Professional Documents
Culture Documents
20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 8
20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 8
Uploaded by
uzair akramOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 8
20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 8
Uploaded by
uzair akramCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
FLUID MECHANICS LAB
Experiment No.8
Submitted By: Uzair Akram
Reg. No.: 20-ME-9
Date: 11-12-2021
Section: A1
Submitted To: Engr Abdul Rehman
Mechanical Engineering Department
Faculty of Mechanical & Aeronautical Engineering
University of Engineering & Technology Taxila
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 1
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
EXPERIMENT NO.8
TITLE: -
To study and draw the characteristic curves of a single centrifugal pump.
APPARATUS: -
Electric Supply
Supply Tank
Submersible Tank
Supply Line of water
Suction Tank
Suction Gauge & Valve
Delivery Gauge & Valve
Single Stage Centrifugal Pumps
Stopwatch
Measuring Tank
THEORY: -
CENTRIFUGAL PUMP:
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move a fluid by means of the transfer of rotational
energy from one or more driven rotors, called impellers. Fluid enters the rapidly rotating impeller along its
axis and is cast out by centrifugal force along its circumference through the impeller's vane tips.
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the
hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric
motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the
pump impeller along or near to the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward
into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exits.
Centrifugal Pumps are useful since they can generally handle large quantities of fluids, provide very high
flow rates.
Centrifugal pumps are generally designed and suitable for liquids with a relatively low viscosity that pours
like water or light oil. More viscous liquids such as 10 or 20 wt. oils at 68-70-degree F will require
additional horsepower for centrifugal pumps to work. For viscous liquids of more than 30 wt. oils, positive
displacement pumps are preferred over centrifugal pumps to help lower energy costs.
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 2
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
TYPES OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP:
1. Depending on the number of impellers in the pump
a) Single-Stage
b) Two-Stage
c) Multi-Stage
Single-Stage:
This pump type houses only one impeller within its casing, making maintenance quite easy. A single-stage centrifugal
pump is best suited to low-pressure operations where a large flow rate is maintained.
Two-Stage:
A two-stage centrifugal pump possesses dual impellers functioning together to pump the associated process liquids.
It is a device best used in medium head applications.
Multi-Stage:
Multiple impellers (three or more) are required in this centrifugal pump system to achieve maximum efficiency.
Multi-stage pumps are best for high head applications.
2. According to the type of case-split:
The Orientation of case-split is another factor used to categorize Centrifugal pumps:
a) Axial split
b) Radial split
Axial split:
In these kinds of pumps, the volute casing is split axially and the split line at which the pump casing
separates is at the shaft’s centerline. Axial Split Pumps are typically mounted horizontally due to ease in
installation and maintenance.
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 3
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
Radial split:
Here, the pump case is split radially; the volute casing split is perpendicular to the shaft centerline.
3. According to the type of impeller design:
a) Single suction
b) Double suction
Single suction:
This kind of pump has a single suction impeller that allows fluid to enter the blades only through one side; It
has a simple design, but impeller has a higher axial thrust imbalance due to flow coming in on one side of
impeller only.
Double suction:
This pump comes with a double suction impeller that allows fluid to enter from both sides of the blades and
has lower NPSHR than a single suction impeller. Split-case pumps are the most common type of pump with
a double suction impeller.
4. According to the type of volute:
Centrifugal pumps can also be categorized based on volute namely Single volute and Double volute:
a) Single volute
b) Double volute
Single volute:
This kind of pump Is usually used in small low-capacity pumps where a double volute design is impractical
due to a relatively small size of the volute passageway which makes obtaining good quality commercial
casting difficult. Pumps with single volute design have higher radial loads.
Double volute:
This kind of pump volute has two partial volutes which are located 180 degrees apart resulting in balanced
radial loads; most centrifugal pumps are of double volute design.
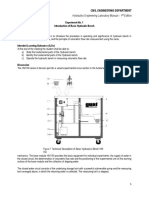
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE: -
First, take the Centrifugal Pump and place it on basic Hydraulic Bench.
