Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polynomial Equation Quadratic Equation
Polynomial Equation Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
Jaswant SubudhiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polynomial Equation Quadratic Equation
Polynomial Equation Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
Jaswant SubudhiCopyright:
Available Formats
Polynomial Equation Quadratic Equation
A polynomial P(x) in one variable x, is an algebraic expression Let P(x) be a quadratic polynomial
of the form (i.e. degree n = 2), then P (x) = 0, known as quadratic equation.
P(x) = an x n + an –1 x n–1 + an –2 x n–2 + ... + a2 x 2 + a1x + a 0 Standard form of quadratic equation is ax2 + bx + c = 0, where,
where, an ≠ 0, a0, a1, a2, ..., an are constants and these are a ≠ 0 and a, b, c are any constants.
also called coefficient of the variable in polynomial. If the terms of P (x) = 0 are written in descending order of their degree, then
If P(x) = 0, then it is known as polynomial equation of this form of equation is called standard form of a quadratic equation, i.e.
degree n. ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 and a, b, c are any constants.
i.e. anx n + an–1x n + an–2x n–2 + ... + a2x 2 + a1x + a0 = 0
is a polynomial equation of degree n.
Solutions Or Roots of a
Solution of a Quadratic Equation Quadratic Equation
by Factorisation A real number is said to be a root or solution of a quadratic
equation, ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0, if aα2 + bα + c = 0.
In factorisation method, we first write the given
quadratic polynomial as product of two linear
factors by splitting the middle term and then
equate each factor to zero to get possible roots Solution of a Quadratic Equation by
of given quadratic equation. Completing the Square
Firstly, write the quadratic equation
ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0
Solution of a Quadratic ⇒ x +—
2 bx =– c
a a
Equation by Quadratic Formula 2
b
2 Adding —
Firstly, find the discriminant, D = b – 4ac of 2a
2
given equation ax + bx + c = 0. If D is negative, on both sides to make LHS as a perfect
then solution does not exist. square of a binomial expression and
– b ± √D simplify RHS, then take square root
Otherwise, x = ———— on both sides and get values of x,
2a
Simplify it to get required roots. b2– 4ac b
which are x = ± ——— 2 –—
4a 2a
Nature of Roots Sum and Product of Roots
Find discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
2 If α and β are the roots of quadratic
(i) If D = b – 4ac = 0, then quadratic equation 2
equation, ax + bx + c = 0,
has two equal real roots or repeated roots.
where a ≠ 0. Then,
(ii) If D = b2 – 4ac > 0, then quadratic equation
–b
has two distinct real roots. Sum of roots (S) = α + β = — a
(iii) If D = b2 – 4ac < 0, then quadratic equation
has no real roots. c
Product of roots (P) = αβ= —
a
Formation of Quadratic Equation
If roots of a quadratic equation are
given, then the quadratic equation
is given by
x2 – Sx + P = 0
⇒ x – (α + β) x + αβ = 0
2
You might also like
- Hans Belting - The Image and Its Public in The Middle Ages - Form and Function of Early Paintings of The Passion-A.D. Caratzas (1990)Document305 pagesHans Belting - The Image and Its Public in The Middle Ages - Form and Function of Early Paintings of The Passion-A.D. Caratzas (1990)SEBASTIAN ZULUAGA SALAZARNo ratings yet
- Your Turn Practice G1Document376 pagesYour Turn Practice G1nia rahmayanti100% (5)
- Leo Spitzer - Linguistics and Literary History PDFDocument17 pagesLeo Spitzer - Linguistics and Literary History PDFluzmoreira8448No ratings yet
- Solving Polynomial Equations L-1Document5 pagesSolving Polynomial Equations L-1Rohinish DeyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Quadratic EquationiiiDocument9 pagesWorksheet Quadratic EquationiiiKartik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument88 pagesIlovepdf MergedRudransh PawarNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged MergedDocument132 pagesIlovepdf Merged MergedRudransh PawarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Lecture-1 Solving Polynomial EquationsDocument5 pagesQuadratic Equations: Lecture-1 Solving Polynomial EquationsSoham RaneNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths N Ch. 1Document6 pages10 Maths N Ch. 1clementjamesmannasNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation BasicsDocument10 pagesQuadratic Equation BasicsMana GargiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument40 pagesQuadratic Equations: Roots of A Quadratic EquationAnshuman BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- 6 Quadratic EquationsDocument8 pages6 Quadratic EquationsNilesh GargNo ratings yet
- QE - 11th (2019C) - EDocument36 pagesQE - 11th (2019C) - EAlbertNo ratings yet
- Algebra - I LectureDocument2 pagesAlgebra - I LectureDwight SolinaNo ratings yet
