Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter Respiration
Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter Respiration
Uploaded by
Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter Respiration
Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter Respiration
Uploaded by
Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobCopyright:
Available Formats
ACOB, CHRISLYN EDS J.
STEM 11-HYGEIA
GENERAL BIOLOGY: RESPIRATION 2ND QUARTER
ACTIVITY 1:
COMPARING AEROBIC FROM ANEAROBIC RESPIRATION
AEROBIC RESPIRATION ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
SIMILARITIES
Uses Oxygen No Oxygen
Makes Lactic Acid Uses Citric Cycle
Makes ATP
Makes Ethanol Uses Oxidative
Makes Carbon Dioxide
Phosphorylation
Uses Glycolysis
B.
1. What is the main source during aerobic exercises?
- Oxygen is the main source during aerobic exercises.
2. What is the benefit of aerobic respiration in the body?
- the benefits of aerobic respiration in our body is that it can help you lose weight and keep it off, may
help lower and control blood pressure, may reduce fatigue during exercise and increase your stamina.
Aerobic respiration in the body also activates immune system making you less likely to get flu, this can
also strengthen your heart, boosts mood, and may help you live longer.
3. What is the benefit of anaerobic respiration in the body?
-anaerobic exercise can be beneficial to build muscle or lose weight. This can also help you to maintain
muscle mass as you get older and it can also strengthen bones.
4. How often does an individual should undergo aerobic and anaerobic exercises?
- the recommended time for adults is at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise at least
5 days a week, or at least 25 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity for 3 days a week.
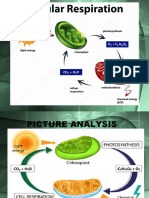
ACTIVITY 2: UNDERSTANDING CELLULAR RESPIRATION
1. Describe in words what these equations tell us about cellular respiration.
-It displays chemical equations that sum up the inputs and outputs of cellular respiration. The curved
arrows represent coupled reactions, in which the top reaction provides energy for the bottom reaction.
2. List Each type of input molecule that is required for cellular respiration, and state whether the
molecule comes mainly form outside of the cell or inside of the cell. For each type of input molecule,
explain how the body gets this molecule or explain how this molecule is regenerated inside each cell.
INPUT SOURCE: OUTSIDE HOW THE BODY GETS THIS MOLECULE OR
MOLECULE OR INSIDE THE CELL HOW THIS MOLECULES IS REGENERATED
INSIDE EACH CELL
SUGAR OUTSIDE SUGAR FROM CARBOHYDATES IS PROCESSED AND
GLUCOSE ABSORBED BY THE CELLS THROUGH THE ACTION OF
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM BY MEANS OF EATING.
OXYGEN OUTSIDE OXYGEN IS ABSORBED AND PROCESSED IN THE
BODY BY THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM THROUGH
BREATHING.
ACTIVITY 3:
WRITING A SONG ( performance task)
Tone: Jingle Bell Rock
We use cell respiration to survive
We take O2 and a lot of food too
Outcomes H2O and CO2
Most importantly ATP.
It all starts with glucose and glycolysis
NADH oxidizes it.
Obtained a net gain of 2 ATP
Most remarkably pyruvates
It is now time to oxidize the pyruvates
Carbons are removed
Outcomes are CO2
This is carried Acetyl CoA
Carbons get dropped off in the Krebs Cycle
4 ATP is made
Oxidation, Phosphorylation are next
NADH turns to NAD+
ATP is made from the protons
They cross the protein synthase pathway
To the final electron acceptor O2
28 ATP is made.
This is why we perform cell respiration to generate energy!
We use cell respiration to survive
We take O2 and a lot of food too
Outcomes H2O and CO2
Most importantly (3x) ATP!
Guide Questions:
1. What is cellular respiration?
- cellular respiration is a complex process by which energy in the form of ATO is
released from food molecules.
2. What are the three processes involved in cellular respiration? Briefly discuss
each.
- The three processes pf cellular respiration are glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and
Electron Transport Chain.
Glycolysis- occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It involves the splitting of 16-
carbon sugar molecules into 23 carbon pyruvate molecules yielding 2 ATP
molecules.
Krebs Cycle- is a series of enzyme- catalyzed reactions that breakdown acetyl-
CoA completely into carbon dioxide and water. The end product are 4ATP,
10NADPH and 2 FADH2 molecules. The cell ejects CO2 as a waste.
Electron Transport Chain- refers to a series oxidation processes where electrons
(H2+) carried by NADPH2 and FADH2 are transferred to electron acceptors.
3. How does the process of cellular respiration affect humans?
-all organisms employ the process of cellular respiration that releases stored
chemical energy, all living things would cease to exist.
REFLECTION/ CLOSURE
I learned that Aerobic Respiration necessitates the presence of oxygen in order to
produce ATP. It is one of the characteristics of Eukaryotic cells when they have
enough oxygen, and it occurs primarily in the mitochondria. Anaerobic
respiration, on the other hand, is the release of a small amount of energy in cells
through the breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen.
I enjoyed most on reading , answering the activities and composing a song.
