Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infografia Origen Petroleo INGLES V1
Infografia Origen Petroleo INGLES V1
Uploaded by
Neiser Olivares arevaloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infografia Origen Petroleo INGLES V1
Infografia Origen Petroleo INGLES V1
Uploaded by
Neiser Olivares arevaloCopyright:
Available Formats
Microscopic
organisms
Accumulation of silt
Ocean
Ocean
The origins Ocean
of oil
Caprock
Caprock
Petroleum
Reservoir rock
Reservoir rock Migration
Reservoir rock
Source rock
Source rock
The exploration, development and Source rock Source rock
Thermal flow
production of crude oil and natural gas
has become one of the main sources
of growth for Cepsa. At the start of the
1990s, the Company discovered the
RKF and Ourhoud oilfields in Algeria,
which provided a great boost to its SOURCE ROCK Reservoir rock CAPROCK Generation and
exploration and production activity. The source rock is a sedimentary rock, Hydrocarbons are found in porous rocks Migration
Cepsa currently operates in four usually composed of black clay with a called reservoir rocks, which, like a Caprock is an impermeable rock that Hydrocarbons are formed by the thermic
high concentration of organic matter sponge, absorb and release fluids. The impedes, like a barrier, any hydrocarbon transformation of the organic matter
continents and has a diverse portfolio through the remains of living organisms most common types of reservoir rocks moving up naturally to the surface. in the source rock. This organic mat-
of onshore, offshore, and deep offshore in the rock deposit including algae, are sandstone and carbonate rocks. ter begins to transform into oil and gas
fragments of land plants and more. The Reservoir rock is porous (the measure of
assets. presence of a source rock is an essential the holes or pores there are between the
when it is subjected to high tempera-
tures and pressure. After being pushed
requirement for the formation of grains of a rock), and permeable (liquid out from the source rock, the oil or gas
Through this infographic we explain hydrocarbons. If there is no source rock, can flow through the pores of a rock). flows (migrates) through a porous rock
there cannot be hydrocarbons either. (reservoir rock) into a geometric configu-
the origins of oil, the main source of ration known as a rock trap where it can
energy today. accumulate. This is covered by the im-
permeable caprock which stops it from
reaching the surface.
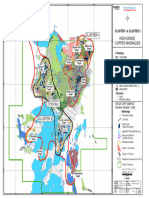
Petroleum System TRAPS
The exploration of hydrocarbons is principally based Traps are the geometric space in a porous, permeable rock (reservoir rock) where the hydrocarbons may be trapped.
on geological and geophysical techniques. Geology and There are different types of trap. The most common are structural traps (anticline fold faults or traps associated with
geophysics are essential sciences in this industry, and they normal faults), and stratigraphic traps.
are fundamental in predicting where potential sources of 1.000 m
hydrocarbons may be located.
Using geological principles and sophisticated and
costly geophysical techniques, explorers reconstruct
the geological history of an area and determine where
the elements and processes needed to produce an
accumulation of hydrocarbons may be. Petroleum
500 m
To do this, an explorer must determine the places where
over time the five elements and essential geological
processes for there to be an accumulation of hydrocarbons
may be.
ANTICLINE STRATIGRAPHIC NORMAL FAULT
Source rock Generation and migration Reservoir rock Trap Caprock Source rock Caprock Reservoir rock Trap
You might also like
- Referee Report DillonDocument2 pagesReferee Report DillonHaseeb AliNo ratings yet
- Isles of Shackles MapDocument1 pageIsles of Shackles MapClawsfingerNo ratings yet
- QLD Resources MapDocument1 pageQLD Resources MapS CollinsNo ratings yet
- 163 - OreOre Deposit Geology (John Ridley, 2013)Document3 pages163 - OreOre Deposit Geology (John Ridley, 2013)hugoluis_hNo ratings yet
- Underground Gravity Sewers Specification CVS02700 PDFDocument12 pagesUnderground Gravity Sewers Specification CVS02700 PDFNassim Sabri0% (1)
- LV Ph2020 - Bid Set - ArchitecturalDocument30 pagesLV Ph2020 - Bid Set - Architecturalart cafeNo ratings yet
- gsdmrb24 p1Document1 pagegsdmrb24 p1jackoNo ratings yet
- 01.overview ArcRelatedDeposits ClassificationDocument75 pages01.overview ArcRelatedDeposits ClassificationMull Mancunians PcgNo ratings yet
- Directions:: Igneous Granite, Basalt, Pumice, ObsidianDocument2 pagesDirections:: Igneous Granite, Basalt, Pumice, ObsidianyusurNo ratings yet
