Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers Marks: C2, Chapter 1
Answers Marks: C2, Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Sikander ShahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers Marks: C2, Chapter 1
Answers Marks: C2, Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Sikander ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
C2, Chapter 1
Answers Marks
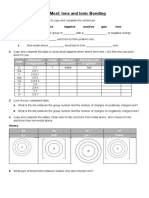
1 a transferred 1
b covalent 1
2 a simple molecule 1
b giant covalent 1
c metal 1
d giant ionic 1
3 a 1 1
b 6 1
c 4 1
d 3 1
4 a FeCl3 1
b i Na2S 1
ii Na2SO4 1
5 Ca2+, OH– 2
6 a i element 1
ii compound 1
b It loses an electron. 2
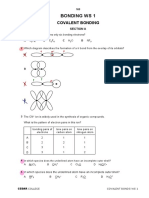
c i Right hand diagram with seven crosses and one dot in outermost shell
(allow diagram with all crosses). 1
ii Oppositely charged ions attract each other. 1
7 a Each correctly drawn part of the diagram should be answered (one mark). 4
• Correctly drawn potassium atom (one electron in outer shell).
• Correctly drawn chlorine atom (seven electrons in outer shell).
• Correctly drawn potassium ion: no electron in outer shell (accept eight
electrons in outer shell) and brackets with charge top right.
• Correctly drawn chloride ion: eight electrons in outer shell and brackets
with – charge top right.
b For example, H atom: circle with a single dot, Cl atom: circle with seven 2
crosses overlapping H circle so that a dot and cross are shared or
alternative with no circles. Must be one electron different from seven others
and a shared pair including that electron clearly shown for two marks. One
mark for a shared pair of electrons, or eight electrons all with the same
symbol.
8 Electrons in the highest (occupied) energy level/outer shell are delocalised/ 3
free (to move), leaving or surrounding positive ions (in regular
lattice/arrangement), electrons attract/hold together the positive ions.
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 1
You might also like
- Activity 4 - Worksheet On Formation of IonsDocument2 pagesActivity 4 - Worksheet On Formation of IonsJohn Lesther PabiloniaNo ratings yet
- Solids Andstructures Mehanics IV NotesDocument98 pagesSolids Andstructures Mehanics IV NotesInno Odira100% (3)
- Analytical Modeling of Carbon Transport Rocesses in Heat Treatment Technology of SteelsDocument14 pagesAnalytical Modeling of Carbon Transport Rocesses in Heat Treatment Technology of SteelsdeimosXNo ratings yet
- C6 Book AnswersDocument4 pagesC6 Book AnswersvijahatNo ratings yet
- 2 Struktur KeramikDocument93 pages2 Struktur KeramikMichael Robert Tua NababanNo ratings yet
- Fisban 02-Struktur Atom Dan IkatanDocument19 pagesFisban 02-Struktur Atom Dan IkatanneolarinsNo ratings yet
- Ch2 BondingDocument31 pagesCh2 BondingSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- Skema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2Document9 pagesSkema PPT Kimia P2 Ting 4 2021, 2leong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument1 pageIonic Compoundsgaurav_718676500No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Material ScienceDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Material ScienceFadhli JapryNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 2Document16 pagesIonic Bonding 2Bira NoNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingDocument12 pagesAS Level Chemistry Notes: BondingAyesha Ahmed100% (1)
- ChapterDocument27 pagesChapterbernabethNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesChapter-8 ElectrolysisOhi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Macam IIkatan Pembentuk Bahan Dan SifatnyaDocument18 pagesMacam IIkatan Pembentuk Bahan Dan SifatnyaNoviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper Set - (10) MSDocument4 pagesChemistry Model Paper Set - (10) MSAditya Kumar 12ANo ratings yet
- Year 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 3 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesYear 10 Semester One Revision Sheet 3 ANSWERSsports.kingdomNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry q2 Week 7Document64 pagesGeneral Chemistry q2 Week 7Keisha Mae Custodio100% (1)
- 1.chem Review & Aquesous Solutions Key.Document34 pages1.chem Review & Aquesous Solutions Key.Calo Is TrashNo ratings yet
