Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Uploaded by
Maria AnnaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Weather and Climate - WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeather and Climate - Worksheetlavender2x2100% (1)
- Plate Tectonics ExamDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics ExamFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3: Week 7 Learning Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesScience: Quarter 3: Week 7 Learning Activity SheetsFrances DatuinNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsBhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Earth Science ADM New Module Format Q2 Module 1 4 32 PAGESDocument32 pagesFINAL - Earth Science ADM New Module Format Q2 Module 1 4 32 PAGESEarl Lawrence IbanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity in Science Quarter 4 - Module 1: Soil - Its Types and CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesLearning Activity in Science Quarter 4 - Module 1: Soil - Its Types and CharacteristicsETHEL WENCESLAONo ratings yet
- Coriolis Effect and Water and Ocean Currents MAPDocument5 pagesCoriolis Effect and Water and Ocean Currents MAPkaseljie lcNo ratings yet
- Ocean Current Activities WSDocument11 pagesOcean Current Activities WSTelang BayawakNo ratings yet
- Science-7 SLM Q4 M2 W2 V1.0-CC-released-24May2021Document15 pagesScience-7 SLM Q4 M2 W2 V1.0-CC-released-24May2021John Lynard ViescaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Plate MovementsDocument60 pagesCauses of Plate MovementsnoliNo ratings yet
- G101ST QuarterDocument21 pagesG101ST QuarterEm EmNo ratings yet
- DLLDocument2 pagesDLLMarjorie Brondo100% (1)
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologyLelouch BritaniaNo ratings yet
- Types of MountainsDocument37 pagesTypes of MountainsRoslan Mansur100% (1)
- DLL-earth-and-life - 4Document4 pagesDLL-earth-and-life - 4Marilla ReybethNo ratings yet
- PR 3 PDFDocument17 pagesPR 3 PDFEdieson Jave CunananNo ratings yet
- DIVERGENT BOUNDARY (Divergence of Plates) Divergent Boundaries Occur When Two PlatesDocument5 pagesDIVERGENT BOUNDARY (Divergence of Plates) Divergent Boundaries Occur When Two Platesdaisy sorianoNo ratings yet
- Exogenic and Endogenic ProcessesDocument32 pagesExogenic and Endogenic ProcessesElss ToonNo ratings yet
- Nature Activities Binder Variant PurpleDocument21 pagesNature Activities Binder Variant PurpleAngel Kate PolitudNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesEarth and Life ScienceAlexander LoyloyNo ratings yet
- 1 Summative Test Science 10Document3 pages1 Summative Test Science 10kimjay languitaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesScience 10 Worksheet 2Washima Bentulina SabtalNo ratings yet
- World Time ZonesDocument1 pageWorld Time ZonesAnastasia Sazonova0% (1)
- Science 10 First QuarterDocument86 pagesScience 10 First QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIANNo ratings yet
- Earthquake QuizDocument4 pagesEarthquake QuizMary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Solotsolot National High School 300081 Earth & Life Science 1 Quarter, 1 Semester Summative Test #3Document3 pagesSolotsolot National High School 300081 Earth & Life Science 1 Quarter, 1 Semester Summative Test #3KENNEDY VAGAYNo ratings yet
- Cot WeatheringDocument7 pagesCot WeatheringMea Joy Dalogdog100% (1)
- G7Q4LAS2W2Document6 pagesG7Q4LAS2W2Hazel RecañaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 7Document12 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 7Lucy Jhamaicka Maruquin Ili100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonicsapi-330049903No ratings yet
- Seafloor Spreading ActivityDocument3 pagesSeafloor Spreading ActivityFrancheska McHaleNo ratings yet
- Science7, q4, Week2 (Validated)Document12 pagesScience7, q4, Week2 (Validated)Gary DiazNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Summative Test First Quarter Grade 10 - ScienceDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Summative Test First Quarter Grade 10 - ScienceChai BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Q1ST1Document3 pagesQ1ST1Des Carbonilla100% (1)
- Climate Change - Demo TeachingDocument54 pagesClimate Change - Demo TeachingPhean ArañoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic: Science 9 Quarter 1 Worksheet 1Document4 pagesPlate Tectonic: Science 9 Quarter 1 Worksheet 1JaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Session Guide. 2Document39 pagesModule 1 Session Guide. 2RJ SemeñaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect ClimateDocument71 pagesFactors That Affect ClimateChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson 7&8Document6 pagesEarthsci Lesson 7&8Dalope CstrNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Earth N SpaceDocument5 pages4th Summative Test Earth N SpaceAbigail Fernandez BatallerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesNoeljaysel AlejoNo ratings yet
