Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUS
Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUS
Uploaded by
Sachidhanandam MOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUS
Supply Chain Management REVISED SYLLABUS
Uploaded by
Sachidhanandam MCopyright:
Available Formats
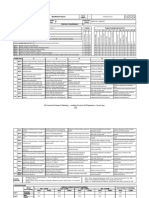
Course Course Course L T P C
18MEE425T SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT E Professional Elective
Code Name Category 3 0 0 3
Pre-requisite Co-requisite
NIL NIL Progressive Courses NIL
Courses Courses
Course Offering Department Mechanical Engineering Data Book / Codes/Standards NIL
Course Learning Rationale (CLR): The purpose of learning this course is to: Learning Program Outcomes (PO) PSO
CLR-1 : Understand the role of logistics 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
CLR-2 : Acquiring the knowledge in the phases of supply chain
Expected Proficiency
Expected Attainment
Modern Tool Usage
CLR-3 : Be familiar on the evolution of supply chain models
Life Long Learning
Individual & Team
Problem Analysis
Society & Culture
Design,
Level of Thinking
CLR-4 : Apply the supply chain activities
Communication
Environment &
Project Mgt. &
Development
Sustainability
CLR-5 : Acquiring the knowledge in the SCM organization and information system
Engineering
Knowledge
Research
Design &
Analysis,
Finance
PSO - 1
PSO - 2
PSO - 3
(Bloom)
Ethics
Work
Course Outcomes (CO): At the end of this course, learners will be able to:
(%)
(%)
CO-1 : Recall The concepts of Logistics and its role of operations. 2 90 85 - 3 - - - - - - - - - - - - -
CO-2 : Recognize the importance of Supply chain and its different phases. 2 90 85 - - - 1 - 2 - - - - - - - - -
CO-3 : Predict the evolution of supply chain models and solution for engineering problem 2 90 85 - - - - - 3 - - - - - - - - -
CO-4 : Carry out the activities of supply chain 2 90 85 - - - 1 - 2 - - - - - - - - -
CO-5 : Compile The different SCM organization and different ERP systems 3 90 85 - - - - 3 - - - - - - - - - -
Scm Organisation and Information
Introduction to Logistics Phases of Supply Chain Evolution of Supply Chain Models Supply Chain Activities
System
Duration (hour) 09 09 09 09 09
Introduction of Logistics and its Introduction of Structuring the supply
S-1 SLO-1 The new paradigm shift Strategy of supply chain The management task
concepts chain
Supply chain challenge – five tasks for
S-2 SLO-1 Logistics definitions The modular company structure of supply chain Types of Logistics organization
management
Introduction to strategic core, network structures, management
S-3 SLO-1 Different Logistics approaches Factors of supply chain Supply Chain as activity systems The logistics in information systems
networks and vertical integration
S-4 SLO-1 Factors influencing logistics The network relations in supply chain Manufacturing strategy stages New products of supply chain Topology of Supply chain application
Supplier relationship, partnerships and alliances, cooperation and
S-5 SLO-1 Basic tasks of supply chain integration, Governance, boundary management, global Supply chain progress Foundation for supply chain change Product Data Management
networks
Introduction of Model for competing
S-6 SLO-1 Defection of supply chain Supply processes in supply chain Functional roles in supply chain change Warehouse management system MRP- I,
through supply chain management
Process flow, product design, product issues, product structure, PLC grid in supply chain
S-7 SLO-1 Approaches of supply chain Frame work Design for supply chain Warehouse management system MRP- 2
logistics issue management
S-8 SLO-1 Influencing supply chain Procurement processes in supply chain Redesigning of supply chain Institutionalizing supply chain changes ERP case study
S-9 SLO-1 A new corporate model. Distribution management in supply chain linking supply chain with customer Collaborative product commerce ERP software’s
3. Nicolas, J. N., Competitive manufacturing management – continuous improvement, Lean production, customer
Learning 1. Shari, P. B. and Lassen, T. S., Managing the global supply chain, Viva books, New Delhi, 2000. focused quality, McGrawHill, New York, 1998.
Resources 2. Ayers, J. B., Hand book of supply chain management, The St. Lencie press, 2000. 1. 4. Steudel, H. J. and Desruelle, P., Manufacturing in the nineteen – How to become a mean, lean and world class
competitor, Van No strand Reinhold, New York, 1992.
