Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding The Operation Process in Wire Edm
Understanding The Operation Process in Wire Edm
Uploaded by
ag cnc & wedm machining shop0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThe document summarizes the 7 stages of the wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) process:
1) Ions in the water between the wire and workpiece form bridges as voltage creates a magnetic field.
2) A spark flashes across the gap as resistance drops, vaporizing material.
3) Pressure from the spark's expansion and the fluid's resistance creates heat and pressure to liquefy materials.
4) Most liquefied material forms a hollow sphere that cools and is washed away, creating a crater with recast layers.
Original Description:
Original Title
UNDERSTANDING%20THE%20OPERATION%20PROCESS%20IN%20WIRE%20EDM (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the 7 stages of the wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) process:
1) Ions in the water between the wire and workpiece form bridges as voltage creates a magnetic field.
2) A spark flashes across the gap as resistance drops, vaporizing material.
3) Pressure from the spark's expansion and the fluid's resistance creates heat and pressure to liquefy materials.
4) Most liquefied material forms a hollow sphere that cools and is washed away, creating a crater with recast layers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageUnderstanding The Operation Process in Wire Edm
Understanding The Operation Process in Wire Edm
Uploaded by
ag cnc & wedm machining shopThe document summarizes the 7 stages of the wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) process:
1) Ions in the water between the wire and workpiece form bridges as voltage creates a magnetic field.
2) A spark flashes across the gap as resistance drops, vaporizing material.
3) Pressure from the spark's expansion and the fluid's resistance creates heat and pressure to liquefy materials.
4) Most liquefied material forms a hollow sphere that cools and is washed away, creating a crater with recast layers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
UNDERSTANDING THE OPERATION
A Technical Publication for your
TECHNEWS
TITLE
PROCESS IN WIRE EDM
Shown below is a step by step layout of how Wire EDM process functions.
Individual Spark Detail
Stage 1 - Ions in the
Table water between the wire
and workpiece.
Table Table
Mitsubishi or Ingersoll EDM
Stage 2 - Open voltage
creates a magnetic field
between the wire and
the workpiece, forcing the
ions to condense into Stage 3 - As resistance
bridges across the gap. drops below the thresh-
As the bridges become old, current (a spark)
more dense, resistance flashes across the gap,
begins to drop. vaporizing a portion of
both the wire and the
workpiece.
Stage 4 - Current con-
tinues to flow across
the gap creating a
massive expansion of
pressure. The fluid Stage 5 - At the
initiation of offtime, the
resists the expansion
heat and pressure source
creating a high pres- is removed, creating an
sure area around the implosion. The liquefied
spark. With the heat material is then sucked
and pressure, the into the vacuum toward
materials (wire and the center of the gap.
metal) break down and
start to boil.
Stage 6 - Most of the WHITE
liquefied material forms
a small hollow sphere LAYER Stage 7 - As the fluid
where it cools, solidifies, cools the area of the
and is washed away spark, the remaining liq-
between sparks. uefied material cools and
resolidifies into the crater,
creating what is known as
recast. Recast consists of
two separate layers: the
Heat Affected Zone and
GENERAL INOFMATION
the White Layer.
HEAT
AFFECTED
PARENT ZONE
MATERIAL
You might also like
- VM1 PLWD r02x2-304Document241 pagesVM1 PLWD r02x2-304ag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Mean Life Time of Cosmic Ray MuonDocument16 pagesMean Life Time of Cosmic Ray Muontaimur_usna100% (1)
- Standards For MV Switchgear Rated For Arc Flash Protection - ABBDocument5 pagesStandards For MV Switchgear Rated For Arc Flash Protection - ABB64107955No ratings yet
- Fins PDFDocument4 pagesFins PDFJin PingNo ratings yet
- PMR Article Plansee 2018Document15 pagesPMR Article Plansee 2018Shariful IslamNo ratings yet
- Spark Plasma Sintering - FundamentalsDocument35 pagesSpark Plasma Sintering - FundamentalsApurv Salunke100% (1)
- Flash Butt Welding 1Document9 pagesFlash Butt Welding 1SamanthaPereraNo ratings yet