- Service Quality of Student Dormitories in MEUEDocument11 pagesService Quality of Student Dormitories in MEUEKhin Sandar TunNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q4 Slem 2 - Earths Resources PDFDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Q4 Slem 2 - Earths Resources PDFEdwin RatioNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesSyllabus Earth and Life ScienceAligora JoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT MetamorphismDocument4 pagesHANDOUT MetamorphismHow Ever100% (1)
- Land and Sea Breeze WorksheetDocument2 pagesLand and Sea Breeze Worksheetmark joseph cometa100% (1)
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJACKSON SANDERS-PUGHNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory NotesDocument3 pagesContinental Drift Theory NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Exam - Earth and Life Science Set ADocument4 pagesExam - Earth and Life Science Set AHester Ann BionaNo ratings yet
- TOS (1stPT)Document2 pagesTOS (1stPT)Sally Pocamas100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument18 pagesPlate TectonicsNinni SinghNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EpicenterDocument29 pagesEarthquake Epicenterhuangrenjun'svoicecrackNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Rock CycleDocument14 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Rock CycleDanika Mae PondangNo ratings yet
- Human Activities and Their Impact On The EnvironmentDocument58 pagesHuman Activities and Their Impact On The Environmentrorlando lewis100% (1)
- Science 10 q1 WK 8 Version 2.1 1Document16 pagesScience 10 q1 WK 8 Version 2.1 1Via Jean AmboNo ratings yet
- Earth - S Seasons Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesEarth - S Seasons Practice Worksheetstephanie grace canonce100% (1)
- Las Science 8 Melc 2 q2 Week-2Document7 pagesLas Science 8 Melc 2 q2 Week-2Tonepher CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Document43 pagesReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science Week 3Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 3Frenny0% (1)
- Earth Science: Quarter 1: Modules 1-4Document32 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 1: Modules 1-4Maria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Black Yellow Recognition CertificateDocument1 pageBlack Yellow Recognition CertificateMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Science - Learning-Activity-Worksheets-8 PagesDocument8 pagesScience - Learning-Activity-Worksheets-8 PagesMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument44 pagesElectron ConfigurationMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheets 3 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 11Document8 pagesLearning Activity Worksheets 3 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 11Maria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Day 8 Empirical Formula Molecular FormulasDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Day 8 Empirical Formula Molecular FormulasMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Relative DatingDocument8 pagesRelative DatingAnnEviteNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan On 3 Types of RocksDocument4 pages5e Lesson Plan On 3 Types of Rocksapi-38497353267% (3)
- Types of RockDocument21 pagesTypes of RockFain AloyanNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Document10 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ebe 2015 Pillay KDocument200 pagesThesis Ebe 2015 Pillay KPesanai GaranowakoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 StoneDocument47 pagesLecture 4 StoneMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Mineral Section DataDocument56 pagesMineral Section DataMuplihan Komi TararapNo ratings yet
- Rock Webquest All RocksDocument3 pagesRock Webquest All Rocksapi-268569185100% (1)
- 6 - Metamorphic RocksDocument50 pages6 - Metamorphic Rocksloralara100% (1)
- Gess 202Document5 pagesGess 202api-309501342No ratings yet
- TOS Earth & Life Science - Mid Term ExamDocument7 pagesTOS Earth & Life Science - Mid Term ExamKemberly Semaña Penton100% (2)
- Our Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its UsesDocument217 pagesOur Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its Useslelo2k3100% (1)
