Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Portfolio
Cell Portfolio
Uploaded by
Chhaya GuptaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Portfolio
Cell Portfolio
Uploaded by
Chhaya GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
CELL
S no. Topic Date
1 Cell 8th April
2 Cell 18th April
3 Cell 25th April
4 Cell 20th June
CELL
A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane.
Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living
matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and
other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks. Some single cells are
complete organisms, such as a bacterium or yeast. Others are specialized
building blocks of multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals.
These were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
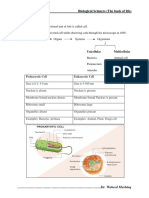
Animal cells
Eukaryotic Well defined
cells nucleus
Plant cells
Prokaryotic Not so well Bracterial
Cell cells defined cell
Singled
Unicellular Amoeba
celled
Multicellular Multicelled Humans
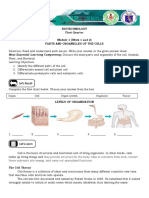
Structure of Cell
Nucleus Cytoplasm Organelles
Main Features of a Plant cell are: -
1) It has a rigid cell wall which
performs a very important
function of giving plant cell
turgidity
2) It’ s 70 – 90% of body is covered
by a vacuole which helps in
storage of various substances.
3) They lack centrioles.
4) They have chloroplast (plastids)
which are semi-autonomous in
nature.
Transport through Plasma Membrane Main Features of a Plant cell are: -
1) It lacks cell wall. So, it could change
it shape easily.
2) It generally has small sized
Processes vacuoles
3) They have centrioles which help it
to divide.
4) They lacks plastids.
5) Unlike plant cell lysosomes are
Physical present. Biological
6) Nucleus is generally is in centre
and often round.
Diffusion Osmosis Endocytosis Exocytosis
Endosmosis Exosmosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis
Osmosis Diffusion
Osmosis happens from a higher Diffusion happens from a higher
concentration of solvent to a concentration of solvent to a
lower concentration. But it only lower concentration. It could
happens when the solvent is happen with all states and it
water and through a semi- does not require any semi-
permeable membrane permeable membrane
A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is
a cell organelle that helps process and package
Organelles are suspended substances in the cytoplasm these
proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins
perform various functions inside the cell.
destined to be exported from the cell. Named
after its discoverer, Camillo Golgi, the Golgi body
appears as a series of stacked membranes.
Organelles
Ribosomes are specialized cell organelles and found in both
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Every living cell requires
ribosomes for the production of proteins.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a continuous
membrane system that forms a series of
flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of
eukaryotic cells and serves multiple
functions, being important particularly in
the synthesis, folding, modification, and
transport of proteins
A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle
that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are
involved with various cell processes. They may
Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell
organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that
generate most of the chemical energy needed to
power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical
energy produced by the mitochondria is stored
A chloroplast is an organelle within the cells of
in a small molecule called adenosine
plants and certain algae that is the site of
triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria contain their
photosynthesis, which is the process by which
energy from the Sun is converted into chemical
energy for growth.
A centrosome is a cellular structure involved in the
process of cell division. Before cell division, the
centrosome duplicates and then, as division
begins, the two centrosomes move to opposite
ends of the cell. Proteins called microtubules
assemble into a spindle between the two
centrosomes and help separate the replicated
chromosomes into the daughter cells.
A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle.
In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small
and help sequester waste products. In plant
cells, vacuoles help maintain water balance.
Sometimes a single vacuole can take up most
of the interior space of the plant cell.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two
or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a
larger cell cycle. Cell division in eukaryote is much more
complicated than prokaryote. Depending upon chromosomal
Cell Theory
number reduced or not; Eukaryotic cell divisions can be classified
as Mitosis (equational division) and Meiosis (reductional division).
A primitive form of cell division is also found which is called
amitosis.
Exceptions
You might also like
- Cell Biology Illustrated ReportDocument21 pagesCell Biology Illustrated ReportIlze Krauze100% (11)
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapPramod Jaiswal81% (21)
- The Venn Diagram Below Shows The Number of Grade 4 Students Who Joined The MathDocument2 pagesThe Venn Diagram Below Shows The Number of Grade 4 Students Who Joined The MathSri WirapatniNo ratings yet
- Thodukuri SastramDocument30 pagesThodukuri Sastramkaushi0% (1)
- 1 Cell Biology PDFDocument29 pages1 Cell Biology PDFRashad AlamNo ratings yet
- Sudha Chandran: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesSudha Chandran: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBrightway ComputersNo ratings yet
- Types of Placenta: VAN-608 EmbryologyDocument16 pagesTypes of Placenta: VAN-608 Embryologymuqadar khanNo ratings yet
- +2MATHS+DrKT+ 5M-Q - (2023-24)Document3 pages+2MATHS+DrKT+ 5M-Q - (2023-24)harishsuriya1986No ratings yet
- Ennavale Adi Ennavale PDFDocument1 pageEnnavale Adi Ennavale PDFAnton Dias33% (3)
- ILearnCANA - November Vol 4Document63 pagesILearnCANA - November Vol 4rahulNo ratings yet
- Gem Industry in Sri LankaDocument16 pagesGem Industry in Sri LankaDon Dilan Buddhika100% (1)
- அதிக ஆற்றல் வாய்ந்த மனிதர்களின் 7 பழக்கங்கள்Document1,558 pagesஅதிக ஆற்றல் வாய்ந்த மனிதர்களின் 7 பழக்கங்கள்Varadarajan Narasimhan100% (1)
- Employment Notification Lic Aao 2013Document9 pagesEmployment Notification Lic Aao 2013Rohit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Irumbile Oru IruthayamDocument14 pagesIrumbile Oru IruthayamNRAJ0% (2)
- Raja RaniDocument58 pagesRaja Ranikingsley_psb100% (1)
