Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cadmium Sulfide Cds Thermodynamic Properties Vapor Pressure Phas
Cadmium Sulfide Cds Thermodynamic Properties Vapor Pressure Phas
Uploaded by
Extrusion Tutorials0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesThis document summarizes thermodynamic properties of cadmium sulfide (CdS), including:
- Enthalpy of melting is estimated to be 38.5-50.6 kJ/mol between 90-96K.
- Volume change upon melting is estimated to be 2.3% at 90K.
- Standard enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of formation are reported from various studies between -149.4 to -159 kJ/mol.
- Entropy and enthalpy are reported from multiple studies ranging from 69.04 to 72.18 J/mol-K and 9.802 to 9.889 kJ/mol, respectively.
- Heat capacity, entropy, enthal
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes thermodynamic properties of cadmium sulfide (CdS), including:
- Enthalpy of melting is estimated to be 38.5-50.6 kJ/mol between 90-96K.
- Volume change upon melting is estimated to be 2.3% at 90K.
- Standard enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of formation are reported from various studies between -149.4 to -159 kJ/mol.
- Entropy and enthalpy are reported from multiple studies ranging from 69.04 to 72.18 J/mol-K and 9.802 to 9.889 kJ/mol, respectively.
- Heat capacity, entropy, enthal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesCadmium Sulfide Cds Thermodynamic Properties Vapor Pressure Phas
Cadmium Sulfide Cds Thermodynamic Properties Vapor Pressure Phas
Uploaded by
Extrusion TutorialsThis document summarizes thermodynamic properties of cadmium sulfide (CdS), including:
- Enthalpy of melting is estimated to be 38.5-50.6 kJ/mol between 90-96K.
- Volume change upon melting is estimated to be 2.3% at 90K.
- Standard enthalpy and Gibbs free energy of formation are reported from various studies between -149.4 to -159 kJ/mol.
- Entropy and enthalpy are reported from multiple studies ranging from 69.04 to 72.18 J/mol-K and 9.802 to 9.889 kJ/mol, respectively.
- Heat capacity, entropy, enthal
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 8
substance: cadmium sulfide (CdS) 26s10d60
property: thermodynamic properties, vapor pressure, phase diagram
enthalpy of melting
∆Hm 38.5 kJ mol–1 estimated 90K
50.6 kJ mol–1 estimated 96S
volume change
∆Vm 2.3 % 90K
characteristic data of formation
∆Hf0(298.15) – 149.4 kJ mol–1 optimized 74M
– 159.0 kJ mol–1 optimized 74M
– 153.3(28) kJ mol–1 calorimetry 92N
∆Gf0(298.15) – 149.8(20) kJ mol–1 emf 92N
reaction: Cd(l) + S(l) → α-CdS(s)
∆Gf0 – 164295 + 31.37 T J mol–1 T = 640...690 K, emf 92N
– 162760 + 40.1786 T J mol–1 T = 600...1400 K, optimized 96S
