Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam Amiono Acids
Exam Amiono Acids
Uploaded by
Behailu Tsegaye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesA patient with a history of recurring pancreatitis attacks, eruptive xanthomas, and increased plasma triglyceride levels associated with chylomicrons most likely has a deficiency in lipoprotein lipase. A 42-year-old man with xanthelasmas and bilateral tendon xanthomas and a high LDL/HDL ratio likely has a deficiency in apoB-100 receptors. Dyslipidemias can be due to increased cholesterol, elevated triglycerides, or decreased high-density lipoprotein, but not decreased low-density lipoprotein. Type I hyperlipidemia incorrectly increases clearance of chylomicrons rather than being due to lipoprotein lipase enzyme deficiency.
Original Description:
Original Title
exam amiono acids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA patient with a history of recurring pancreatitis attacks, eruptive xanthomas, and increased plasma triglyceride levels associated with chylomicrons most likely has a deficiency in lipoprotein lipase. A 42-year-old man with xanthelasmas and bilateral tendon xanthomas and a high LDL/HDL ratio likely has a deficiency in apoB-100 receptors. Dyslipidemias can be due to increased cholesterol, elevated triglycerides, or decreased high-density lipoprotein, but not decreased low-density lipoprotein. Type I hyperlipidemia incorrectly increases clearance of chylomicrons rather than being due to lipoprotein lipase enzyme deficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesExam Amiono Acids
Exam Amiono Acids
Uploaded by
Behailu TsegayeA patient with a history of recurring pancreatitis attacks, eruptive xanthomas, and increased plasma triglyceride levels associated with chylomicrons most likely has a deficiency in lipoprotein lipase. A 42-year-old man with xanthelasmas and bilateral tendon xanthomas and a high LDL/HDL ratio likely has a deficiency in apoB-100 receptors. Dyslipidemias can be due to increased cholesterol, elevated triglycerides, or decreased high-density lipoprotein, but not decreased low-density lipoprotein. Type I hyperlipidemia incorrectly increases clearance of chylomicrons rather than being due to lipoprotein lipase enzyme deficiency.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1.
A patient with a history of recurring attacks of pancreatitis, eruptive xanthomas, and
increased plasma triglyceride levels associated with chylomicrons, most likely has a
deficiency in
A. Lipoprotein lipase
B. HMG-CoA reductase
C. apoB-48
D. apoB-100receptor
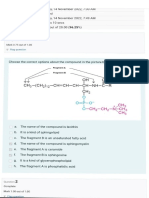
2. A 42-year-old man his physical exam reveals xanthelasmas and bilateral tendon
xanthomas. A plasma lipid profile reveals a cholesterol level of 340 mg/dL, with a high
LDL/HDL ratio. What is the cause of deficient for this patient?
