Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MSCAT - One Page Format
MSCAT - One Page Format
Uploaded by
George EspejoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tanker Management and Self Assessment 3Document130 pagesTanker Management and Self Assessment 3Omar F. Mauco60% (10)
- Appendix II DNV-M-scatDocument1 pageAppendix II DNV-M-scatGökhan Ulukuz100% (2)
- RA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureDocument3 pagesRA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureHarman Sandhu100% (3)
- M-SCAT Guidance On Incident InvestigationDocument16 pagesM-SCAT Guidance On Incident InvestigationRachit Jain100% (1)
- SCAT Chart - EnglishDocument2 pagesSCAT Chart - Englishmaruli pakpahan100% (3)
- The Big Book of Horrors PDFDocument78 pagesThe Big Book of Horrors PDFNot human75% (4)
- Anchor Handling Preparation Checklist300312 Rev01Document3 pagesAnchor Handling Preparation Checklist300312 Rev01Kunal Singh100% (1)
- Systematic Cause Analysis TechniqueDocument1 pageSystematic Cause Analysis Techniquescribd@omoa.co.ukNo ratings yet
- FCV-A.13.01 Emergency Drill ScheduleDocument3 pagesFCV-A.13.01 Emergency Drill Schedulea.gomonovs26100% (3)
- Aby Warburg: Bilderatlas Mnemosyne: The OriginalDocument36 pagesAby Warburg: Bilderatlas Mnemosyne: The OriginalAntonis100% (1)
- QMS 75A - Navigation Audit Report Rev 6-UnprotectedDocument7 pagesQMS 75A - Navigation Audit Report Rev 6-Unprotectedhoangminh2209100% (1)
- QSE SystemDocument17 pagesQSE SystemAnonymous JIHJTWw4Th0% (1)
- ExxonMobil Marine Safety Criteria Guidance 2017 Final - R01a (Clean)Document60 pagesExxonMobil Marine Safety Criteria Guidance 2017 Final - R01a (Clean)maxtrap73100% (1)
- ABS Class NotationsDocument285 pagesABS Class NotationsndesigngmailNo ratings yet
- MSCAT 8.2 - Basic Causes ExplainedDocument18 pagesMSCAT 8.2 - Basic Causes ExplainedAhmet SolakNo ratings yet
- Checklist ISM AuditDocument14 pagesChecklist ISM AuditjunNo ratings yet
- Self CHK Ship e Audit Ism ChecklistDocument10 pagesSelf CHK Ship e Audit Ism ChecklistIrdam Jono100% (2)
- Sample-Masters Standing OrdersDocument6 pagesSample-Masters Standing Orderssinghal.ns4497100% (2)
- (4.9) TMSA Report (VNLS-3556-6207-6159) PDFDocument106 pages(4.9) TMSA Report (VNLS-3556-6207-6159) PDFEdy SukmonoNo ratings yet
- D18 ECDIS - Speed Log Input FailureDocument1 pageD18 ECDIS - Speed Log Input FailureRiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Chief Engineer Pre-Vetting ChecklistDocument6 pagesChief Engineer Pre-Vetting ChecklistWilson Aye100% (3)
- Solas Training ManualDocument6 pagesSolas Training Manualquick100% (1)
- 47 Drill Report - Salvage of Own ShipDocument1 page47 Drill Report - Salvage of Own ShipmitchsipNo ratings yet
- Plans and Procedures Recovery Persons From Water FINALDocument38 pagesPlans and Procedures Recovery Persons From Water FINALRihards67% (6)
- Master's Sms Review FormDocument4 pagesMaster's Sms Review FormJeet Singh100% (3)
- Eisenmann Nineteenth Century ArtDocument380 pagesEisenmann Nineteenth Century ArtFilip100% (2)
- (1-2) Nvestigation Analysis & M-SCAT CapstanDocument22 pages(1-2) Nvestigation Analysis & M-SCAT Capstan洪力No ratings yet
- DPA Training Rev02 2010 4 29Document230 pagesDPA Training Rev02 2010 4 29majdirossross100% (1)
- MBW - Iarkbe Systeiatkc Cause Abanysks) Ec'bkque (I-Scat 0. )Document1 pageMBW - Iarkbe Systeiatkc Cause Abanysks) Ec'bkque (I-Scat 0. )洪力No ratings yet
- Tmsa 3Document1 pageTmsa 3St GRNo ratings yet
- Sire InspectionDocument8 pagesSire InspectionAnil yucebasNo ratings yet
- H - SMS - Manual PDFDocument7 pagesH - SMS - Manual PDFRabahNo ratings yet
- Guidance To Masters and Officers in Conducting An OvidDocument33 pagesGuidance To Masters and Officers in Conducting An OvidСтанислав Георгиев100% (1)
- Angola General General (See Plan) : Platform Lat. Long. LightDocument30 pagesAngola General General (See Plan) : Platform Lat. Long. LightPavel ViktorNo ratings yet
- ER06 BunkeringDocument2 pagesER06 BunkeringNang D. VuNo ratings yet
- VSL Inspection Form 300611Document6 pagesVSL Inspection Form 300611Kunal SinghNo ratings yet
- Processes For The Development and Maintenance of Part 1 of The Inventory of Hazardous MaterialsDocument19 pagesProcesses For The Development and Maintenance of Part 1 of The Inventory of Hazardous MaterialsReda HmrNo ratings yet
- 500 MTR Zone Checklist - IsMSBDocument4 pages500 MTR Zone Checklist - IsMSBRamli DisaNo ratings yet
- GL ND Guidelines For Towage of ShipsDocument40 pagesGL ND Guidelines For Towage of ShipsTomkel VoonNo ratings yet
- SMM ManualDocument197 pagesSMM ManualAlessandro MxNo ratings yet
- Vessel S Guide To Vetting InspectionsDocument11 pagesVessel S Guide To Vetting Inspectionsmatan55100% (5)
- Checklist Audit Ism Office EngDocument9 pagesChecklist Audit Ism Office EngAji ArnowoNo ratings yet
