Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 6
Week 6
Uploaded by
Joanna BakOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 6
Week 6
Uploaded by
Joanna BakCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 6: Drugs for Heart Failure, Angina, Coagulation Modifier Drugs, Statins
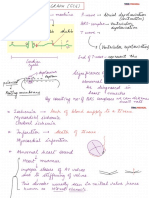
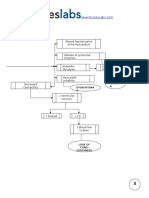
Heart Failure
specific disease : complex clinical syndrome resulting from
-
vote a any functional & structural
impairment to the ,
specifically ejection of blood OR ventrical filling
control risk factors Obesity & diabetes
-
; HTN , CAD .
.
is unable to DUMP enough blood from ventricles to meet body's metabolic needs
-
⑥ HF coughing SOB dyspnea
-
's pulmonary edema . , ,
⑧ HF 's systemic venous congestion , pedal edema .
jugular venous distension .
ascites .
& hepatic congestion8 .
Classifications of
-
4 Failure :
↳
Class I :
No physical activity limitations
↳ class I :
ordinary physical activity results in fatigue dyspnea ,
↳
class Ii
:
Marked limitation in physical activity
↳
class II :
symptoms @ rest / no physical activity
Cardiac Glycosides
Digoxin llano ✗ in )
NO longer used as first eine tx mortality
-
.
not shown to reduce
MOA
A myocardial contractility 1 positive inotropic effect between SA & AV node cardiac
-
* area .
changes electrical conduction properties of the cells remain in a state of depolarization
> Iv rate of electrical conduction for a longer period & are unable to
↳
prolong refractory period start another electrical impulse .
Which
used in HF & to control ventricular response to to HR & A cardiac efficiency .
*
atrial fibrillation
Adverse Effects
cardio bradycardia tachycardia hypotension
-
:
these are symptoms of anxiety
}
, ,
Headache Confusion convulsions
-
CNS :
. .
fatigue ,
visual :
coloured vision .
halo vision
GI anorexia
:
,
nausea .
vomiting diarrhea ,
Digoxin Toxicity
interactions
-
was 1st Choice drug ,
but not anymore dit adverse effects & drug
contraindicated in pts w/ hypersensitivity to it & ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation
-
therapeutic index (therapeutic dose is close toxic dose)
-
LOW to
Digoxin levels monitored when 1St start taking drug monitor if there
-
are .
When steady . only
is suspicion of toxicity nonadherence , .
& deteriorating kidney fxn .
LOW potassium OR magnesium levels A potential for toxicity .
Monitor electrolyte levels
-
Pt may be treated WI digoxin immune Fab (digi bind )
↳
Recognizes digoxin as an antigen & forms an antigen antibody complex WI the drug
inactivating the free digoxin
Diltiazem hydrochloride ( card izem )
calcium channel blocker
-
used for temporary control Of rapid ventricular response for Dt Wl atrial fib & .
paroxysmal supra ventricular tactics .
contraindication hypersensitivity pulmonary congestion
-
's acute M1 .
, ,
Angina
Chest pain i
When the supply of oxygen in the blood is insufficient to meet the demands of
requires a large supply of oxygen to meet demands placed on it
ischemia 's
-
poor blood supply to organ .
Chronic stable angina ( classic 1 effort angina ) i
occurs due to artherosclerosis
( pre infarction angina ) WI
-
unstable angina ; most dangerous .
acute coronary syndrome
cardiac ischemia WIO persistent ST segment elevation on ECG & no detectable release
of the enzymes & biomarkers of myocardial necrosis .
Often ends in MI
Vaso Das tic angina ( variant angina ) ; results from spasms from smooth muscle that surrounds
the art hero sclerotic coronary arteries .
↳
occurs @ rest Wto any precipitating cause
>
follows same schedule ,
happens @ same time of day .
Drugs for angina
:
nitrates / nitrites .
b- blockers ,
calcium channel blockers .
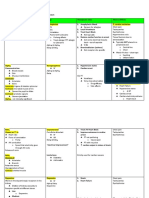
Nitrates
Rapid acting forms
-
>
treat acute angina / attacks Available Forms :
↳
sublingual tablets or spray ; Nlnfusion sublingual #
chewable tablets
-
acting forms
-
Long
-
used to prevent anginal episodes
-
>
oralcapsule / tablets
N solutions
-
*
Nitroglycerin
prototypical nitrate transdermal patch #
-
>
>
Large 1St bypass effect moral forms ointments
used for symptomatic + ✗ of ischemic transiingual sprays #
-
>
conditions langina ) *
Bypasses Liver & first-pass effect
>
Oral .