A. lethicin cholesterol acyltransferase
B. apoB-100 receptors
C. Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
D. Cholesterol ester transfer protein
3. Which one is not true about dyslipidemias?
A. It is due to cholesterol increase
B. It is due to elevation of triacylglycerols
C. It is due to decrease of low-density lipoprotein
D. It is due to low high- density lipoprotein
4. One of the following is not correct about type I hyperlipidemia
A. It increases level of VLDL
B. Apo-C II deficiency
C. It increases clearance of chylomicrons
D. It is due to lipoprotein Lipase enzyme deficiency
5. Development of Xanthelesma in the eyelid is most happening due to?
A. Deficiency of LDL receptors region of apoB100
B. Increase in apoE-apoB-rich chylomicron remnants
C. Abnormal conversion of normal VLDL to β-VLDL
D. Complex abnormal lipoprotein metabolism
6. One of the following is not true about management of dyslipidemia?
A. Increase intake of High unsaturated fats
B. Decrease intake of trans-fatty acids
C. Perform regular physical exercise
D. Increase intake of processed food
7. Bassen-Kornzweig syndrome is due to?
A. Increase plasma cholesterol
B. Increase chylomicron
C. Deficiency of apo-B
D. Increase LDL level
8. One of the following is not relate to Tangier’s disease
A. decrease level of HDL
B. defect of apo-A I
C. Decrease triglyceride
D. Mutations of ABCA1 transporter
9. Lipid Storage Diseases is characterized with
A. Defect of Sphingolipids catabolism
B. Increase lipoprotein catabolism
C. Over secretion of lysosome enzymes
D. defect of lipid synthesis
10. A 9-week-old boy, healthy at birth, begins to develop symptoms of ketoacidosis, vomiting,
lethargy, seizures, hypertonia and urine has characteristic odor is
A. Homocystinuria
B. Phenylketonuria
C. Maple syrup
D. Alkaptonuria
11. A child with white-blond hair, blue eyes, and pale complexion due to defect of enzyme of
dihydrobiopeterin reductase considered as
A. Homocystinuria
B. Phenylketonuria
C. Maple syrup
D. Alkaptonuria
12. 55-year-old man with a rare recessive condition is at high risk for deep vein thrombosis and
stroke and has had replacement of ectopic lenses. Which of the following a mutation in the
gene encoding is most likely to cause this disease?
A. Cystathionine β synthase
B. Homocysteine methyltransferase
C. Branched chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase
D. Lysyl oxidase
13. A 56-year-old man with a history of genetic disease undergoes hip replacement surgery
for arthritis. During the operation the surgeon notes a dark pigmentation (ochronosis) in the
man's cartilage. His ochronotic arthritis is most likely caused by oxidation and polymerization of
excess tissue
A. Homogentisic acid
B. Orotic acid
C. Methylmalonic acid
D. Ascorbic acid
14. One of the following amino acid is not the cause of development of autosomal recessive
metabolic disorder Cystinuria
A. Glycine
B. Arginine
C. Ornithine
D. Lysine
15. The precursor for the synthesis of melanin is
A. Tryptophan
B. Arginine
C. Tyrosine
D. Gultamin
16. Which of the following acts as a central molecule when transamination and deamination
occur simultaneously?
A. Aspartate
B. Alanine
C. Oxaloacetate
D. Alpha-ketoglutarate
17. Deamination reactions that are performed by removing of amino group without oxidation is?
A. Hydrolytic deamination
B. Reductive deamination
C. Specific Deamination
D. Transdeamination
18. Oxidative deamination is the conversion of an amino acid to
A. α - keto acid
B. Carboxylic acid plus ammonia
C. Keto acid plus ammonia
D. Carboxylic acid
19. Transamination is the process where
A. α-amino group is removed from the amino acid
B. Carboxyl group is transferred from amino acid
C. Polymerisation of amino acid takes place
D. Carboxylic group is removed by forming keto acid
20. Which one of the following is not related to high concentration of NH3
A. It can decrease the concentration of α-ketoglutarate
B. It can increase glutamine formation
C. It can disturb as neurotransmitter inhibitor
D. It can increase over production of energy
You might also like
- NAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)From EverandNAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 03.sabiston Surgery Questions 17th EdDocument117 pages03.sabiston Surgery Questions 17th EdRebeca Carvalho89% (28)
- Hoeltke Chapter5 RevisedDocument34 pagesHoeltke Chapter5 RevisedPrincess Weiyoung100% (1)
- MCQ of HematologyDocument22 pagesMCQ of Hematologydrafq200063% (8)
- Topnotch Practice Exam 1 For MARCH 2020 and SEPT 2020 BatchesDocument104 pagesTopnotch Practice Exam 1 For MARCH 2020 and SEPT 2020 BatchesJerome AndresNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ia 2Document2 pagesMCQ Ia 2Vikrantt DhayalNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates-Lipids 1Document6 pagesCarbohydrates-Lipids 1Michal VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Pre Proff 2021Document6 pagesBiochem Pre Proff 2021TAHANo ratings yet