- 150 Top Most Building Materials and CONSTRUCTION Interview Questions - Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument44 pages150 Top Most Building Materials and CONSTRUCTION Interview Questions - Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersAbdulrahman JawdatNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet RocksDocument3 pagesRevision Sheet Rocksmofid monirNo ratings yet
- Hunt Cut Set Gems LapidaryDocument15 pagesHunt Cut Set Gems LapidaryAlina Margarit50% (2)
- Rocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation GCSE IGCSE Environmental Management Geography 0680Document54 pagesRocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation GCSE IGCSE Environmental Management Geography 0680IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (2)
- Bsi Recommended PracticesDocument31 pagesBsi Recommended PracticesKimon ZagkourisNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks by JDDocument123 pagesMinerals and Rocks by JDShaniah TorrefloresNo ratings yet
- Sandstone Thin Section StudyDocument7 pagesSandstone Thin Section StudyIjlal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Casquet 2014Document15 pagesCasquet 2014Lucas ContalbaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument13 pagesCritical ThinkingmfhfhfNo ratings yet
- Els Week 2Document45 pagesEls Week 2Paolin Pearl Ortiola Rapisura40% (5)
- Metamorphic Phase Equilibria and Presure-Temperature-Time-PathsDocument823 pagesMetamorphic Phase Equilibria and Presure-Temperature-Time-PathsPaola TraslaviñaNo ratings yet
- Identification of Rocks and Minerals PDFDocument22 pagesIdentification of Rocks and Minerals PDFIkhwan Z.80% (15)
- Metamorphic Rocks PracticalDocument27 pagesMetamorphic Rocks PracticalMr Gk meenaNo ratings yet
- TEST I. MUTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Option That Corresponds To The Best AnswerDocument6 pagesTEST I. MUTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Option That Corresponds To The Best AnswerShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Geologyical Succession of The Chin State AGE UnitDocument3 pagesTable 1. Geologyical Succession of The Chin State AGE UnitmyatNo ratings yet
- PRAYAS - Geography Workbook - Questions - CompressedDocument108 pagesPRAYAS - Geography Workbook - Questions - CompressedKumar ShivrajNo ratings yet
- Geology of Sri Lanka in Relation To Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesGeology of Sri Lanka in Relation To Plate TectonicsdillysriNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Rock CycleDocument3 pagesChocolate Rock CycleKhynia DijenoNo ratings yet
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Uploaded by
Maria AnnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Learning Activity Worksheets Grade 11 - Earth Science
Uploaded by
Maria AnnaCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
Name: ___________________________ Date: _________ Rating/Score_________
Weathering and The Earth’s Interior
Activity 1: Match it!
Directions: Match the descriptions in column B to the terms in Column A. Write the
correct letter beside the number.
COLUMN A COLUMN B
_______1. Weathering A. dissociation of molecules into ions; Common
examples include dissolution of calcite and salt
_______2. Biological activity B. wearing away of rocks by constant collision of
loose particles
_______3. Abrasion C. reaction between minerals and oxygen dissolve
water
_______4. Salt crystal growth D. change in the composition of minerals when they
react with water
_______5. Frost wedging E. physical disintegration and reduction in the size of
the rocks without changing their chemical
composition.
_______6. Dissolution F. describes the breaking down or dissolving of rocks
and minerals on the surface of the Earth.
_______7. Oxidation G. decomposes, dissolves, alters or weakens the rock
through chemical processes to form residual
materials.
_______8. Hydrolysis H. plants and animals (including humans) as agent of
mechanical weathering
_______9. Mechanical I. when water gets inside the joints, alternate freezing
Weathering and thawing episodes pry the rock apart.
_______10. Chemical J. force exerted by salt crystal that formed as water
weathering evaporates from pore spaces or cracks in rocks
can causes the rock to fall apart
Q2 Week 1 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 1 of 8
Target Competency: Describe how rocks undergo weathering (S11ES-IIb-c-22)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
Activity 2: Weathering with Two
Directions: Choose any 2 types of weathering. Draw the BEFORE and AFTER images
for each. Include an explanation for the changes. For example, in a BEFORE image, a
drawing of a hillside along a road may be shown, in the AFTER image, there is a
landslide shown, which includes an explanation related to the event. You may add other
details to your answer.
