Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energetics: Energy Input (Activation Energy) E
Energetics: Energy Input (Activation Energy) E
Uploaded by
ayeshaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Energetics: Energy Input (Activation Energy) E
Energetics: Energy Input (Activation Energy) E
Uploaded by
ayeshaCopyright:
Available Formats
Energetics
Heat:
Flow of energy
• Measure in J or KJ (joules)
1 KJ = 1000 J
Temperature:
Measure of kinetic energy measured in oC or K
K= oC +273 Measure of kinetic energy
Add heat (Energy) --> Heat energy converted to kinetic energy --> Kinetic energy of particles increases :. Temp increases
Stability in chemistry
Stable= low energy
• Calm
Unstable = high energy
• wobbles around
Bonds in chemical reactions Breaking bonds require energy
Forming bonds releases energy
Law of conservation of energy: energy cant be created or destroyed, only transferred
Low energy state ----------------------------------------> high energy state
Unbonded atom Extra energy must come from surroundings
(energy input)
Partially filled valance shell
=
Unstable High energy state -------------------------------------> Low energy state
:. Higher energy Extra energy released to surroundings
(energy output)
Energy Energy
Energy input output
Bonded atom Bonded atom
Full valence shell
=
Stable
:. Lower energy
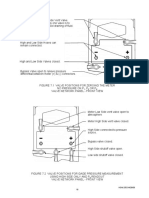
Reactants ---------> products
E.g.
H2 + Cl2 ----------------> 2HCl
H - H Cl - Cl H - Cl
Bonds break Energy is released
Energy is absorbed (require H - Cl
energy)
New bonds form
Called (releases
activation energy)
energy
EA
Endothermic Vs Exothermic rxns
Endothermic: rxns that has an overall absorption of energy from
surroundings
Exothermic: rxns that has an overall release of energy into
surroundings
More energy is absorbed by reactants in endo
More energy is released by products in exo
Energy level diagrams
IB: know how to draw your diagrams!
• Exothermic energy diagram
Energy input Unbonded atoms (Less stable than
(Activation
energy) reactants :. Higher energy)
Have high energy
EA
Reactants Energy output
H = Overall enthalpy difference between reactants and products
Excess energy
Energy released
(exo) H
Products
rxn For an exothermic rxn
• Reactants have higher energy than products
:. Reactants are less stable than products
For an exothermic rxn
• Reactants have lower energy than products
• Endothermic energy level diagram :. Reactants are more stable than products
Endo
Unbonded atoms Output energy Delta H = over all energy absorbed from surroundings Reactant + heat -->
New Section 1 Page 1
• Reactants have lower energy than products
• Endothermic energy level diagram :. Reactants are more stable than products
Endo
Unbonded atoms Output energy Delta H = over all energy absorbed from surroundings Reactant + heat -->
Input energy products
Energy • Temp of system increases
Products
EA rxn
reactants H (overall energy absorbed)
Exo
Delta H = overall energy released into surroundings
Energy
Reactants --> products +
rxn • Temp of system decreases heat
New Section 1 Page 2
You might also like
- Shortridge HDM-250 OIM1 - 081759Document2 pagesShortridge HDM-250 OIM1 - 081759Roberto RiveraNo ratings yet
- Carpigiani Uc 711 Operations ManualDocument35 pagesCarpigiani Uc 711 Operations Manualمحمود موسویNo ratings yet
- Reactive Processes - Topic 1 - Heat of Reaction, Hear of FormationDocument6 pagesReactive Processes - Topic 1 - Heat of Reaction, Hear of FormationXclipsionNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Enzymes FAODocument8 pages1.2 Enzymes FAO2023822032No ratings yet
- 12 Enzymes 9 28 05Document52 pages12 Enzymes 9 28 05chpa.dalisay.auNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)Document28 pagesChapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- 화학공학입문설계 강의노트 9Document19 pages화학공학입문설계 강의노트 9wani anaNo ratings yet
- Energy, Energy Transfer, Energy AnalysisDocument17 pagesEnergy, Energy Transfer, Energy AnalysisTHADDEUS LEE CHUN HAU A21EM0317No ratings yet
- Principles of Energy ConversionDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Energy Conversionأحمد إبراهيم شواربNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Exergy New 2020 Simplified PP Online FullDocument64 pagesChapter 1 Exergy New 2020 Simplified PP Online FullKhairul HishamNo ratings yet
- LasersDocument29 pagesLasersasadNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemDocument65 pagesThermo ChemalinNo ratings yet
- 5..1-Endothermic-And-Exothermic ReactionsDocument2 pages5..1-Endothermic-And-Exothermic ReactionsKULDEEP PALANo ratings yet
- 1.4 EnergeticsDocument14 pages1.4 EnergeticsBhPO2023No ratings yet