Learning Assessment
Continuous Learning Assessment (50% weightage) Final Examination
Bloom’s (50% weightage)
Level of Thinking CLA – 1 (10%) CLA – 2 (15%) CLA – 3 (15%) CLA – 4 (10%)#
Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice Theory Practice
Level 1 Remember 50 - 50 - 40 - 50 - 40 -
Level 2 Understand 50 - 50 - 40 - 50 - 40 -
Level 3 Apply - - - - 20 - - - 20 -
Level 4 Analyze - - - - - - - - - -
Level 5 Evaluate - - - - - - - - - -
Level 6 Create - - - - - - - - - -
Total 100% 100% 100% 100% 100%
# CLA – 4 can be from any combination of these: Assignments, Seminars, Tech Talks, Mini-Projects, Case-Studies, Self-Study, MOOCs, Certifications, Conf. Paper etc.,
Course Designers
Experts from Industry Experts from Higher Technical Institutions Internal Experts
1. Mr.M. SachidhanandhamAsst. Professor, ME
1. Dr. R. Kalimuthu, ISRO, Mahendragiri, r_kalimuthu@vssc.gov.in, rkpearls@yahoo.com 1. Dr.M. K. Marichelvam, Mepco Schlenk Engineering College, Sivakasi.
SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur,
2. Dr. A. Velayutham, DRDO, Avadi, velayudham.a@cvrde.drdo.in 2.Mr.A.Prabukarthi A, PSG College of Technology Coimbatore-641004 Dr. M. Iqbal, SRMIST
You might also like
- Allen Heath Ag8700 1 Qu16 PsuDocument7 pagesAllen Heath Ag8700 1 Qu16 PsuSugeng HariadiNo ratings yet
- Plate Load Test Standard ASTM D1196 D1196M-12Document3 pagesPlate Load Test Standard ASTM D1196 D1196M-12راجہ شہزاد انور100% (3)
- Reil Training ReportDocument210 pagesReil Training ReportRahul Gupta67% (3)
- Syllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegDocument241 pagesSyllabus For All Professional Electives Btech Programmes School of Computing 18 RegMonica Bhavani MNo ratings yet
- 18cse392t SyllabusDocument2 pages18cse392t SyllabusKavipriya VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- SylabusDocument3 pagesSylabusveeramatNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlsuchiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegDocument181 pagesSyllabus For All Open Electives Btech Programmes Faculty of E&t 18 RegSAPTARSHI BHATTACHARYA (RA2011003010182)No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDurga Devi PNo ratings yet
- Programming For Problem Solving SyllabusDocument2 pagesProgramming For Problem Solving SyllabusSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument3 pagesOperating SystemsSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- EEE Approved SyllabusDocument2 pagesEEE Approved SyllabusBavin KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Building Rehabilitation Anfd Forensic en - 220825 - 181244Document3 pagesSyllabus - Building Rehabilitation Anfd Forensic en - 220825 - 181244M O H A N A V E LNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicDocument2 pagesArtificial Neural Networks and Fuzzy LogicChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument3 pagesEnvironmental StudiesKatelin JoyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus PDFNARESH SRIRAM G (RA2111038010004)No ratings yet
- Solid State Device SyllabusDocument2 pagesSolid State Device Syllabusnikunj sharmaNo ratings yet
- 18CSC304J - Compiler DesignDocument2 pages18CSC304J - Compiler Designthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- Cn-18cse379t - Internet of ThingsDocument2 pagesCn-18cse379t - Internet of Thingsnagamalleswari2010No ratings yet
- Nil Nil Faculty of ManagementDocument19 pagesNil Nil Faculty of ManagementDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital ElectronicsDocument2 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronicsravi gokaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument4 pagesSyllabus - 18CSC203J - Computer Organization and ArchitectureVaijayanthiNo ratings yet
- 18CSC303J - Database Management SystemsDocument2 pages18CSC303J - Database Management Systemsthreee.six.five.365No ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations)Document2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations)Hell YessNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Professional ElectiveDocument310 pagesMechanical Professional ElectivearunrajNo ratings yet
- Vehicle DynamicsDocument2 pagesVehicle DynamicsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDiksha NasaNo ratings yet
- Sensors SyllabusDocument2 pagesSensors Syllabusdirector.sportssrmistNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 21CSS101J PpsDocument3 pagesSyllabus 21CSS101J PpsGhoulNo ratings yet
- 18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratoryDocument2 pages18CEC304L Construction Engineering and Management LaboratorymekalaNo ratings yet