- ISM - ISO - ISPS - MLC Internal Audit - SafetyCultureDocument28 pagesISM - ISO - ISPS - MLC Internal Audit - SafetyCultureAbner Llenos100% (4)
- Ism The Role of DpaDocument17 pagesIsm The Role of DpaΑΝΝΑ ΒΛΑΣΣΟΠΟΥΛΟΥNo ratings yet
- UscgDocument82 pagesUscgAldy KurniaNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Internal AuditsDocument3 pages12.1 Internal Auditsfredy2212No ratings yet
- Good MaintenanceDocument53 pagesGood MaintenancejohnEnglish100% (1)
- Guide For Vetting InspectionsDocument6 pagesGuide For Vetting InspectionsAnonymous b68EQR100% (1)
- INTERTANKO Vetting Committee 26.05.2022Document29 pagesINTERTANKO Vetting Committee 26.05.2022soner100% (1)
- Annual Audit Checklist PDFDocument38 pagesAnnual Audit Checklist PDFTankcare MarineNo ratings yet
- IMO MSC Circ 645 DP SystemsDocument17 pagesIMO MSC Circ 645 DP Systemsgreensail1No ratings yet
- Contingency Manual - 15-July-22Document102 pagesContingency Manual - 15-July-22Rachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- STCW 2010Document46 pagesSTCW 2010Vikram Shetty100% (1)
- Causes For Safety ObservationsDocument1 pageCauses For Safety ObservationsAlberto CastilloNo ratings yet
- Incident & Investigation Report Procedure - Near Miss-EVidence Communication Report-Hse Statistics & RecordsDocument83 pagesIncident & Investigation Report Procedure - Near Miss-EVidence Communication Report-Hse Statistics & RecordsAhmed Reda100% (1)
- IR1209Document2 pagesIR1209JoliboysNo ratings yet
- QPMO-700-00-FM-030 Incident Report Rev 0Document6 pagesQPMO-700-00-FM-030 Incident Report Rev 0IslamAl-BazNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument4 pagesRisk Assesmentapi-589160120No ratings yet
- IR Jan 13 2023Document4 pagesIR Jan 13 2023JoliboysNo ratings yet
- IR Jan 10 2023Document3 pagesIR Jan 10 2023JoliboysNo ratings yet
- Near Miss#rmco-Ir-005 ReportDocument6 pagesNear Miss#rmco-Ir-005 ReportQADEER SHANNo ratings yet
- Production Risk Assessment Location 2Document3 pagesProduction Risk Assessment Location 2SkyeNo ratings yet
- Report Format Conditions Unsafe Acts and IncidentsDocument3 pagesReport Format Conditions Unsafe Acts and IncidentsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Edp Micro Project Roll-28-Converted (1)Document20 pagesEdp Micro Project Roll-28-Converted (1)sarthak KulatNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 3Document39 pages07 - Chapter 3RAKTIM PUJARINo ratings yet
- Urbane LandscapesDocument13 pagesUrbane LandscapesUvoBubaNo ratings yet
- Snowdon, P. Animalism and The LivesDocument14 pagesSnowdon, P. Animalism and The LivesThiago DelaídeNo ratings yet
- Evidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelDocument45 pagesEvidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelNoha Ibraheem Helmy100% (1)
- Nike Complaint 23Document94 pagesNike Complaint 23Martin LeafNo ratings yet
- Teaching English Language To Young School-Age ChilDocument13 pagesTeaching English Language To Young School-Age Chilnour fouaniNo ratings yet
- Solomon Rprc4ce Mytest Ch04-TIFDocument53 pagesSolomon Rprc4ce Mytest Ch04-TIFTinagraceNo ratings yet
- William Alston, The Reliability of Sense Perception, Chapter 2: " Track Record and Other Simple Empirical Arguments For Reliability"Document7 pagesWilliam Alston, The Reliability of Sense Perception, Chapter 2: " Track Record and Other Simple Empirical Arguments For Reliability"Carlos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Management StylesDocument8 pagesManagement StylesSergio Felipe Nuñez RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Krisha PlarasNo ratings yet
- Kognitivni Razvoj U Odojastvu PERCEPCIJADocument36 pagesKognitivni Razvoj U Odojastvu PERCEPCIJAIvan DjukicNo ratings yet
- Racial Stereotypes About LatinDocument57 pagesRacial Stereotypes About LatinNatalie RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument323 pagesBusiness CommunicationRadhika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Parts and Wholes Visual PresentationDocument39 pagesParts and Wholes Visual Presentationjonniel caadanNo ratings yet
- English AssessmentDocument13 pagesEnglish AssessmentGUI DING QUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- (Comparative Politics) Gauja Anika-Party Reform - The Causes ChallengesDocument227 pages(Comparative Politics) Gauja Anika-Party Reform - The Causes Challengeskarahe100% (1)
- If You Stop Speaking They Kill You Kind of Freedom Volume1Document13 pagesIf You Stop Speaking They Kill You Kind of Freedom Volume1Waris WaljiNo ratings yet
- Zeki - Art and The BrainDocument34 pagesZeki - Art and The BrainIvan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Erzen, Jale Nejdet - Islamic Aesthetics, An Alternative Way To KnowledgeDocument7 pagesErzen, Jale Nejdet - Islamic Aesthetics, An Alternative Way To KnowledgeharisdcNo ratings yet
- Brand IdentityDocument12 pagesBrand IdentityNajam ul SaharNo ratings yet