Sublingual .me/-reddOseaerosol
sprayed under tongue ,
IV. & topical
MOA Adverse Effects
cause vasodilation through relaxation Headaches ,
dizziness eotatigue
Of smooth muscles > usually diminishes in intensity & frequency
potent dilating effects on coronary WI continued use
arteries allowing oxygen to ischemic reflex tactics :
when nitrate induced
-
vasodilation
myocardial tissue occurs torabidlb.ws overcompensates &THR
usedfortx & prevention of angina >
huge shift in blood volume toward the systemic
Tolerance venous circulation & away from the
taking nitrates around the orthostatic hypotension
-
occurs in Des
CIOCKORWI long-acting forms
prevented Disallowing a regular nitrate
free period to allow enzyme pathways to
replenish
Nitroglycerin
administered orally blc Of first pass effect
-
Not
-
commonly taken sublingual lb.cl/tTvascUlarity-- quick absorption
Route onset of action peak Action Duration Of Action
IV I -2 mins NIA 3- 5 mins
sublingual 2- 3 mins unknown 30-60 mins .
topical 15 -
60min18 0.5 -
2hr8 3-8 hours .
transdermal 30 -60 mins I -3 hours 8- 12 hours
translingual 2 mins 4- 10min 3- 60min
Hemostasis
process of halting bleeding
>
complex relationship btwn what promotes clot formation OR inhibit coagulation
blood clot
-
Thrombus i a
Embolus thrombus that moves through blood vessels
-
; a .
coagulation system :
cascade WI each activated factor acting as a catalyst that
-
amplifies the next rxn .
Drugs Affecting coagulation
> Results in fibrin ( clot forming ) ① Anticoagulants ; inhibits the action OR formation of
clotting factors ( prevents clot formation )
② Anti platelets ; inhibits platelet aggregation
( prevent platelet plug )
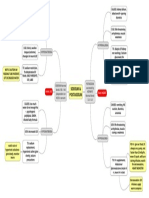
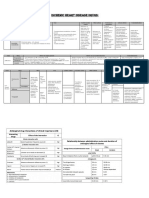
Anticoagulants
Heparin
interfere clotting factors that activate thrombin
-
Usually injected 110 10.000 Units 1 mL )
-
to
always use 1mL Syringes dosing MUST BE EXACT DO NOT ROUND
Toxicity petechia eccnymoses
-
sx ; hematuria ,
Melena , ,
weight heparin8 ( LMWH )
-
LOW molecular
>
enoxapar in cloven OX) & da Heparin (frag min )
↳ more predictable response
C- no ✗ A Darin ( Love nox)
injectable
-
only
prophylaxis
-
commonly used
better than heparin blc no need for monitor & can be given for home tx of DVT
-
DO NOT give heparin + enoxabarin in combination
-
warfarin sodium lcoumad in )
inhibits ✓ it K synthesis by bacteria in GI tract
-
>
inhibit Vit K dependent clotting factors III. V11 , IX. X ) Which are typically synthesized
in the liver .
Most commonly prescribed ORALLY
Dabigatran ( Prada ✗ a) Apixaban ( Eliquis )
direct thrombin inhibitor direct factor ✗ a inhibitor
-
-
prevents stroke & thrombosis in pts anticoagulant used for prophylaxis ( after knee
- -
w/ non valvular atrial fibrillation surgery )
dose dependent on kidney fxn prevents formation of thrombus
-
-
prodrug activated by liver administered PO
- -
Normal dose 150mg bid side effects bruising minor bleed
-
: i
nausea
-
,
,
NO antidote
-
Rivaroxabancxarelto )
direct factor ✗ a inhibitor
-
treats DVT
-
-
+
aspirin to to risk for heart attack
administered PO
-
Antiplatelets
works by inhibiting the enzymes that cause the platelets to clump together
Aspirin ( Acetyl salicylic acid )
18-1
-
Only for
don't use for children WI flu-like sx
-
Clopidogrel ( Plavi × )
only PO
-
ADP inhibitor
-
most widely used .
