Professional Documents
Culture Documents
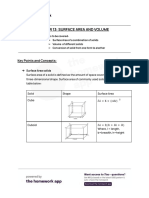
Surface Areas and Volumes
Surface Areas and Volumes
Uploaded by
Jaswant Subudhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThe document discusses surface area and volume of solids and combinations of solids. It provides formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of spheres, cylinders, and combinations of solids. It also discusses converting solids from one shape to another, where the total volume remains the same. Finally, it discusses frustums of cones and provides formulas for calculating the volume, curved surface area, and total surface area of a frustum of a cone.
Original Description:
Original Title
1188204570
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses surface area and volume of solids and combinations of solids. It provides formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of spheres, cylinders, and combinations of solids. It also discusses converting solids from one shape to another, where the total volume remains the same. Finally, it discusses frustums of cones and provides formulas for calculating the volume, curved surface area, and total surface area of a frustum of a cone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageSurface Areas and Volumes
Surface Areas and Volumes
Uploaded by
Jaswant SubudhiThe document discusses surface area and volume of solids and combinations of solids. It provides formulas for calculating the surface area and volume of spheres, cylinders, and combinations of solids. It also discusses converting solids from one shape to another, where the total volume remains the same. Finally, it discusses frustums of cones and provides formulas for calculating the volume, curved surface area, and total surface area of a frustum of a cone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
MIND
Surface Areas and Volumes
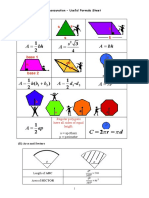
Surface Area Volume
Surface area of a solid body is the Space occupied by an object/solid
area of all of its surfaces together and body is called the volume of that
it is always measured in square unit. particular object/solid. Volume is
always measured in cube unit.
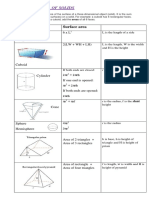
Surface Area and Volume Conversion of Solid from Frustum of a Cone
of Combination of Solids One Shape to Another If a right circular cone is cut-off by a plane parallel to its
Whenever we have to find the surface area of a Sometimes, we need to convert solid of base, then the portion of the cone between the cutting
solid, which is a combination of other solids, we one shape to another. When we come plane and the base of the cone is called a frustum of the
add the curved surface area of individual solids across objects which are converted from cone.
and for finding the volume of this solid, we add the one shape to another or when a liquid Height of frustum The height or thickness of a frustum
volume of individual solid. which originally filled in one container of a is the perpendicular distance between its two circular
In calculating the surface area, we have not added particular shape is poured into another bases.
the surface areas of the two individual solids container of a different shape or size, the Slant height of frustum The slant height of a frustum of
because some part of the surface area disappeared volume remains same. a right circular cone is the length of the line segment
in the process of joining them. But this will not be the which is obtained by joining the end points of two
case when we calculate the volume. parallel radii, drawn in the same direction of the two
circular bases.