(1) Type of Weathering:
BEFORE AFTER
Explanation:
(2) Type of Weathering:
BEFORE AFTER
Explanation:
Activity 3: The Rate of Weathering
Directions: Directions: Fill out the table with the factors that affect the rate of
weathering.
1. The minerals that constitute rocks have different
susceptibilities to weathering. The susceptibility of
minerals (from high to low) roughly follows the
inverse of the order of crystallization of minerals _________________________
in the Bowen’s reaction series. Thus, olivine which
crystallizes first is the least resistant whereas;
quartz which crystallizes last is the most resistant.
2. Physical weathering occurs more quickly on a
steep slope than on a gentle one. On a gentle
_________________________
slope, water may stay longer in contact with the
rocks, hence chemical weathering is enhanced.
3. Areas that are cold and dry tend to have slow
_________________________
rates of chemical weathering and weathering is
Q2 Week 1 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 2 of 8
Target Competency: Describe how rocks undergo weathering (S11ES-IIb-c-22)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
mostly physical; chemical weathering is most active
in areas with high temperature and rainfall.
4. Rate of weathering is affected by the presence of
joints, folds, faults, bedding planes through which
agents of weathering enter a rock mass. Highly _________________________
jointed/fractured rocks disintegrate faster than a
solid mass of rock of the same dimension
5. Length of exposure to agents of weather
_________________________
determines the degree of weathering of a rock
Activity 4: The Earth’s Internal Heat
Directions: Read each statement below carefully. Write T on the space provided if the
statement it correct. Write F on the line if you think the statement is incorrect.
________1. Primordial heat. The general term for the heat imparted to a planetary body
by the processes of its formation and differentiation.
________2. Radioactive heat (the heat generated by short-term radioactive decay).
________3. Geothermal gradient or geotherm: the temperature increase with depth into
Earth.
________4. Mantle is considerably hotter than the crust, and the core is much hotter
than the mantle.
________5. Convection occurs at the mantle but not between the core and mantle or
even between the asthenosphere and lithosphere (except at sea-floor
spreading zones).
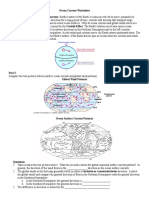
Activity 5: The Earth’s Interior
Directions: Fill in the component words or phrases on the blank boxes to complete the
diagram.
Q2 Week 1 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 3 of 8
Target Competency: Describe how rocks undergo weathering (S11ES-IIb-c-22)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
Activity 6: Processes of Magma Formation
Directions: Demonstrate your understanding of special conditions required for the
formation of magma by explaining what happens in each of the diagrams
DIAGRAM EXPLANATION
Source: Source: K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – Earth and Life Science August 2016.
Activity 7: Locations of Magma Formation
Directions: Match the picture in column A with column B then match column B with column C.
Write the letter of the corresponding image or statement on the space provided before the
number.
A B C
_________1. _________4.
D.)As the oceanic slab is down-thrusted along
A.) Mid- subduction zones, the change in temperature and
oceanic pressure conditions brings about mineral instability
ridges (e.g. hydrous minerals) and the release of water to
the surrounding hot rocks.
_________2. _________5. E.)the rising magma in mantle convection cell brings
heat to the surface, transferring heat to the overlying
B.) Mantle rocks. The transfer of heat due to convection is
plumes(hot accompanied by a decrease in pressure or
spots): "decompression" associated with the spreading of
the lithospheric plates. These two work in tandem
promoting the partial melting of rocks along the
spreading center.
_________3. _________6. F.)Similar to mid-oceanic ridges, the transfer of heat
C.)Subduction and decompression result to magma generation.
zones The source of heat for mantle plumes is much
deeper.
Q2 Week 1 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 4 of 8
Target Competency: Describe how rocks undergo weathering (S11ES-IIb-c-22)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
Source: Source: K to 12 Senior High School Core Curriculum – Earth and Life Science August 2016.