- 00, Business Communication 7, Psychological and Cultural Dimensions of Business CommunicationDocument15 pages00, Business Communication 7, Psychological and Cultural Dimensions of Business CommunicationYash goyalNo ratings yet
- 06 The Ascension of MindDocument122 pages06 The Ascension of Mindyharoon99No ratings yet
- The Youth Activity Center, Old Garment Factory RenovationDocument9 pagesThe Youth Activity Center, Old Garment Factory RenovationAbdul SuheemNo ratings yet
- Steps To An Ecology of PsychotherapyDocument13 pagesSteps To An Ecology of PsychotherapyRoman BenderskijNo ratings yet
- Subject - Organisational Behaviour: Pramod B. Shrawage MDP - Thermax DATE - 25 SEPT. 2005Document10 pagesSubject - Organisational Behaviour: Pramod B. Shrawage MDP - Thermax DATE - 25 SEPT. 2005Darius PavriNo ratings yet
- Opening The Third EyeDocument4 pagesOpening The Third Eyetower1No ratings yet
MSCAT - One Page Format
MSCAT - One Page Format
Uploaded by
George EspejoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MSCAT - One Page Format
MSCAT - One Page Format
Uploaded by
George EspejoCopyright:
Available Formats
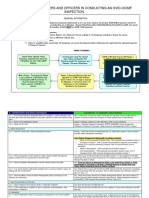
DNV – Marine Systematic Cause Analysis
Technique (M-SCAT 8.2)
TYPE OF LOSS DESCRIPTION OF EVENT
People (Safety/Health) Non-Conformity (Product/Service)
Asset (Damage) Reputation/Complaint
Environmental Process/Business
Financial (Fines, Claims, Insurance)
RISK EVALUATION
A risk evaluation of the event is required based on an analysis of the consequence potential and the probability/frequency of the event recurring by a competent individual against defined evaluation
criteria. The risk evaluation is used to assess the significance of the event relative to others and prioritise the implementation of improvement actions.
TYPE OF EVENT
1. Fall from Elevation (Person/Equipment/Material) 8. Exposure to Noise 14. Ship Grounding 21. Failure of Instrumentation/Logic/Loop
2. Fall on Same Level (Slip and Fall/Trip Over) 9. Exposure to Vibration 15. Ship Contact Damage (Docks, Locks, Buoys, etc.) 22. Cargo Damage and/or Loss
3. Struck against (bump into / run into) 10. Exposure to Radiation 16. Fire 23. Environmental Release (to Air/Water/Soil)
4. Struck By (Hit By Moving Object) 11. Contact with Hazardous Substance/Dose (Toxic/Corrosive/ Carcinogenic/ 17. Explosion 24. Loss of Ship Stability
5. Caught In, On, Between or Under Biological/Viral) 18. Loss of Ship Hull/Watertight Integrity 25. Customers/Stakeholders Complaints
6. Contact with Temperature Extremes (Heat/Cold) 12. Overstress by Overexertion, Overload, Ergonomic Factors 19. Failure of Mechanical Equipment 26. Act of Violence
7. Contact with Electricity 13. Ship Collision 20. Failure of Electrical System
IMMEDIATE CAUSES – SUBSTANDARD ACTS
1. Under the Influence of Medicine/Alcohol/Drugs 8. Improper Placement 15. Inadequate Servicing of Equipment/Machinery in Operation 19.3 Terminal Personnel
2. Failure to Follow Procedure/Instruction 9. Improper Position for Task 16. Using Defective Tool/Equipment/Machinery/Device 19.4 Local Authorities
3. Failure to Secure 10. Incorrect Navigation or Ship Handling 17. Improper Operation of Tool/Equipment/Machinery/Device 19.5 Incorrect Supply of Documents/Information
4. Failing to Use Personal Protective Equipment Properly 11. Making Safety Devices Inoperable 18. Foul Play/Sabotage 19.6 Other External Party Not Under The Control of The Company/Shipboard Management
5. Failure to Inform/Warn 12. Operating at Improper Speed 19. Substandard Act by External Party (Not Under Own Control) 20. Failure to Comply with Customers/Stakeholders Requirements
6. Improper Lifting 13. Operating Equipment Without Authority 19.1 Pilots 21. Civil Disturbance (Riot, Unrest, Warfare)
7. Improper Loading 14. Removing Safety Devices 19.2 Boatmen 22. Criminal Activities
IMMEDIATE CAUSES – SUBSTANDARD CONDITIONS
23. Cargo 30. Exposure to Low Temperature 37. Inadequate/Improper Personal Protective Equipment 44. Exposure to Adverse Weather Condition
24. Congestion/Restricted Space for Action 31. Noise Level Over Threshold 38. Inadequate Ventilation 45. Extreme Adverse Sea Conditions
25. Defective Tool/Equipment 32. Radiation Hazard Over Threshold 39. Inadequate Warning Systems 46. Inadequate Port and Berthing Facilities
26. Incorrect Material 33. Presence of Flammable/Explosive Atmosphere 40. Incorrect/Inadequate Tool/Equipment
27. Electric Current Hazards 34. Exposure to Dangerous Atmosphere Causing Suffocation or Poisoning 41. Outdated Charts, Publications and Other Documentation
28. Exposure to Chemicals 35. Inadequate Guard/Barrier 42. Poor Housekeeping/Order
29. Exposure to High Temperature 36. Insufficient/Excessive Illumination 43. Inadequate Condition of Floor/Surface
BASIC CAUSES – PERSONAL FACTORS
1. Inadequate Physical/Physiological Capability 2.8. Low mechanical aptitude 4.5. Extreme concentration/perception demands 6. Improper Motivation