Important Results or Formulae
1. If solid (or solids) of one shape is converted into solid
(or solids) of another shape, then
Total volume of the solids to be converted Area of the Metal Sheet Formulae Related
= Total volume of the solids into which the given used to Make a Bucket to Frustum of a Cone
solids is (are) to be converted Let h be the height or depth, l be the Let h be the height, l be the slant
2. Number of solids of a given shape in which a given slant height, r1 be the radius of top height and r1 and r2 be the radii
solid is to be converted which is open and r2 be the radius of the of the ends (r1> r2) of the
Total volume of the solid to be converted bottom which is closed, of a bucket frustum of a cone. Then,
= which is in the shape of a frustum of a 1. Volume of the frustum of the
Volume of one converted solid right circular hollow cone. cone
3. Volume of the material of a spherical shell top 1
(or hollow sphere) r1 = ph(r12 + r22 + r1r2)
3
4
= p(R 3 – r 3 ) cu units
3 2. The curved surface area of
where, R = outer radius and r = inner radius the frustum of the cone
4. Volume of the material of a cylindrical shell h = p (r1 + r2)l
l
(or hollow cylinder) where, l = Öh2 + (r1 – r2)2
= ph(R2 – r2) cu units
3. Total surface area of the
where, R = external radius and r = internal radius r2 frustum of the cone
Bottom
= p l(r1+r2) +pr12 + pr22
Area of the metal sheet used for making
the bucket where, l = Öh2 + (r1 – r2)2
= Outer (or inner) curved surface area
You might also like
- Plane and Solid Geometry 2Document3 pagesPlane and Solid Geometry 2ARNOLD MORANNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Part 2 (2) CH 8.5-11Document56 pagesSSLC Maths Part 2 (2) CH 8.5-11davis mathewNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Geometry: Keerti Vardhan MadaharDocument8 pagesCalculus and Geometry: Keerti Vardhan MadaharReko BasNo ratings yet
- Surface Area Volumes Class 10Document10 pagesSurface Area Volumes Class 10Avantika S100% (3)
- Surface Area Is The Measure of How Much Exposed Area A Solid Object HasDocument4 pagesSurface Area Is The Measure of How Much Exposed Area A Solid Object HasMiko AkimotoNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out No.12: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)Document1 pageHand-Out No.12: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)julius daparNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Important Formulas Chapter 13 - Surface Area and VolumeDocument6 pagesClass 9 Important Formulas Chapter 13 - Surface Area and VolumeSai Tutors TutorsNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Formula Chapter 13Document6 pagesClass 9 Maths Formula Chapter 13bhai ki gameNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out No.12: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)Document2 pagesHand-Out No.12: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)julius daparNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out No.11: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)Document2 pagesHand-Out No.11: (Plane and Solid Mensuration)julius daparNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Unit 5 Motion of System of Particle and Rigid BodyDocument38 pagesClass 11 Physics Unit 5 Motion of System of Particle and Rigid Bodymatre.nishuNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Chapter-13 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter-13 Surface Areas and VolumesSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesDocument4 pagesCylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume) Summary NotesAbdella KarimeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Surface Area and Volume: Key Points and ConceptsDocument8 pagesChapter 13: Surface Area and Volume: Key Points and ConceptssudhaNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volume of 3d FiguresDocument13 pagesSurface Area and Volume of 3d Figuresapi-3731257100% (15)
- Key Notes: Chapter-13 Surface Areas and VolumesDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter-13 Surface Areas and VolumesManu VermaNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgDpem6234 ntKV5CGBYl6FJqV4IQA5An75NmdaJkeuC1yOEVkwax0N2 ZCP gL27XIMoWy0gIeHmCNRKogiLKuu15zbSnS4lMULMCzPBjZX3gUgAeH OIojoYgkyfPmIK 8bAClXW8cDWsBDocument2 pagesACFrOgDpem6234 ntKV5CGBYl6FJqV4IQA5An75NmdaJkeuC1yOEVkwax0N2 ZCP gL27XIMoWy0gIeHmCNRKogiLKuu15zbSnS4lMULMCzPBjZX3gUgAeH OIojoYgkyfPmIK 8bAClXW8cDWsBmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic of InterfacesDocument33 pagesThermodynamic of InterfacesTeka KamNo ratings yet
- Surface Areas and VolumesDocument10 pagesSurface Areas and VolumesBharani SriNo ratings yet