- Cotabambas Clusters JulyDocument1 pageCotabambas Clusters JulyEfani Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Basics On ExplorationDocument76 pagesBasics On Explorationlakhan Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Sedimentologi Batuan SedimenDocument49 pagesSedimentologi Batuan SedimenArdiyan SyhNo ratings yet
- MR DolkosDocument10 pagesMR DolkosÁlvaro Ramos Fustero100% (1)
- Key Facts: The Petroleum Story - From Fossils To FuelDocument3 pagesKey Facts: The Petroleum Story - From Fossils To FuelAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary RocksDocument41 pagesSedimentary RocksAhmad MasaroNo ratings yet
- Noatak Cape Krusenstern Gates of The Arctic: Beaufort SeaDocument2 pagesNoatak Cape Krusenstern Gates of The Arctic: Beaufort SeaWulfert IngliansNo ratings yet
- Bushveld Minerals Limited: Annual Report 2014Document50 pagesBushveld Minerals Limited: Annual Report 2014djokouwmNo ratings yet
- Lihir Fs PDFDocument1 pageLihir Fs PDFKaye ReiesNo ratings yet
- Petrolum System NE-JAVADocument37 pagesPetrolum System NE-JAVARyanuarBachtiarNo ratings yet
- Topic 6A - Sedimentary RocksDocument21 pagesTopic 6A - Sedimentary Rockssalwa aaNo ratings yet
- H3 LandscapeSeries Geology Climate and Hydrology 10-10-2016-1Document17 pagesH3 LandscapeSeries Geology Climate and Hydrology 10-10-2016-1inigo38No ratings yet
- Coal MozambiqueDocument11 pagesCoal MozambiqueKelvenNo ratings yet
- Source Rock Potential of The Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous Succession in The Southern Mesopotamian Basin, Southern IraqDocument18 pagesSource Rock Potential of The Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous Succession in The Southern Mesopotamian Basin, Southern IraqSanat AidarbayevNo ratings yet
- Geopedologi2021 - LDS - OreDeposits3 - Nickel LateriteDocument19 pagesGeopedologi2021 - LDS - OreDeposits3 - Nickel LateriteRidho FirdausmanNo ratings yet
- Mako Gold Mine: LOM AiscDocument2 pagesMako Gold Mine: LOM AiscAMADOUNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Reference TablesDocument15 pagesEarth Science Reference Tables83science100% (2)
- Hydrocarbon GeologyDocument30 pagesHydrocarbon Geologyemanuelemanuel9829No ratings yet
- Porphyry Deposits - Introduction Porphyry Deposits - CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesPorphyry Deposits - Introduction Porphyry Deposits - Characteristicscarlin1980No ratings yet
- Petroleum Blocks Atlas 2022Document88 pagesPetroleum Blocks Atlas 2022BAKALA IGNANGA VANESSANo ratings yet
- Combined Geology RamappaDocument1 pageCombined Geology RamappapankajNo ratings yet
- An Attempt To Determine The Age of Geological FracDocument9 pagesAn Attempt To Determine The Age of Geological FracVavachi vavaNo ratings yet
- NDX KoningDocument4 pagesNDX KoningFadly RozamuriNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento Rojas2018Document75 pagesSarmiento Rojas2018chris17tianNo ratings yet
- Namibia Critical Metals First Phase Drilling To Commence at Nambia Copper ProjectDocument1 pageNamibia Critical Metals First Phase Drilling To Commence at Nambia Copper ProjectJesusSalamancaNo ratings yet
- Log ResponsesDocument1 pageLog ResponsesHamza Lahbiben0% (1)
- Terminacion en Pozos de Gas ShaleDocument123 pagesTerminacion en Pozos de Gas ShalecesarherreragarzaNo ratings yet
- WK3 - Divergent MarginsDocument21 pagesWK3 - Divergent MarginsJames BowkettNo ratings yet
- GSM EuropePoster2009ADocument1 pageGSM EuropePoster2009AЖеня ТрииксаNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2020-06-16 at 8.58.11 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2020-06-16 at 8.58.11 PMm.curryNo ratings yet
- 01 A2 Atlantic SeaboardDocument2 pages01 A2 Atlantic SeaboardmapsinfosaNo ratings yet
- Lec5 Exploration-Geology-Overview Delr 20221022Document40 pagesLec5 Exploration-Geology-Overview Delr 20221022crystal deligeroNo ratings yet
- Kalgoorlie OperationDocument13 pagesKalgoorlie OperationHerman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Mapa Geotectonico2018Document1 pageMapa Geotectonico2018Francisco Pérez QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Arg Chile Aug 2009Document37 pagesArg Chile Aug 2009Santino AdroverNo ratings yet
- General - Cook Islands Cook IslandsDocument1 pageGeneral - Cook Islands Cook Islandswaleed yehiaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum System Definition: Elements ProcessesDocument29 pagesPetroleum System Definition: Elements ProcessesAlameen GandelaNo ratings yet
- Corrected 13's-15's Mult. WheelDocument3 pagesCorrected 13's-15's Mult. WheelmarloNo ratings yet