1.1. Inappropriate height/weight/size/strength/reach, etc. 2.9. Low learning aptitude 4.6. Meaningless/degrading activities 6.1. Improper performance/behavior is tolerated/rewarded
1.2. Restricted range of body movement 2.10. Memory failure/lapse 4.7. Confusing directions/demands 6.2. Proper performance/behavior is discouraged/punished
1.3. Limited ability/inability to sustain body positions 3. Physical/Physiological Stress 4.8. Conflicting demands/directions 6.3. Lack of incentive
1.4. Substance sensitivity/allergy 3.1. Injury or illness 4.9. Preoccupation with problems/Distraction by concern 6.4. Improper production incentive
1.5. Sensitivities to sensory extreme (temperature/sound/etc.) 3.2. Fatigue due to task load or duration 4.10. Frustration 6.5. Improper Cost Reduction Incentive
1.6. Vision deficiency 3.3. Fatigue due to lack of rest 4.11. Mental illness 6.6. Excessive frustration
1.7. Hearing deficiency 3.4. Fatigue due to sensory overload 5. Lack of Competence 6.7. Inappropriate aggression
1.8. Other sensory deficiency (touch/taste/smell/balance) 3.5. Exposure to health hazard 5.1. Inadequate experience 6.8. Improper attempt to save time/effort
1.9. Respiratory incapacity 3.6. Exposure to temperature extreme 5.2. Inadequate orientation/induction 6.9. Improper attempt to avoid discomfort
1.10. Other permanent physical disability 3.7. Oxygen deficiency 5.3. Inadequate initial training 6.10. Improper attempt to gain attention
1.11. Temporary disability 3.8. Atmospheric pressure variation 5.4. Inadequate update/refresher training 6.11. Inadequate discipline
2. Inadequate Mental/Psychological Capability 3.9. Constrained movement 5.5. Misunderstood instruction/information 6.12. Inappropriate peer pressure
2.1. Fears and phobias 3.10. Blood sugar insufficiency 5.6. Lack of situational awareness/risk perception/risk awareness 6.13. Improper leadership example
2.2. Emotional disturbance 3.11. Alcohol/Drugs/Other Self Imposed Stress 5.7. Inadequate initial instruction/skill training 6.14. Inadequate performance feedback
2.3. Mental illness 4. Mental/Psychological Stress 5.8. Inadequate practice 6.15. Inadequate reinforcement of proper behavior
2.4. Intelligence level 4.1. Emotional overload 5.9. Infrequent performance 6.16. Abuse (intentionally)
2.5. Inability to comprehend 4.2. Fatigue due to mental task load or speed 5.10. Inadequate coaching 6.17. Misuse (unintentionally)
2.6. Poor coordination 4.3. Extreme judgment/decision demands 5.11. Inadequate review instruction
2.7. Slow reaction time 4.4. Routine/monotony/boredom/overly routine tasks
BASIC CAUSES – JOB/SYSTEM FACTORS
7. Unclear Organizational Structure 10.5. Inadequate consideration of human/ergonomic factor in design 12.5. Inadequate communication of corrective maintenance needs 15.7. Inadequate product/service planning
7.1. Unclear/conflicting reporting relationship 10.6. Inadequate design process / standard / specification / criterion 12.6. Inadequate scheduling of maintenance work 15.8. Inadequate product/service quality verification
7.2. Unclear/conflicting assignment of function/role 10.7. Inadequate process control automation 12.7. Inadequate assessment of repair needs 16. Inadequate Work/Production Standards
7.3. Unclear/conflicting accountability/responsibility/task 10.8. Inadequate (technical) standard/specification or absence thereof 12.8. Inadequate parts substitution/replacement 16.1. Inadequate identification of requirements
8. Inadequate Leadership 10.9. Inadequate review of project risks 12.9. Inadequate inspection method/interval (regulatory/industry code/permit-to-operate)
8.1. Inadequate HSEQ/asset strategy 10.10. Inadequate monitoring of construction / fabrication / assembly 12.10. Unable to inspect 16.2. Inadequate risk identification/evaluation in development of standard
8.2. Inadequate leadership development 10.11. Inadequate assessment of operational readiness 13. Excessive Wear/Tear 16.3. Inadequate standard from supplier/contractor
8.3. Inadequate delegation 10.12. Inadequate commissioning/handover process 13.1. Inadequate planning of use 16.4. Inadequate coordination with process design when developing standard
8.4. Inadequate standards 10.13. Inadequate monitoring of initial operation 13.2. Improper decision on extension of service life 16.5. Inadequate employee involvement in developing standard
8.5. Inadequate communication/implementation of policy/procedure/practice 10.14. Inadequate management of change process 13.3. Inadequate inspection/monitoring 16.6. Conflicting standards/improper prioritization of standards
8.6. Conflicting policy/procedure/practice 11. Inadequate Supply Chain Management 13.4. Improper loading/rate of use 16.7. Inadequate publication of standard
8.7. Inadequate work/process planning/programming 11.1. Inadequate specification on requisition/purchase order 13.5. Used for wrong purpose/task/activity 16.8. Inadequate distribution of standard