- Business EnglishDocument2 pagesBusiness EnglishshreeyasinghhhNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument3 pagesOperating SystemSindhuja VigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- 18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pages18CEO302J Modern Civil Engineering EconomicsmekalaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Document24 pagesCurriculum and Syllabus Btech Mathematics Reg 2020 21Surya NathanNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2019 Part Time Regulations) 37Document2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2019 Part Time Regulations) 37skarthikpriyaNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument4 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - Controlsateesh shivhareNo ratings yet
- 18CEC303T Highway Engg and DesignDocument3 pages18CEC303T Highway Engg and DesignmekalaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabussaranya_subakaranNo ratings yet
- 18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusDocument2 pages18BTC106J-Immunology SyllabusChris PenielNo ratings yet
- SRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlDocument2 pagesSRM Institute of Science & Technology - Academic Curricula (2018 Regulations) - ControlEric LonewolfNo ratings yet
- 18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedDocument3 pages18CSC205J OS Syllabus UpdatedHarsh DeepNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Automotive EnginesDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Automotive EnginesChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusDocument3 pages18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC Lab Manual 2022 2023 EvenVAMSI TIYYAGURA (RA2111026010205)No ratings yet
- 18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFDocument2 pages18MEC108T 120 Zoomed Syllabus-Rotated PDFChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- Aut0motive Fault DiagnosticsDocument2 pagesAut0motive Fault DiagnosticsChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- 18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusDocument3 pages18CSC204J - DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS SyllabusMeenakshi AryaNo ratings yet
- 18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bDocument77 pages18CSS202J CC LAB MANUAL 2021 2022 EVEN 7bSAI ANDALAM (RA2111003011353)No ratings yet
- MCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterDocument19 pagesMCA-SYLLABUS I SemesterMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)No ratings yet
- 19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusDocument2 pages19PEEO65T - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing SyllabusSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Solids PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- PT CSE 2019 Curriculum and SyllabusDocument2 pagesPT CSE 2019 Curriculum and Syllabusneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Sample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Document3 pagesSample - Syllabus Template Revised - 13.07.2022Sowmmiya UNo ratings yet
- Pps SyllabusDocument4 pagesPps SyllabusØmÊn GamingNo ratings yet
- USA20C102J Digital Logic Fundamentals C Professional CoreDocument3 pagesUSA20C102J Digital Logic Fundamentals C Professional CoreAarthi ENo ratings yet
- ITSM&O Syllabus - SRMDocument2 pagesITSM&O Syllabus - SRMSanthosh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- 6th Semester Food & Beverage ServiceDocument3 pages6th Semester Food & Beverage ServiceSrikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- NDM SyllabusDocument2 pagesNDM Syllabuskrisha vasuNo ratings yet
- 18PYB103J Physics-Syllabus PDFDocument2 pages18PYB103J Physics-Syllabus PDFAnime ExtremeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFSREEJAUN T J (RA2111025010015)No ratings yet
- Automotive Control EngineeringDocument2 pagesAutomotive Control EngineeringChatrapal SinghNo ratings yet
- Oops Syllabus - Jan 2024Document3 pagesOops Syllabus - Jan 2024Abishek DevNo ratings yet
- Fits and TolerancesDocument115 pagesFits and TolerancesSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- WORKSHOP Practical - Attendance Sheet BATCH2Document2 pagesWORKSHOP Practical - Attendance Sheet BATCH2Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Ex. No 4 - Orthographic Multi-View Projections (Orthographic Projections of Straight Lines and Planes Inclined To Both The Planes)Document57 pagesEx. No 4 - Orthographic Multi-View Projections (Orthographic Projections of Straight Lines and Planes Inclined To Both The Planes)Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Power PlantsDocument136 pagesUnit 4 Power PlantsSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 4Document6 pages4Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Manufacturing Process Complete PortionDocument231 pagesUnit 5 Manufacturing Process Complete PortionSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MCQ QuestionsDocument28 pagesUnit 5 MCQ QuestionsSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 IC ENGINESDocument107 pagesUnit 3 IC ENGINESSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 MCQ QuestionsDocument19 pagesUnit 5 