- Seaworld Abu Dhabi MapDocument1 pageSeaworld Abu Dhabi MapBinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Geoscience For Petroleum EngineersDocument39 pagesGeoscience For Petroleum EngineersStélio SalatielNo ratings yet
- And Their History: The CatacombsDocument2 pagesAnd Their History: The CatacombsPedro Martins SantosNo ratings yet
- Noamer 072838Document1 pageNoamer 072838Elaina MominNo ratings yet
- The Baguio Mineral District, A Giant Multi-Episodic Clustered Copper-Gold SystemDocument7 pagesThe Baguio Mineral District, A Giant Multi-Episodic Clustered Copper-Gold SystemajreateguicNo ratings yet
- GCP Alternatives 508 2019-04-04 LowDocument19 pagesGCP Alternatives 508 2019-04-04 LowtophermathewsNo ratings yet
- 8 JOANZ Group 1 ReportDocument3 pages8 JOANZ Group 1 ReportHannah ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Map LithiumDocument1 pageMap LithiumMatias AciarNo ratings yet
- Table of Density Values& Log ResponsesDocument1 pageTable of Density Values& Log Responsesgeo_mmsNo ratings yet
- Log ResponsesDocument1 pageLog ResponsesAy Oub BenNo ratings yet
- MDMW Zinc&Lead03Document2 pagesMDMW Zinc&Lead03miningnovaNo ratings yet
- Godrej Platinum Kolkata E BrochureDocument19 pagesGodrej Platinum Kolkata E BrochureplannersandadvisorsNo ratings yet
- Lecture PE2-1Document37 pagesLecture PE2-1mohammed sheikhNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Log Responses PDFDocument1 pageAtlas of Log Responses PDFFaizin Mulia RizkikaNo ratings yet
- 3D ConverterDocument3 pages3D ConverterFazlur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow 1Document6 pagesAbraham Maslow 1api-267620055No ratings yet
- Project Report On DYEING OF FabricsDocument2 pagesProject Report On DYEING OF FabricsChasity ColeNo ratings yet
- Surveying and MeasurementDocument51 pagesSurveying and MeasurementJireh GraceNo ratings yet
- Ten Lessons of Arabic Ver 2 1Document84 pagesTen Lessons of Arabic Ver 2 1asd12312350% (2)
- Newtec Mdm3100 On The Dialog PlatformDocument2 pagesNewtec Mdm3100 On The Dialog PlatformMahrus SyafiieNo ratings yet
- Business Guide 2020Document68 pagesBusiness Guide 2020Elenca KyweNo ratings yet
- Scientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23Document4 pagesScientix4 New Ambassadors T&C-Feb-23dada_dadyNo ratings yet
- Teaching Reading Lesson Plan 1Document2 pagesTeaching Reading Lesson Plan 1api-301343173No ratings yet
- Module No 1 :automobile Engineering (Mumbai University)Document78 pagesModule No 1 :automobile Engineering (Mumbai University)Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (4)
- Hilgard ErnestDocument29 pagesHilgard ErnestPhuong Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Self-Learning Module For BS Criminology Course Code: Cdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationDocument28 pagesA Self-Learning Module For BS Criminology Course Code: Cdi 6 Fire Technology and Arson InvestigationMelanie Garcia CanonizadoNo ratings yet
- Engleza Curs + Exam ExamplesDocument92 pagesEngleza Curs + Exam ExamplessebiNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment For MGT162Document9 pagesIndividual Assignment For MGT162Iyad AmeenNo ratings yet
- Cray Valley GuideDocument16 pagesCray Valley GuideAlejandro JassoNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument11 pagesAnnotated BibliographyTyler AyresNo ratings yet
- CH 13 WorkbookDocument12 pagesCH 13 Workbookapi-237586441No ratings yet
- Process Safety and Risk Management: 2. Visible Felt Leadership and Operating DisciplineDocument3 pagesProcess Safety and Risk Management: 2. Visible Felt Leadership and Operating DisciplineAbdul Hai MohammedNo ratings yet
- How Is Cheese MadeDocument7 pagesHow Is Cheese MadeAdrian Joel ColombetNo ratings yet
- Human CommunicationDocument13 pagesHuman Communicationbeyouty suitsNo ratings yet
- AP Honor List 2018Document2 pagesAP Honor List 2018Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Matiltan HPP (Vol-II A) Specs NTDCDocument258 pagesMatiltan HPP (Vol-II A) Specs NTDCsami ul haqNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report 20bcs1330Document48 pagesFinal Project Report 20bcs1330kiran kiruNo ratings yet
- Crop Improvement of WheatDocument24 pagesCrop Improvement of WheatRabeesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Crombie. The Writings of Origen. 1869. Volume 1.Document524 pagesCrombie. The Writings of Origen. 1869. Volume 1.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et Orientalis100% (1)
- 1138250-Into The Dragons Maw v3.00Document31 pages1138250-Into The Dragons Maw v3.00Jonathan ElsNo ratings yet
- The Power of Letting Go - Part OneDocument4 pagesThe Power of Letting Go - Part OneMichael CliftonNo ratings yet