Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences Between Hashset, Linkedhashset and Treeset in Java
Differences Between Hashset, Linkedhashset and Treeset in Java
Uploaded by
drdomarkOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences Between Hashset, Linkedhashset and Treeset in Java
Differences Between Hashset, Linkedhashset and Treeset in Java
Uploaded by
drdomarkCopyright:
Available Formats
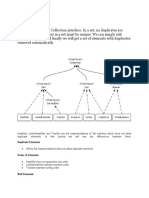
Differences Between HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet In
Java
How they work internally?
HashSet uses HashMap internally to store it’s elements.
LinkedHashSet uses LinkedHashMap internally to store it’s elements.
TreeSet uses TreeMap internally to store it’s elements.
Order Of Elements
HashSet doesn’t maintain any order of elements.
LinkedHashSet maintains insertion order of elements. i.e elements are placed as they are
inserted.
TreeSet orders the elements according to supplied Comparator. If no comparator is
supplied, elements will be placed in their natural ascending order.
Performance
HashSet gives better performance than the LinkedHashSet and TreeSet.
The performance of LinkedHashSet is between HashSet and TreeSet. It’s performance is
almost similar to HashSet. But slightly in the slower side as it also maintains LinkedList
internally to maintain the insertion order of elements.
TreeSet gives less performance than the HashSet and LinkedHashSet as it has to sort the
elements after each insertion and removal operations.
Insertion, Removal And Retrieval Operations
HashSet gives performance of order O(1) for insertion, removal and retrieval operations.
LinkedHashSet also gives performance of order O(1) for insertion, removal and retrieval
operations.
TreeSet gives performance of order O(log(n)) for insertion, removal and retrieval
operations.
How they compare the elements?
HashSet uses equals() and hashCode() methods to compare the elements and thus
removing the possible duplicate elements.
LinkedHashSet also uses equals() and hashCode() methods to compare the elements.
TreeSet uses compare() or compareTo() methods to compare the elements and thus
removing the possible duplicate elements. It doesn’t use equals() and hashCode() methods
for comparision of elements.
Null elements
HashSet allows maximum one null element.
LinkedHashSet also allows maximum one null element.
TreeSet doesn’t allow even a single null element. If you try to insert null element into
TreeSet, it throws NullPointerException.
Memory Occupation
HashSet requires less memory than LinkedHashSet and TreeSet as it uses only HashMap
internally to store its elements.
LinkedHashSet requires more memory than HashSet as it also maintains LinkedList along
with HashMap to store its elements.
TreeSet also requires more memory than HashSet as it also maintains Comparator to sort
the elements along with the TreeMap.
When To Use?
Use HashSet if you don’t want to maintain any order of elements.
Use LinkedHashSet if you want to maintain insertion order of elements.
Use TreeSet if you want to sort the elements according to some Comparator.
You might also like
- Pedroni MITPress 1stedition SolutionSamplesDocument14 pagesPedroni MITPress 1stedition SolutionSamplesTrần Anh DũngNo ratings yet
- Comparsion of List and Set InterfacesDocument10 pagesComparsion of List and Set InterfacesrohithkumarceoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between HashMap and HashSet in JavaDocument2 pagesDifference Between HashMap and HashSet in JavajogishokeenNo ratings yet
- 04 - Java Collection - FA Q&ADocument8 pages04 - Java Collection - FA Q&Arajay2r1548No ratings yet
- Java Unit 10Document5 pagesJava Unit 10anonymousNo ratings yet
- Java Collection DetailsDocument9 pagesJava Collection DetailspukhrajsharmaNo ratings yet
- Defined Manner.: Collections Are Nothing But Group of Objects Stored in WellDocument5 pagesDefined Manner.: Collections Are Nothing But Group of Objects Stored in WellGaneshNo ratings yet
- Collection Interview WquestionDocument4 pagesCollection Interview WquestionSivaChitrabanuNo ratings yet
- Hash Tables An Advanced SortingDocument43 pagesHash Tables An Advanced SortingrizamaebaqueroNo ratings yet
- HashSet and HashMapDocument2 pagesHashSet and HashMapArala FolaNo ratings yet
- Java DifferencesDocument4 pagesJava Differencesmalli.gontla3724No ratings yet
- Java Collections:: Custom Implementation of Collections and Data StructureDocument9 pagesJava Collections:: Custom Implementation of Collections and Data StructureRavi Chandra Reddy MuliNo ratings yet