8.8. Condone deviation from policy/procedure/practice 11.2. Inadequate research on material / equipment / tool / supply / etc. 14. Inadequate Tool/Equipment/Machinery/Device 16.9. Inadequate translation of appropriate language
8.9. Condone misuse of equipment/tool 11.3. Inadequate specification to vendor 14.1. Inadequate assessment of needs and risks 16.10. Improper use of language
8.10. Condone improper/inappropriate behavior 11.4. Inadequate mode/route of shipment 14.2. Inadequate consideration of human factors/ergonomics 16.11. Inadequate training of standard
8.11. Inadequate management information 11.5. Inadequate receiving inspection/acceptance 14.3. Inadequate (supplier) standard/specification 16.12. Inadequate reinforcing of standard with signs, color codes and job aids
8.12. Inadequate monitoring/closure of audit actions 11.6. Inadequate communication of information about hazards 14.4. Incorrect measurement/detection/(process) control 16.13. Inadequate monitoring of standard compliance
9. Inadequate Supervision/Coaching 11.7. Improper handling of material 14.5. Inadequate availability of tool / equipment / machinery / device 17. Inadequate Communication/Information
9.1. Inadequate instruction/orientation/training 11.8. Improper storage of material 14.6. Inadequate inspection/repair/maintenance 17.1. Inadequate information handling
9.2. Inadequate information documents in supervision/coaching 11.9. Improper transporting of material 14.7. Inadequate adjustment/calibration 17.2. Unclear information
9.3. Lack of supervisory/management job knowledge 11.10. Inadequate shelf life/validation for re-use of materials/equipment 14.8. Inadequate salvage and reclamation 17.3. Inadequate transfer of information between internal parties
9.4. Inadequate match between qualifications and job/task requirements 11.11. Inadequate identification of material 14.9. Inadequate removal and replacement of unsuitable items 17.4. Inadequate transfer of information with client/stakeholder
9.5. Inadequate performance measurement and evaluation 11.12. Improper salvage/waste disposal 15. Inadequate Product/Service Design 17.5. Inadequate transfer of information with authorities
9.6. Inadequate performance feedback 11.13. Inadequate selection of contractor/supplier 15.1. Inadequate assessment of needs and risks 17.6. Inadequate transfer of information with other external parties
10. Inadequate Management of Change 12. Inadequate Maintenance/Inspection 15.2. Inadequate product/service standard/specification/concession system 17.7. Inadequate communication structure
10.1. Inadequate hazard identification/risk evaluation in design 12.1. Inadequate assessment of preventive maintenance needs 15.3. Inadequate product/service design/development 17.8. Inadequate databases/information system
10.2. Inadequate identification of failure mode 12.2. Inadequate preventive lubrication and servicing 15.4. Inadequate product/service standard 17.9. Inadequate communication method/technique used
10.3. Inadequate evaluation of customer/stakeholder requirement 12.3. Inadequate adjustment/assembly 15.5. Inadequate product/service design validation
10.4. Inadequate identification of legal requirement 12.4. Inadequate preventive cleaning/resurfacing 15.6. Inadequate product/service design verification
CONTROL AREAS FOR IMPROVEMENT ACTIONS
S PS C s PS C S PS C S PS C
1 - LEADERSHIP 5.5. Information Security 9.8. Work Permits 12.13. Medical Support
1.1. Purpose and Values 5.6. Product Stewardship 9.9. Warning Signs and Notices 12.14. Organized Outside Help and Mutual Aid
1.2. Goals 5.7. Compliance Assessment 9.10. Personal Protective Equipment 12.15. Preparedness for Major Accidents
1.3. Policy 5.8. Process Safety Regulations 9.11. Process Hazard Controls 13 - LEARNING FROM EVENTS
1.4. Strategy 5.9. Security of Process Information 9.12. Operating Procedures for Controlling Process Risks 13.1. Learning from Events System
1.5. Stakeholder Engagement 6 - PROJECT MANAGEMENT 9.13. Major Hazard Reports 13.2. Learning from Success
1.6. Business Processes 6.1. Project Co-ordination 10 - ASSET MANAGEMENT 13.3. Participation in Investigations
1.7. Business Risks 6.2. Project Planning 10.1. Maintenance Program 13.4. Near-Miss and Substandard Conditions
1.8. Accountabilities 6.3. Project Execution 10.2. Maintenance Planning and Scheduling 13.5. Complaints Management
1.9. Management Commitment 6.4. Project Control 10.3. Execution of Maintenance 13.6. Event Announcements
1.10. Process Safety Leadership 6.5. Project Close Out 10.4. Maintenance Review 13.7. Away-from-Work Accidents
2 - PLANNING AND ADMINISTRATION 6.6. Process Safety Project Reviews 10.5. General Conditions Inspections 13.8. Action Follow-Up
2.1. Business Planning 7 - TRAINING AND COMPETENCE 10.6. Physical Conditions Tour 13.9. LFE Reporting Verification
