Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.1 Number Patterns and Sigma Notation: XX X X
1.1 Number Patterns and Sigma Notation: XX X X
Uploaded by
elyas bergerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.1 Number Patterns and Sigma Notation: XX X X
1.1 Number Patterns and Sigma Notation: XX X X
Uploaded by
elyas bergerCopyright:
Available Formats
Additional exercise
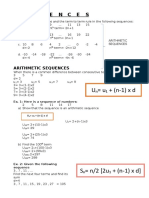
1.1 Number patterns and sigma
notation
1 For each of the following sequences,
i write down the next three terms in each sequence
ii find an expression for the nth term
iii state whether the sequence is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.
a 6, 13, 20, 27, ... b 400, 200, 100, 50, ...
1 3 5 7
c , , , ,... d 3x , 6 x 2 , 9 x 3 ,12 x 4 ,...
5 10 15 20
e 15, 11, 7, 3, ... f 4, -12, 36, -108, ...
2 Write the first six terms of each recursive sequence.
a =
un un −1 + 4 , u1 = −7 b=un 3 ( un −1 − 1) , u1 = 5
4
un = ( un −1 ) , u1 = −2
2
c un = , u1 = 27 d
un −1 + 1
3 Find a recursive formula for the general term of each sequence.
a 4, 16, 256, 65536, ... b 5, 7, 11, 19, ...
1 2 4 8
c , , , ,... d x, 2 x + 1, 4 x + 3, 8 x + 7,...
3 3 3 3
4 For each of the following series in sigma notation, find the terms and calculate the sum.
5 6 6
a ∑2
n =1
n −1
b ∑ (3k + 8)
k =0
c ∑ (a
a =2
2
− 3a )
4 4
2x 3
∑n ∑ x +1 ∑ ( −4)
n
d 3
e f
n =1 x =1 n= 0
5 Write each of the following series in sigma notation.
a 4 + 7 + 10 + 13 + 16 + 19 b 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16
1 1 2 5
c + + + +1 d 3x + 5x + 7 x + 9 x + 11x + 13x + 15x
3 2 3 6
e −5 + 8 − 11 + 14 − 17 + 20 − 23 f 3 + 9 + 27 + 81 + ...
© Oxford University Press 2019 Additional exercise 1
Additional exercise
Answers
1 a i 34, 41, 48
ii u1 = 6 , and d = 13 − 6 = 7 , so un = 6 + 7 ( n − 1) = 7n − 1
iii The sequence is arithmetic, because there is a common difference between each
of the terms.
b i 25, 12.5, 6.25
200
ii u1 = 400 , and
= r = 2 , so un = 400 2n −1
400
( )
iii The sequence is geometric, because there is a common ratio between terms.
9 11 13
c i , ,
25 30 35
ii We can look at the numerator and denominator as two different sequences.
The numerator has a first term of 1 and a common difference of 2.
The denominator has a first term of 5 and a common difference of 5.
1 + 2 ( n − 1) 2n − 1
So un
= =
5 + 5 ( n − 1) 5n
iii The sequence is neither arithmetic nor geometric.
d i 15x 5 ,18 x 6 ,21x 7
ii We can look at the coefficient and the power as two different sequences.
The coefficient is arithmetic with a first term of 3 and a common difference of 3.
The power is geometric with a first term of x and a common ratio of x.
( )( (
So un =3 + 3 ( n − 1) x x n −1 )) =3nx n
iii The sequence is neither arithmetic nor geometric.
e i -1, -5, -9
ii u1 = 15 , and d = −4 , so un= 15 + ( −4 ) ( n − 1)= 19 − 4n
11 − 15 =
iii The sequence is arithmetic, because there is a common difference between each
of the terms.
f i 324, -972, 2916
−12
= −3 , so un = 4 ⋅ ( −3)
n −1
ii u1 = 4 , and r =
4
iii The sequence is geometric, because there is a common ratio between terms.
2 a The first term is -7, and each subsequent term is 4 more than the previous term, so
the first six terms are 7, 11, 15, 19, 23, 30.
b The first term is 5. To find each subsequent term, we subtract 1 from the previous
term and multiply the result by 3, so the first six terms are 5, 12, 33, 96, 285, 852.
c The first term is 27, and to find each subsequent term, we divide 4 by one more than
1 7 8 36 68
the previous term. The first six terms are 27, , , , , .