- 15 Dec 2022Document13 pages15 Dec 2022Anjali ThakurNo ratings yet
- Java Collections Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesJava Collections Interview QuestionsKedar NathNo ratings yet
- Java CollectionsDocument4 pagesJava CollectionsMartin De LucaNo ratings yet
- Java NotesDocument5 pagesJava Notesgauravdafale11No ratings yet
- Java CollectionsDocument4 pagesJava CollectionsSaurabh WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Interface Description Concrete Classes: Summary of Collection and Map ImplementationsDocument5 pagesInterface Description Concrete Classes: Summary of Collection and Map Implementationsapi-3831588No ratings yet
- Arraylist Vs LinkedlistDocument1 pageArraylist Vs LinkedlistAnonymous rgJcpUNo ratings yet
- Java Collections Q&ADocument65 pagesJava Collections Q&Arahulbadhe2No ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Sets and MapsDocument3 pagesChapter 23 Sets and MapsAleksandar PečenkovićNo ratings yet
- Collections JavaDocument20 pagesCollections Javamythra1994No ratings yet
- 20 Equals and HashCode-1Document2 pages20 Equals and HashCode-1poorna.bellamNo ratings yet
- The HashSet Class Implements The Set Interface, Backed by A Hash Table Which Is Actually A HashMap InstanceDocument2 pagesThe HashSet Class Implements The Set Interface, Backed by A Hash Table Which Is Actually A HashMap InstanceAnjaniNo ratings yet
- Mitin .ItDocument3 pagesMitin .Italemreta5No ratings yet
- CollectionDocument5 pagesCollection5006-Barani RajNo ratings yet
- Map ComparisonDocument7 pagesMap ComparisonAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Collections: Using System - CollectionDocument32 pagesCollections: Using System - Collectionbhanu455No ratings yet
- CollectionDocument11 pagesCollectionPraveen Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Java Concepts 2Document6 pagesJava Concepts 2Seema NegiNo ratings yet
- Collection Framework PDFDocument8 pagesCollection Framework PDFSuryateja KokaNo ratings yet
- DistinguishDocument11 pagesDistinguishANURAG SINGHNo ratings yet
- 07A CollectionsDocument27 pages07A CollectionsDo Cao Dat (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- 02 CollectionsDocument12 pages02 CollectionsthrillzdummyNo ratings yet
- Sets and Maps in JavaDocument4 pagesSets and Maps in Javasathwik vaguNo ratings yet
- Java 12 Collection New MethodDocument3 pagesJava 12 Collection New MethodGourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Java The HashSet ClassDocument2 pagesJava The HashSet ClassRahulKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- 1000 Java Interview Questions-2Document250 pages1000 Java Interview Questions-2Yannick TCHATONo ratings yet
- Last in First Out: Linked List, Tree, Etc. A Programmer Selects An Appropriate Data Structure and Uses ItDocument2 pagesLast in First Out: Linked List, Tree, Etc. A Programmer Selects An Appropriate Data Structure and Uses ItanilperfectNo ratings yet
- Collections: Index - HTML)Document27 pagesCollections: Index - HTML)Vu Minh Hieu (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- Java Collection FrameworkDocument21 pagesJava Collection Frameworkvinay MurakambattuNo ratings yet
- Collection PresentationsDocument18 pagesCollection PresentationsgpalanimcaNo ratings yet
- 5.collections GenericDocument16 pages5.collections Generictemp tempNo ratings yet
- Java Collections and Generics: - Prashant KumarDocument48 pagesJava Collections and Generics: - Prashant KumarPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- The Java - Util Package: General Area Interface/Abstract Class Concrete ClassDocument3 pagesThe Java - Util Package: General Area Interface/Abstract Class Concrete ClasskishoreramanaNo ratings yet
- CollectionsDocument12 pagesCollections22ad030No ratings yet
- Ict HomeworkDocument15 pagesIct HomeworkКаримов ӘділбекNo ratings yet
- Iterable (Interface) : Abstractset (Abstract Class)Document3 pagesIterable (Interface) : Abstractset (Abstract Class)mitrshipNo ratings yet
- Sets and Maps: Part of The Collections FrameworkDocument23 pagesSets and Maps: Part of The Collections Frameworkعبدالرؤوف مناصرNo ratings yet
- Dsa U4Document13 pagesDsa U4Harshada BavaleNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 5 Cs 2203Document1 pageDiscussion Forum Unit 5 Cs 2203Julio LouzanoNo ratings yet
- Collections in JavaDocument4 pagesCollections in JavaGauri BansalNo ratings yet