You might also like
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- Cell Division GizmoDocument5 pagesCell Division GizmoMeg //No ratings yet
- Chloroplasts and MitochondriaDocument6 pagesChloroplasts and Mitochondriaapi-3277246050% (2)
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Q2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Document8 pagesQ2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Samantha ManibogNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- 8-C1.2 Cell RespirationDocument47 pages8-C1.2 Cell Respirationmakaya02No ratings yet
- Jinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHDocument11 pagesJinky Oraiz@deped Gov PHAnnejhel Mae Poralan100% (1)
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- Jinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDocument13 pagesJinnah University For Women: Group Members: Javeria Shahzad Kanza Naseer Muqaddas Raees Zainab GhufranDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Intro To Cellular Respiration and GlycolysisDocument2 pagesIntro To Cellular Respiration and GlycolysisMacky DacilloNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-5Document6 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-5Leah Jean PonlaonNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W3-5Document9 pagesGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Celluar Resp 2009Document58 pagesCelluar Resp 2009Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Pearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationDocument77 pagesPearson CH 10 Cellular RespirationMetaknight360 LiveNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaDocument15 pages7.1 Respiration: by Ana Nurnasuha & Irina KesumaLyana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- General Biology Q2W3Document2 pagesGeneral Biology Q2W3Geronimo, Jonamae S.No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- Chap7F4 Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesChap7F4 Cellular RespirationSyahir NajmiNo ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesBasis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationLia JeonNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Periodic Term III NotesDocument22 pagesPeriodic Term III Notessm2524363No ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesNCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 14 Respiration in PlantsHafiz HussainNo ratings yet
- CellRespi 2Document21 pagesCellRespi 2Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Respiration Worksheet CsecDocument2 pagesRespiration Worksheet CsecjhoyvanNo ratings yet
- Cellular1 2Document16 pagesCellular1 2Kaeshamaureen DresNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Energy SystemDocument27 pagesAerobic Energy SystemKavya KavyasujathaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument34 pagesAnaerobic RespirationArmero, Mariah Sophia V.No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDocument13 pagesClass 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDivyansheeNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument7 pagesRespirationmandonaldboikanyoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument52 pagesCellular RespirationVinz Arvhil MatagayNo ratings yet
- Biology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaDocument3 pagesBiology Adenosine Triphosphate Oxygen Respiration BacteriaAmirul HakimNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision - NewDocument14 pagesBiology Revision - NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- 88 RespirationDocument25 pages88 RespirationJohn VukeniNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationJethroNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesGen Bio - Reactions That Produce and Consume ATP - 2nd QuarterChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Role of Oxygen in Cellular Respiration - 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesGen Bio - Role of Oxygen in Cellular Respiration - 2nd QuarterChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - Advantages and Disadvantages Od Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation - 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesGen Bio - Advantages and Disadvantages Od Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation - 2nd QuarterChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 2Document3 pagesGen Bio Module 2Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 7Document5 pagesGen Bio Module 7Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document1 pageGen Bio Module 3Chrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateDocument5 pagesCell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateAnicia ToscanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter+5 19+McKee+Suggested+ProblemsDocument30 pagesChapter+5 19+McKee+Suggested+ProblemsShivam PatelNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA QuizDocument3 pagesDNA and RNA QuizDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumNo ratings yet
- Signal Transduction and Gene Regulation in Plant DevelopmentDocument55 pagesSignal Transduction and Gene Regulation in Plant Developmentlordniklaus100% (1)
- Ebook PDF Campbell Biology 2nd Canadian Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Campbell Biology 2nd Canadian Edition PDFinga.morley147100% (40)
- Bio ReviewerDocument7 pagesBio ReviewerKhristyn RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cytosol 1Document20 pagesCytosol 1Swastu Nurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 9Document55 pagesBiology Ch. 9ddNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science 8 Mitosis ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLesson Plan Science 8 Mitosis ObjectivesCassy Joy Ellopo RellamaNo ratings yet
- Vitis OutputDocument3,573 pagesVitis OutputKian Bigovic VilliNo ratings yet
- A Truncated Intracellular HER2neu Receptor Produced by Alternative RNA Processing Affects Growth of Human Carcinoma CellsDocument11 pagesA Truncated Intracellular HER2neu Receptor Produced by Alternative RNA Processing Affects Growth of Human Carcinoma CellsSean KwanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Review HomeworkDocument7 pagesCell Cycle Review HomeworkM.V.MatíasNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Cells) Practice Questions For Quiz (Anatomy and Physiology)Document3 pagesModule 3 (Cells) Practice Questions For Quiz (Anatomy and Physiology)Shaina Marie RamosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Cancer and ImmunotherapyDocument38 pagesLecture 2 Cancer and ImmunotherapyMustafa Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter TestDocument4 pagesPractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument6 pagesGeneral BiologyErwin AllijohNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument39 pagesMeiosisGrachiella JanenNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Cell CycleDocument5 pagesRegulation of Cell CyclemohsinNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Crustacean Molting-A Review and Our PerspectivesDocument8 pagesRegulation of Crustacean Molting-A Review and Our PerspectivesJ HNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NOTESDocument11 pagesMitosis Meiosis NOTESCaden DiazNo ratings yet
- 08 HL Metabolism A3 Revision-SheetDocument1 page08 HL Metabolism A3 Revision-SheetLexieNo ratings yet
- 3cce171c-d4d7-49b0-8dda-425b225fb1f5 (1)Document2 pages3cce171c-d4d7-49b0-8dda-425b225fb1f5 (1)j4606074No ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Late-Onset Alzheimers Disease Is Associated WithDocument13 pagesLate-Onset Alzheimers Disease Is Associated WithAlix AliNo ratings yet
- 18 Lecture PresentationDocument49 pages18 Lecture PresentationMuhammad Rifki RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain and ChemiosmosisDocument3 pagesElectron Transport Chain and ChemiosmosisAddisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell Energyclaryl alexaNo ratings yet