You might also like
- Miscellaneous For FinalsDocument30 pagesMiscellaneous For Finalsjames.a.blairNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Illustrated NotesDocument148 pagesPharmacology Illustrated NotesShikha Khemani91% (11)
- Adaptive QuizzingDocument166 pagesAdaptive QuizzingHuawei Li100% (1)
- Dengue Case StudyDocument20 pagesDengue Case Studyjohn jumborockNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument10 pagesCongestive Heart FailureScatty's ChannelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RleDocument23 pagesDrug Study Rlehazel sergioNo ratings yet
- SF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - NotesDocument7 pagesSF1-Lecture-03 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Notesdisha shuklaNo ratings yet
- 2 2PharmaCHFDiureticsVISION-EDITED PDFDocument12 pages2 2PharmaCHFDiureticsVISION-EDITED PDFMarinelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Vasodilatation Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy Hyperdynamic CirculationDocument3 pagesVasodilatation Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy Hyperdynamic CirculationMarcel DocNo ratings yet
- Concepts Work PhysiologyDocument2 pagesConcepts Work Physiologylidy2211No ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac Output Patho NewDocument2 pagesDecrease Cardiac Output Patho NewGenette Sy SolisNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhage PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesHemorrhage PathophysiologyJubelle Sipalay0% (1)
- Edema - EffusionsDocument4 pagesEdema - EffusionsEsayas NashaNo ratings yet
- Summary C19-20Document15 pagesSummary C19-20EleanorNo ratings yet
- M) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (Document1 pageM) IV Anticoagulation M) Arterial Thrombolytic (christine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Adult/Child: IV 2-5 Tachycardia, Anginal PainDocument10 pagesAdult/Child: IV 2-5 Tachycardia, Anginal PainKenneth Rhoel RolaNo ratings yet
- AdrenoleukodystrophyDocument5 pagesAdrenoleukodystrophyvictorjeetabhiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DopamineDocument1 pageDrug Study Dopaminejulesubayubay542880% (5)
- Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssesment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationI Am SmilingNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintDocument3 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output Ready To PrintAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Arrythmias For 4th YearDocument79 pagesPharmacotherapy of Arrythmias For 4th Yeartolcharegasa100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Action Rationale EvaluationJames Czar FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFnadzwa velascoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- A18 BODY FLUIDS in Human BodyDocument1 pageA18 BODY FLUIDS in Human Bodyservoculus machatteNo ratings yet
- Ascites: Saag Albumin AlbuminDocument7 pagesAscites: Saag Albumin AlbuminMike GNo ratings yet
- CVA RestrokeDocument1 pageCVA RestrokeLorelyn DelfinNo ratings yet
- PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3 PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3: Pharmacy (San Pedro College) Pharmacy (San Pedro College)Document9 pagesPCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3 PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3: Pharmacy (San Pedro College) Pharmacy (San Pedro College)Mhiel Bhon RamzNo ratings yet
- Final Oral EditedDocument1 pageFinal Oral EditedRey CortezNo ratings yet
- CHF NCPDocument8 pagesCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- Basic Cardio 2Document6 pagesBasic Cardio 2Malek ZanNo ratings yet
- PCOL Second YearDocument8 pagesPCOL Second YearNorhana BarambanganNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Neurologic NursingDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Neurologic Nursingjulia marie candelarioNo ratings yet
- Blue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSDocument10 pagesBlue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSMarisella ReadonNo ratings yet
- Icu 4Document7 pagesIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanMay Anne ManuzonNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument1 pageSodium and Potassiumjoan1alejo1espirituNo ratings yet
- Institute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesInstitute of Nursing: Far Eastern UniversityaleccespirituNo ratings yet
- Colonic Mass PathophysioDocument1 pageColonic Mass PathophysioAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Quizzes RationaleDocument22 pagesQuizzes RationaleElla OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Laphar AddDocument2 pagesLaphar AddTessa RuliantyNo ratings yet
- Sympatholytic DrugsDocument8 pagesSympatholytic DrugsAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline: PlasmaDocument3 pagesTopic Outline: PlasmaChristian AlacarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Document2 pagesDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- CVS Theory September 2021Document20 pagesCVS Theory September 2021Alex FandoNo ratings yet