- Sorting Hashing: Sam Dominic B. Antonio March 15, 2017 Ms - Jovy Ruth Obliosca IS211Document6 pagesSorting Hashing: Sam Dominic B. Antonio March 15, 2017 Ms - Jovy Ruth Obliosca IS211Sam antonioNo ratings yet
- CH OllectionDocument33 pagesCH OllectionadityaNo ratings yet
- Java Collections FrameworkDocument2 pagesJava Collections FrameworkkishoreramanaNo ratings yet
- Sample Linked Lists Chapter (Data Structure and Algorithmic Thinking With Python)Document47 pagesSample Linked Lists Chapter (Data Structure and Algorithmic Thinking With Python)Karthikeyan BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- OOP Chapter 6Document23 pagesOOP Chapter 6Abdex AliyiNo ratings yet
- Common Sorting AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesCommon Sorting AlgorithmsTetiana IvchykNo ratings yet
- Collection FrameworkDocument17 pagesCollection Frameworkanil rathodNo ratings yet
- Arraylist, Hashtable, DictionaryDocument4 pagesArraylist, Hashtable, DictionaryManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- NVNGX ConfigDocument1 pageNVNGX ConfigdrdomarkNo ratings yet
- HCL Sap Means in Self Declaration FormDocument13 pagesHCL Sap Means in Self Declaration FormdrdomarkNo ratings yet
- Vaadin Designer FactsheetDocument13 pagesVaadin Designer FactsheetdrdomarkNo ratings yet
- Vaadin Designer FactsheetDocument13 pagesVaadin Designer FactsheetdrdomarkNo ratings yet
- How Tomcat WorksDocument476 pagesHow Tomcat WorksRavinder YadavNo ratings yet
- Lab Test - 02 (CSE-16th)Document1 pageLab Test - 02 (CSE-16th)kamruzaman shuvoNo ratings yet
- Session 4 ReviewerDocument7 pagesSession 4 ReviewerAhnNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document9 pagesPractical 2guptaricha419No ratings yet
- Numerical ControlDocument52 pagesNumerical ControlmishariNo ratings yet
- ABC's of AutoLISP Chapter 8 - Interacting With AutoLISP - Copyright © 1997 George OmuraDocument19 pagesABC's of AutoLISP Chapter 8 - Interacting With AutoLISP - Copyright © 1997 George OmuraMACARTSONNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Admin+Development+LightningDocument13 pagesSalesforce Admin+Development+LightningHarsha KNo ratings yet
- Asset-V1 MITx+6.86x+3T2020+typeasset+blockslides Lecture2 CompressedDocument21 pagesAsset-V1 MITx+6.86x+3T2020+typeasset+blockslides Lecture2 CompressedRahul VasanthNo ratings yet
- Steps To Create Authorization FieldDocument2 pagesSteps To Create Authorization FieldPiyushkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Practical FileDocument18 pagesComputer Graphics Practical Filerobin singhNo ratings yet
- Cst308 Comprehensive June 2023Document6 pagesCst308 Comprehensive June 2023revathyrevuzzz9976No ratings yet
- C++ Lab Manual - 2011Document19 pagesC++ Lab Manual - 2011Subhrendu Guha Neogi50% (2)
- PLC-5 Structured Text: User ManualDocument75 pagesPLC-5 Structured Text: User Manualralejaga5970No ratings yet
- Oracle 9 I 10 GDocument974 pagesOracle 9 I 10 GNarsimuluAkulaNo ratings yet
- CS PaperDocument7 pagesCS PaperMohd Kaif KhanNo ratings yet
- ANTLR Reference ManualDocument152 pagesANTLR Reference ManualFabrizio TorelliNo ratings yet
- New-Oop Lab Manual Sp22 - v3.1Document111 pagesNew-Oop Lab Manual Sp22 - v3.1Raja Haris SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Module 3 ProblemsDocument4 pagesAnswers To Module 3 ProblemsRomNo ratings yet
- Active Record Relationships: A Ruby On Rails Cheat SheetDocument1 pageActive Record Relationships: A Ruby On Rails Cheat SheetMatt Jaynes94% (17)
- Hunti NG: Work InstructionDocument2 pagesHunti NG: Work InstructionSidik FajarNo ratings yet
- Resume Vivek JulyDocument1 pageResume Vivek Julyvemula shivaniNo ratings yet
- Facebook LeetcodeDocument30 pagesFacebook LeetcodeRitik GargNo ratings yet
- RapidSMS DocumentationDocument188 pagesRapidSMS DocumentationotorbusNo ratings yet
- Cemat V 8.2 Function Block Library ILS - CEMDocument15 pagesCemat V 8.2 Function Block Library ILS - CEMJacob Lester AndresNo ratings yet
- Python Full Course PDFDocument5 pagesPython Full Course PDFVijayKumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- OOP Lecture 6 Dated 03-12-2019Document32 pagesOOP Lecture 6 Dated 03-12-2019Nimra FarooqNo ratings yet
- Dlbcsoopj01 Course BookDocument164 pagesDlbcsoopj01 Course Bookpetr.tinNo ratings yet
- Excel INDIRECT FunctionDocument40 pagesExcel INDIRECT FunctionENRIQUENo ratings yet
- Garbage Collection in Java - What Is GC and How It Works in The JVMDocument19 pagesGarbage Collection in Java - What Is GC and How It Works in The JVMHarapriya MohantaNo ratings yet