- Tests Krok2005-09 KeysDocument21 pagesTests Krok2005-09 KeysHaruna BzakiNo ratings yet
- Lipids Review QuestionsDocument10 pagesLipids Review QuestionsDavid TamayoNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 2008 by ModulsDocument12 pagesKrok 1 2008 by Modulsa_friend_in_neeedNo ratings yet
- Bio - Chemistry T& D PaperDocument12 pagesBio - Chemistry T& D PaperPNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1Document3 pagesEnhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1Kevin AlonzoNo ratings yet
- B4 Last OneDocument9 pagesB4 Last OneYousef El-AbbarNo ratings yet
- CC P2 LecDocument199 pagesCC P2 Lecgeorgemayhew1030No ratings yet
- Bio Chem Important MCQsDocument4 pagesBio Chem Important MCQsAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Body Fluids and Fluid TherapybookwormMDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Lipids and LipoproteinsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Lipids and LipoproteinsmryamNo ratings yet
- Glucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Document4 pagesGlucose Quiz 1 @ukrok1Omran BashirNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Key: CDocument22 pagesEndocrine System: Key: CJinnah GandhiNo ratings yet
- MBM Home Quiz BEFORE MIDTERMDocument38 pagesMBM Home Quiz BEFORE MIDTERMbhagavan prasadNo ratings yet
- База Англ тестовDocument760 pagesБаза Англ тестовpokemonldesNo ratings yet
- Krok1 EngDocument27 pagesKrok1 Engdeekshit dcNo ratings yet
- Enzymes. Coenzymes. Bioenergetics. Citric Acid Cycle of Krebs. Tissue RespirationDocument27 pagesEnzymes. Coenzymes. Bioenergetics. Citric Acid Cycle of Krebs. Tissue RespirationHart ElettNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Clinical Chemistry For Students1 1Document9 pagesQuestionnaire On Clinical Chemistry For Students1 1Inah Mae Coleen CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Pgi Board Review - Biochemistry 2021Document50 pagesPgi Board Review - Biochemistry 2021Sherrie Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Review Questions Chapter 17 Chapter 18 and Chapter 19Document5 pagesBiochemistry Review Questions Chapter 17 Chapter 18 and Chapter 19Jan Fernan Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsehh2027No ratings yet
- Biochem CBDocument114 pagesBiochem CBNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics MCQs-Inborn Errors of Metabolism 1Document9 pagesPediatrics MCQs-Inborn Errors of Metabolism 1Omar Ahmed0% (1)
- Final- Questionsاالااا- ClinicalDocument15 pagesFinal- Questionsاالااا- Clinicalahmed9065432No ratings yet
- All BaseDocument281 pagesAll BaseafrahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document32 pagesBiochemistry 1zaydeeeeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry (Elsevier)Document9 pagesClinical Chemistry (Elsevier)JenepNo ratings yet
- Dip Dec 2015Document21 pagesDip Dec 2015SAMMYNo ratings yet
- JRRMMC Biochem Exam Answer KeyDocument4 pagesJRRMMC Biochem Exam Answer KeyBom Tna100% (2)
- 6 Krok GitDocument14 pages6 Krok GitRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- QDocument9 pagesQEbaa AbdullatifNo ratings yet
- Prelim Ans KeyDocument13 pagesPrelim Ans KeyBernz KyNo ratings yet
- NCM 116Document32 pagesNCM 116Yeany IddiNo ratings yet
- Biological ChemistryDocument28 pagesBiological ChemistryArsilan Aziz LoneNo ratings yet
- Lec. B12Document94 pagesLec. B12Arshad Mehmood MinhasNo ratings yet
- Board-Exam-Recall 2017Document109 pagesBoard-Exam-Recall 2017Nica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument60 pagesLipidsMargarette Ann MontinolaNo ratings yet
- CC MB RatioDocument49 pagesCC MB RatioKhoreen ObisoNo ratings yet
- En-Metabolism LipidicDocument25 pagesEn-Metabolism LipidicCristina THCSNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MCQs RevisionDocument31 pagesBiochemistry MCQs RevisionMarwan elmezayenNo ratings yet
- Mockboards Reviewer FinalDocument161 pagesMockboards Reviewer FinalRoselle Joyce Arce CalubanNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument3 pagesBiochemistrysummer168No ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2017 PDFDocument32 pagesAIIMS May 2017 PDFStelaWatsonNo ratings yet
- Let's Do (Searchable)Document11 pagesLet's Do (Searchable)Johnny BravoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 4 BDocument10 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism - MCQs 4 BSaroja Veeresh100% (1)
- NCLEX HomeostasisDocument10 pagesNCLEX HomeostasisAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For The MCB FinalDocument7 pagesPractice Questions For The MCB FinalDrew LorenNo ratings yet