- 5 Chapter PDFDocument52 pages5 Chapter PDFKhaja NusrathNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesDocument23 pagesQuadratic Equations and InequalitiesgladiatortorqueNo ratings yet
- 8 Maths - Formula - Pocket - Book - Maths - FormulaDocument93 pages8 Maths - Formula - Pocket - Book - Maths - Formulaalba mathNo ratings yet
- B086 PDFDocument4 pagesB086 PDFqwertyqazqazNo ratings yet
- 10 Qua MathsDocument54 pages10 Qua MathsPriya TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Basic Maths in Physics and Vector NewDocument41 pagesBasic Maths in Physics and Vector NewShiv SinghNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Nature of Roots and Common Roots of Quadratic EquationsDocument9 pagesQuadratic Equations: Nature of Roots and Common Roots of Quadratic EquationsAnujeetMishraNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Notes JeeDocument39 pagesQuadratic Equation Notes JeeSwastika DasNo ratings yet
- M-10-T1-03 Quadratic Equation PDFDocument45 pagesM-10-T1-03 Quadratic Equation PDFAniketNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument33 pagesQuadratic EquationBadal KumarNo ratings yet
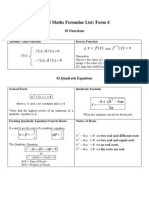
- Add Maths Formulae List: Form 4: y F y FXDocument16 pagesAdd Maths Formulae List: Form 4: y F y FXMurulikrishan NandakumarNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Quadratic Equation TheoryeDocument14 pagesQdoc - Tips Quadratic Equation TheoryeKrisha Mae ChaNo ratings yet
- Maths Notes For Class 10 Chapter 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesMaths Notes For Class 10 Chapter 4 Quadratic Equationspreeti.2405No ratings yet
- Pelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2Document22 pagesPelangi Top One Add Math f4 AnsChap2PK ChunNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Worksheet PDFDocument19 pagesQuadratic Equations Worksheet PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Math Formula Sheet AIEEEDocument93 pagesMath Formula Sheet AIEEELokesh Kumar83% (6)
- Chapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study ModuleDocument27 pagesChapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study Modulevwxyzxyz729No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study Module - Prayas JEE 2025Document25 pagesChapter 02 - Quadratic Equations - Study Module - Prayas JEE 2025xnvktjvzdNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation & Expression: Maths Formula - Pocket Book Maths Formula - Pocket BookDocument93 pagesQuadratic Equation & Expression: Maths Formula - Pocket Book Maths Formula - Pocket Bookbannudasari111No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument30 pagesQuadratic EquationsChandra Vamsi AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Esempio LezioneDocument2 pagesEsempio LezionePaolaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Short Notes6606dba7a1250b0018512651Document2 pagesQuadratic Equations Short Notes6606dba7a1250b0018512651prateekritiksahuNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation-1Document6 pagesQuadratic Equation-1NILMADHUNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument17 pagesQuadratic EquationJewel AgichaNo ratings yet
- Grade-10 Mathematics Chapter04 Quadratic-Equations-1Document9 pagesGrade-10 Mathematics Chapter04 Quadratic-Equations-1raviskskskNo ratings yet
- Add Maths O Level Quick Revision Sheet With All FormulasDocument16 pagesAdd Maths O Level Quick Revision Sheet With All FormulasÅzmâñ Khäñ50% (2)
- Qee 1Document80 pagesQee 1Hetasvi patelNo ratings yet
- Math 9 QUARTER 1: Weeks 2-3: CompetencyDocument10 pagesMath 9 QUARTER 1: Weeks 2-3: CompetencyGraceRasdasNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument3 pagesQuadratic Equationssumit67No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument14 pagesQuadratic Equationssingh.aaradhya2007No ratings yet
- Add Maths Formulae List: Form 4 (Update 18/9/08) : y FX F y XDocument16 pagesAdd Maths Formulae List: Form 4 (Update 18/9/08) : y FX F y XAmir FathullahNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations and Expressions: Chapter HighlightsDocument51 pagesQuadratic Equations and Expressions: Chapter HighlightsAditya WanwadeNo ratings yet
- What Is Quadratic Equation?: Algebraic Expression Quadratic Equation in Its Standard Form CoefficientDocument6 pagesWhat Is Quadratic Equation?: Algebraic Expression Quadratic Equation in Its Standard Form CoefficientSukhveen 1No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation TN FDocument12 pagesQuadratic Equation TN FDrkhan JdpNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation For Class 10Document6 pagesQuadratic Equation For Class 10abhayaps975No ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument8 pagesQuadratic EquationsLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Summary NotesDocument3 pagesAdditional Mathematics Summary NotesDavid Ardiansyah100% (1)