Join the water delivery pipe and fill the tank up to certain level.
Now open the foot valve of the pump and switch the pump on. Keep the delivery valve on and note
the reading on output or delivery pressure gauge.
Open the delivery tube valve so that water is delivered to the output tank. Note the reading of
delivery pressure gauge.
Use the stopwatch to calculate the time for the volume.
Calculate flow rate for each reading.
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 4
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
APPLICATIONS: -
Centrifugal pump uses are common throughout a diverse range of domestic, commercial, and industrial
markets. Examples of centrifugal pump applications include but are not limited to:
Water supply for residential areas
Fire protection systems
Sewage/slurry disposal
Food and beverage manufacturing
Chemical manufacturing
Oil and gas industrial operations
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS: -
FORMULA:
V
Q=
T
UNIT:
mm3/sec
Sr No. P1=Psuction P2=PDelivery P=P2-P1 Volume Time Q=V/t
(Bar) (Bar) (Bar) (m3) (sec) (m3/sec)
01 0 4 4 0 60 0
02 0 3 3 0.012 60 2 ×10-4
03 0 2 2 0.020 60 3.3 ×10-4
04 0 1 1 0.034 60 5.7 ×10-4
05 0 0 0 0.040 60 6.7 ×10-4
GRAPH: - Draw the graph between P and flow rate.
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 5
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
P and Q(flow rate)
8
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5
CONCLUSION:
In this lab, we learned about different parts of a centrifugal pump. We learned about the usage of centrifugal
pumps and about the effect of change in pressure at suction and delivery on the flow rate of fluid.
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 6
Lab Manual Course Title: Fluid Mechanics Lab
Taxonomy Contributio Max. Obtained
Knowledge components Domain
level n marks marks
1. Student has conducted the
experiment by practicing the
hands on skills. Psychomoto
Precision (P3) 60% 15
2. Student has achieved r
required accuracy in
performance.
3. Student has contributed or
responded affectively in form Affective Respond (A2) 20% 5
of group or team.
4. Student has knowledge
regarding the experiment and
successfully applied the input Cognitive Apply (C3) 20% 5
values for required
calculations.
Total 25
Experiment Title: To study and draw the characteristic curves of a single centrifugal pump.
Course title: Fluid Mechanics Lab Total Marks: ___________
Practical No. 8 Date of experiment performed: 06-12-2021
Course teacher/Lab Instructor: Engr. Abdul Rehman Date of marking: ____________
Student Name: Uzair Akram
Registration no:20-ME-9
Marking Evaluation Sheet
Signed by Course teacher/ Lab Instructor
Lab Title: Fluid Mechanics 7
You might also like
- Lab 1 Series Parallel PumpsDocument16 pagesLab 1 Series Parallel PumpsSasys Rgl100% (13)
- Series & Parallel Pump TestDocument22 pagesSeries & Parallel Pump TestIkhwan Z.100% (23)
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 9Document7 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 9uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 10Document7 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 10uzair akramNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Hydraulics and Pneumatics .Document56 pagesLab Manual Hydraulics and Pneumatics .Aniket ChavanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics-II Lab Manual: University College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument27 pagesFluid Mechanics-II Lab Manual: University College of Engineering and Technologyzia malikNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet 1Document12 pagesLab Sheet 1Danis HakimNo ratings yet
- 1.course Plan-text-ME 3111Document4 pages1.course Plan-text-ME 3111mama dullaNo ratings yet
- Fluid 9Document7 pagesFluid 9asdNo ratings yet
- Performance Test of Centrifugal PumpDocument10 pagesPerformance Test of Centrifugal Pumpcha100% (1)