–(G0T–H00)/T 39.31(33) J mol–1K–1 83B
entropy and enthalpy
S0298.15 69.04 J mol–1 K–1 74M
72.18(16) J mol–1 K–1 83B
72.0 J mol–1 K–1 92N
H0298.15_H00 9.802(19) kJ mol–1 83B
thermodynamic functions
adiabatic calorimetry, polycrystalline sample 83B
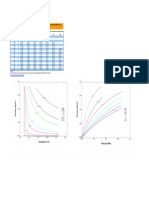
T Cp ∆ST0 –(G0−HT)/RT H298.150 − H00
[K] [J mol–1 K–1] [J mol–1 K–1] [J mol–1]
5 0.043 0.030 0.002 0.000
10 0.889 0.237 0.051 0.002
15 3.137 0.986 0.221 0.011
20 5.799 2.255 0.563 0.034
25 8.321 3.824 1.054 0.069
30 10.560 5.544 1.658 0.117
35 12.504 7.321 2.340 0.174
40 14.207 9.104 3.074 0.241
45 15.748 10.868 3.842 0.316
50 17.197 12.603 4.632 0.399
60 19.971 15.985 6.244 0.584
70 22.644 19.265 7.871 0.798
80 25.204 22.458 9.495 1.037
90 27.613 25.567 11.109 1.301
100 29.845 28.593 12.707 1.589
110 31.887 31.535 14.286 1.897
120 33.735 34.390 15.843 2.226
130 35.393 37.157 17.376 2.572
140 36.872 39.835 18.885 2.933
150 38.185 42.425 20.369 3.308
160 39.348 44.927 21.826 3.696
170 40.379 47.344 23.256 4.095
180 41.295 49.679 24.660 4.503
190 42.112 51.934 26.036 4.920
200 42.845 54.113 27.386 5.345
210 43.506 56.219 28.709 5.777
220 44.106 58.257 30.006 6.215
230 44.653 60.230 31.278 6.659
240 45.153 62.141 32.527 7.108
250 45.609 63.994 33.746 7.562
260 46.024 65.791 34.944 8.020
270 46.401 67.535 36.119 8.482
280 46.743 69.229 37.271 8.948
290 47.055 70.875 38.402 9.417
298.15 47.293 72.182 39.307 9.802
300 47.345 72.475 39.511 9.889
400 49.475 86.461 49.572 14.755
500 50.688 97.638 58.105 19.766
600 51.672 106.968 65.492 24.886
700 52.546 115.000 72.004 30.097
800 53.363 122.071 77.829 35.393
900 54.146 128.401 83.103 40.796
1000 54.909 134.146 87.924 46.222
1100 55.657 139.414 92.369 51.750
vapor pressure
log p 7.376 – 11601 T –1 T in K, p in bar 74M
see Figs. 1 and 2.
phase diagrams: Figs. 3...5.
References:
63W Woodbury, H. H.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids 24 (1963) 881.
74M Mills, K. C.: Thermodynamic Data of Inorganic Sulphides, Selenides and Tellurides, Butterworth,
London, (1974).
83B Beyer, R. P., Ferrante, M. J., Mrazek, R. V.: J. Chem. Thermodyn. 15 (1983) 827.
90K Kulakov, M. P.: Inorg. Mater. 26 (1990) 1947.
92N Nasar, A., Shamsuddin, M.: Thermochim. Acta 197 (1992) 373.
96S Sharma, R. C., Chang. Y. A.: J. Phase Equilibria 17 (1996) 425
Fig. 1.
CdS. Calculated partial pressure of Cd along the Cd-S liquidus [96S].
Fig. 2.
CdS. Calculated partial pressure of S2 along the Cd-S liquidus [96S].
Fig. 3.
CdS. Phase diagram for the system Cd−S [63W].
Fig. 4.
CdS. Assessed phase diagram, symbols are experimental points [96S].
Fig. 5.
CdS. p- T diagram, symbols are experimental points [96S].