- Sotagliflozin in Patients With Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure - The TrialDocument27 pagesSotagliflozin in Patients With Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure - The Trialdpwppni riauNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rujukan Kasus Baru Lama Untuk KopoDocument34 pagesLaporan Rujukan Kasus Baru Lama Untuk KopoRuciNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - AKI (Bana) 3Document1 pagePathophysiology - AKI (Bana) 3Elizalde HusbandNo ratings yet
- Compensate D: Less of Autoregulation of MicrocirculationDocument8 pagesCompensate D: Less of Autoregulation of MicrocirculationRhykha DariellaFespuci MirchlosNo ratings yet
- ST Elevation MI, STEMIDocument3 pagesST Elevation MI, STEMInmyza89No ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineMika Kudo100% (2)
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- 5,6.heart FailureDocument12 pages5,6.heart FailureKUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANNo ratings yet
- Case Apsc 2023 - FdaDocument18 pagesCase Apsc 2023 - FdaFariz DwikyNo ratings yet
- Pink Book QuizletDocument14 pagesPink Book QuizletDRYGOODSNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CHF and ArryhtmiasDocument5 pagesDrugs For CHF and ArryhtmiasConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease DrugsDocument3 pagesIschemic Heart Disease DrugsRiyam WannasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Common Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitie S Brand NameDocument23 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Common Side Effects Nursing Responsibilitie S Brand NameJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Process: InjuryDocument19 pagesThe Nursing Process: InjuryJoanna BakNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document5 pagesWeek 5Joanna BakNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document5 pagesWeek 8Joanna BakNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document4 pagesWeek 7Joanna BakNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Maternal Physiology During PregnancyDocument139 pagesDefinition:: Maternal Physiology During PregnancygibreilNo ratings yet
- Haematology and Transfusion BSC Practise Questions 2012-2013Document3 pagesHaematology and Transfusion BSC Practise Questions 2012-2013Dinusha RajapakseNo ratings yet
- ER Clinical NotesDocument23 pagesER Clinical NotesmngaNo ratings yet
- Merging Result MergedDocument35 pagesMerging Result MergedEdmarie GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Hematology ReviewDocument4 pagesHematology ReviewAlfred ChowNo ratings yet
- Med Exam Physiology دفعة 40Document7 pagesMed Exam Physiology دفعة 40Khalid AlhemyariNo ratings yet
- URIT-610 User Manual-Coagulation AnalyzerDocument28 pagesURIT-610 User Manual-Coagulation Analyzeranhhp8x80% (5)
- Chapter 10Document29 pagesChapter 10MaskManNo ratings yet
- Anti Angina (Hany)Document51 pagesAnti Angina (Hany)Angga AhadiyatNo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting MechanismDocument19 pagesBlood Clotting Mechanismchinecheremstephanie2022No ratings yet
- Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders: An Update: Philippe de Moerloose, MD Alessandro Casini, MD Marguerite Neerman-Arbez, PHDDocument11 pagesCongenital Fibrinogen Disorders: An Update: Philippe de Moerloose, MD Alessandro Casini, MD Marguerite Neerman-Arbez, PHDadrianarjonaNo ratings yet
- (Prothrombin Time) : Intended UseDocument2 pages(Prothrombin Time) : Intended UseDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- 31 Coagulation Disorders in PregnancyDocument12 pages31 Coagulation Disorders in PregnancyParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- ThrombocytopeniaDocument12 pagesThrombocytopeniatantyNo ratings yet
- PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3 PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3: Pharmacy (San Pedro College) Pharmacy (San Pedro College)Document9 pagesPCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3 PCOL CV - Lecture Notes 3: Pharmacy (San Pedro College) Pharmacy (San Pedro College)Mhiel Bhon RamzNo ratings yet
- 2934 Hemochron ManualDocument32 pages2934 Hemochron ManualFrank QuitianNo ratings yet
- Hemostatic Abnormalities in Dogs With HemangiosarcomaDocument4 pagesHemostatic Abnormalities in Dogs With HemangiosarcomaAllana Valau MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Case Study ON: Blood DyscrasiaDocument40 pagesCase Study ON: Blood DyscrasiaJM RomiasNo ratings yet
- Liquicellin E: For APTT DeterminationDocument2 pagesLiquicellin E: For APTT Determinationm sdNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallDocument25 pagesMechanisms of Hemostasis - Contributions of Platelets, Coagulation Factors, and The Vessel WallelhierofanteNo ratings yet
- Functions and Properties of Blood - Plasma - Blood Cell Production - Erythrocytes - Blood Types - Leukocytes - Hemostasis (Stoppage of Bleeding)Document47 pagesFunctions and Properties of Blood - Plasma - Blood Cell Production - Erythrocytes - Blood Types - Leukocytes - Hemostasis (Stoppage of Bleeding)vanderphysNo ratings yet
- Animal Venoms in MedicineDocument9 pagesAnimal Venoms in MedicinelimperbiscuitNo ratings yet
- GRD121 The Blood S3 21-22Document71 pagesGRD121 The Blood S3 21-22ASHERNo ratings yet
- Rivaroxaban PresentationDocument13 pagesRivaroxaban PresentationReem El-HusseinyNo ratings yet
- Leiomyoma UteriDocument81 pagesLeiomyoma UteriLea Rose Dictaran Aronza100% (2)
- H P2T1Document5 pagesH P2T1mhik296No ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument36 pagesHemostasisPutri Rara BalernaPratiwiNo ratings yet