Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section3 10
Section3 10
Uploaded by
mudabbir muhammadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Section3 10
Section3 10
Uploaded by
mudabbir muhammadCopyright:
Available Formats
Example
Example 3.10.1
Sketch the hyperbola with equation
9x 2 + 36x − 16y 2 + 160y = 220.
Find its eccentricity, centre and asymptotes.
Solution: We complete the square:
9x 2 + 36x − 16y 2 + 160y = 220
9(x 2 + 4x) − 16(y 2 − 10y ) = 220
9((x + 2)2 − 4) − 16((y − 5)2 − 25) = 220
9(x + 2)2 − 16(y − 5)2 = 220 + 36 − 400
9(x + 2)2 − 16(y − 5)2 = −144
9(x + 2)2 16(y − 5)2
− + =1
144 144
(x + 2)2 (y − 5)2
− + = 1.
16 9
Example continued
Note that the sign of the first term is negative. So we choose new
coordinates X = y − 5 and Y = x + 2. This gives us the standard form
equation
X2 Y2
− = 1,
32 42
with a = 3 and b = 4.
The eccentricity is
r r r
b2 16 25 5
e= 1+ 2 = 1+ = = .
a 9 9 3
The centre is at (X , Y ) = (0, 0), which corresponds to (x, y ) = (−2, 5).
Example continued
X Y
The asymptotes are a ± b = 0, i.e.
y −5 x +2
+ = 0 and
3 4
y −5 x +2
− =0
3 4
The first one simplifies to 3x + 4y − 14 = 0, while the second simplifies
to 3x − 4y + 26 = 0.
√
We compute the axis intercepts: (0, 5 + 245 ) ≈ (0, 8.35),
√
(0, 5 − 245 ) ≈ (0, 1.65), ( 10 22
3 , 0) ≈ (3.33, 0) and (− 3 , 0) ≈ (−7.33, 0).
The vertices are (±3, 0) in X , Y -coordinates, which correspond to
(−2, 2) and (−2, 8) in x, y -coordinates.
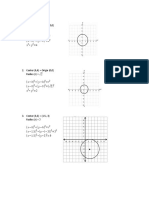
Hence, we obtain a sketch of the hyperbola:
Example continued
√
45
• − 5+ 2
(−2, 8)
• − 5−
√
45
2
(−2, 2)
| |
x
− 22
3
10
3
You might also like
- MJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 2 Solutions PDFDocument10 pagesMJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 2 Solutions PDFRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- Physics MathematicsDocument36 pagesPhysics Mathematicsmudabbir muhammad33% (3)
- Magnus EffectDocument6 pagesMagnus EffectAbdurrahman Abu AdibNo ratings yet
- bXlzZ2RzZW9qMDEzNTI0Mzk4WA PDFDocument2 pagesbXlzZ2RzZW9qMDEzNTI0Mzk4WA PDFMadhuri100% (1)
- Advanced Fluid W2Document14 pagesAdvanced Fluid W2Vijayan SnNo ratings yet
- Eew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)Document3 pagesEew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)James WigtonNo ratings yet
- Answer 32347Document3 pagesAnswer 32347Lysander Four DelimaNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics 1: Quadrati CSDocument11 pagesPure Mathematics 1: Quadrati CSTest BigbenNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7Document8 pagesAnalytic Geometry and Calculus I Exam 1 Practice Problems Solutions 2/19/7Huges ApolNo ratings yet
- 2.monomials and PolynomialsDocument6 pages2.monomials and PolynomialsMohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- Translating Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesTranslating Conic SectionsNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument2 pagesCompleting The Squarebrendonsithole6No ratings yet
- Genform To Center and RadiusDocument3 pagesGenform To Center and RadiusRedante FernandezNo ratings yet
- Q1 LAS W5-6 Nondegenerate and Degenerate ConicsDocument2 pagesQ1 LAS W5-6 Nondegenerate and Degenerate ConicsPamela Nicole DomingoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Chapter Review 2 (Solution)Document19 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Chapter Review 2 (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- Y X BX C: Analytical Geometry: SolutionsDocument2 pagesY X BX C: Analytical Geometry: SolutionsMarcus PrangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations Week 1 and 2Document21 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations Week 1 and 2Pinky DaisiesNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers - Part 1Document3 pagesComplex Numbers - Part 1zithasiphosethu1No ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Exercise 2C (Solution)Document6 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Exercise 2C (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- MATH2018 - 2019 Exam T1 2020 SolutionsDocument10 pagesMATH2018 - 2019 Exam T1 2020 SolutionsNorris wongNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations MethodsDocument29 pagesQuadratic Equations MethodsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Circle (Exercise)Document34 pagesCircle (Exercise)Rohan GubbaNo ratings yet
- Maths Practicesheet-01 - (Code-A) - Sol.Document9 pagesMaths Practicesheet-01 - (Code-A) - Sol.ksanthosh29112006No ratings yet
- Higher Mathematics - Circles (Solutions To Q1-Q4) - LeahDocument3 pagesHigher Mathematics - Circles (Solutions To Q1-Q4) - LeahThomas ChanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.0 (Main)Document19 pagesExercise 1.0 (Main)rockydalabehera94No ratings yet
- Sample Problems - Logarithms and ExponentsDocument2 pagesSample Problems - Logarithms and ExponentsANo ratings yet
- E-Mail: Alfadhel@ksu - Edu.saDocument30 pagesE-Mail: Alfadhel@ksu - Edu.samasrawy eduNo ratings yet