- Baku Higher Oil SchoolDocument13 pagesBaku Higher Oil SchoolKenan GojayevNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument12 pagesTable of ContentsSyikin FauziNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document7 pagesExperiment No. 1Judith LacapNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Lab 1 Fluid Lab ReportDocument31 pagesGroup 4 Lab 1 Fluid Lab ReportHarizx SaufixNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic ResearchDocument10 pagesHydraulic Researchibrahim matterNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document9 pagesExperiment 3Abigail RadubanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics Lab ManualDocument21 pagesHydraulics and Pneumatics Lab ManualNAVEEN KUMAR S NNo ratings yet
- Cavitation Analysis CFDDocument4 pagesCavitation Analysis CFDshdjjfNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg Lab2 Midterm Module 5 Reciprocating PumpDocument7 pagesMechanical Engg Lab2 Midterm Module 5 Reciprocating PumpKurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- MET206 - Ktu QbankDocument10 pagesMET206 - Ktu QbankNidheesh NarayanNo ratings yet
- Fluids 2 Lab Report 4 FinalDocument9 pagesFluids 2 Lab Report 4 FinalJay-ar BensOnNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual PMFMDocument79 pagesLab Manual PMFMSiddharth SridharNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Centrifugal Pump2021Document31 pagesLab 4 Centrifugal Pump2021S. ThivyanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg Lab2 Midterm Module 7 Pump PerformanceDocument11 pagesMechanical Engg Lab2 Midterm Module 7 Pump PerformanceKurt PalacioNo ratings yet
- Gatpu Me152l c3 Experiment 1Document18 pagesGatpu Me152l c3 Experiment 1Dikimbie Aldrei GatpuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Machinery Manual 2022-23Document40 pagesFluid Machinery Manual 2022-23Aviansh MalhotraNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 7Document8 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 7uzair akramNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Fluid Machinery KCRDocument6 pagesSyllabus For Fluid Machinery KCRbsmeNo ratings yet
- Comparision of PumpsDocument18 pagesComparision of PumpscaviourNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument23 pagesCentrifugal Pumpm7394197No ratings yet
- T-MEET324LA Experiment No.7 Centrifugal Pump MEE31Document11 pagesT-MEET324LA Experiment No.7 Centrifugal Pump MEE31Paul Ryan GeneralNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine Lab ManualDocument47 pagesHeat Engine Lab ManualAurangzaib ArshadNo ratings yet
- FM - FP - CompressedDocument215 pagesFM - FP - CompressedKumar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Multistage Centrifugal Pump Test RigDocument13 pagesMultistage Centrifugal Pump Test Rigأشرف علي100% (1)
- Double Suction Centrifugal PumpDocument8 pagesDouble Suction Centrifugal PumpBilal WaseemNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 The Application of Pressure Compensated VaneDocument15 pagesLab 01 The Application of Pressure Compensated Vaneafiqcivil980No ratings yet
- MEET 422L2 Finals Group4 Experiment 7 Centrifugal Pump PerformanceDocument10 pagesMEET 422L2 Finals Group4 Experiment 7 Centrifugal Pump Performancekimbenedictaguilar19No ratings yet
- B45 Hydraulicsand Hydraulic MachineryDocument7 pagesB45 Hydraulicsand Hydraulic MachineryRa BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Turning Blades in Front of CDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Turning Blades in Front of Cdixie0630No ratings yet
- EM3210 Fluid 2 Lab Report 1 (Loeng ME)Document10 pagesEM3210 Fluid 2 Lab Report 1 (Loeng ME)Liew Yu LoengNo ratings yet
- Flow Around CylinderDocument24 pagesFlow Around Cylinderengrvj57No ratings yet
- Serial and Parallel Pump Operations-Variable Speed Pump DriveDocument10 pagesSerial and Parallel Pump Operations-Variable Speed Pump DriveAyberk ArdıçNo ratings yet
- Flow Analysis of Butterfly Valve Using CFDDocument7 pagesFlow Analysis of Butterfly Valve Using CFDIJMERNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering: Experiment 4Document18 pagesChemical Engineering: Experiment 4Kenan GojayevNo ratings yet
- TM - 17BEM0043 - Exp 10Document4 pagesTM - 17BEM0043 - Exp 10Kartik BhathireNo ratings yet
- Sona College of Technology: Department of Mechatronics EngineeringDocument41 pagesSona College of Technology: Department of Mechatronics EngineeringKanishk KannaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesExperiment No. 1Judith LacapNo ratings yet
