Professional Documents
Culture Documents
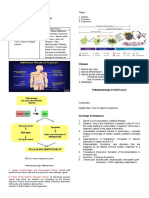
Cancer Notes
Cancer Notes
Uploaded by
PCIs DR RotationOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
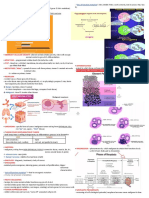
Cancer Notes
Cancer Notes
Uploaded by
PCIs DR RotationCopyright:
Available Formats
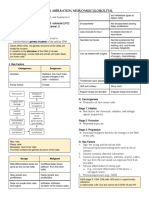
Cancer Notes Hyperplasia-
Pain and Death Compensatory Hyperplasia - proliferation
of cells while they maintain their
CA Nurse – support pt & family through differentiated structure and function.
physical, emotional, social, cultural & spiritual
crises. Hormonal Hyperplasia -
Cancer
Dilatation and curettage
Med term – Malignant Neoplasm
Hypertrophy - increase size of cells
Abnormal proliferation of cells.
Atrophy – decrease size in cell
Angiogenesis – formation of blood vessels
Dysplasia – Deranged cell growth
Necrosis – traumatic cell death
Metaplasia – Substitution of one cell with
Apoptosis – programmed self death other type
Produce apoptotic bodies – it collects cellular Factors which contribute to the devt of CA
debris that may cause mutation of cell.
1. Oncogenic Viruses + Oncogene
Metastasis – spread of cancer by blood vessel
– Ability to transform normal cell to a
Gold standard test is Tissue Biopsy malignant cell. Theory by Francis
Peyton Rous in 1911.
Carcinoma – CA from epithelial cells
2. Carcinogens
Sarcoma – CA from non epithelial tissue , blood -post close & prolong exposure;
vessel, muscles, skin and bones cause cell and alteration
Melanoma – skin sarcoma
Chemical – forms electrophiles
Oncogenes – discovered by Francis a. Industrial compounds
Peyton Rous b. Foods and preservatives
- Cancer Radiation – adaptive effect (high
energy)
Proto oncogenes – benign forms of
oncogenes necessary for normal cell Chemical carcinogen
functions.
Vinyl chloride
Proto oncogenes
- Plastic manufacture
Retrovirus –
-Asbestos factories
Cellular Adaptive Process –
- construction works
Differentiation – cells transformed into
different specialized types as they Polycyclic Aromatic
proliferate from a single stem cell. Hydrocarbons
In blood formation stem cell comes from - Vehicle emissions
bone marrow - Oil refineries
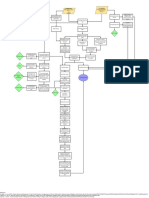
B. Food & Preservatives 1. Initiation – Alteration of atructure of
cellular DNA
- nitrates
2. Latency/ Promotion (incubation
- talc (Pulbos) stage ) – Proliferation of AbN cells
d/t repeated exposure of promoting
- Food sweeteners (formal dehide, agents
aspartane) Protein 53 guardian angel gene
C. Radiation 3. Progression – Exhibit increased
malignant behavior rapid
- Ionizing Radiation – Cancer proliferation of CA cells Irreversible.
induction 4. Invasion
- Regional Invasion – CA cells
-X-ray
invade surrounding tissues & organs
-Radioactive Isotopes - Metastasis – spread to a distant
body sites
-Sunlight/ Ultraviolet rays –Sarcoma
and melanoma Regional Invasion occurs by
-Radon – decay of uranium found in 1. Cellular proliferation
soil and rocks 2. Loss of contact inhibition
3. Secretion of cystic Substance
-Electromagnetic Radiation
Mechanism of metastasis
3. Immunologic Defects
1. Invation of neoplastic cells to
4. Age adjacent tissues caused by
5. Gender
6. Heredity Main management in CA
7. Poverty 1. Surgery
2. Radiation
8. Stress
3. Chemotherapy
Characteristics of cancer cells
Cell surface and membrane alteration
Metabolic changes
- Angiogenesis – have own blood supply
Antigenic Changes
- during intrauterine and early post-natal life
working as a protection, When repressed in
later stage in life it becomes tumor marker.