You might also like
- Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight 7Th Edition Atkins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesChemical Principles The Quest For Insight 7Th Edition Atkins Test Bank Full Chapter PDFpauline.wilson221100% (21)
- Chi Square TableDocument2 pagesChi Square TableRagil setyo laksono100% (1)
- Table G The Chi-Sqrd TableDocument1 pageTable G The Chi-Sqrd Tableyuta100% (1)
- Vtu Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 20101Document175 pagesVtu Mechanical Engineering Syllabus 20101api-257789307No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 3Document23 pagesThermodynamics 3Jo Ces27% (11)
- 8 Deep Foundation SystemDocument4 pages8 Deep Foundation SystemEr S Thirumarai NathanNo ratings yet
- GMB Prediction WeDocument20 pagesGMB Prediction WeJawad AlassalNo ratings yet
- Entropy (SI)Document6 pagesEntropy (SI)Juan Antonio SánchezNo ratings yet
- HEAT DISSIPATION 380mmDocument1 pageHEAT DISSIPATION 380mmFelipe FlorezNo ratings yet
- 30 10 0.005 0 0.015 1 Sistema Internacional 6.364 Nota: Cambiar Solo Color AzulDocument8 pages30 10 0.005 0 0.015 1 Sistema Internacional 6.364 Nota: Cambiar Solo Color Azulerick cardenasNo ratings yet
- Chi Square TableDocument1 pageChi Square TableAlvin XuNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Density (KG/M) at Different Temperatures (C) and Pressures (Mpa)Document1 pageHydrogen Density (KG/M) at Different Temperatures (C) and Pressures (Mpa)ppglNo ratings yet
- Testing Hypotyesis Chi SquareDocument23 pagesTesting Hypotyesis Chi SquareIshrat Hussain TuriNo ratings yet
- N° Depth (M) SOW (Kips) ROT (Kips) PUW (Kips) Max Pull (Kips) Pull at Bit (Kips) Max Slack (Kips)Document2 pagesN° Depth (M) SOW (Kips) ROT (Kips) PUW (Kips) Max Pull (Kips) Pull at Bit (Kips) Max Slack (Kips)tonyNo ratings yet
- Table A22Document2 pagesTable A22고대윤0% (1)
- Resolución Práctica Calificada 3: Subcuenca 01 Subcuenca 02 TC TCDocument2 pagesResolución Práctica Calificada 3: Subcuenca 01 Subcuenca 02 TC TCNicole HuamaníNo ratings yet
- Properties of PipeDocument2 pagesProperties of PipeMelissa Filizzola MerlanoNo ratings yet
- Appendix A PonceDocument9 pagesAppendix A PonceMarlon ÑacariNo ratings yet
- 2b. Thermal Resistant AlloyDocument4 pages2b. Thermal Resistant AlloyBhagawati Prasad SharmaNo ratings yet
- (Revisi 1) Supplementary InformationDocument5 pages(Revisi 1) Supplementary InformationAulia D.RNo ratings yet
- SDOF Damped Forced Vibration - NewmarkDocument5 pagesSDOF Damped Forced Vibration - NewmarkMazharYasinNo ratings yet
- Excel Perhitungan Hss NakayasuDocument23 pagesExcel Perhitungan Hss NakayasuNevandria Satrya YudhaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 29-09-2022Document8 pagesEjercicio 29-09-2022nemo davoNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Nuevo AlausiDocument16 pagesProyecto Nuevo AlausiSantiago CujiNo ratings yet
- 2-3 Site ConditionDocument43 pages2-3 Site ConditionAnsar ValiNo ratings yet
- Tabla Gas IdealDocument2 pagesTabla Gas IdealSubadraNo ratings yet
- Band Induction CellsDocument2 pagesBand Induction Cellssyed02No ratings yet
- Stat Tables-23Document1 pageStat Tables-23Suyog KhanalNo ratings yet
- Interpol Ac I OnDocument15 pagesInterpol Ac I OnGabriel Esteban González FrancoNo ratings yet
- English/Metric (SI) Impact Strength Conversion Chart: Covered ElectrodesDocument1 pageEnglish/Metric (SI) Impact Strength Conversion Chart: Covered ElectrodesTAMILNo ratings yet
- I:/Lubes Crude Distillation/ephyde/example - Out: TBP AstmDocument8 pagesI:/Lubes Crude Distillation/ephyde/example - Out: TBP AstmEHNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Title of The Experiment: (Partial Molar Volume)Document8 pagesExperiment 1: Title of The Experiment: (Partial Molar Volume)Hazem Al-hazmiNo ratings yet