- CEM1008F Thermodynamics Part I Thermochemistry and the First Law of Thermodynamics 2024 Lectures Notes (1)Document37 pagesCEM1008F Thermodynamics Part I Thermochemistry and the First Law of Thermodynamics 2024 Lectures Notes (1)tgmarozvaNo ratings yet
- BV IR SHO ModelDocument7 pagesBV IR SHO ModelAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Energetics: Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument6 pagesEnergetics: Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsRhea FrancisNo ratings yet
- Electrical OscillatorDocument6 pagesElectrical OscillatorM TahirNo ratings yet
- Condensadores MV Power QualityDocument45 pagesCondensadores MV Power QualityjoseNo ratings yet
- Bioseparation MESD Part1-3Document97 pagesBioseparation MESD Part1-3fjasfNo ratings yet
- 2023-08-18 Enzymes KineticsDocument52 pages2023-08-18 Enzymes KineticsAjay MahalkaNo ratings yet
- Physics GoodDocument5 pagesPhysics GoodFinleyNo ratings yet
- 05 - 2022 en SummaryDocument2 pages05 - 2022 en Summary2022 BALAKRISHNAN ADHITHINo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate 1Document8 pagesReaction Rate 1matseawangagift3dNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 Flashcards - QuizletDocument17 pagesPhysics Paper 1 Flashcards - QuizletNirgurfateh SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Mind MapDocument1 pageElectrolysis Mind MapThomas BudiartoNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesMoon Kim100% (1)
- Chem 121 Chapter 5Document7 pagesChem 121 Chapter 5nsorsokNo ratings yet
- 6A Chemical Energetics IDocument40 pages6A Chemical Energetics IArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1MUHAMMAD LUKMAN ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Energy ProductionDocument31 pagesEnzyme and Energy ProductionBONAVENTURA ALVINO DESMONDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Thermochemistry: Energy ChangesDocument23 pagesChapter 13: Thermochemistry: Energy ChangesnorsurianiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-Biology PresentationDocument52 pagesEnzymes-Biology PresentationAdeenNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument1 page5.1. Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsAkt PhyNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Pres StudentDocument12 pagesCH 6 Pres StudentReyzhel Mae MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4Document13 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Reaction Kinetics) Part 4ridwan100% (1)
- TLE - Basic Electricity-1Document44 pagesTLE - Basic Electricity-1lesllyhabulan84No ratings yet
- The First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument50 pagesThe First Law of Thermodynamicsgediongedisha0No ratings yet
- NoteDocument7 pagesNoteRosina KaneNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocument1 page5.1. Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsRethabile LekgethoNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 06Document40 pagesNotes Chapter 06Biruk BtNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - DXA TheoryDocument5 pages6.2 - DXA TheoryOmar Stalin Lucio RonNo ratings yet
- PB - Device Physics 2021 Lecture 3Document33 pagesPB - Device Physics 2021 Lecture 3keke renNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry (3a)Document36 pagesElectrochemistry (3a)zerathjanginNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate Notes CompletDocument57 pagesReaction Rate Notes CompletTasha AusmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Lec 1,2,3,4,5 SummaryDocument5 pagesElectrical Circuits Lec 1,2,3,4,5 SummaryRaghad Al-ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction - Freestate 2024 ComboDocument52 pagesRate of Reaction - Freestate 2024 ComboresegomohontiNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedDocument68 pagesChm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedNurfarhanah AsyknNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes - Unit 2 AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument16 pagesRevision Notes - Unit 2 AQA Chemistry A-LevelWajid AliNo ratings yet
- Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Linking Energy Profile Diagrams To Thermometer ReadingsDocument28 pagesExothermic and Endothermic Reactions: Linking Energy Profile Diagrams To Thermometer ReadingsHanifa Uly AmrinaNo ratings yet
- Energy of ActivationDocument10 pagesEnergy of ActivationAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry (CETE1B1) 2017 - UpDocument43 pagesThermochemistry (CETE1B1) 2017 - UpEstherNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fundamentals ThermodynamicsDocument133 pagesEngineering Fundamentals ThermodynamicsDHASARAIAH SNEHANo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument31 pagesCooling TowerAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- ExergyDocument64 pagesExergyAndree RosalesNo ratings yet