Magma and Metamorphism
Activity 8: Composition of Magma
Directions: Find and encircle the vocabulary words in the grid. Describe the terms in relation to
magma in the table.
Terms Description Terms Description
BUOYANCY MAGMA
DENSITY
MAGMA CHAMBER
CONTRAST
DISSOLVE WATER SILICA
FELSIC TEMPERATURE
MAFIC VISCOSITY
Activity 9: Bowen’s Reaction Series
Directions: Use the diagram to answer the following questions that follow.
Source: https://zengeology.weebly.com/uploads/4/1/5/3/41533293/bowen_reaction_series_activity2.pdf
1. What minerals would you expect to find in the following rocks?
Basalt - __________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Q2 Week 2 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 5 of 8
Target Competency: Describe what happens after magma is formed (S11ES-IIc-25)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
1. Diorite - _________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
2. Granite - _________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
3. Gabbro- _________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
You have a magma that is at very high temperature and pressure. What minerals would
be present in the rock that would form from this magma if it solidified quickly inside the
earth (intrusive)? Why?
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Activity 10: Magmatic Differentiation
Directions: Identify the magmatic differentiation being described. Choose your answer
from the box below.
Partial Melting Assimilation/contamination of magma by crustal rocks
Bowen’s reaction Magma mixing
Crystal Fractionation Crystallization
______________________ 1. A series that describes the sequence of mineral
crystallization in a cooling magma.
______________________ 2. A chemical process by which the composition of a
liquid, such as magma, changes due to
crystallization
______________________ 3. As described in Bowen’s reaction series, quartz and
muscovite are basically formed under low
temperature conditions, making them the first ones
to melt from the parent rock once exposed in higher
temperature and/or pressure
______________________ 4. This may occur when two different magma rises,
with the more buoyant mass overtakes the more
slowly rising body.
______________________ 5. A reaction that occurs when the crust is mixed up
with the rising magma.
Q2 Week 2 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 6 of 8
Target Competency: Describe what happens after magma is formed (S11ES-IIc-25)
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
Activity 11: Metamorphism
Directions: Match the descriptions in column B to the terms in Column A. Write the
correct letter beside the number.
COLUMN A COLUMN B
_______1. Metamorphism A. have a layered or banded appearance
that is produced by exposure to heat and
directed pressure.
_______2. Metamorphic grade B. pertains to the temperature and/or
pressure condition(s) to which a rock has
been subjected during metamorphism.
_______3. Foliation C. is the recrystallization of minerals in
rocks due to a change in pressure and
temperature conditions.
_______4. Pelitic rock D. is a term applied to metamorphic rocks
derived from a fine-grained
_______5. Non-foliated E. do not have a platy or sheet-like
metamorphic rocks structure it is formed when heat is the
main agent of metamorphism.
_______6. Foliated metamorphic rocks F. is the pervasive planar structure that
results from the nearly parallel alignment
of sheet silicate mineral sand/or
compositional and mineralogical in the
rock.
Activity 12: Index Minerals in Metamorphism
Directions: Answer the following questions using the image as reference.
Source: http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/visualgeology/geology101/Geology100Exams/MetamorphicVers2.pdf
1. What minerals would be stable at temperatures around:
400 °C - _________________________________________________________
600 °C - _________________________________________________________
710 °C – _________________________________________________________
Q2 Week 2 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 7 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the changes in mineral components and texture of rocks due to
changes in pressure and temperature (metamorphism) (S11ES-IIc-26)
•
LEARNING ACTIVITY WORKSHEETS
Grade 11 – EARTH SCIENCE
2. What is the relationship between textural type of metamorphic rock and
metamorphic grade?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
3. What is the relationship between metamorphic grade and facies development?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
4. What is the average temperature for the onset of metamorphism?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
5. If a mudstone undergoes metamorphism under wet conditions at temperatures
above ~700o C, then what will happen?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Activity 13: Characteristics of Metamorphic Rocks
Directions: Write true if the statement is correct. Otherwise, change the underlined
term to make the statement correct.