Possible presence of cancer cells
Stages of CA development
You might also like
- Cancer Biology 2023Document82 pagesCancer Biology 2023STACEY SALVILLANo ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesOncology Nursing Notesjoyrena ochondra100% (9)
- The Cell Definition of Related Terms: Oncology / Cancer NursingDocument23 pagesThe Cell Definition of Related Terms: Oncology / Cancer Nursingjesperdomincilbayaua100% (1)
- Science 1987 Slamon 177 82 PDFDocument6 pagesScience 1987 Slamon 177 82 PDFAmin ArabNo ratings yet
- Cell Ab Midterm MesiDocument9 pagesCell Ab Midterm MesiSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations NotesDocument23 pagesCellular Aberrations NotesPamela Ria HensonNo ratings yet
- Cell Ab Midterm MesiDocument7 pagesCell Ab Midterm MesiSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Cancer NotesDocument7 pagesCancer NotesKyla Mae JumaritoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations NotesDocument22 pagesCellular Aberrations NotesH50% (2)
- Factor Normal Cancer CytoplasmDocument2 pagesFactor Normal Cancer CytoplasmYuji TanakaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document32 pagesTopic 1Exo SaranghajaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderDocument5 pagesCellular Aberrations Cancer, Malignant Neoplasm, Oncologic DisorderIrish Eunice Felix100% (1)
- Cancer Hallmarks of Cancer CellDocument4 pagesCancer Hallmarks of Cancer CellMark James GavinaNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerPaul AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- 16ONCODocument7 pages16ONCOEkoy TheRealNo ratings yet
- What Is CancerDocument7 pagesWhat Is CancerDarlyn AmplayoNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument19 pagesOncology NursingMarlowe DulayNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument4 pagesOncologymyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsDocument49 pagesNCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsStephanie Mhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With CancerDocument15 pagesCare of Patients With CancerArturo M. Ongkeko Jr.100% (6)
- Molecular Biology of Cancer-Biotech ReviewerDocument3 pagesMolecular Biology of Cancer-Biotech Reviewermirandajealyn28No ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesOncology Nursing NotesBavitha BNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisorderDocument107 pagesMusculoskeletal DisorderdNo ratings yet
- Aula 6 FBMCCR 2324Document28 pagesAula 6 FBMCCR 2324VanessaMarquesNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument8 pagesCancerHannah CaseriaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Course PackDocument29 pagesCytogenetics Course Packanonymous squashNo ratings yet
- Biotech ReviewerDocument1 pageBiotech Reviewerdenmarkde22No ratings yet
- Oncology NotesDocument9 pagesOncology NotesmakbbmakNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Cancer in Children Ncma219 Lec Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesWeek 13 Cancer in Children Ncma219 Lec Midterm ReviewerWynahNo ratings yet
- 7a. Cellular Aberration With PAIN ConceptDocument25 pages7a. Cellular Aberration With PAIN ConceptRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- GenpathDocument10 pagesGenpathNatural Science BiologyNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument6 pagesCellular AberrationNeslie Lagare SamonteNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts Oncology NursingDocument12 pagesLecture Handouts Oncology NursingTiffany Luv AdriasNo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsDocument45 pagesNCM 112-Care of Clients With Problems in Cellular AberrationsClaraNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lecture Module 4 Cellular AberrationDocument16 pagesNCM 112 Lecture Module 4 Cellular AberrationMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Oncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesDocument17 pagesOncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesNagesh NNo ratings yet
- To Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksDocument34 pagesTo Appreciate The Animations and Explanations, PLS. Download As A Power Point. ThanksPawpaw Chan0% (1)
- c-DNA Dan Mt-DNA-2Document17 pagesc-DNA Dan Mt-DNA-2Andik RohmanaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Pathophysiology 4th SemDocument43 pagesCancer Pathophysiology 4th SemRadhika PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom LecDocument2 pages1 Cancer HO Set1 (Intro) Zoom Leckarl montanoNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Cellular-AberrationDocument6 pagesNCM 106 Cellular-AberrationJoanne TolopiaNo ratings yet
- Oncology NursingDocument3 pagesOncology NursingJalishia Mae DumdumaNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With CancerDocument57 pagesCare of Patients With CancerAyessa Yvonne PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document4 pagesGenetics 1Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document4 pagesGenetics 1Agyao Yam FaithNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DDocument51 pagesNeoplasia: Benito K. Lim Hong III, M.DGokul PoudelNo ratings yet