- Solids: Source: Solid Mensuration: Understanding The 3-D SpaceDocument10 pagesSolids: Source: Solid Mensuration: Understanding The 3-D SpaceQueen GaleonNo ratings yet
- Area Wiki PDFDocument6 pagesArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionDocument5 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Trigonometry Angle Unit ConversionZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument25 pagesSolid GeometryHafiz Row100% (1)
- Surface Area and Volume FormulasDocument9 pagesSurface Area and Volume FormulasParth AcademyNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Formula Chapter 11 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 8 Maths Formula Chapter 11 PDFmekala deevena kumariNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes On Surface Areas and VolumesDocument11 pagesDetailed Notes On Surface Areas and VolumesVandana JohnNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 New PDFDocument40 pagesUnit 6 New PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 New PDFDocument40 pagesUnit 6 New PDFAashish BhandariNo ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument1 pageIntegrationjoebloggs01No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document4 pagesChapter 11Preetham RaajNo ratings yet
- Shear ModulusDocument6 pagesShear ModulusArnon AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 Maths NotesDocument6 pagesCh-13 Maths NotesJsjn NNo ratings yet
- 9 XSag CAr 1 DTSYgaa ZZCJDocument14 pages9 XSag CAr 1 DTSYgaa ZZCJdeepavadivel1979No ratings yet
- Solid AngleDocument9 pagesSolid AngleDimitrios Christos SarvanisNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematik / Mathematical Formulae Tingkatan 1Document1 pageRumus Matematik / Mathematical Formulae Tingkatan 1NORHAYATI BINTI SALLEH MoeNo ratings yet
- 12 - Solid Geometry & Mensuration BBADocument5 pages12 - Solid Geometry & Mensuration BBAVeerannaSHiremathNo ratings yet
- Measurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsDocument14 pagesMeasurement Notes For Grade 10 MathematicsBanekeNo ratings yet
- SOLIDS Formulae SheetDocument2 pagesSOLIDS Formulae SheetDaja SewNo ratings yet
- Strain: Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität TübingenDocument7 pagesStrain: Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität TübingenRMNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 MOMENT OF INERTIADocument5 pagesUnit 4 MOMENT OF INERTIAmaingimutisya21No ratings yet
- Mensuration Formula SheetDocument4 pagesMensuration Formula SheetProdip SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 MomDocument9 pagesChapter-3 MomAleahNo ratings yet
- Formula and Theorems For Class XDocument12 pagesFormula and Theorems For Class XPraneel .SNo ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics (11th P) (Egnlish) - WADocument44 pagesRotational Dynamics (11th P) (Egnlish) - WASwarnlata MishraNo ratings yet
- Phy 115 Dynamics of Rigid BodyDocument16 pagesPhy 115 Dynamics of Rigid Bodyabdulmaliqopeyemi04No ratings yet
- IIT-JEE and MH-CET Surface TensionDocument43 pagesIIT-JEE and MH-CET Surface Tensionnitin100% (4)
- LeaP Math G6 Week 7 Q3Document4 pagesLeaP Math G6 Week 7 Q3Akira Hector NorthNo ratings yet
- Surfaces and Volumes of Spheres in CalculusDocument8 pagesSurfaces and Volumes of Spheres in CalculusNISSIBETINo ratings yet
- Geometry Vocabulary and PostulatesDocument9 pagesGeometry Vocabulary and PostulatesWilson ZhangNo ratings yet
- And VolumesDocument31 pagesAnd Volumesdev mittalNo ratings yet
- Final 06PEDocument17 pagesFinal 06PEVaibhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Revision - Formulae-Gr8Document14 pagesRevision - Formulae-Gr8Aaesha ZaveryNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations 13Document20 pagesUnit Operations 13Mazen rommanNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion - DPP 03 (Of Lec 07) - Arjuna JEE 2024Document3 pagesCircular Motion - DPP 03 (Of Lec 07) - Arjuna JEE 2024Ishaan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- H206 Circular Motion - 1. Notes (1718)Document23 pagesH206 Circular Motion - 1. Notes (1718)shakthee sivakumarNo ratings yet
- 24 - Mathematics - Trigonometrical Ratio Functions IdentitiesDocument22 pages24 - Mathematics - Trigonometrical Ratio Functions IdentitiesKumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - NolDocument95 pagesEngineering Mechanics - NolVEERAMANIKANDANNo ratings yet