- Models - Mixer.centrifugal PumpDocument22 pagesModels - Mixer.centrifugal Pumpcarlos tNo ratings yet
- Ce 2211 Applied HydraulicsDocument4 pagesCe 2211 Applied HydraulicsGERARD HAULENo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: II Year B. Tech I-Semester Mechanical EngineeringDocument45 pagesLaboratory Manual: II Year B. Tech I-Semester Mechanical Engineeringmuhammad ahsanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Cavitating Flow in A Centrifugal Pump As TurbineDocument21 pagesNumerical Simulation of Cavitating Flow in A Centrifugal Pump As TurbineAung Myat ThuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 (1) Loses in ValveDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 (1) Loses in ValveAfzaFarzanaAhmadNo ratings yet
- Level 0 - Pump EfficiencyDocument6 pagesLevel 0 - Pump EfficiencySAYA HENSEMNo ratings yet
- Virtual Instruments and Experiments in Engineering Education Lab Setup With Hydraulic PumpDocument8 pagesVirtual Instruments and Experiments in Engineering Education Lab Setup With Hydraulic PumpFabian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Aguilar Module 1 Activity No. 5 Experiment No. 1Document21 pagesAguilar Module 1 Activity No. 5 Experiment No. 1Lenovo LaptopNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 7+8+9Document32 pagesExperiment No 7+8+9Muhammad kamran AmjadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument37 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualMohith MarripatiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraullic Machines Lab ManualDocument43 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraullic Machines Lab Manualm udaya kumarNo ratings yet
- Driving LicenseDocument1 pageDriving Licenseuzair akramNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Manual 7Document4 pagesThermodynamics Manual 7uzair akramNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ADocument4 pagesLab 6 Auzair akramNo ratings yet
- Uzair AkramDocument2 pagesUzair Akramuzair akramNo ratings yet
- Internship Letter 2023 FinalDocument1 pageInternship Letter 2023 Finaluzair akramNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Title: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 6: Title: Objectiveuzair akramNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Manual 9Document7 pagesThermodynamics Manual 9uzair akramNo ratings yet
- Qasim Ali Resume - Mechanical UET LHRDocument1 pageQasim Ali Resume - Mechanical UET LHRuzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 10Document7 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 10uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 14Document12 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 14uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 13Document12 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 13uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 4Document8 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 4uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 7Document8 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 7uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 6Document7 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 6uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 12Document10 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 12uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 9Document7 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 9uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 11Document9 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 11uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 3Document5 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 3uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 2Document5 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 2uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 1Document9 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 1uzair akramNo ratings yet
- 20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 5Document8 pages20-ME-9 Uzair Akram FM Lab 5uzair akramNo ratings yet