- NBCD Long ExamDocument13 pagesNBCD Long ExamJohn Michael MacabentaNo ratings yet
- B. Affinity: FWA v1Document14 pagesB. Affinity: FWA v1fftemmmNo ratings yet
- A. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean OilDocument8 pagesA. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean Oildrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Fast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementFrom EverandFast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome: Raising awareness of a rare genetic diseaseFrom EverandFast Facts: Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome: Raising awareness of a rare genetic diseaseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument4 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryBehailu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism (Catabolism) and Clinical SignificantDocument33 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism (Catabolism) and Clinical SignificantBehailu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Absorbation and Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument49 pagesAbsorbation and Digestion of CarbohydratesBehailu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Uronic Acid PathwayDocument19 pagesUronic Acid PathwayBehailu Tsegaye100% (1)
- Home: Correspondence:: Ala N Aragon's Research Review - May 2015)Document26 pagesHome: Correspondence:: Ala N Aragon's Research Review - May 2015)Andra SpatarNo ratings yet
- Mia Schow Consumer Interest Article FinalDocument4 pagesMia Schow Consumer Interest Article Finalapi-741989823No ratings yet
- Blood Test ResultsDocument5 pagesBlood Test ResultsWendylina BuikNo ratings yet
- WS IV - PPT Dr. Tjan Sian - Six Sigma Konas FINALDocument40 pagesWS IV - PPT Dr. Tjan Sian - Six Sigma Konas FINALHerbanu PramonoNo ratings yet
- Lipid Profile: Dr. MD Razib HasanDocument26 pagesLipid Profile: Dr. MD Razib HasanRazib Hasan100% (1)
- Gerde 2020Document68 pagesGerde 2020kevin chenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentDocument22 pagesNursing Process: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - HemostanDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Hemostangoody1286No ratings yet
- Testosterone: Mechanism of ActionDocument3 pagesTestosterone: Mechanism of Actionvasu VermaNo ratings yet
- 12 Antilipemics UpdDocument46 pages12 Antilipemics Updone_nd_onlyuNo ratings yet
- Vii. Laboratory Results: Hemoglobin 129 MG/DL 140-160 MG/DL LowDocument2 pagesVii. Laboratory Results: Hemoglobin 129 MG/DL 140-160 MG/DL LowAdrian Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembranesajmirNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Data - Action - Response: St. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing A.Y. 2nd SEMESTER 2020-2021Document2 pagesData - Action - Response: St. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing A.Y. 2nd SEMESTER 2020-2021Quinonez Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- 2007 Reduction of C-Reactive Protein and The Use of Anti-HypertensivesDocument10 pages2007 Reduction of C-Reactive Protein and The Use of Anti-HypertensivesVladimir BasurtoNo ratings yet
- What Is An Orange?: Orange Peel (Citrus × Sinensis) As Wound Healing AgentDocument4 pagesWhat Is An Orange?: Orange Peel (Citrus × Sinensis) As Wound Healing AgentCamille Anne RabajanteNo ratings yet
- Kimia Dumo 2023Document1 pageKimia Dumo 2023Dani IndahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument17 pagesBiomolecules NotesManit Grover0% (1)
- Cholesterol Liquicolor CHOD-PAPDocument1 pageCholesterol Liquicolor CHOD-PAPmaarboleda1100% (2)
- h1 in GlucometerDocument1 pageh1 in GlucometerKepler12 QuemadaNo ratings yet
- Tarife Servicii Medicale Amb 2Document8 pagesTarife Servicii Medicale Amb 2Ioana RaduNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Nuts - Gapped TExtDocument2 pagesHealth Benefits of Nuts - Gapped TExttirthakaraNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Composition of Dried Curry Leaf Powder (Murraya Koenigii)Document5 pagesNutritional Composition of Dried Curry Leaf Powder (Murraya Koenigii)anithaNo ratings yet
- Blood Test: ExtractionDocument4 pagesBlood Test: ExtractionMajd AlzobaideNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesDRUGSTUDY AtorvastatinMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Apolipoprotein A1 (Immunoturbidimetric) V1.1eDocument2 pagesApolipoprotein A1 (Immunoturbidimetric) V1.1eTrần Thanh ViệnNo ratings yet
- HDL Cholesterol: HDLC - PDocument2 pagesHDL Cholesterol: HDLC - PMariiCarmen Ferez FeraldhNo ratings yet
- SouthPath Reference RangesDocument1 pageSouthPath Reference Rangesddp2710No ratings yet
- PIIS2213858723001195Document15 pagesPIIS2213858723001195Aparajita PraharajNo ratings yet