Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data
Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data
Uploaded by
Abdallah Alasal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
270 views4 pagesThe patient presented with symptoms of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome including extreme thirst, drowsiness, confusion, loss of vision, and a blood glucose level over 600 mg/dL. The nursing care plan involved monitoring the patient's fluid balance, blood glucose levels, and vital signs while administering IV fluids and insulin to rehydrate the patient and lower their blood sugar, as well as educating them on preventing infections. The goals of the plan were to maintain normovolemia, attain optimal hydration and fluid balance, reduce the patient's blood glucose to a target range of 70-200 mg/
Original Description:
Original Title
Care Plan Hyperosmolar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient presented with symptoms of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome including extreme thirst, drowsiness, confusion, loss of vision, and a blood glucose level over 600 mg/dL. The nursing care plan involved monitoring the patient's fluid balance, blood glucose levels, and vital signs while administering IV fluids and insulin to rehydrate the patient and lower their blood sugar, as well as educating them on preventing infections. The goals of the plan were to maintain normovolemia, attain optimal hydration and fluid balance, reduce the patient's blood glucose to a target range of 70-200 mg/
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
270 views4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data
Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data
Uploaded by
Abdallah AlasalThe patient presented with symptoms of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome including extreme thirst, drowsiness, confusion, loss of vision, and a blood glucose level over 600 mg/dL. The nursing care plan involved monitoring the patient's fluid balance, blood glucose levels, and vital signs while administering IV fluids and insulin to rehydrate the patient and lower their blood sugar, as well as educating them on preventing infections. The goals of the plan were to maintain normovolemia, attain optimal hydration and fluid balance, reduce the patient's blood glucose to a target range of 70-200 mg/
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
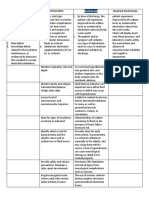
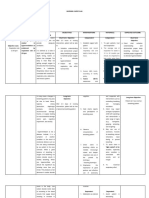
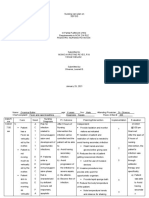
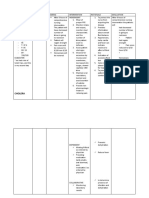
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Monitor blood glucose The hallmark of
Risk For Fluid Client will remain levels HHNS is extremely Maintain blood
Subjective Data: Volume Deficit normovolemic as elevated blood glucose glucose levels within
Risk For Infection evidenced by Encourage optimal levels >600 mg/dL target range for
Extreme thirst Deficient urinary output hydration and administer patient, attain optimal
Drowsiness Knowledge greater than 30 IV fluids (Normal Excessive urination hydration and fluid
Confusion Imbalanced ml/hr, normal skin Saline) to maintain fluid can cause dehydration. balance.
Nutrition: Less turgor, good balance. Encourage oral fluids
Loss of vision
Than Body capillary refill, as tolerated and
Weakness on one side normal blood Insulin (Regular) administer IV fluids to
Requirements
of the body pressure, palpable infusion to reduce blood re-establish tissue
Hallucinations peripheral pulses, glucose level. Monitor perfusion and maintain
and blood glucose for hypokalemia. electrolyte balance
Objective Data: levels between 70-
200 mg/dL. Frequently assess level
Blood glucose level Client will of consciousness and Monitor blood glucose
>600 mg/dL identify mentation levels and serum
Dry mucous interventions to potassium. As insulin
Monitor for hyperthermia is administered,
membranes prevent reduce and treat with potassium is lost.
Warm, dry skin that risk of infection. antipyretics (fever Initiate potassium
does not sweat Client will reducers), cool supplementation as
High fever compresses and cooled necessary.
demonstrate
techniques, IV fluids
The brain is an insulin-
lifestyle changes
Thermoregulation is dependent tissue. With
to prevent impaired as urine elevated glucose
the development production decreases; levels, there is not
of infection. sweating decreases and enough insulin to
electrolytes become normalize and the
imbalanced. patient becomes
confused, dizzy and
Monitor vitals for may have changes in
hypotension and level of consciousness.
tachycardia Patients often
experience drowsiness.
Most likely related to
dehydration and
hypovolemia. Patient is
at risk for hypovolemic
shock.
Collaborative:
Refer to physical
therapy.