7 2 9 17 53
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
Additional exercise
d The first term is -2, and to find each subsequent term, we square the previous term.
The first six terms are -2, 4, 16, 256, 65536, 4294967296.
un = ( un −1 ) , u1 = 4
2
3 a b =
un un −1 + 2n −1 , u1 = 5
1
c un = 2un −1 , u1 = d un 2 ( un −1 ) + 1 , u1 = x
=
3
4 a 21−1 + 22 −1 + 23 −1 + 24 −1 + 25 −1 = 20 + 21 + 22 + 23 + 24
= 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 =31
b (3 (0) + 8) + (3 (1) + 8) + (3 (2) + 8) + (3 (3) + 8) + (3 ( 4) + 8) + (3 (5) + 8) + (3 (6 ) + 8)
= 8 + 11 + 14 + 17 + 20 + 23 + 26 =
119
c (2 2
) ( ) (
− 3 (2 ) + 32 − 3 (3) + 42 − 3 ( 4 ) + 52 − 3 (5) + 62 − 3 ( 6 )) ( ) ( )
= −2 + 0 + 4 + 10 + 18 =30
d 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 = 1 + 8 + 27 + 64 =
100
2 (1) 2 (2 ) 2 (3) 2 ( 4) 4 3 8 163
e + + + =1 + + + =
1+1 2 +1 3+1 4 +1 3 2 5 30
( −4) + ( −4 ) + ( −4 ) + ( −4 ) = 1 + ( −4 ) + 16 + ( −64 ) =−51
0 1 2 3
f
5 Note: In this question, other answers are possible, depending on the letter used for the index,
and the values selected for the upper and lower limits.
6 5 5
k +1
a ∑ 3n + 1
n =1
b ∑2
x =1
x −1
c ∑
k =1 6
7 7 ∞
∑ x (2n + 1) ∑ ( −1) (3n + 2) ∑3
n
d e f k
n =1 n =1 k =1
© Oxford University Press 2019 3
You might also like
- Oxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesDocument172 pagesOxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesSıla Deniz100% (1)
- Systems Graphing Si 1 AnswersDocument1 pageSystems Graphing Si 1 AnswersDa'Mya GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basic Number Theory SolnDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Basic Number Theory SolnMOHAMAD HAZRIL ASH'ARINo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document3 pagesTutorial 7zassinvisoofficialNo ratings yet
- (PRE-TEST) UPCAT Review 2014 - Math Questionnaire-1Document7 pages(PRE-TEST) UPCAT Review 2014 - Math Questionnaire-1Strawberry PancakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TestDocument5 pagesChapter 1 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- MAthematical Preliminaries and Matrices (Tutorial 1) - 021644Document5 pagesMAthematical Preliminaries and Matrices (Tutorial 1) - 021644gerald07bwalyaNo ratings yet
- DLP Sequence and SeriesDocument3 pagesDLP Sequence and Seriessunshine sunooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document21 pagesChapter 6Ira LyanaNo ratings yet
- 2 PreCalculusDocument2 pages2 PreCalculusField StudyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Patterns Sequences and SeriesDocument42 pagesChapter 2 Patterns Sequences and Seriesnaidoojayshree903No ratings yet
- S S S 1fur Maths 2nd Term E-Note 2017Document64 pagesS S S 1fur Maths 2nd Term E-Note 2017praiseforever90100% (1)
- Find A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDocument48 pagesFind A Formula or Conjecture For Each of The Patterns Shown Below, and Give The Next Three Terms of Each PatternDineo MasipaNo ratings yet
- Test-7-EE - Signals & Systems PDFDocument18 pagesTest-7-EE - Signals & Systems PDFchiranji lal bairwaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 10-11 Pre-CalculusDocument11 pagesQ2 Week 10-11 Pre-CalculusJONELL PADONGAONo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument7 pagesFinal ExamZaisharyani Mohd HasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Sequences: Arithmetic SequenceDocument3 pagesLesson 2: Sequences: Arithmetic SequenceChriselda CabangonNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths PDFDocument9 pages11 Maths PDFkumar shivamNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6.1 (Solutions) : A N A A A ADocument2 pagesExercise 6.1 (Solutions) : A N A A A Aabdul qadeer AwanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Worksheet and NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 2 Worksheet and NotesCaletha BurtonNo ratings yet