- 5.2.1.2 Ions QuestionsDocument2 pages5.2.1.2 Ions QuestionsVietnamese Expert VS ZTNTSTNo ratings yet
- Yousef 6Document4 pagesYousef 6Karim AL-TijaniNo ratings yet
- A+ Blog-Std-9-First Term Exam 2022-Anser Key-Em PDFDocument2 pagesA+ Blog-Std-9-First Term Exam 2022-Anser Key-Em PDFKaashinath Ayyappan (Kaashi)No ratings yet
- ChembondDocument43 pagesChembondroziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedDocument13 pagesTest4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-MarkedEga SukmaNo ratings yet
- A+ BLOG-A+ BLOG-STD-9-CHEMISTRY-ANNUAL EXAM 2024-ANS KEY EMDocument2 pagesA+ BLOG-A+ BLOG-STD-9-CHEMISTRY-ANNUAL EXAM 2024-ANS KEY EMdiaan866No ratings yet
- 1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionDocument3 pages1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 - Atomic BondingDocument19 pagesChapter - 02 - Atomic BondingIlham AkbarNo ratings yet
- Naming of Compounds - Part2Document2 pagesNaming of Compounds - Part2Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesMarking Schemessankar3108No ratings yet
- Unit Test Sample Paper - 1 Answer KeyDocument7 pagesUnit Test Sample Paper - 1 Answer Keymilonee lNo ratings yet
- BS Chemistry MCQsDocument6 pagesBS Chemistry MCQsRamsha saeedNo ratings yet
- Keira Resalsingh - Metallic and Ionic Bonding Worksheet Week 1 April 20th-24thDocument3 pagesKeira Resalsingh - Metallic and Ionic Bonding Worksheet Week 1 April 20th-24thSideka ResalsinghNo ratings yet
- Week 7. The Electronic Structure of The Atom: Science ConceptsDocument16 pagesWeek 7. The Electronic Structure of The Atom: Science ConceptsCupang Senior High School (NCR - Muntinlupa City)No ratings yet
- Skema - Bab 1 Ting. 5Document4 pagesSkema - Bab 1 Ting. 5SMK MERSING (SEK-JEA4035)No ratings yet
- AQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Document6 pagesAQA Chem 1 Answers ch03Ellie AndersonNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..Document19 pagesAtomic Structure and Interatomic Bonding: Issues To Address..gebreslassie gereziherNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument29 pagesAtomic Structuremahmad123412374No ratings yet
- Answred Chem Mid TermDocument12 pagesAnswred Chem Mid Termlife of yomnaNo ratings yet
- Structures of Engineering MaterialsDocument43 pagesStructures of Engineering MaterialsZahra KaylNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 - Atomic BondingDocument21 pagesChapter - 02 - Atomic BondingJames WilliamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 AviDocument19 pagesChapter 02 AviJames WilliamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Document4 pagesChemistry U3&4 TEST 2 Suggested Solutions - 2017Neyaz RazaviNo ratings yet
- Bonding Forces and Energies Al Francis Asuncion EE 3bDocument8 pagesBonding Forces and Energies Al Francis Asuncion EE 3bAce John OliverNo ratings yet
- Chm221 Chapter 5Document42 pagesChm221 Chapter 5Badrudin JundailiNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument56 pagesBondingAngel Joy CATALAN (SHS)No ratings yet
- Module in Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesModule in Chemical BondingJaycee De LeonNo ratings yet
- Electrons WS 5 Electron Configuration IonsDocument3 pagesElectrons WS 5 Electron Configuration IonsAna Marie Corales TabunarNo ratings yet
- 4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedDocument2 pages4TH QUARTER EXAM ADVANCE CHEM - EditedWilsonNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA GCSE Chem C2 Summary Question Answersanusha.bariraNo ratings yet
- Notas de Clase 0 EnlacesDocument4 pagesNotas de Clase 0 EnlacesLEANDRO ORTIZ TABARESNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Bonding PDFDocument14 pagesInteratomic Bonding PDFFaysal Qadeer KhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledSuzuki YatoNo ratings yet
- Chemsitry Bridging The GapDocument26 pagesChemsitry Bridging The Gapnhussain1747No ratings yet
- Ions Grade 9 Q2 Science LASDocument10 pagesIons Grade 9 Q2 Science LASmelicyn maristelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Crystal Structures of MaterialsDocument105 pagesChapter 2 Crystal Structures of MaterialsMuhd Akram Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Oxides, Chlorides and HydridesDocument31 pagesChapter 4 - Oxides, Chlorides and HydridesTasha RaviendranNo ratings yet