- Ies Indoor Report Photometric Filename: Bs101Ecoled4Sawt40120V-277V - P.Ies DESCRIPTION INFORMATION (From Photometric File)Document11 pagesIes Indoor Report Photometric Filename: Bs101Ecoled4Sawt40120V-277V - P.Ies DESCRIPTION INFORMATION (From Photometric File)Ankit JainNo ratings yet
- TablasDocument6 pagesTablasDanielaNo ratings yet
- Ppoo, PP00 A, XP00, XP00 ADocument12 pagesPpoo, PP00 A, XP00, XP00 AKenan KuloglijaNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument2 pagesIdeal GasGreg FelizartaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Conditions:: Lampiran 1. Grafik XRDDocument18 pagesMeasurement Conditions:: Lampiran 1. Grafik XRDDina PradinaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition-1021-1030Document10 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition-1021-1030Andres Eduardo Diaz MartinezNo ratings yet
- B GasturbineDocument11 pagesB GasturbineRIPUDAMAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Saturated Pressure R134aDocument1 pageSaturated Pressure R134akhairuddin safri100% (3)
- Chi Square TableDocument1 pageChi Square Tablesorayamuhamad18No ratings yet
- Appendix A PonceDocument9 pagesAppendix A PonceMarlon ÑacariNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4Document10 pagesTugas 4Andi Wardiman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Meng V - Civ. Eng. 17TP21337: Fankam Noukimi CabrelDocument1 pageMeng V - Civ. Eng. 17TP21337: Fankam Noukimi CabrelCabrel FankamNo ratings yet
- C (Kpa) 60 F 30 Depth of The Pile (M) 20 Dia of The Pile (M) 0.5 D/B 40 A 0.45 0.7 F/D 0.6 Fos (Skin) 2.5 Fos (Base) 2.5 KS/KDocument6 pagesC (Kpa) 60 F 30 Depth of The Pile (M) 20 Dia of The Pile (M) 0.5 D/B 40 A 0.45 0.7 F/D 0.6 Fos (Skin) 2.5 Fos (Base) 2.5 KS/KNita NabanitaNo ratings yet
- Resultados de L&G Según PrecioDocument6 pagesResultados de L&G Según PrecioJoseDanielLimacheCoronacionNo ratings yet
- App3Document2 pagesApp3hamidrezaee008No ratings yet
- 2a. Thermal Resistant AlloyDocument3 pages2a. Thermal Resistant AlloyMohyedin Ganjian aboukheiliNo ratings yet
- KLB Mathematics Students Book 2Document328 pagesKLB Mathematics Students Book 2Nicholas KinotiNo ratings yet
- 01 Cubes and Cube RootsDocument4 pages01 Cubes and Cube Rootskevin muchungaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Skills Chi-Squared TableDocument1 pageQuantitative Skills Chi-Squared TablejasonNo ratings yet
- Hidrograf Banjir Metode Nakayasu: Daerah Aliran Sungai LimbotoDocument6 pagesHidrograf Banjir Metode Nakayasu: Daerah Aliran Sungai LimbotoBarry LabdulNo ratings yet
- Aaac - Tabela CabosDocument4 pagesAaac - Tabela CabosKarin SpringerNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Section Properties of Standard Precast Concrete GirdersDocument10 pagesAppendix: Section Properties of Standard Precast Concrete Girdersسجى وليدNo ratings yet
- Cernica VerificationDocument5 pagesCernica VerificationlouispriceNo ratings yet
- Gas Ideal SiDocument2 pagesGas Ideal SiValentina OrtizNo ratings yet
- PX Khi: Phaân Phoái Chi - Bình PhöôngDocument1 pagePX Khi: Phaân Phoái Chi - Bình PhöôngMinh BáchNo ratings yet
- Table A.23 Physical Properties of Selected Fluids (Engineering Thermodynamics by Burghardt & Harbach)Document1 pageTable A.23 Physical Properties of Selected Fluids (Engineering Thermodynamics by Burghardt & Harbach)lemuel andrezaNo ratings yet
- ISA Temp and Pressures vs. AltitudeDocument5 pagesISA Temp and Pressures vs. AltitudeRalph SandfordNo ratings yet
- United States Census Figures Back to 1630From EverandUnited States Census Figures Back to 1630No ratings yet