- MEE 3262 Mechanical Vibrations (Notes)Document110 pagesMEE 3262 Mechanical Vibrations (Notes)Mï XavierNo ratings yet
- Design of Composite Slab-Bondek IIDocument25 pagesDesign of Composite Slab-Bondek IIteferi tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Fisher and Paykel Airvo 2 Technical ManualDocument37 pagesFisher and Paykel Airvo 2 Technical ManualE- MedNo ratings yet
- Rating Sheet For Demonstration With Oral QuestioningDocument4 pagesRating Sheet For Demonstration With Oral QuestioningRinalyn G. Canetes100% (1)
- Jempson Bridge 1997Document16 pagesJempson Bridge 1997Luis Fernando Zapata LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Roket Makale InglizceDocument55 pagesRoket Makale InglizceHakan ErenNo ratings yet
- Objectives: The Nature of MatterDocument31 pagesObjectives: The Nature of MatterJoanna Marie R. PeranteNo ratings yet
- Brainkart 1NQKLHuNY5E 83rhvrbqCeQMF4f5KTkGz - pdf-1Document16 pagesBrainkart 1NQKLHuNY5E 83rhvrbqCeQMF4f5KTkGz - pdf-1Revanth RamineniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - CulvertDocument40 pagesChapter 18 - CulvertJohnyReubenNo ratings yet
- Rod 320.002 2500 254 847 01 Enkoder Heidenhain ManualDocument72 pagesRod 320.002 2500 254 847 01 Enkoder Heidenhain Manualkaori quinteroNo ratings yet
- 11 - 1 2 SAT READING SMART BOARD WEEK 2cDocument9 pages11 - 1 2 SAT READING SMART BOARD WEEK 2ccansu aybaşNo ratings yet
- Material Approval Request CWH DankosDocument4 pagesMaterial Approval Request CWH Dankosmelati puspitaNo ratings yet
- 5.TIFR Previous Year's Pattern (2019-2020)Document3 pages5.TIFR Previous Year's Pattern (2019-2020)Kanishk ChitranshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Textbook For Class XIDocument280 pagesChemistry: Textbook For Class XISiraj JamadarNo ratings yet
- MOTOR ID23005 128W: Ratings Symbol UnitsDocument2 pagesMOTOR ID23005 128W: Ratings Symbol Unitsdoppler9effectNo ratings yet
- Recent Progress in The Development of High-Efficiency Inverted Perovskite Solar CellsDocument28 pagesRecent Progress in The Development of High-Efficiency Inverted Perovskite Solar CellsLIU BOWENNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Warm Deep Drawing Process For 2017T4 Aluminum Alloy: Parametric Significance Using Taguchi TechniqueDocument9 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Warm Deep Drawing Process For 2017T4 Aluminum Alloy: Parametric Significance Using Taguchi Techniquearshad121233No ratings yet
- Retrofitting Arch Bridges PragueDocument13 pagesRetrofitting Arch Bridges PragueTamaduianu IoanNo ratings yet
- C04 Calculus TopicsDocument90 pagesC04 Calculus TopicsAzizmanvaNo ratings yet
- Lenses and TelescopesDocument43 pagesLenses and TelescopesKev WattsNo ratings yet
- FCH Mth301a 2021-22 (I)Document2 pagesFCH Mth301a 2021-22 (I)Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- Datasheet-Ultisys 52-KIRAN - V1.2GFFTDocument2 pagesDatasheet-Ultisys 52-KIRAN - V1.2GFFTMaría Renee Salazar HerbasNo ratings yet
- M0707 Acabados SuperficialDocument29 pagesM0707 Acabados SuperficialUbaldo Garcia ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- LADUMA: Discovery of A Luminous OH Megamaser at Z 0.5: Marcin - Glowacki@curtin - Edu.auDocument10 pagesLADUMA: Discovery of A Luminous OH Megamaser at Z 0.5: Marcin - Glowacki@curtin - Edu.auMazimba BrasilNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic SchematicsDocument15 pagesPneumatic SchematicsAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Megapal-Catalogue2021Document28 pagesScaffolding Megapal-Catalogue2021Hoang Cong DungNo ratings yet
- Anexo Iii - DatasheetDocument8 pagesAnexo Iii - Datasheetevellyne.projetosNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Solar/wind Hybrid Energy System Using MTALAB SimulinkDocument4 pagesModeling of Solar/wind Hybrid Energy System Using MTALAB SimulinkMahar Nadir AliNo ratings yet
- Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi Linear IC's and Applications Laboratory (18EEL46)Document30 pagesDept. of Electrical and Electronics Gogte Institute of Technology, Belagavi Linear IC's and Applications Laboratory (18EEL46)BaakdNo ratings yet
- Network Exam 2Document3 pagesNetwork Exam 2DavidRubeomNo ratings yet