__________________1. Metamorphic rocks are classified according to their shapes.
__________________2. A foliated metamorphic rock has mineral crystals arranged in
bands.
__________________3. The texture of a metamorphic rock refers to the arrangement
of its mineral crystals.
__________________4. Foliated metamorphic rocks usually break along their outer
edges.
__________________5. Marble contains large mineral crystals of quartz.
Activity 14: Characteristics of Metamorphic Rocks 2.0
Directions: Classify each rock listed as foliated or non-foliated. Write your answer in
the space provided.
__________________1. Quartzite
__________________2. Gneiss
__________________3. Slate
__________________4. Marble
__________________5. Schist
Q2 Week 2 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 8 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the changes in mineral components and texture of rocks due to
changes in pressure and temperature (metamorphism) (S11ES-IIc-26)
•
You might also like
- Weather and Climate - WorksheetDocument4 pagesWeather and Climate - Worksheetlavender2x2100% (1)
- Plate Tectonics ExamDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics ExamFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3: Week 7 Learning Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesScience: Quarter 3: Week 7 Learning Activity SheetsFrances DatuinNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Worksheet: Name Use Your Book and Your Rock LabsBhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Earth Science ADM New Module Format Q2 Module 1 4 32 PAGESDocument32 pagesFINAL - Earth Science ADM New Module Format Q2 Module 1 4 32 PAGESEarl Lawrence IbanNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity in Science Quarter 4 - Module 1: Soil - Its Types and CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesLearning Activity in Science Quarter 4 - Module 1: Soil - Its Types and CharacteristicsETHEL WENCESLAONo ratings yet
- Coriolis Effect and Water and Ocean Currents MAPDocument5 pagesCoriolis Effect and Water and Ocean Currents MAPkaseljie lcNo ratings yet
- Ocean Current Activities WSDocument11 pagesOcean Current Activities WSTelang BayawakNo ratings yet
- Science-7 SLM Q4 M2 W2 V1.0-CC-released-24May2021Document15 pagesScience-7 SLM Q4 M2 W2 V1.0-CC-released-24May2021John Lynard ViescaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Plate MovementsDocument60 pagesCauses of Plate MovementsnoliNo ratings yet
- G101ST QuarterDocument21 pagesG101ST QuarterEm EmNo ratings yet
- DLLDocument2 pagesDLLMarjorie Brondo100% (1)
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologyLelouch BritaniaNo ratings yet
- Types of MountainsDocument37 pagesTypes of MountainsRoslan Mansur100% (1)
- DLL-earth-and-life - 4Document4 pagesDLL-earth-and-life - 4Marilla ReybethNo ratings yet
- PR 3 PDFDocument17 pagesPR 3 PDFEdieson Jave CunananNo ratings yet
- DIVERGENT BOUNDARY (Divergence of Plates) Divergent Boundaries Occur When Two PlatesDocument5 pagesDIVERGENT BOUNDARY (Divergence of Plates) Divergent Boundaries Occur When Two Platesdaisy sorianoNo ratings yet
- Exogenic and Endogenic ProcessesDocument32 pagesExogenic and Endogenic ProcessesElss ToonNo ratings yet
- Nature Activities Binder Variant PurpleDocument21 pagesNature Activities Binder Variant PurpleAngel Kate PolitudNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument22 pagesEarth and Life ScienceAlexander LoyloyNo ratings yet
- 1 Summative Test Science 10Document3 pages1 Summative Test Science 10kimjay languitaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesScience 10 Worksheet 2Washima Bentulina SabtalNo ratings yet
- World Time ZonesDocument1 pageWorld Time ZonesAnastasia Sazonova0% (1)
- Science 10 First QuarterDocument86 pagesScience 10 First QuarterAPPLE GRACE MARIE SEBASTIANNo ratings yet
- Earthquake QuizDocument4 pagesEarthquake QuizMary Ann DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Daily Lesson Log: I. ObjectivesJaenicaPaulineCristobalNo ratings yet
- Solotsolot National High School 300081 Earth & Life Science 1 Quarter, 1 Semester Summative Test #3Document3 pagesSolotsolot National High School 300081 Earth & Life Science 1 Quarter, 1 Semester Summative Test #3KENNEDY VAGAYNo ratings yet
- Cot WeatheringDocument7 pagesCot WeatheringMea Joy Dalogdog100% (1)