- Examples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesDocument6 pagesExamples of Exothermic Reactions : NotesAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- The First Law of Thermodynamics - 040170170000Document50 pagesThe First Law of Thermodynamics - 040170170000xixoNo ratings yet
- Energy, Work and PowerDocument78 pagesEnergy, Work and PowerSereniNo ratings yet
- Revision Lecture 2: PhasorsDocument43 pagesRevision Lecture 2: PhasorsMohsin NaushadNo ratings yet
- Regenerative TechnologyDocument8 pagesRegenerative TechnologymrusdiantoNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument226 pagesGen ChemKemal PujabNo ratings yet
- SDS - EM#53 - 53HD - REV.B (Msia, SG)Document5 pagesSDS - EM#53 - 53HD - REV.B (Msia, SG)killsty1eeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 1 (Chapters 1-8)Document20 pagesChemistry Worksheet 1 (Chapters 1-8)firaollulu4No ratings yet
- Does Immediate Dentin Sealing Influence The Polymerization of Impression Materials?Document7 pagesDoes Immediate Dentin Sealing Influence The Polymerization of Impression Materials?claudiaNo ratings yet
- Winkelmann2018 2 Diffusion CoefficientDocument3,605 pagesWinkelmann2018 2 Diffusion CoefficientDavidchengNo ratings yet
- Bello Zon CDVC Part 1 English Proinent ClO2 GenDocument48 pagesBello Zon CDVC Part 1 English Proinent ClO2 GenPaul IvanNo ratings yet
- Evaporation Rate Esters, Derivatives and Other SolventsDocument2 pagesEvaporation Rate Esters, Derivatives and Other SolventsAminulIslamNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pump Primer and Pumping Aid: AdvantagesDocument2 pagesConcrete Pump Primer and Pumping Aid: AdvantagesJonathan Guzmán MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12 CH10NotesDocument28 pagesChemistry 12 CH10NotesAquib MalikNo ratings yet
- NSM 3-5 ManualDocument23 pagesNSM 3-5 Manualatamed32No ratings yet
- Solvent Cements For Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping SystemsDocument5 pagesSolvent Cements For Poly (Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Piping SystemsHussein BeqaiNo ratings yet
- Ms-035, Rev.03 FF Equipt - (B)Document146 pagesMs-035, Rev.03 FF Equipt - (B)Ragul0042No ratings yet
- Package Blower Systems Revision January 2017Document21 pagesPackage Blower Systems Revision January 2017cosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-1 NewDocument49 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-1 Newmohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- Ionization EnergyDocument8 pagesIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ip - Food PreservativeDocument23 pagesChemistry Ip - Food PreservativeAriesMascarhenasNo ratings yet
- Joining of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer CFRP Composites and Aluminium AlloyDocument72 pagesJoining of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Polymer CFRP Composites and Aluminium AlloySorina gNo ratings yet
- Transport Number, T, Is The Fraction of The Total Current Carried by AnDocument12 pagesTransport Number, T, Is The Fraction of The Total Current Carried by AnErnest Nana Yaw AggreyNo ratings yet
- Total Lipid Content-1Document11 pagesTotal Lipid Content-1Sara magdyNo ratings yet
- B.6 Nalco© EC9610ADocument14 pagesB.6 Nalco© EC9610Afidan muradovaNo ratings yet
- Chem Academy: Daily Assignment Iit-Jam Home Work DPPDocument3 pagesChem Academy: Daily Assignment Iit-Jam Home Work DPPjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- Data 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349Document3 pagesData 1-Clinoptilolite-00-025-1349BUSTANUL RIZKY RIZKYNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Mass SpectrometryDocument7 pagesWorksheet Mass SpectrometryMinh Thy Nguyen LeNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry: Principles and Practice: January 1994Document13 pagesMedicinal Chemistry: Principles and Practice: January 1994نیاز اشرفNo ratings yet
- Food Processing Technology - Separation ProcessesDocument25 pagesFood Processing Technology - Separation ProcessesAnonymousNo ratings yet
- BIO307 Lecture (Protein Structure and Function)Document18 pagesBIO307 Lecture (Protein Structure and Function)Kerstin MarobelaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument7 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International Educationigloo79No ratings yet
- Lecture For Production Well PlanningDocument63 pagesLecture For Production Well PlanningmanashNo ratings yet