- Sa02000001e 150 PDFDocument2 pagesSa02000001e 150 PDFMuhammad FaqihNo ratings yet
- MEEN744 Week7M S2023Document16 pagesMEEN744 Week7M S2023Sameer OsmanNo ratings yet
- The Voice Coil (Part 1) : Parts and ProductionDocument5 pagesThe Voice Coil (Part 1) : Parts and ProductionMallickarjuna A.SNo ratings yet
- Why The Operation Failure of High Breaking Capacity Fuses Is So Frequent?Document5 pagesWhy The Operation Failure of High Breaking Capacity Fuses Is So Frequent?BalusamyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Runaway Initiation of Large Prismatic CellsDocument16 pagesThermal Runaway Initiation of Large Prismatic Cellssm.shahabul64No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Welding 2009Document21 pagesUltrasonic Welding 2009Rodrigo Toasa100% (1)
- Perpendicular Magnetic Recording Technology: Roger Wood, Yimin Hsu, Marilee SchultzDocument4 pagesPerpendicular Magnetic Recording Technology: Roger Wood, Yimin Hsu, Marilee Schultzvirtualraidz.comNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Resistance WeldingDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Resistance Weldingvui01No ratings yet
- Relazione 1 WordDocument7 pagesRelazione 1 WordGiulia GiuffridaNo ratings yet
- What Is Partial Discharge - BasicsDocument153 pagesWhat Is Partial Discharge - BasicsAries d100% (6)
- Evaporation of Difficult Products: Processing ChemicalDocument4 pagesEvaporation of Difficult Products: Processing ChemicalmisaelNo ratings yet
- Ennio Mognato - ShortDocument7 pagesEnnio Mognato - ShortKhurshed Alam IndiaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of A Silicon-Pyrex-Silicon Stack by A.C. Anodic BondingDocument6 pagesFabrication of A Silicon-Pyrex-Silicon Stack by A.C. Anodic BondingPuneet ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 3.5.1 Observation of Electrical Breakdown and FailureDocument4 pages3.5.1 Observation of Electrical Breakdown and FailureValeria Orannel Lopez MorilloNo ratings yet
- Cross-Sectional STM Study of InAs Quantum Dots For Laser Devices (Surface and Interface Analysis, Vol. 27, Issue 5-6) (1999)Document6 pagesCross-Sectional STM Study of InAs Quantum Dots For Laser Devices (Surface and Interface Analysis, Vol. 27, Issue 5-6) (1999)sepot24093No ratings yet
- Surface Engineering TypesDocument5 pagesSurface Engineering TypesMatthew CurmiNo ratings yet
- Resistance Welding FundamentalsDocument8 pagesResistance Welding FundamentalsAek JayNo ratings yet
- Sohrabji Godrej Green Business Center: Case StudyDocument8 pagesSohrabji Godrej Green Business Center: Case StudyShivani KothawadeNo ratings yet
- Termografía BasicaDocument4 pagesTermografía BasicaPablo BentancurNo ratings yet
- (2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayDocument4 pages(2014) (Longtin Et Al) Sensors For Harsh Enviroments by Direct Write Thermal SprayRenkuReNo ratings yet
- Camesa TechBulletin-021 PDFDocument2 pagesCamesa TechBulletin-021 PDFDmz FreakzNo ratings yet
- Heeg 2011Document8 pagesHeeg 2011bensNo ratings yet
- Nanoscale Coating-PVDDocument60 pagesNanoscale Coating-PVDAli ErarslanNo ratings yet
- 0032 5910 (73) 80021 X PDFDocument15 pages0032 5910 (73) 80021 X PDFaghilifNo ratings yet
- BilletCooler Oval Cone Techn Datenblatt Lechler GBDocument2 pagesBilletCooler Oval Cone Techn Datenblatt Lechler GBKoushik RayNo ratings yet
- Insulation Co-Ordination of Power SystemDocument43 pagesInsulation Co-Ordination of Power SystemFaisal MagsiNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation: Thermal Probe Maskless LithographyDocument4 pagesPaper Presentation: Thermal Probe Maskless LithographyANJUNo ratings yet
- Fundemental Principes of Working in Resonant ConveDocument6 pagesFundemental Principes of Working in Resonant Convejawali supriyoNo ratings yet
- SweepsDocument1 pageSweepsSimran UtwalNo ratings yet
- 05115G Sample BuyNow PDFDocument8 pages05115G Sample BuyNow PDFEdwar Villavicencio JaimesNo ratings yet
- Icrosystems Ngineering: Dr.-Ing. Ronny GerbachDocument24 pagesIcrosystems Ngineering: Dr.-Ing. Ronny GerbachRahul ReddyNo ratings yet
- Maz Umder 1982Document9 pagesMaz Umder 1982Alejandra PradoNo ratings yet
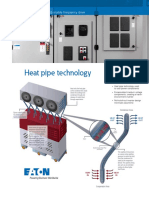
- Understanding Impedance HeatingDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Impedance HeatingMarco SilvaNo ratings yet
- Do More With Less: PARTIAL DISCHARGE: PD, Common in Air-Cooled Stator Windings, Is Not Well Understood at The Plant LevelDocument4 pagesDo More With Less: PARTIAL DISCHARGE: PD, Common in Air-Cooled Stator Windings, Is Not Well Understood at The Plant LevelAnonymous 1AAjd0No ratings yet