- S5 W15 V06 Equation-Of-Circle Ver2022 Homework SolutionDocument6 pagesS5 W15 V06 Equation-Of-Circle Ver2022 Homework Solutionno ehNo ratings yet
- Circle (Solved Example + Exercise)Document24 pagesCircle (Solved Example + Exercise)Ankit sharma100% (1)
- Sheet - 01 - Circle (1) - BookletDocument2 pagesSheet - 01 - Circle (1) - BookletPiro Brol Star Nai MariNo ratings yet
- E-Mail: Alfadhel@ksu - Edu.saDocument22 pagesE-Mail: Alfadhel@ksu - Edu.samasrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Solution P 1 Jan 19Document16 pagesSolution P 1 Jan 19hasan zaidiNo ratings yet
- 2016 - June - P1.3Document10 pages2016 - June - P1.3cris yeNo ratings yet
- Circles Determine by Different ConditionsDocument44 pagesCircles Determine by Different ConditionsbagolcoltyraNo ratings yet
- 6-1 Circles: Unit 6 ConicsDocument20 pages6-1 Circles: Unit 6 ConicsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry NotesDocument3 pagesCoordinate Geometry NotesVishwesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Eew - ps2 - Sol (Functions and Equations)Document6 pagesEew - ps2 - Sol (Functions and Equations)James WigtonNo ratings yet
- S5 W13 V06 Equation-of-Circle Ver2022 Homework SolutionDocument4 pagesS5 W13 V06 Equation-of-Circle Ver2022 Homework Solutionno ehNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Exercise 2D (Solution)Document7 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Exercise 2D (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- Math 114 - Discussion 307 & 309 Worksheet 3 (9/18 Mon)Document2 pagesMath 114 - Discussion 307 & 309 Worksheet 3 (9/18 Mon)Tesfaye Utopia UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Exam # 3: F (X) X 9x + 24x F F F F XDocument4 pagesSolutions For Exam # 3: F (X) X 9x + 24x F F F F XparcaperuNo ratings yet
- 2024 Math 2 - WA2 - Practice Paper 4 and SolutionsDocument5 pages2024 Math 2 - WA2 - Practice Paper 4 and SolutionsTarun Rana Rajdevar (Victoriasch)No ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problems 2newDocument6 pagesBoundary Value Problems 2newKidist TaluNo ratings yet
- Wing Hong Tony Wong: R R R 2RDocument5 pagesWing Hong Tony Wong: R R R 2RRich WongNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1991 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument7 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1991 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- MH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnDocument11 pagesMH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnYachen WuNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Quadratics HardDocument18 pages1 1 Quadratics HardShanayaNo ratings yet
- Precal - Lesson 2Document4 pagesPrecal - Lesson 2alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- EMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015Document6 pagesEMT 1101 End of Semester Supplementary Exam December 2015jonathane nhlaneNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Section 2-6: CirclesDocument27 pagesAnalytic Geometry Section 2-6: CirclesenggNo ratings yet
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1Document15 pagesNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1shahidNo ratings yet
- PHYS 112 Seatwork 1Document3 pagesPHYS 112 Seatwork 1AlessandraNo ratings yet
- Equation of CircleDocument5 pagesEquation of CircleBjorn AbuboNo ratings yet
- Straight Line 3Document9 pagesStraight Line 3aeeeelvishbhaiiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Methods 1/2 - Chapter 8 Revision of 1 To 7Document32 pagesCambridge Methods 1/2 - Chapter 8 Revision of 1 To 7Esther CheungNo ratings yet
- Acsbr 2018 Prelim 4exp Am P1 AnsDocument6 pagesAcsbr 2018 Prelim 4exp Am P1 Ansc8ftcky9zwNo ratings yet
- Amath Revision 4 Solution PDFDocument6 pagesAmath Revision 4 Solution PDFJia Hao Chai (JamesChai123)No ratings yet
- Solutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsDocument12 pagesSolutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsMaruf_007No ratings yet
- Handout 2Document6 pagesHandout 2Marvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- Solution: (X-H) (X-H) + (Y-K) (Y-K) - RDocument2 pagesSolution: (X-H) (X-H) + (Y-K) (Y-K) - RReighnar louisse FernandezNo ratings yet
- Manifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamDocument21 pagesManifolds, Tensor Analysis and Applications 3rd Ed. - Marsden, Ratiu and AbrahamSreerag S KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 4 Exercise 4.4Document21 pagesNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 4 Exercise 4.4shahidNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Section3 9Document10 pagesSection3 9mudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics MKMM 1213: C23-316 Ibthisham@utm - MyDocument34 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics MKMM 1213: C23-316 Ibthisham@utm - Mymudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics MKMM 1213: C23-316 Ibthisham@utm - MyDocument23 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics MKMM 1213: C23-316 Ibthisham@utm - Mymudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Theorem 3.7.1: The Standard EllipseDocument13 pagesTheorem 3.7.1: The Standard Ellipsemudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Lemma 3.6.1: Consider A Conic Choose X - and Y - Axes So That F Is The Origin and L Is Parallel To The The Equation ofDocument11 pagesLemma 3.6.1: Consider A Conic Choose X - and Y - Axes So That F Is The Origin and L Is Parallel To The The Equation ofmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- FPSC@FPSC Gov PKDocument2 pagesFPSC@FPSC Gov PKmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Conjugate Gradient Method: 1 GoalDocument5 pagesDerivation of The Conjugate Gradient Method: 1 Goalmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory: Mr. Umar FaryazDocument22 pagesGraph Theory: Mr. Umar Faryazmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Derivation of The Conjugate Gradient Method: 1 GoalDocument5 pagesDerivation of The Conjugate Gradient Method: 1 Goalmudabbir muhammadNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual Numerical Methods by Vedamurthy PDFDocument70 pagesSolution Manual Numerical Methods by Vedamurthy PDFmudabbir muhammad100% (1)
- Graph Theory Lecture Series: Mr. Umar Faryaz Assistant Professor Department of MathematicsDocument55 pagesGraph Theory Lecture Series: Mr. Umar Faryaz Assistant Professor Department of Mathematicsmudabbir muhammad100% (1)
- Regression Analysis - Chapter 4 - Model Adequacy Checking - Shalabh, IIT KanpurDocument36 pagesRegression Analysis - Chapter 4 - Model Adequacy Checking - Shalabh, IIT KanpurAbcNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Q4-Module-6Document16 pagesMath 7-Q4-Module-6Cher Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Vector Field: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesVector Field: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarachitNo ratings yet
- Array: Write A C Program To Check Whether The Matrix Is SymmetricDocument4 pagesArray: Write A C Program To Check Whether The Matrix Is SymmetricAkshat PattiwarNo ratings yet
- Convention Paper: in Situ Determination of Acoustic Absorption CoefficientsDocument10 pagesConvention Paper: in Situ Determination of Acoustic Absorption CoefficientsJulian ForondaNo ratings yet
- Optimisation OF Machining Parameters IN Machining of Aisi 4130 Steel Using Wire - Electric Discharge MachiningDocument61 pagesOptimisation OF Machining Parameters IN Machining of Aisi 4130 Steel Using Wire - Electric Discharge MachiningTejesh KolathurNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity and PlasticityDocument3 pagesTheory of Elasticity and Plasticityrameshbabu_1979100% (1)
- You Have The Mark of The Beast Not Forwarding This To Nine People So Saith The Lord Your GodDocument70 pagesYou Have The Mark of The Beast Not Forwarding This To Nine People So Saith The Lord Your GodGo Og100% (1)
- Digital Electronics 1Document8 pagesDigital Electronics 1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Term 2 (Mathematics) SyllabusDocument2 pagesTerm 2 (Mathematics) SyllabusKislay AnandNo ratings yet
- Indefinite IntegrationDocument29 pagesIndefinite IntegrationBharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Association RuleDocument41 pagesChapter 10 Association Rulenadia frizaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus TestDocument4 pagesPre-Calculus TestRaffy CeeNo ratings yet
- 4.0 - Matrix InverseDocument2 pages4.0 - Matrix InverseHabib MradNo ratings yet
- SMCh03 FinalDocument11 pagesSMCh03 FinalSharmaine SurNo ratings yet
- Module 9: Worked Out ProblemsDocument18 pagesModule 9: Worked Out Problemscaptainhass100% (1)
- Markov Chain BlackjackDocument15 pagesMarkov Chain BlackjackstupidchatbotNo ratings yet
- Samrat Ashok Technological Institute: Cs/It Department, S.A.T.I VidishaDocument13 pagesSamrat Ashok Technological Institute: Cs/It Department, S.A.T.I VidishaK DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Ali RazaDocument20 pagesAli RazaJawad HussainNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - 5.2 Magnetic Flux - Induced EmfDocument4 pages5.1 - 5.2 Magnetic Flux - Induced EmfAFIQ HAFIZ NAJMI BIN KHUSAIRIE MUAZAM MoeNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1938-14 Standard Test Method For Tear PropagationDocument4 pagesASTM D1938-14 Standard Test Method For Tear PropagationLicitacion04 msNo ratings yet
- D.E. DPP 5Document3 pagesD.E. DPP 5Priyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses PresentationDocument14 pagesHypotheses Presentationsidhartha jainNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document46 pagesCH 04AlonsoNo ratings yet
- LM-1st Quarter - Stage 3Document26 pagesLM-1st Quarter - Stage 3An Neh GynNo ratings yet
- MMW Mod#4 StatisticsDocument6 pagesMMW Mod#4 StatisticsAldrich FelixNo ratings yet
- Soil Dynamic & EQ Engineering by B B PrasadDocument583 pagesSoil Dynamic & EQ Engineering by B B PrasadBernathTurnip0% (1)