- Final Report - IllinoisDocument40 pagesFinal Report - IllinoisExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & Engineering BDocument31 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering BExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Properties of Cdte Thin Films Grown by Close Spaced Sublimation (CSS) Technique For Photovoltaic ApplicationDocument29 pagesProperties of Cdte Thin Films Grown by Close Spaced Sublimation (CSS) Technique For Photovoltaic ApplicationExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & Engineering BDocument9 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering BExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Ontheelectricalandopticalpropertiesof CD SfilmsthermallydepositedDocument4 pagesOntheelectricalandopticalpropertiesof CD SfilmsthermallydepositedExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Raman and Ellipsometric Investigation of 570 NM CDDocument9 pagesRaman and Ellipsometric Investigation of 570 NM CDExtrusion TutorialsNo ratings yet
- 3 Properties of Ideal GasesDocument52 pages3 Properties of Ideal GasesBERN CERTEZANo ratings yet
- UDS-110-Propane Refrigeration Loop PDFDocument28 pagesUDS-110-Propane Refrigeration Loop PDFmujeebmehar100% (1)
- Determining Hydrogen Pre-Cooling Temperature From Fueling ParametersDocument6 pagesDetermining Hydrogen Pre-Cooling Temperature From Fueling Parametersfatanrudi123No ratings yet
- 7.44.session VI EHa and LTR Process Flow and Steam Gathering System v3 PDFDocument56 pages7.44.session VI EHa and LTR Process Flow and Steam Gathering System v3 PDFadityaNo ratings yet
- BS en 27841 1991 1999 Iso 7841 1988Document20 pagesBS en 27841 1991 1999 Iso 7841 1988Raghvendra Pratap Singh0% (1)
- Open Rack Vaporizer Mass and Energy BalanceDocument12 pagesOpen Rack Vaporizer Mass and Energy BalanceMuhammad Nanda100% (1)
- Pertemuan Ke-3 Dan 4Document32 pagesPertemuan Ke-3 Dan 4Habib Faisal YahyaNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Thermodynamic Exp 5Document16 pagesCooling Tower Thermodynamic Exp 5hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Thermo Dynamics Question BankDocument3 pagesThermo Dynamics Question Banknisar_ulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 (1) - 1Document54 pagesChapter 03 (1) - 1Vinay DograNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 pagesIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics IDocument21 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics ImihretuNo ratings yet
- Combustion TheoryDocument44 pagesCombustion TheoryyaidragonNo ratings yet
- 1556 RFA Manual TehnicDocument36 pages1556 RFA Manual Tehnicd403242No ratings yet
- Adiabatic Filling and Discharging of Pressure Vessels - v2Document11 pagesAdiabatic Filling and Discharging of Pressure Vessels - v2MariaXimenaAnguloVergaraNo ratings yet
- Steady-State Non-Isothermal Reactor DesignDocument25 pagesSteady-State Non-Isothermal Reactor DesignSulabh JainNo ratings yet
- Energetics QPDocument11 pagesEnergetics QPKarim WaelNo ratings yet
- Experimental Thermodynamics and Surface Properties of Ag-Cu-Ge Solder/Braze AlloysDocument11 pagesExperimental Thermodynamics and Surface Properties of Ag-Cu-Ge Solder/Braze AlloysDilmurod JuraevNo ratings yet
- CFX Multiphase 14.5 L07 Interphase Mass TransferDocument116 pagesCFX Multiphase 14.5 L07 Interphase Mass Transferedersalcedocastro100% (1)
- Energy Changes in Chemical ReactionsDocument23 pagesEnergy Changes in Chemical ReactionsKester Maucesa60% (5)
- Termodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2Document38 pagesTermodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2david tennantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-College 3Document10 pagesChemistry-College 3Subhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- MT 306 01 EquilibriumDocument18 pagesMT 306 01 EquilibriumLokesh MeghwalNo ratings yet
- 2016 Technical Paper 7Document58 pages2016 Technical Paper 7Eugenio DurbanNo ratings yet
- PYROX - Heating and Ventilation TutorialDocument66 pagesPYROX - Heating and Ventilation Tutorialdanenic100% (1)
- Kessel 1998Document11 pagesKessel 1998yosiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 3 - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument91 pagesLecture - 3 - Properties of Pure SubstancesAbrar Hussain AwanNo ratings yet