MCQ QuestionsSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 QuestionsDocument2 pagesUnit 4 QuestionsSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusDocument3 pages18mee304t - Dfma SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document9 pagesUnit 5Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document4 pagesUnit 2Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document5 pagesUnit 4Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Me508 5 SemfDocument1 pageMe508 5 SemfSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- ME2109 1 SemDocument1 pageME2109 1 SemSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document3 pagesUnit 3Sachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Me508 5 SemeDocument1 pageMe508 5 SemeSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Me508 5 SemDocument1 pageMe508 5 SemSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusDocument5 pages18MEC208T - Mechanical Engineering Design SyllabusSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- 2.introduction To RoboticsDocument65 pages2.introduction To RoboticsSachidhanandam MNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Potential Compressive Strength of Portland Clinker From Its MineralogyDocument12 pagesPrediction of Potential Compressive Strength of Portland Clinker From Its MineralogyAnonymous NxpnI6jC100% (1)
- 347 804 2501 Op Manual Nov07Document91 pages347 804 2501 Op Manual Nov07Luis MironNo ratings yet
- Citizen JournalismDocument25 pagesCitizen JournalismRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- A Genre Analysis of The Results Section of Sociology ArticlesDocument13 pagesA Genre Analysis of The Results Section of Sociology ArticlesAntonio IJNo ratings yet
- Trinidad and Tobago - ACP - 2007 Eng PDFDocument116 pagesTrinidad and Tobago - ACP - 2007 Eng PDFsmith ortega martinezNo ratings yet
- Error Codes - Roland - XJ740Document2 pagesError Codes - Roland - XJ740DimaNo ratings yet
- Work Industry and Canadian Society 7th Edition Krahn Test BankDocument7 pagesWork Industry and Canadian Society 7th Edition Krahn Test BankSamanthaRamospfozx100% (10)
- Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 6th Edition 201 270Document70 pagesData Structures and Algorithms in Java 6th Edition 201 270longle18704No ratings yet
- Doi:10.6323/Jocrp.2010.26.3.1: Meaning-Centered Group Psychotherapy-Introduction and CommentsDocument12 pagesDoi:10.6323/Jocrp.2010.26.3.1: Meaning-Centered Group Psychotherapy-Introduction and CommentsJoan ChuNo ratings yet
- OMCI ExtensionDocument7 pagesOMCI ExtensionChida GowdaNo ratings yet
- 11 1561009 Rev A - OQ ChecklistDocument3 pages11 1561009 Rev A - OQ ChecklistZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Two Phase Interleaved Buck ConverterDocument8 pagesDesign and Simulation of Two Phase Interleaved Buck ConverterNeelakanta KallaNo ratings yet
- Barcham DeConstructing The Politics of Indigeneity-With-Cover-Page-V2Document11 pagesBarcham DeConstructing The Politics of Indigeneity-With-Cover-Page-V2Anh Ngữ MercuryNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Department of EducationDocument10 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Department of EducationStevenson Libranda BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Crude Sampling Device IOM-053Document57 pagesCrude Sampling Device IOM-053Stephen MalobaNo ratings yet
- Sukkrivaa Vijayan's Recommendation LetterDocument2 pagesSukkrivaa Vijayan's Recommendation LetterSukkrivaaNo ratings yet
- Research2Module 3writing The SummaryDocument7 pagesResearch2Module 3writing The Summarynoresa comaraNo ratings yet
- TS-GE3 - Soil and Rock AnchorsDocument4 pagesTS-GE3 - Soil and Rock AnchorsAntonio BrasilNo ratings yet
- MasterSeal 940 MasterFlex Aquastop - EngDocument7 pagesMasterSeal 940 MasterFlex Aquastop - EngyounesshammouyouNo ratings yet
- Systems Engineering: Designing, Implementing, Deploying and Operating Systems Which Include Hardware, Software and PeopleDocument47 pagesSystems Engineering: Designing, Implementing, Deploying and Operating Systems Which Include Hardware, Software and Peoplebilal ahmadNo ratings yet
- CV 53001 IntroductionDocument49 pagesCV 53001 IntroductionVictor OmotoriogunNo ratings yet
- Exp.1 Basic SignalsDocument8 pagesExp.1 Basic SignalsDeepesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Strauss PDEch 1 S 6 P 06Document2 pagesStrauss PDEch 1 S 6 P 06Rudi JuliantoNo ratings yet
- Unified Facilities Criteria (Ufc)Document56 pagesUnified Facilities Criteria (Ufc)Ashoka MithiranNo ratings yet
- Presented by M Rahul Chandra Roll Number 11603027: Thermal Power StationDocument20 pagesPresented by M Rahul Chandra Roll Number 11603027: Thermal Power StationManiswari MothukuruNo ratings yet
- Trouble CodesDocument171 pagesTrouble Codeswawan100% (1)
- Operation Safety ManualDocument90 pagesOperation Safety Manualpablo romeroNo ratings yet