2.2. Work Planning and Control 7.1. Training System 10.7. Special Equipment Inspections 13.10. Event Analysis
2.3. Action Tracking 7.2. Training Needs Analysis 10.8. Pre-Use Equipment Inspections 13.11. Improvement Teams
2.4. Management System Documentation 7.3. Instructor Competence 10.9. Engineering Change Management 14 - RISK MONITORING
2.5. Records 7.4. Delivery of Training 10.10. Inspection, Measuring and Test Equipment 14.1. Health Hazard Monitoring
2.6. Process Safety Planning 7.5. Leadership Orientation/Induction 10.11. Acquisition and Sale 14.2. Safety Hazard Monitoring
3 - RISK EVALUATION 7.6. General Orientation/Induction 10.12. Asset Integrity Program 14.3. Security Hazard Monitoring
3.1. Health Hazard Identification and Evaluation 7.7. Job Orientation/Induction 10.13. Process Safety Inspections 14.4. Environmental Hazard Monitoring
3.2. Safety Hazard Identification and Evaluation 7.8. Training Systems Evaluation 11 - CONTRACTOR MANAGEMENT / PURCHASING 14.5. Customer Satisfaction
3.3. Security Hazard Identification and Evaluation 8 - COMMUNICATIONS AND PROMOTION 11.1. Contractor/Supplier Selection 14.6. Effectiveness of Monitoring
3.4. Environmental Hazards Identification and Evaluation 8.1. Communication System 11.2. Contractor Operations 14.7. Perception Surveys
3.5. Customer Expectations Identification and Evaluation 8.2. Meeting Co-ordination 11.3. Contractor/Supplier Assurance 14.8. Behavioral Observation
3.6. Task Risk Evaluation 8.3. Management Meetings 11.4. Supply Chain and Purchasing 14.9. Task Observations
3.7. Process Safety Information 8.4. Group Meetings 11.5. Logistics 14.10. Audits
3.8. Process Hazard Analysis 8.5. Joint Committee/Council 11.6. Managing Contractors in Process Areas 14.11. Process Hazard Monitoring
4 - HUMAN RESOURCES 8.6. Coaching 12 - EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS 15 - RESULTS AND REVIEW
4.1. Human Resources System 8.7. Recognition 12.1. Emergency Needs Assessment 15.1. Business Results
4.2. Recruitment 8.8. Promotion Campaigns 12.2. Site Emergency Plan 15.2. Management Review
4.3. Managing Individual Performance 8.9. Away from Work Safety Information 12.3. Off-Site Emergency Plan 15.3. Reporting to Stakeholders
4.4. Recognition and Discipline 8.10. Process Safety Awareness 12.4. Crisis Plan 15.4. Residual Risk Management
4.5. Leaving the Organization 9 - RISK CONTROL 12.5. Business Continuity Plan
4.6. Management of Organizational Change 9.1. Health Hazards Controls 12.6. Emergency Plan Review LEGEND
4.7. Process Safety Human Resources 9.2. Safety Hazards Controls 12.7. Emergency Communications S - System Inadequate. Action required to fill the gap in our management system e.g.,
5 - COMPLIANCE ASSURANCE 9.3. Security Controls 12.8. Emergency Protection Systems improvement team to develop a new system, process or procedure.
PS - Performance Standard Inadequate. Action required to define better WHO does WHAT
5.1. Regulations 9.4. Environmental Hazard Controls 12.9. Energy Controls
and WHEN e.g., change the procedure, instruction or rule.
5.2. External Authorizations to Operate 9.5. Quality Control of Materials and Products 12.10. Emergency Teams
C - Compliance with Performance Standard Inadequate. Action required to improve
5.3. Industry Codes and Standards 9.6. Process Control and Operating Procedures 12.11. Drills and Exercises
compliance e.g., implement a program of training, coaching or promotion.
5.4. Reporting to Authorities 9.7. Rules 12.12. First Aid
© COPYRIGHT 2021 DNV 30 Stamford Street Vivo Building, 4th Floor, London SE1 9LQ.
All rights reserved. Pacific Basin Shipping (HK) Limited is granted the right to print and distribute this document within the Pacific Basin Shipping (HK) Limited organisation as described in License Agreement ref L02210400.This document may not be modified, revised, changed, translated,
sold, lent, given or transcribed, in any form or by any means, or otherwise transferred for commercial or other purposes without the prior written permission of DNV. Pacific Basin Shipping (HK) Limited MSCAT8.2
You might also like
- Tanker Management and Self Assessment 3Document130 pagesTanker Management and Self Assessment 3Omar F. Mauco60% (10)
- Appendix II DNV-M-scatDocument1 pageAppendix II DNV-M-scatGökhan Ulukuz100% (2)
- RA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureDocument3 pagesRA Export 20230303-171712 (TEMPLATE-04 Haz) - ID230303164833 - Rev2023-03-03 - Cargo & Ballast Works - Ballast Water Treatment System FailureHarman Sandhu100% (3)
- M-SCAT Guidance On Incident InvestigationDocument16 pagesM-SCAT Guidance On Incident InvestigationRachit Jain100% (1)
- SCAT Chart - EnglishDocument2 pagesSCAT Chart - Englishmaruli pakpahan100% (3)
- The Big Book of Horrors PDFDocument78 pagesThe Big Book of Horrors PDFNot human75% (4)