- Roots of A Quadratic Equation PDFDocument2 pagesRoots of A Quadratic Equation PDFRafena MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Quadratics ExpressionDocument6 pagesQuadratics Expressionsvenkatk737No ratings yet
- Class 10 Mathematics Important Formulae: Real NumbersDocument25 pagesClass 10 Mathematics Important Formulae: Real NumbersBabaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MathematicsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Mathematicsnjihiawambui29No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation (TN)Document19 pagesQuadratic Equation (TN)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)Document16 pagesAdditional Mathematics - List of Formulae (Form 4)AimanAz100% (3)
- IIT 23 Maths CH 2 Quadratic Eqn Expression 1620295836759Document55 pagesIIT 23 Maths CH 2 Quadratic Eqn Expression 1620295836759Swaroop NaikNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument57 pagesQuadratic EquationNIKHIL MITTALNo ratings yet
- Classification of A Quadratic EquationDocument3 pagesClassification of A Quadratic EquationruchiNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Scan 19 Oct 23 19 29 25Document17 pagesScan 19 Oct 23 19 29 25Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyDocument1 pageStatistics: Measures of Central TendencyJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Sequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Document1 pageSequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Trigonometry: Heights and DistancesDocument1 pageSome Applications of Trigonometry: Heights and DistancesJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument1 pageConstructionJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Speaking Activities Rubic GridDocument4 pagesCambridge Speaking Activities Rubic GridEdu OneNo ratings yet
- वीर शिवाजी PDFDocument35 pagesवीर शिवाजी PDFAmit GoriyanNo ratings yet
- Dumpstate BoardDocument463 pagesDumpstate BoardMoonton Njiir2No ratings yet
- VoiceDocument24 pagesVoiceTouhid AnikNo ratings yet
- Full Download Java Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Java Programming 7th Edition Joyce Farrell Test Bankbenjaminmfp7hof100% (46)
- Bhagavad Gita - Chapter 03Document91 pagesBhagavad Gita - Chapter 03ParthaNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 1Document14 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 1gerlie maeNo ratings yet
- Forms of Contemporary ProseDocument25 pagesForms of Contemporary ProseGARCIA, Arjhei Gon RyukiNo ratings yet
- Amy Hollywood "Sensible Ecstasy" ReviewDocument6 pagesAmy Hollywood "Sensible Ecstasy" ReviewJack MitchellNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 (Part2) TUPAZ - REFLECTIONDocument2 pagesWEEK 4 (Part2) TUPAZ - REFLECTIONReynelyne TupazNo ratings yet
- Rubrics CE ORIENT Written ReportDocument2 pagesRubrics CE ORIENT Written ReportjocelNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Transmitting KnowledgeDocument3 pagesCH 13 Transmitting KnowledgeYoshita ShahNo ratings yet
- 300+ React Js Interview Questions With AnswersDocument157 pages300+ React Js Interview Questions With AnswersMukesh Mangal100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Phil. HistoryDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Phil. HistoryJaylene AlbayNo ratings yet
- LCD and Keyboard InterfacingDocument21 pagesLCD and Keyboard InterfacingAmmar EhabNo ratings yet
- Space-Vector State-Equation Analysis of Three-PhasDocument11 pagesSpace-Vector State-Equation Analysis of Three-PhasMohid Khan TariqNo ratings yet
- MidsemDocument3 pagesMidsemHarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Ingles Orden de Los AdjetivosDocument3 pagesIngles Orden de Los AdjetivosJosé Antonio Romero100% (1)
- Ent INSTRUMENTSDocument28 pagesEnt INSTRUMENTS凛No ratings yet
- Jurnal Analisis Pengendalian Mutu Pada Proses Pembekuan Udang Vaname (Litopenaeus Vannamei) Dengan Six SigmaDocument12 pagesJurnal Analisis Pengendalian Mutu Pada Proses Pembekuan Udang Vaname (Litopenaeus Vannamei) Dengan Six SigmaIrham FadhillaNo ratings yet
- Total Coloring of Some Cycle Related GraphsDocument3 pagesTotal Coloring of Some Cycle Related GraphsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- English 9 - Revision - Unit 123 172202014Document7 pagesEnglish 9 - Revision - Unit 123 172202014Duy HoangNo ratings yet
- Page Replacement AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesPage Replacement AlgorithmsIsha RangariNo ratings yet
- Kashful AsrarDocument40 pagesKashful AsrarSalman Selamat100% (1)
- CS111 - Lecture Note 03Document33 pagesCS111 - Lecture Note 03Jaber SangcopanNo ratings yet
- Course Materials Seminar On ELTDocument23 pagesCourse Materials Seminar On ELTKhusnul Khotimah0% (1)
- Synopsis of Don QuixoteDocument3 pagesSynopsis of Don QuixoteDOLORFEY L. SUMILENo ratings yet