16Document5 pagesUnit Planner - DataManagement - Y16Deema El MasriNo ratings yet
- Myp Math Extended Unit 02Document6 pagesMyp Math Extended Unit 02vato otavNo ratings yet
- Unit - Planner - Bivariate - Data Y35Document6 pagesUnit - Planner - Bivariate - Data Y35moukoddim sadikouNo ratings yet
- Elastic and Inelastic CollisionsDocument11 pagesElastic and Inelastic CollisionsFatehNo ratings yet
- Predictors of Trachomatous Trichiasis Surgery OutcomeDocument13 pagesPredictors of Trachomatous Trichiasis Surgery OutcomeRania ENo ratings yet
- 169 Functional EquationsDocument83 pages169 Functional Equationshungchng100% (5)
- Effect of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Image & Loyalty Intention: A Study of Cosmetic ProductDocument13 pagesEffect of Customer Satisfaction On Brand Image & Loyalty Intention: A Study of Cosmetic ProductSagar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- AssDocument8 pagesAssEngr. Sohaib JamalNo ratings yet
- Empty Cores in Airline MarketsDocument17 pagesEmpty Cores in Airline MarketsW.J. ZondagNo ratings yet
- Aptitude GoodDocument139 pagesAptitude GoodrupeshkumarinfoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 8: Quarter 2 - Module 3A, Graph of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesDocument15 pagesMathematics 8: Quarter 2 - Module 3A, Graph of Linear Inequalities in Two VariablesKai VrixtoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Spring 2010 CS507-Information Systems: OrganizationDocument46 pagesMidterm Examination Spring 2010 CS507-Information Systems: Organizationpiyara222No ratings yet
- Sum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonDocument15 pagesSum of The Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonMaricel Balbuena100% (1)
- Mbe2036 1Document43 pagesMbe2036 1WylieNo ratings yet
- Pumps Rotordynamics PDFDocument16 pagesPumps Rotordynamics PDFDiego PugaNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On The Aims and Objectives of Teaching MathematicsDocument8 pagesBrief Notes On The Aims and Objectives of Teaching MathematicsRafiqueAbdullahParhiarNo ratings yet
- Udaydaa1 7Document75 pagesUdaydaa1 7uday bariNo ratings yet
- Final LitNum 8 Lesson Plans-1-1Document109 pagesFinal LitNum 8 Lesson Plans-1-1UhNo ratings yet
- Direct Drive Systems With Transverse Flux Reluctance MotorsDocument8 pagesDirect Drive Systems With Transverse Flux Reluctance Motorsarnika33No ratings yet
- Programming Logic and Design: Ninth EditionDocument49 pagesProgramming Logic and Design: Ninth EditionBry CamelNo ratings yet
- Ee6401 em - I PDFDocument143 pagesEe6401 em - I PDFTuhin techNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2013 SyllabusDocument8 pagesJEE Advanced 2013 SyllabusPragnesh ParekhNo ratings yet
- DLL Math G4 Q2 W3Document6 pagesDLL Math G4 Q2 W3Daniel MingoyNo ratings yet
- Present Worth AnalysisDocument27 pagesPresent Worth AnalysisMclyn Jeszarre JaymeNo ratings yet
- A Unified Approach To Performance-Based Design of RC Frame BuildingsDocument10 pagesA Unified Approach To Performance-Based Design of RC Frame BuildingsSuman BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- A Method of Thirdtypart Logistics Providers Selection and TransporntationDocument4 pagesA Method of Thirdtypart Logistics Providers Selection and TransporntationthanhthoaktNo ratings yet
- CoventorWare TutorialDocument41 pagesCoventorWare TutorialforceofconstructionNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Practice ProblemsDocument28 pagesUnit 3 Practice ProblemsSheyla GuallpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gear Drive-3Document41 pagesChapter 2 Gear Drive-3Abaziz Mousa OutlawZzNo ratings yet
- Panel Data Analysis Sunita AroraDocument28 pagesPanel Data Analysis Sunita Aroralukgv,h100% (1)
- Comparison of The Seismic Design Code For Buildings of Nepal With The Chinese, European and American Seismic Design CodesDocument5 pagesComparison of The Seismic Design Code For Buildings of Nepal With The Chinese, European and American Seismic Design CodesRupesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance: An ExampleDocument32 pagesRepeated Measures Analysis of Variance: An Examplegore_11No ratings yet