- Past Year Questions: Compiled By: Lee Kian Keong September 14, 2010Document40 pagesPast Year Questions: Compiled By: Lee Kian Keong September 14, 2010Loy Jing ShienNo ratings yet
- AMA2111 HW1 21221 Sol2Document7 pagesAMA2111 HW1 21221 Sol2mkkkNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Math 10Document2 pagesActivity 1 Math 10Reymar PadayaoNo ratings yet
- University of Malta Junior College: Subject: Advanced Pure Mathematics Date: June 2013 Time: 9.00 - 12.00Document20 pagesUniversity of Malta Junior College: Subject: Advanced Pure Mathematics Date: June 2013 Time: 9.00 - 12.00Brendon ChiwengaNo ratings yet
- SeriesDocument16 pagesSeriesMav CastilloNo ratings yet
- Little Wonders Convent School: Qno.1. 15 MarkDocument3 pagesLittle Wonders Convent School: Qno.1. 15 MarkArpan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- StuddyDocument11 pagesStuddyeerturan25No ratings yet
- Hit Bulls Eye Algebra QuestionsDocument22 pagesHit Bulls Eye Algebra QuestionsJack Looser100% (1)
- Review Q2 Chapters 9 and 1Document4 pagesReview Q2 Chapters 9 and 1Jeronimo Jr. NacordaNo ratings yet
- IX - Oly - 12 - 3 - 23 (Solution)Document8 pagesIX - Oly - 12 - 3 - 23 (Solution)Mihir DhankarNo ratings yet
- Find Terms of Sequences Given The General or NTH Term. Convert Between Sigma Notation and Other Notation For A SeriesDocument99 pagesFind Terms of Sequences Given The General or NTH Term. Convert Between Sigma Notation and Other Notation For A SeriesChristina Aguila NavarroNo ratings yet
- Handouts 4 5 and 6Document4 pagesHandouts 4 5 and 6Arvin Paul A. SorianoNo ratings yet
- CPT ReviewDocument18 pagesCPT ReviewSteven Diaz100% (4)
- Class 9 Maths Ws 06 PDFDocument9 pagesClass 9 Maths Ws 06 PDFPoorv KantNo ratings yet
- CSEC ADD Maths SPECIMEN PAPER 1 PDFDocument26 pagesCSEC ADD Maths SPECIMEN PAPER 1 PDFreeta ram100% (1)
- Pre-Calculus: Sigma NotationDocument12 pagesPre-Calculus: Sigma NotationKeithlan Rosie Fetil LlanzaNo ratings yet
- FURTHERMATHSDocument6 pagesFURTHERMATHSMadu Cecilia chiomaNo ratings yet
- Question Bnak On Applied MathematicsDocument6 pagesQuestion Bnak On Applied MathematicsShreya ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences: U U U U U X X X UDocument3 pages1.2 Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences: U U U U U X X X UOmarioh KhaledNo ratings yet
- f1 Maths Take Home Assignment WDocument5 pagesf1 Maths Take Home Assignment WDavid AmegashitsiNo ratings yet
- Math 10Document6 pagesMath 10Monica Joyce NaperiNo ratings yet
- Blog PostDocument2 pagesBlog PostLetsogile BaloiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Sequences and SeriesDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 - Sequences and SeriesHALIMATUN NADHIRAH BINTI ABDUL AZIZ FS21110438No ratings yet
- Integer Exponents: A A A A ADocument5 pagesInteger Exponents: A A A A Achloe NavarroNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths PDFDocument6 pages11 Maths PDFkumar shivamNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions: 3.1 Introduction To AlgebraDocument8 pagesAlgebraic Expressions: 3.1 Introduction To Algebras2023038No ratings yet
- Add Math ProgressionsDocument15 pagesAdd Math Progressionskamil muhammad100% (1)
- Week6 Equation of A Linea 1Document50 pagesWeek6 Equation of A Linea 1Dame YooheeNo ratings yet
- PriiiintDocument30 pagesPriiiintisnaira bloNo ratings yet
- GUESS PAPER-2m, 3m & 5m QuestionsDocument13 pagesGUESS PAPER-2m, 3m & 5m Questionsdevananth070No ratings yet
- Sequences and Series Practice Questions For JEEDocument14 pagesSequences and Series Practice Questions For JEEAarush KaletwadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 - Sequences and SeriesDocument2 pagesWorksheet 3 - Sequences and SeriesSta KerNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Revision Set DDocument2 pagesMid Term Revision Set DsnadzhaniNo ratings yet