- The Turning Movement of a Particle About the Axis of Rotation is Called the Angular Momentum of the Particle and is Measured by the Product of the Linear Momentum and the Perpendicular Distance of the Line of Action From the AxDocument24 pagesThe Turning Movement of a Particle About the Axis of Rotation is Called the Angular Momentum of the Particle and is Measured by the Product of the Linear Momentum and the Perpendicular Distance of the Line of Action From the AxSURAJ MAHATONo ratings yet
- Scan 19 Oct 23 19 29 25Document17 pagesScan 19 Oct 23 19 29 25Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Sequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Document1 pageSequence (List of Numbers) Arithmetic Progression (AP)Jaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Measures of Central TendencyDocument1 pageStatistics: Measures of Central TendencyJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument1 pageConstructionJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Trigonometry: Heights and DistancesDocument1 pageSome Applications of Trigonometry: Heights and DistancesJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Equation Quadratic EquationDocument1 pagePolynomial Equation Quadratic EquationJaswant SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Circle Print - QuizizzDocument6 pagesParts of A Circle Print - Quizizzapi-462871381No ratings yet
- Everyday Geometry Powerpoint LessonDocument31 pagesEveryday Geometry Powerpoint LessonMernie Grace DionesioNo ratings yet
- 7 Math Wotksheets CH 11 1Document4 pages7 Math Wotksheets CH 11 1Raghuvardhan KanduriNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Formulae PDFDocument4 pagesMensuration Formulae PDFDavid PeterNo ratings yet
- Double: Cheat Sheet - CircleDocument1 pageDouble: Cheat Sheet - CircleYieksh BernaldeNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals IntroductionDocument19 pagesQuadrilaterals IntroductionBeajoy ManalangNo ratings yet
- MISOSA Gr. 6 Module 43 Finding The Surface Area of A CubeDocument6 pagesMISOSA Gr. 6 Module 43 Finding The Surface Area of A CubemerNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 9 Notes For Volume and Surface AreaDocument5 pagesMaths Class 9 Notes For Volume and Surface AreaMd. Humayun KabirNo ratings yet
- Appleton's Cyclopædia of Drawing, Designed As A Textbook For The Mechanic, Architect, Engineer, and SurveyorDocument654 pagesAppleton's Cyclopædia of Drawing, Designed As A Textbook For The Mechanic, Architect, Engineer, and SurveyorBillW56No ratings yet
- SLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - AllDocument29 pagesSLC - Compulsory Math - Model Question - Allwww.bhawesh.com.np75% (8)
- Circle - MaximizeDocument8 pagesCircle - Maximizerockingr90No ratings yet
- Area Surface Area and Volume Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageArea Surface Area and Volume Knowledge OrganiserHarryParadoxWayneNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola - WikipediaDocument115 pagesHyperbola - WikipediaRishabNo ratings yet
- Sides: Angles: Vertices:: Sides Angles Ver Ver V Sides: Angles: TicesDocument20 pagesSides: Angles: Vertices:: Sides Angles Ver Ver V Sides: Angles: Ticesom printersNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2May Fatima MingoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Year 9 MathsDocument44 pagesChapter 16 - Year 9 MathsEklavya WangooNo ratings yet
- USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/19Document4 pagesUSA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions To Problem 5/2/19ArsyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formula SheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Formula SheetAkash Kumar Bhoi100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Maths Form 2 BulatanhafizahNo ratings yet
- F2 CH 13 AnglesDocument9 pagesF2 CH 13 Anglesseyka4No ratings yet
- Mensuration 1st ChapterDocument23 pagesMensuration 1st ChaptersanthoshNo ratings yet
- 3D-Shapes Pattern Y1Document16 pages3D-Shapes Pattern Y1sathiah2802No ratings yet
- TessellationDocument24 pagesTessellationShazwani AzizulNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Grade 6 MathDocument11 pagesReviewer Grade 6 MathOlive L. GabunalNo ratings yet
- WT 7 (Circle)Document2 pagesWT 7 (Circle)Sipra PaulNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument2 pagesSurface Area and Volumedivya goyalNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Final Exam (Eng'g)Document5 pagesAnalytic Geometry Final Exam (Eng'g)Jacky Boy Endencio AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Quadric SurfacesDocument8 pagesCalculus Quadric Surfacestaucci123100% (1)
- Co Ordinates GeometryDocument6 pagesCo Ordinates GeometryPavithra ManickamNo ratings yet
- محاضرة أوتوكاد - (أوامر الرسم) -2Document12 pagesمحاضرة أوتوكاد - (أوامر الرسم) -2Checking Any LinkNo ratings yet