- Human Body RubricDocument2 pagesHuman Body Rubricapi-262892467No ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- The Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONDocument48 pagesThe Cell Structure & Fxns FOR OBSERVATIONAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Bio 221 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesBio 221 Lecture NotesMuhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- 1 The CellDocument75 pages1 The CelllorenzegeneblaNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- Act 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportDocument8 pagesAct 3 The Plant Cell - Laboratory ReportRicky SalazarNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L5 NIADocument31 pagesBio 103 L5 NIAsubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesRahul ManhasNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 5Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 5shinyy566No ratings yet
- Sample AssignmentDocument4 pagesSample Assignmentmuhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Botany Full PDF EMDocument72 pagesBotany Full PDF EMAbinaya PalaniNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDocument6 pagesAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Basis of LifeDocument17 pagesThe Basis of LifeKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- Cell Grade 7Document65 pagesCell Grade 7SUDARAT THONGPHAYONGNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument45 pagesCELLKimberly Clarisse VegaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Module I-Cocepts in BiologyDocument46 pagesModule I-Cocepts in BiologyManan MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- What Are CellsHS PDFDocument12 pagesWhat Are CellsHS PDFIbrahim SiddigNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Biochem The Celleluar Basis of LifeDocument21 pagesBiochem The Celleluar Basis of Lifealmira garciaNo ratings yet
- Found-1 Science NotesDocument15 pagesFound-1 Science NotesSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionFahim Abid100% (1)
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDocument9 pagesPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument23 pagesCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science BDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomNo ratings yet
- Dr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangDocument90 pagesDr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangFaridNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 6th LectureDocument37 pagesBIO 001 6th LectureManuelNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio Exam ReviewerMarlon JonasNo ratings yet
- On BrazilDocument22 pagesOn BrazilChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- On BrazilDocument22 pagesOn BrazilChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- S.S.T PoorviDocument4 pagesS.S.T PoorviChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Science PoorviDocument3 pagesScience PoorviChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Tempest Ariel MonologueDocument2 pagesThe Tempest Ariel MonologueChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Revision Class Timetable Class 4 &5Document1 pageRevision Class Timetable Class 4 &5Chhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- MypartDocument4 pagesMypartChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- House AssemblyDocument1 pageHouse AssemblyChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- English PlayDocument1 pageEnglish PlayChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall Ill - Part IiDocument12 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill - Part IiChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall Ill - Part IDocument15 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill - Part IChhaya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Inflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueDocument3 pagesInflammation & Healing of Soft & Hard TissueLakshita PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Grading MENINGIOMADocument11 pagesGrading MENINGIOMAnurul fardillahNo ratings yet
- (Chenoa L) Unit 1 Review Drop & DragDocument10 pages(Chenoa L) Unit 1 Review Drop & DragChenoa LocklearNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentJoy PanesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Remedial AnsweranDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Remedial AnsweranJoviNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ThesisDocument5 pagesBone Marrow Thesisjennifermowerwestvalleycity100% (2)
- Intercellular Junctions: Alan S. L. Yu, Fiona Hanner and Ja Nos Peti-PeterdiDocument1 pageIntercellular Junctions: Alan S. L. Yu, Fiona Hanner and Ja Nos Peti-PeterdiaaaatniNo ratings yet
- 9bio AssignmentDocument2 pages9bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument8 pagesAnatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfpka25No ratings yet
- Biologi Molekuler - Lipid BilayerDocument1 pageBiologi Molekuler - Lipid BilayerCinsy PaskalineNo ratings yet
- Plant Cytoskeleton PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Cytoskeleton PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Histo Lab Exercise #2Document6 pagesHisto Lab Exercise #2Gela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Bio9 r2Document1 pageBio9 r2M Usama AnsaryNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Chapter 1Document8 pagesBiology VCE Chapter 1Rachel JNo ratings yet
- Isbb FC Part 3Document13 pagesIsbb FC Part 3Lynther Myle Arizo100% (1)
- DHA Policy On Health Information Asset Management PDFDocument65 pagesDHA Policy On Health Information Asset Management PDFcyril bennyNo ratings yet
- Locomotary Organelles in ProtozoaDocument25 pagesLocomotary Organelles in Protozoaashley clintonNo ratings yet
- 2018 Bookmatter PlantAnatomy PDFDocument15 pages2018 Bookmatter PlantAnatomy PDFmichaelaapilat026No ratings yet
- L2 Introduction To HematologyDocument3 pagesL2 Introduction To HematologyJamil LausNo ratings yet
- Bio 14 NotesDocument5 pagesBio 14 Noteshey lungNo ratings yet
- 280754 - 5. MUSCULAR SYSTEM 59 ใช้สอนDocument29 pages280754 - 5. MUSCULAR SYSTEM 59 ใช้สอนEngkarat BuakeawNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Muscular System BrochureDocument2 pagesAnatomy Muscular System Brochureapi-462608096No ratings yet
- Micropara 2nd Laboratory PDFDocument6 pagesMicropara 2nd Laboratory PDFLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Biology IXDocument89 pagesBiology IXKanchan SawantNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 6Document4 pagesBiology Notes Class 6Prashant JainNo ratings yet
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Seeleys Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition by Seeley PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Seeleys Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition by Seeley PDF Full Chapterremovaltinemangkvk100% (25)
- Reticulocyte CountDocument25 pagesReticulocyte CountMahmoud RamlawiNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping SystemDocument3 pagesBlood Grouping SystemCharmaine Gorge DangsiNo ratings yet
- Biological Membranes 1 QPDocument12 pagesBiological Membranes 1 QParvibainNo ratings yet