You might also like
- Translated Copy of Rubrica Proyecto - Voronoi Project RubricDocument2 pagesTranslated Copy of Rubrica Proyecto - Voronoi Project RubricCarlos Josué Aguilar Sánchez100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- Kiss Me Hard Before YouDocument43 pagesKiss Me Hard Before YoukimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNo ratings yet
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONDocument43 pagesINTUSSUSCEPTIONValarmathi100% (3)
- Q1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesDocument16 pagesQ1 PR2 LAS WEEK 3 Kinds of VariablesAnalie Cabanlit100% (4)
- Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Care Plan HyponitremiaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionBesael BaccolNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan2Document13 pagesNursing Care Plan2Nna ANn CastleNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityDocument6 pagesIncomplete Spinal Cord Injury Nursing Care Plan (ACTUAL) Patient's Name: Alvarez, Marcelo Age: 59y.o. Sex: M Address: Bacolod CityTherese MargaretNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients in CCUDocument75 pagesAssessment of Patients in CCUShubham Singh BishtNo ratings yet
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 LRDR For PrintDocument2 pagesNCP 2 LRDR For PrintGeorge PandaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationDocument6 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationCamille T. SanchezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermFrancis Xavier S. MendezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- NCP M7Document3 pagesNCP M7rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- L&D Careplan 1 KarenDocument4 pagesL&D Careplan 1 KarenSimran SandhuNo ratings yet
- NCP - Multiple BruisesDocument3 pagesNCP - Multiple BruisesLeogalvez BedanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Document6 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For TB 2003Princess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- NCP Meningitis Sure NaniDocument2 pagesNCP Meningitis Sure NaniARISNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanZamranosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- NCP For ConcussionDocument3 pagesNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAlyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesNursing Care PlanZhel Geron MercadoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDocument3 pagesHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Diabetes 2Ysun Espino100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Anemia NevinDocument69 pagesAnemia NevinAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Z (H) IV GE Human Growth HormoneDocument18 pagesZ (H) IV GE Human Growth HormoneAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsDocument2 pagesRespiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy & HistologyDocument7 pagesDigestive System Anatomy & HistologyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Animal Signals Nervous Tissue Wormlike Organisms Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Nerves AxonsDocument8 pagesAnimal Signals Nervous Tissue Wormlike Organisms Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Nerves AxonsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 10epidemiology and PolicyDocument15 pages10epidemiology and PolicyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Analytical Studies in Epidemiology:advanced DesigneDocument50 pagesAnalytical Studies in Epidemiology:advanced DesigneAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 5-2data and EpidemiologyDocument27 pages5-2data and EpidemiologyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 9program EvaluationDocument10 pages9program EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Summary of Positive Vs Negative FeedbackDocument1 pageSummary of Positive Vs Negative FeedbackAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 5-1data and Epidemiology, The Link To BiostatisticsDocument56 pages5-1data and Epidemiology, The Link To BiostatisticsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 2 - SterilizationDocument4 pages2 - SterilizationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 1-Lab SafetyDocument22 pages1-Lab SafetyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Lipids MetabolismDocument31 pages5.1 Lipids MetabolismAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- علم تشريحDocument58 pagesعلم تشريحAbdallah Alasal100% (1)
- 3 Using Pulse OximeterDocument2 pages3 Using Pulse OximeterAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Diagnosis of DMDocument28 pages4.3 Diagnosis of DMAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 4-1pulmonary DisordersDocument38 pages4-1pulmonary DisordersAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 pagesLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Lec 10 Feeding Patients Oral Diets and Enteral and Parenteral NutritionDocument39 pagesLec 10 Feeding Patients Oral Diets and Enteral and Parenteral NutritionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Thou Shall Not StealDocument4 pagesThou Shall Not StealGiselle MarNo ratings yet
- MA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1Document127 pagesMA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1avers990% (1)
- Chemistry in Pictures - Turn Your Pennies Into "Gold" Rosemarie Pittenger,.Document3 pagesChemistry in Pictures - Turn Your Pennies Into "Gold" Rosemarie Pittenger,.Igor LukacevicNo ratings yet
- P113A Quantum Mechanics Midterm 1, UCI (Undergraduate)Document2 pagesP113A Quantum Mechanics Midterm 1, UCI (Undergraduate)palisonNo ratings yet
- Bible Greek VpodDocument134 pagesBible Greek VpodEmanuel AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Content and Contextual Analysis of The Parisian LifeDocument7 pagesContent and Contextual Analysis of The Parisian LifeSowla sidoNo ratings yet
- Grammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1Document1 pageGrammar BeGoingTo1 18821-1CristinaNo ratings yet
- My PastorDocument3 pagesMy PastorPastor Emma MukisaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric LayersDocument5 pagesAtmospheric LayersMary Jane Magat EspirituNo ratings yet
- Economics SubwayDocument3 pagesEconomics SubwayRaghvi AryaNo ratings yet
- Eco Map 3Document1 pageEco Map 3Ferent Diana-roxanaNo ratings yet
- English4am Revision DechichaDocument6 pagesEnglish4am Revision Dechichaligue d'Alger de basket ballNo ratings yet
- Westbourne Baptist Church NW CalgaryDocument4 pagesWestbourne Baptist Church NW CalgaryBonnie BaldwinNo ratings yet
- Kufr Can Occur...Document2 pagesKufr Can Occur...TheEmigrantNo ratings yet
- PoeticsDocument4 pagesPoeticsCalvin PenacoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary + Grammar Unit 3 Test ADocument3 pagesVocabulary + Grammar Unit 3 Test AJoana FernandesNo ratings yet
- Does God ExistDocument8 pagesDoes God ExistNeda StefanovicNo ratings yet
- Pakistan (1964) Government Servants (Conduct) Rules, (EN)Document11 pagesPakistan (1964) Government Servants (Conduct) Rules, (EN)Imran Khan SharNo ratings yet
- Entre AssignmentDocument5 pagesEntre AssignmentPunum JaggNo ratings yet
- Kelley C.T. Iterative Methods For Linear and Nonlinear Equations (SIAM 1995) (ISBN 0898713528) (171Document171 pagesKelley C.T. Iterative Methods For Linear and Nonlinear Equations (SIAM 1995) (ISBN 0898713528) (171Regino ZurcaledahNo ratings yet
- Use of Realism in Mulk Raj Anand's Novels: Karan SharmaDocument2 pagesUse of Realism in Mulk Raj Anand's Novels: Karan SharmasirajahmedsNo ratings yet
- Step 7 Err Code125936644Document37 pagesStep 7 Err Code125936644mohammadNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 2: The Arts of Renaissance and Baroque PeriodDocument16 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 2: The Arts of Renaissance and Baroque PeriodFrancisco ManabatNo ratings yet
- C1 - U5 - Grammar - Revision (1) - CONDITIONALSDocument2 pagesC1 - U5 - Grammar - Revision (1) - CONDITIONALSAdriana Merlos CasadoNo ratings yet
- 99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)Document11 pages99 Names of Allah SWT and Mohammed (PBUH)api-26870382100% (1)
- 2nd Bimonth Test 7th FORMDocument7 pages2nd Bimonth Test 7th FORMFranco AleNo ratings yet