- Anchor Handling Preparation Checklist300312 Rev01Document3 pagesAnchor Handling Preparation Checklist300312 Rev01Kunal Singh100% (1)
- Systematic Cause Analysis TechniqueDocument1 pageSystematic Cause Analysis Techniquescribd@omoa.co.ukNo ratings yet
- FCV-A.13.01 Emergency Drill ScheduleDocument3 pagesFCV-A.13.01 Emergency Drill Schedulea.gomonovs26100% (3)
- Aby Warburg: Bilderatlas Mnemosyne: The OriginalDocument36 pagesAby Warburg: Bilderatlas Mnemosyne: The OriginalAntonis100% (1)
- QMS 75A - Navigation Audit Report Rev 6-UnprotectedDocument7 pagesQMS 75A - Navigation Audit Report Rev 6-Unprotectedhoangminh2209100% (1)
- QSE SystemDocument17 pagesQSE SystemAnonymous JIHJTWw4Th0% (1)
- ExxonMobil Marine Safety Criteria Guidance 2017 Final - R01a (Clean)Document60 pagesExxonMobil Marine Safety Criteria Guidance 2017 Final - R01a (Clean)maxtrap73100% (1)
- ABS Class NotationsDocument285 pagesABS Class NotationsndesigngmailNo ratings yet
- MSCAT 8.2 - Basic Causes ExplainedDocument18 pagesMSCAT 8.2 - Basic Causes ExplainedAhmet SolakNo ratings yet
- Checklist ISM AuditDocument14 pagesChecklist ISM AuditjunNo ratings yet
- Self CHK Ship e Audit Ism ChecklistDocument10 pagesSelf CHK Ship e Audit Ism ChecklistIrdam Jono100% (2)
- Sample-Masters Standing OrdersDocument6 pagesSample-Masters Standing Orderssinghal.ns4497100% (2)
- (4.9) TMSA Report (VNLS-3556-6207-6159) PDFDocument106 pages(4.9) TMSA Report (VNLS-3556-6207-6159) PDFEdy SukmonoNo ratings yet
- D18 ECDIS - Speed Log Input FailureDocument1 pageD18 ECDIS - Speed Log Input FailureRiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Chief Engineer Pre-Vetting ChecklistDocument6 pagesChief Engineer Pre-Vetting ChecklistWilson Aye100% (3)
- Solas Training ManualDocument6 pagesSolas Training Manualquick100% (1)
- 47 Drill Report - Salvage of Own ShipDocument1 page47 Drill Report - Salvage of Own ShipmitchsipNo ratings yet
- Plans and Procedures Recovery Persons From Water FINALDocument38 pagesPlans and Procedures Recovery Persons From Water FINALRihards67% (6)
- Master's Sms Review FormDocument4 pagesMaster's Sms Review FormJeet Singh100% (3)
- Eisenmann Nineteenth Century ArtDocument380 pagesEisenmann Nineteenth Century ArtFilip100% (2)
- (1-2) Nvestigation Analysis & M-SCAT CapstanDocument22 pages(1-2) Nvestigation Analysis & M-SCAT Capstan洪力No ratings yet
- DPA Training Rev02 2010 4 29Document230 pagesDPA Training Rev02 2010 4 29majdirossross100% (1)
- MBW - Iarkbe Systeiatkc Cause Abanysks) Ec'bkque (I-Scat 0. )Document1 pageMBW - Iarkbe Systeiatkc Cause Abanysks) Ec'bkque (I-Scat 0. )洪力No ratings yet
- Tmsa 3Document1 pageTmsa 3St GRNo ratings yet
- Sire InspectionDocument8 pagesSire InspectionAnil yucebasNo ratings yet
- H - SMS - Manual PDFDocument7 pagesH - SMS - Manual PDFRabahNo ratings yet
- Guidance To Masters and Officers in Conducting An OvidDocument33 pagesGuidance To Masters and Officers in Conducting An OvidСтанислав Георгиев100% (1)
- Angola General General (See Plan) : Platform Lat. Long. LightDocument30 pagesAngola General General (See Plan) : Platform Lat. Long. LightPavel ViktorNo ratings yet
- ER06 BunkeringDocument2 pagesER06 BunkeringNang D. VuNo ratings yet
- VSL Inspection Form 300611Document6 pagesVSL Inspection Form 300611Kunal SinghNo ratings yet
- Processes For The Development and Maintenance of Part 1 of The Inventory of Hazardous MaterialsDocument19 pagesProcesses For The Development and Maintenance of Part 1 of The Inventory of Hazardous MaterialsReda HmrNo ratings yet
- 500 MTR Zone Checklist - IsMSBDocument4 pages500 MTR Zone Checklist - IsMSBRamli DisaNo ratings yet
- GL ND Guidelines For Towage of ShipsDocument40 pagesGL ND Guidelines For Towage of ShipsTomkel VoonNo ratings yet
- SMM ManualDocument197 pagesSMM ManualAlessandro MxNo ratings yet
- Vessel S Guide To Vetting InspectionsDocument11 pagesVessel S Guide To Vetting Inspectionsmatan55100% (5)
- Checklist Audit Ism Office EngDocument9 pagesChecklist Audit Ism Office EngAji ArnowoNo ratings yet
- ISM - ISO - ISPS - MLC Internal Audit - SafetyCultureDocument28 pagesISM - ISO - ISPS - MLC Internal Audit - SafetyCultureAbner Llenos100% (4)
- Ism The Role of DpaDocument17 pagesIsm The Role of DpaΑΝΝΑ ΒΛΑΣΣΟΠΟΥΛΟΥNo ratings yet
- UscgDocument82 pagesUscgAldy KurniaNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Internal AuditsDocument3 pages12.1 Internal Auditsfredy2212No ratings yet
- Good MaintenanceDocument53 pagesGood MaintenancejohnEnglish100% (1)
- Guide For Vetting InspectionsDocument6 pagesGuide For Vetting InspectionsAnonymous b68EQR100% (1)
- INTERTANKO Vetting Committee 26.05.2022Document29 pagesINTERTANKO Vetting Committee 26.05.2022soner100% (1)
- Annual Audit Checklist PDFDocument38 pagesAnnual Audit Checklist PDFTankcare MarineNo ratings yet
- IMO MSC Circ 645 DP SystemsDocument17 pagesIMO MSC Circ 645 DP Systemsgreensail1No ratings yet