- G7Q4LAS2W2Document6 pagesG7Q4LAS2W2Hazel RecañaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 7Document12 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Week 7Lucy Jhamaicka Maruquin Ili100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonicsapi-330049903No ratings yet
- Seafloor Spreading ActivityDocument3 pagesSeafloor Spreading ActivityFrancheska McHaleNo ratings yet
- Science7, q4, Week2 (Validated)Document12 pagesScience7, q4, Week2 (Validated)Gary DiazNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Summative Test First Quarter Grade 10 - ScienceDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Summative Test First Quarter Grade 10 - ScienceChai BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Q1ST1Document3 pagesQ1ST1Des Carbonilla100% (1)
- Climate Change - Demo TeachingDocument54 pagesClimate Change - Demo TeachingPhean ArañoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic: Science 9 Quarter 1 Worksheet 1Document4 pagesPlate Tectonic: Science 9 Quarter 1 Worksheet 1JaimeCrispinoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Session Guide. 2Document39 pagesModule 1 Session Guide. 2RJ SemeñaNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect ClimateDocument71 pagesFactors That Affect ClimateChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson 7&8Document6 pagesEarthsci Lesson 7&8Dalope CstrNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Earth N SpaceDocument5 pages4th Summative Test Earth N SpaceAbigail Fernandez BatallerNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesDocument6 pagesWorksheet 1: Types of Plate BoundariesNoeljaysel AlejoNo ratings yet
- Service Quality of Student Dormitories in MEUEDocument11 pagesService Quality of Student Dormitories in MEUEKhin Sandar TunNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q4 Slem 2 - Earths Resources PDFDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Q4 Slem 2 - Earths Resources PDFEdwin RatioNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Earth and Life ScienceDocument2 pagesSyllabus Earth and Life ScienceAligora JoNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT MetamorphismDocument4 pagesHANDOUT MetamorphismHow Ever100% (1)
- Land and Sea Breeze WorksheetDocument2 pagesLand and Sea Breeze Worksheetmark joseph cometa100% (1)
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDocument4 pagesRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJACKSON SANDERS-PUGHNo ratings yet
- Continental Drift Theory NotesDocument3 pagesContinental Drift Theory NotesGirli JoseeNo ratings yet
- Exam - Earth and Life Science Set ADocument4 pagesExam - Earth and Life Science Set AHester Ann BionaNo ratings yet
- TOS (1stPT)Document2 pagesTOS (1stPT)Sally Pocamas100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument18 pagesPlate TectonicsNinni SinghNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EpicenterDocument29 pagesEarthquake Epicenterhuangrenjun'svoicecrackNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Rock CycleDocument14 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Rock CycleDanika Mae PondangNo ratings yet
- Human Activities and Their Impact On The EnvironmentDocument58 pagesHuman Activities and Their Impact On The Environmentrorlando lewis100% (1)
- Science 10 q1 WK 8 Version 2.1 1Document16 pagesScience 10 q1 WK 8 Version 2.1 1Via Jean AmboNo ratings yet
- Earth - S Seasons Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesEarth - S Seasons Practice Worksheetstephanie grace canonce100% (1)
- Las Science 8 Melc 2 q2 Week-2Document7 pagesLas Science 8 Melc 2 q2 Week-2Tonepher CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?Document43 pagesReview Lessons: Essential Questions: 1.what Are The Three Types of 2.when Do They Occur?maris100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science Week 3Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 3Frenny0% (1)