- Merit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 1 YearDocument1 pageMerit Science Academy Faisalabad: Chemistry 1 YearShakaibNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 02 NewDocument36 pagesChapter - 02 NewmaheshNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 10QP - Chemistry - JVPDocument4 pagesSummative Test 10QP - Chemistry - JVPjv peridoNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectronegativity QuestionsThe ImmortalNo ratings yet
- 9 and 19 MCQDocument18 pages9 and 19 MCQrania samirNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingFrom EverandCorrosion Resistance of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys: Understanding, Performance, and TestingNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study On 3D Effect and Practical Design in Shield TunnelingDocument9 pagesNumerical Study On 3D Effect and Practical Design in Shield TunnelingDidaBouchNo ratings yet
- Schmidt Rebound Hammer TestDocument3 pagesSchmidt Rebound Hammer Testh4m0n4ng4nNo ratings yet
- Ball Valve MTRDocument5 pagesBall Valve MTRThiva karNo ratings yet
- Specification For General Requirements For Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled BarDocument16 pagesSpecification For General Requirements For Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled BarJolettitoNo ratings yet
- Estimate FinalDocument105 pagesEstimate Finalbiswabhusan biswalNo ratings yet
- Everything About Material & Render Settings: June 28, 2018Document46 pagesEverything About Material & Render Settings: June 28, 2018ltdemonNo ratings yet
- Latest-Emerging Manufacturing Processes PDFDocument25 pagesLatest-Emerging Manufacturing Processes PDFSaifullah AlamNo ratings yet
- Limestone CalcinationDocument11 pagesLimestone Calcinationfaizah_ismail0308No ratings yet
- Basalt FiberDocument19 pagesBasalt FiberShariqKhanNo ratings yet
- High Energy Beams and Related Welding and Cutting Process PrinciplesDocument8 pagesHigh Energy Beams and Related Welding and Cutting Process PrinciplesWilly UioNo ratings yet
- Electric SparkDocument5 pagesElectric SparkpepeNo ratings yet
- Determination of Pore Volume and Pore Volume Distribution of Soil and Rock by Mercury Intrusion PorosimetryDocument8 pagesDetermination of Pore Volume and Pore Volume Distribution of Soil and Rock by Mercury Intrusion PorosimetryWanucy Barroso RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Constitutive Modeling of Γ-irradiated Silicone Rubber Foams Under Compression and Shear LoadingDocument9 pagesConstitutive Modeling of Γ-irradiated Silicone Rubber Foams Under Compression and Shear LoadingzhuhaitingtaoNo ratings yet
- 10-Storey Commercial Building Stair PlanDocument1 page10-Storey Commercial Building Stair Planpaglinawan.lovelle18No ratings yet
- Chapter 16-Macro-Etching-ExaminationDocument10 pagesChapter 16-Macro-Etching-ExaminationBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESNo ratings yet
- GrrtyhvhDocument20 pagesGrrtyhvhDebolina DasNo ratings yet
- Wirand Application Re3 ValuesDocument2 pagesWirand Application Re3 ValuesSerbanDragosNo ratings yet
- AmitrazDocument21 pagesAmitrazSriram SNo ratings yet
- S-Oil Hydro Fluid Aw: Product DescriptionDocument1 pageS-Oil Hydro Fluid Aw: Product DescriptionJonhNo ratings yet
- TB Grinding EnglishDocument20 pagesTB Grinding EnglishVk PrabakranNo ratings yet
- Brick and Stone MasonryDocument36 pagesBrick and Stone Masonrym tahirNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSab Ka Malik EkNo ratings yet
- TR7232 1E Powercell 760Document1 pageTR7232 1E Powercell 760Omar LichtjahreNo ratings yet
- TCVN 9888-3 - 2013 - IEC 62305-3 - 2010 - 1049711 EN VerDocument137 pagesTCVN 9888-3 - 2013 - IEC 62305-3 - 2010 - 1049711 EN VerNam NguyenNo ratings yet
- 12 20 (24) KV HXLP DSTA - Pdic01114Document2 pages12 20 (24) KV HXLP DSTA - Pdic01114Luis MurilloNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Aug 17, 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Aug 17, 2023gulatisrishti15No ratings yet
- 2011-6 TechPresentation SperkoDocument46 pages2011-6 TechPresentation SperkoConnie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron FibreDocument6 pagesExperimental Investigation of Self Compacting Concrete by Partially Replacing Fine Aggregate With Quartz Sand With Use of Recron Fibreshivanand hippargaNo ratings yet