- Contingency Manual - 15-July-22Document102 pagesContingency Manual - 15-July-22Rachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- STCW 2010Document46 pagesSTCW 2010Vikram Shetty100% (1)
- Causes For Safety ObservationsDocument1 pageCauses For Safety ObservationsAlberto CastilloNo ratings yet
- Incident & Investigation Report Procedure - Near Miss-EVidence Communication Report-Hse Statistics & RecordsDocument83 pagesIncident & Investigation Report Procedure - Near Miss-EVidence Communication Report-Hse Statistics & RecordsAhmed Reda100% (1)
- IR1209Document2 pagesIR1209JoliboysNo ratings yet
- QPMO-700-00-FM-030 Incident Report Rev 0Document6 pagesQPMO-700-00-FM-030 Incident Report Rev 0IslamAl-BazNo ratings yet
- Risk AssesmentDocument4 pagesRisk Assesmentapi-589160120No ratings yet
- IR Jan 13 2023Document4 pagesIR Jan 13 2023JoliboysNo ratings yet
- IR Jan 10 2023Document3 pagesIR Jan 10 2023JoliboysNo ratings yet
- Near Miss#rmco-Ir-005 ReportDocument6 pagesNear Miss#rmco-Ir-005 ReportQADEER SHANNo ratings yet
- Production Risk Assessment Location 2Document3 pagesProduction Risk Assessment Location 2SkyeNo ratings yet
- Report Format Conditions Unsafe Acts and IncidentsDocument3 pagesReport Format Conditions Unsafe Acts and IncidentsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Edp Micro Project Roll-28-Converted (1)Document20 pagesEdp Micro Project Roll-28-Converted (1)sarthak KulatNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter 3Document39 pages07 - Chapter 3RAKTIM PUJARINo ratings yet
- Urbane LandscapesDocument13 pagesUrbane LandscapesUvoBubaNo ratings yet
- Snowdon, P. Animalism and The LivesDocument14 pagesSnowdon, P. Animalism and The LivesThiago DelaídeNo ratings yet
- Evidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelDocument45 pagesEvidence+Based+Practices+for+Early+R+Therapy Full+Handout Lindsey+HockelNoha Ibraheem Helmy100% (1)
- Nike Complaint 23Document94 pagesNike Complaint 23Martin LeafNo ratings yet
- Teaching English Language To Young School-Age ChilDocument13 pagesTeaching English Language To Young School-Age Chilnour fouaniNo ratings yet
- Solomon Rprc4ce Mytest Ch04-TIFDocument53 pagesSolomon Rprc4ce Mytest Ch04-TIFTinagraceNo ratings yet
- William Alston, The Reliability of Sense Perception, Chapter 2: " Track Record and Other Simple Empirical Arguments For Reliability"Document7 pagesWilliam Alston, The Reliability of Sense Perception, Chapter 2: " Track Record and Other Simple Empirical Arguments For Reliability"Carlos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Management StylesDocument8 pagesManagement StylesSergio Felipe Nuñez RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Krisha PlarasNo ratings yet
- Kognitivni Razvoj U Odojastvu PERCEPCIJADocument36 pagesKognitivni Razvoj U Odojastvu PERCEPCIJAIvan DjukicNo ratings yet
- Racial Stereotypes About LatinDocument57 pagesRacial Stereotypes About LatinNatalie RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument323 pagesBusiness CommunicationRadhika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Parts and Wholes Visual PresentationDocument39 pagesParts and Wholes Visual Presentationjonniel caadanNo ratings yet
- English AssessmentDocument13 pagesEnglish AssessmentGUI DING QUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- (Comparative Politics) Gauja Anika-Party Reform - The Causes ChallengesDocument227 pages(Comparative Politics) Gauja Anika-Party Reform - The Causes Challengeskarahe100% (1)
- If You Stop Speaking They Kill You Kind of Freedom Volume1Document13 pagesIf You Stop Speaking They Kill You Kind of Freedom Volume1Waris WaljiNo ratings yet
- Zeki - Art and The BrainDocument34 pagesZeki - Art and The BrainIvan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Erzen, Jale Nejdet - Islamic Aesthetics, An Alternative Way To KnowledgeDocument7 pagesErzen, Jale Nejdet - Islamic Aesthetics, An Alternative Way To KnowledgeharisdcNo ratings yet
- Brand IdentityDocument12 pagesBrand IdentityNajam ul SaharNo ratings yet
- 00, Business Communication 7, Psychological and Cultural Dimensions of Business CommunicationDocument15 pages00, Business Communication 7, Psychological and Cultural Dimensions of Business CommunicationYash goyalNo ratings yet
- 06 The Ascension of MindDocument122 pages06 The Ascension of Mindyharoon99No ratings yet
- The Youth Activity Center, Old Garment Factory RenovationDocument9 pagesThe Youth Activity Center, Old Garment Factory RenovationAbdul SuheemNo ratings yet
- Steps To An Ecology of PsychotherapyDocument13 pagesSteps To An Ecology of PsychotherapyRoman BenderskijNo ratings yet
- Subject - Organisational Behaviour: Pramod B. Shrawage MDP - Thermax DATE - 25 SEPT. 2005Document10 pagesSubject - Organisational Behaviour: Pramod B. Shrawage MDP - Thermax DATE - 25 SEPT. 2005Darius PavriNo ratings yet
- Opening The Third EyeDocument4 pagesOpening The Third Eyetower1No ratings yet