- Earth Science: Quarter 1: Modules 1-4Document32 pagesEarth Science: Quarter 1: Modules 1-4Maria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Black Yellow Recognition CertificateDocument1 pageBlack Yellow Recognition CertificateMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Science - Learning-Activity-Worksheets-8 PagesDocument8 pagesScience - Learning-Activity-Worksheets-8 PagesMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationDocument44 pagesElectron ConfigurationMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheets 3 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 11Document8 pagesLearning Activity Worksheets 3 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person 11Maria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Day 8 Empirical Formula Molecular FormulasDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Day 8 Empirical Formula Molecular FormulasMaria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Relative DatingDocument8 pagesRelative DatingAnnEviteNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson Plan On 3 Types of RocksDocument4 pages5e Lesson Plan On 3 Types of Rocksapi-38497353267% (3)
- Types of RockDocument21 pagesTypes of RockFain AloyanNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Document10 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 4Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ebe 2015 Pillay KDocument200 pagesThesis Ebe 2015 Pillay KPesanai GaranowakoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 StoneDocument47 pagesLecture 4 StoneMa. Alyzandra G. LopezNo ratings yet
- Mineral Section DataDocument56 pagesMineral Section DataMuplihan Komi TararapNo ratings yet
- Rock Webquest All RocksDocument3 pagesRock Webquest All Rocksapi-268569185100% (1)
- 6 - Metamorphic RocksDocument50 pages6 - Metamorphic Rocksloralara100% (1)
- Gess 202Document5 pagesGess 202api-309501342No ratings yet
- TOS Earth & Life Science - Mid Term ExamDocument7 pagesTOS Earth & Life Science - Mid Term ExamKemberly Semaña Penton100% (2)
- Our Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its UsesDocument217 pagesOur Fragile Planet - Geosphere - The Land and Its Useslelo2k3100% (1)
- 150 Top Most Building Materials and CONSTRUCTION Interview Questions - Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument44 pages150 Top Most Building Materials and CONSTRUCTION Interview Questions - Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersAbdulrahman JawdatNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet RocksDocument3 pagesRevision Sheet Rocksmofid monirNo ratings yet
- Hunt Cut Set Gems LapidaryDocument15 pagesHunt Cut Set Gems LapidaryAlina Margarit50% (2)
- Rocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation GCSE IGCSE Environmental Management Geography 0680Document54 pagesRocks and Minerals and Their Exploitation GCSE IGCSE Environmental Management Geography 0680IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (2)
- Bsi Recommended PracticesDocument31 pagesBsi Recommended PracticesKimon ZagkourisNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks by JDDocument123 pagesMinerals and Rocks by JDShaniah TorrefloresNo ratings yet
- Sandstone Thin Section StudyDocument7 pagesSandstone Thin Section StudyIjlal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Casquet 2014Document15 pagesCasquet 2014Lucas ContalbaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument13 pagesCritical ThinkingmfhfhfNo ratings yet
- Els Week 2Document45 pagesEls Week 2Paolin Pearl Ortiola Rapisura40% (5)
- Metamorphic Phase Equilibria and Presure-Temperature-Time-PathsDocument823 pagesMetamorphic Phase Equilibria and Presure-Temperature-Time-PathsPaola TraslaviñaNo ratings yet
- Identification of Rocks and Minerals PDFDocument22 pagesIdentification of Rocks and Minerals PDFIkhwan Z.80% (15)
- Metamorphic Rocks PracticalDocument27 pagesMetamorphic Rocks PracticalMr Gk meenaNo ratings yet
- TEST I. MUTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Option That Corresponds To The Best AnswerDocument6 pagesTEST I. MUTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Option That Corresponds To The Best AnswerShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Table 1. Geologyical Succession of The Chin State AGE UnitDocument3 pagesTable 1. Geologyical Succession of The Chin State AGE UnitmyatNo ratings yet
- PRAYAS - Geography Workbook - Questions - CompressedDocument108 pagesPRAYAS - Geography Workbook - Questions - CompressedKumar ShivrajNo ratings yet
- Geology of Sri Lanka in Relation To Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesGeology of Sri Lanka in Relation To Plate TectonicsdillysriNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Rock CycleDocument3 pagesChocolate Rock CycleKhynia DijenoNo ratings yet