- 4-Cancer and Embryonic CellsDocument25 pages4-Cancer and Embryonic Cellsmohmmad-0-50No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BiologyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 BiologyMarina ArvanitopoulouNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument17 pagesCancerShyenNo ratings yet
- Modern Therapeutic ApproachDocument48 pagesModern Therapeutic ApproachVirtuoso EumoirietyNo ratings yet
- Biology F4C6 WatermarkDocument9 pagesBiology F4C6 Watermarkpitopi7277No ratings yet
- Cancer Pathophysiology: Radhika D Prabhu MS124129Document43 pagesCancer Pathophysiology: Radhika D Prabhu MS124129Radhika PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Eca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalDocument29 pagesEca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY RevDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY Revjoshua abrioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyJen JenNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Features of Microbiology: VirusesDocument21 pagesFundamental Features of Microbiology: VirusesGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Revised and Extended Copy - 39 BCSDocument48 pagesAnatomy Revised and Extended Copy - 39 BCSAjob ArafatNo ratings yet
- Biological Transcendence and the Tao: An Exposé on the Potential to Alleviate Disease and Ageing and the Considerations of Age-Old WisdomFrom EverandBiological Transcendence and the Tao: An Exposé on the Potential to Alleviate Disease and Ageing and the Considerations of Age-Old WisdomNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Nomenclature Epidemiology OncogenesDocument7 pagesNeoplasia: Nomenclature Epidemiology OncogenespriyaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleDocument11 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module - : Title: Cell CycleAron Chua FababeirNo ratings yet
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDocument17 pagesFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasNo ratings yet
- D 2.1 HL Cell Division Student NotesDocument12 pagesD 2.1 HL Cell Division Student Notesgiselle veneziaNo ratings yet
- Plants That Fight CancerDocument314 pagesPlants That Fight CancerMai Elnaggar100% (4)
- Oncogene EtcDocument48 pagesOncogene EtcInsyirah JohariNo ratings yet
- Cancer PPT On The BiologyDocument55 pagesCancer PPT On The Biologyjohnbharot91No ratings yet
- Respon Neoplastik: Program Magister Ilmu Biomedik Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas AndalasDocument66 pagesRespon Neoplastik: Program Magister Ilmu Biomedik Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas AndalasMirna WatiNo ratings yet
- 11 - How Genes Are Controlled - 2022 UploadDocument170 pages11 - How Genes Are Controlled - 2022 UploadbutvNo ratings yet
- Kaposi-Sarcoma PathophysiologyDocument1 pageKaposi-Sarcoma PathophysiologyChiara FajardoNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Document35 pagesKuliah 8, (Pras2021) Obat Anti Kanker (Kemoterapi)Nur Afiya NandaNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsDocument9 pagesModule 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- K - 1 Perspective and The Future of OncologyDocument36 pagesK - 1 Perspective and The Future of OncologyPRAGAATHYRAJANNo ratings yet
- Cancer Genetics: Sreekutty S 2 MSC ZoologyDocument34 pagesCancer Genetics: Sreekutty S 2 MSC ZoologyShamsudheen maharajasNo ratings yet
- NikitaDocument41 pagesNikitaAtika AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument9 pagesNeoplasiaRinaldo GintingNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus For "BIO404: Cancer Biology"Document5 pagesCourse Syllabus For "BIO404: Cancer Biology"medp7060No ratings yet
- Activity1and2 Overview TeacherDocument10 pagesActivity1and2 Overview TeacherIsmael FernandezNo ratings yet
- PDF The Biology of Cancer DDDocument21 pagesPDF The Biology of Cancer DDLunactic ThanosNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument98 pagesNeoplasiaassica0% (1)
- 1.biokimia KankerDocument94 pages1.biokimia Kankersebastian chendraNo ratings yet
- CellDocument14 pagesCellSyrian AsadNo ratings yet
- Zebra FishDocument552 pagesZebra FishmcvalledorNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Module 6 MCQsDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Module 6 MCQsbcristoforiNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene ExpressionDocument20 pagesRegulation of Gene ExpressionrainabtNo ratings yet
- Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeDocument8 pagesOrganisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Desmoid Tumor PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesDesmoid Tumor Pathophysiologyjo_annamae4413No ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: An Overview: About This WorksheetDocument4 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and Cancer: An Overview: About This WorksheetJean Alexander Nazario SotoNo ratings yet
- Biology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesBiology The Core 2nd Edition Simon Solutions Manualaureliacharmaine7pxw9100% (24)