- Math Summary 5Document5 pagesMath Summary 5as12No ratings yet
- JEE Mains Mathematics 2023 13-April-Shift 1Document8 pagesJEE Mains Mathematics 2023 13-April-Shift 1rupeshvrkvnr08092005No ratings yet
- ABSTRACT ALGEBRA NotesDocument28 pagesABSTRACT ALGEBRA Notesjakedioqueno23No ratings yet
- Geometric ProgressionDocument7 pagesGeometric ProgressionFarhad HossainNo ratings yet
- DeMoiveres Theorem Trig ExpansionsDocument2 pagesDeMoiveres Theorem Trig ExpansionsKarthik BingiNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Matrix Estimate and The Perron-Frobenius TheoremDocument6 pagesMatrix Estimate and The Perron-Frobenius TheoremChenhui HuNo ratings yet
- RPT Matematik t5 (2018)Document8 pagesRPT Matematik t5 (2018)ckgfiezahNo ratings yet
- Mod 3-Laplace Transform - QB PDFDocument2 pagesMod 3-Laplace Transform - QB PDFAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Maths Integers WorksheetDocument3 pagesClass 6 Maths Integers WorksheetMishti MandaviyaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) PairsDocument23 pagesDiscrete Fourier Transform (DFT) PairsgoutamkrsahooNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiaryDocument5 pagesIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C2 Advanced SubsidiaryssmithNo ratings yet
- USN 17MAT21: Model Question Paper With Effect From 2017-18Document3 pagesUSN 17MAT21: Model Question Paper With Effect From 2017-18VyshnaviNo ratings yet
- TEST 15 (Intermediate Algebra & Statistics)Document41 pagesTEST 15 (Intermediate Algebra & Statistics)Bblack DeathNo ratings yet
- CBCS - GE For BA and BCom (Prog)Document6 pagesCBCS - GE For BA and BCom (Prog)Kunal chandoliyaNo ratings yet
- A Textbook of Engineering Mathematics (Volume I)Document379 pagesA Textbook of Engineering Mathematics (Volume I)Ngwe ThinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0Document21 pagesMathematics: 1St Generation Modules - Version 2.0Mii Kiwi-anNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Practice: Solve For X. Round To The Nearest Tenth When NecessaryDocument3 pagesTrigonometry Practice: Solve For X. Round To The Nearest Tenth When NecessaryHORACIO VIRAMONTESSALDANANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Topics: FX X X GX X F FDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Topics: FX X X GX X F Fapi-168512039No ratings yet
- 02 Summation NotationDocument6 pages02 Summation NotationReinaNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations Maths WorksheetDocument3 pagesLinear Equations Maths WorksheetHUSSAIN MATHS0% (1)
- Algebraclassified PDFDocument21 pagesAlgebraclassified PDFCassandra LauNo ratings yet
- MA2311 Chapter 5Document118 pagesMA2311 Chapter 5Brandon OuyangNo ratings yet
- Chap29 - 472-486Document15 pagesChap29 - 472-486ommathNo ratings yet
- Heaviside Step FunctionDocument6 pagesHeaviside Step FunctionJohnStratigakisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations 5.3Document5 pagesChapter 5 Quadratic Equations 5.3Ayush sharmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Final Practice Sol)Document30 pagesMathematics Final Practice Sol)TEJASSINGH ARORANo ratings yet
- Equations: Right Angled Triangles: Soh Sin ( °) - Cah Cos ( °) - Toa Tan ( °)Document1 pageEquations: Right Angled Triangles: Soh Sin ( °) - Cah Cos ( °) - Toa Tan ( °)Jay AmbadkarNo ratings yet
- Notes 1.2 - Significant FiguresDocument6 pagesNotes 1.2 - Significant FiguresBilly JenkinsNo ratings yet
- MODULE Limits-And-ContinuityDocument64 pagesMODULE Limits-And-ContinuityAudie T. MataNo ratings yet
- Cbjemapu 04Document8 pagesCbjemapu 04Dashdaber 154No ratings yet
- CS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 4 (Part I) : 3D Affine TransformsDocument26 pagesCS 543: Computer Graphics Lecture 4 (Part I) : 3D Affine TransformsThanasis AnthopoulosNo ratings yet
- Solving Absolute Value EquationsDocument24 pagesSolving Absolute Value EquationsAdnan BukhariNo ratings yet