- Study of Surface Properties of Molten Tin, Exposed To Air Up To 600 KDocument15 pagesStudy of Surface Properties of Molten Tin, Exposed To Air Up To 600 KPlamen PetkovNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Work - ECE021Document10 pagesReview of Related Work - ECE021jonalie anne ferrerNo ratings yet
- Robert Gleichman Lyondell-Citgo Refining LP: Failure Modes and Field Testing Medium Voltage Motor WindingsDocument4 pagesRobert Gleichman Lyondell-Citgo Refining LP: Failure Modes and Field Testing Medium Voltage Motor WindingsMayurNo ratings yet
- Failure Reasons For InsulationsDocument7 pagesFailure Reasons For InsulationsjovenlouNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Cloud Chamber: Background InformationDocument3 pagesDiffusion Cloud Chamber: Background Informationraydio 4No ratings yet
- Ttrans Therm EnergyDocument1 pageTtrans Therm EnergyZafirah SuffianNo ratings yet
- Polarity Charge 11Document4 pagesPolarity Charge 11Deepu MishraNo ratings yet
- Glow Discharge in Sputtering PDFDocument8 pagesGlow Discharge in Sputtering PDFRaja Pathamuthu.GNo ratings yet
- Super Power Gadget Thermal BlastDocument1 pageSuper Power Gadget Thermal BlastRamersote YTNo ratings yet
- Of Metallurgical and Metalworking Terms 43: GlossaryDocument14 pagesOf Metallurgical and Metalworking Terms 43: GlossaryKasia MazurNo ratings yet
- A333 Revision Notes (P1-P13)Document61 pagesA333 Revision Notes (P1-P13)Prakkash RajantheranNo ratings yet
- Nonvolatile, High Density, High Performance Phase Change MemoryDocument8 pagesNonvolatile, High Density, High Performance Phase Change MemorySoumyadeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- Surface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)Document19 pagesSurface Engineering of Nanomaterials: Lecture 12: Physical Vapour Deposition (PVD)hrana287No ratings yet
- Sequential Lamination in PCBsDocument3 pagesSequential Lamination in PCBsmasoudsadNo ratings yet
- Section 2.4 - Lightning EarthDocument3 pagesSection 2.4 - Lightning EarthyosriNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques in PhysicsDocument41 pagesExperimental Techniques in PhysicsTejinder SinghNo ratings yet
- NSE - 847 Essentials of NEMS/MEMS: in The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most MercifulDocument35 pagesNSE - 847 Essentials of NEMS/MEMS: in The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most MercifulBahroz RashidNo ratings yet
- Poster Iccf 23 Direct ConversionDocument2 pagesPoster Iccf 23 Direct ConversionFabrice DavidNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument22 pagesUnit IiMagambo Sahiil MorisNo ratings yet
- Part Design Specification: Spring 2011 Dr. R. A. WyskDocument52 pagesPart Design Specification: Spring 2011 Dr. R. A. Wyskag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- From Design To Inspection: The Use of GDT For Predictable AssemblyDocument19 pagesFrom Design To Inspection: The Use of GDT For Predictable Assemblyag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- A Series Software Loading Instruction ManualDocument12 pagesA Series Software Loading Instruction Manualag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Ra Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 12 - ApplicationsDocument33 pagesRa Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 12 - Applicationsag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- MD+PRO Series STD Cu 12wDocument20 pagesMD+PRO Series STD Cu 12wag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- The Best Time You'Ve Ever SpentDocument41 pagesThe Best Time You'Ve Ever Spentag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Ra Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 4 - MaintenanceDocument53 pagesRa Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 4 - Maintenanceag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- MD+PRO Series STD WC 10wDocument19 pagesMD+PRO Series STD WC 10wag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- MD+PRO Series Land Steel 8wDocument19 pagesMD+PRO Series Land Steel 8wag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- MD+PRO Series SPD Steel 10wDocument19 pagesMD+PRO Series SPD Steel 10wag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- MD+PRO SeriesDocument3 pagesMD+PRO Seriesag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Ra Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 1 - ScreensDocument33 pagesRa Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 1 - Screensag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Ra Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 7 - ProgramDocument15 pagesRa Qa Fa Series Training - Chap 7 - Programag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice Series 02 Vertical Milling in The Home WorkshopDocument49 pagesWorkshop Practice Series 02 Vertical Milling in The Home Workshopag cnc & wedm machining shopNo ratings yet
- Physics I ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics I ProblemsbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is The Second Law of Thermodynamics?Document7 pagesTop 50 Mechanical Engineering Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is The Second Law of Thermodynamics?Aslam AzeezNo ratings yet
- Main Af Form 1458 Daily Steam Plant Operating LogDocument2 pagesMain Af Form 1458 Daily Steam Plant Operating LogRitche Lim BragaisNo ratings yet
- SH∕T 3503-2017 石油化工建设工程项目交工技术文件规定 非正式版Document457 pagesSH∕T 3503-2017 石油化工建设工程项目交工技术文件规定 非正式版陈俊松No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledلازلت احلمNo ratings yet
- To Comparative Study of Different HSLA Grade of Steel: A Project ReportDocument21 pagesTo Comparative Study of Different HSLA Grade of Steel: A Project ReportKamlesh RanaNo ratings yet
- ASE301 Part1Document70 pagesASE301 Part1Sahil KaushalNo ratings yet
- Piping S1Document44 pagesPiping S1Rajkumar ANo ratings yet
- Title: Experiment 3: Investigating Cell Membrane Permeability Using Tumeric (Curcuma Longa)Document5 pagesTitle: Experiment 3: Investigating Cell Membrane Permeability Using Tumeric (Curcuma Longa)Elden TojukaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of the α, β, And γ Relaxations in PolychlorotrifluoroethyleneDocument63 pagesAnalysis of the α, β, And γ Relaxations in PolychlorotrifluoroethylenezakariiNo ratings yet
- Numerical and Experimental Study of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine at Different Number of BladeDocument9 pagesNumerical and Experimental Study of Gravitational Water Vortex Turbine at Different Number of BladeBung HaFiedNo ratings yet
- Schaum Physical ChemistryDocument513 pagesSchaum Physical ChemistryRishabh Kumar100% (2)
- Presentation ON Minerals: Submitted By:Shubham Gupta Submitted To:Mr. Rajesh Bijalwan SirDocument8 pagesPresentation ON Minerals: Submitted By:Shubham Gupta Submitted To:Mr. Rajesh Bijalwan SirTitiksha NegiNo ratings yet
- 08-BHS IntroDocument28 pages08-BHS IntroĐẠT TRẦNNo ratings yet
- Engineering Structures: Melina Bosco, Giovanna A.F. Ferrara, Aurelio Ghersi, Edoardo M. Marino, Pier Paolo RossiDocument15 pagesEngineering Structures: Melina Bosco, Giovanna A.F. Ferrara, Aurelio Ghersi, Edoardo M. Marino, Pier Paolo RossimohamedNo ratings yet
- 10march - Grade 6 - Test PDFDocument27 pages10march - Grade 6 - Test PDFEron Roi Centina-gacutanNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: St. Joseph's Residential SchoolDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: St. Joseph's Residential SchoolDivydarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesDocument10 pages1.5 Analysing Interference of WavesCik Rokiah GhaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 7 Plate TectonicsDocument10 pagesLab Activity 7 Plate TectonicskleinkeaNo ratings yet
- CBSE+9+Umang +force+&+laws+of+motion+in+1+shotDocument105 pagesCBSE+9+Umang +force+&+laws+of+motion+in+1+shotDushyant Singh100% (1)
- Installation and Instruction Manual: Alfa Laval Copenhagen A/SDocument242 pagesInstallation and Instruction Manual: Alfa Laval Copenhagen A/SKunpeng ZhouNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Results and DiscussionDocument17 pagesChapter-5 Results and DiscussionSunil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Resolution of Forces 2021Document43 pages1.2 Resolution of Forces 2021faisalazah85No ratings yet
- FMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDocument13 pagesFMHM GTU Study Material E-Notes Unit-2 04042021064559PMDarshana GajjarNo ratings yet
- VRV Condensing UnitDocument24 pagesVRV Condensing UnitLeo NgNo ratings yet
- 18-SAMSS-493 - Two Part Polyurethane Duct SealantDocument5 pages18-SAMSS-493 - Two Part Polyurethane Duct Sealantmedication abbasNo ratings yet
- The Ocean CurrentsDocument10 pagesThe Ocean CurrentsAdiNo ratings yet
- CIG WELD Deposition Rate PDFDocument7 pagesCIG WELD Deposition Rate PDFgitaNo ratings yet