Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen Released
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen Released
Uploaded by
DATO-ON JOANA PAULAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen Released
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen Released
Uploaded by
DATO-ON JOANA PAULACopyright:
Available Formats
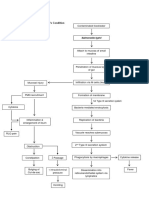
PREDISPOSING FACTORS PRECIPITATING FACTORS
- glomerulonephritis - chronic strep throat
- strep - post streptococcal
- hepatitis B glomerulonephritis
- chronic kidney disease
(CKD)
Bacterial exposure to Streptococcus a.
Bacterial invasion of mucosa
Bacterial adherence to pharyngeal cells
Inflammation sets in
Release of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and prostaglandins
Mucosal irritation
Increasing release of local toxins and proteases
Streptococcal pyrogenes and superantigen released
Acts as superantigen stimulating T-cell production Stimulation of agranulocytes release
Cytokine release Hypothalamic temperature TNF at release
control is stimulated
Endothelial damage and injury
Hemolysis
Vasodilation and edema formation
Leukocyte adhesion to epithelium through expression of adhesion of adhesion molecule
WBC infiltration
Histamine, bradykinins, leukotrienes release
Lymphatic vessels undergo pronounced enlargement in inflamed tissue causing ______ and decreased functionality
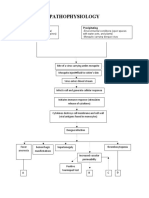
PHARYNGITIS (STREP THROAT)
GROUP A STREPTOCCOCAL INFECTION
Pharyngitis left untreated and continually recur (24 x a year for 5 years); proper medication and management adherence
Strep bacteria travel to the kidney and make filtering units (glomeruli) inflamed
Immune complex formation and deposited in glomerular basement membrane
Complement system is activated to fight pathogens
ACUTE POSTSTREPTOCOCCAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Immune injuries
Cellular proliferation Glomerular basement membrane ___
Capillary lumen narrowed Hematuria; proteinuria
Glomerular blood flow decreased Exposure to infected fluids with Hep. B virus
GFR Virus enter through break of the or mucous membrane
or by injection site into the bloodstream
Oliguria Distal sodium reabsorption Virus reaches liver cells, multiplies and releases
viruses into blood
Sodium and water retention
As hepatocytes are attacked and infiltrated by HBV,
they appear groundglass because HBS Ag
Blood volume infiltrates cells’ cytoplasm
Hypertension and edema set in HEPATITIS B
Recurring for 2 years with hospitalization Immunocomplexes form
Deposited in the glomeruli of the kidney
CHRONIC GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Exacerbate glomerulonephritis
Disease progression is not halted with therapeutic management
Progressive damage caused by chronic glomerulonephritis
reduce the kidneys’ ability to filter blood properly
Further causes hepatocyte destruction and scarring of liver
GFR at ≥ 90 mL/min with UO ____
STAGE 1 KIDNEY DISEASE Liver fibrosis sets in
Decreased functional and physical damage is probable; Obstructed portal circulation
GFR: 60-89 mL/min with UO _____
STAGE 2: MILD CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Portal HTN s/t deposition
of hepatic cellular matrix
Waste product start to build up causing uremia with onset of anemia and HTN
Exacerbate worsening of GFR to 30-59 mL/min with UO _______
STAGE 3: MODERATE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
Progressive uremia where dialysis is necessary;
GFR: 15-29 mL/min with UO _____
STAGE 4: SEVERE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Hydrostatic pressure
UREMIA Blood backs up to spleen
Impaired vit. D Phosphate excretion impaired Suppression of RBC Epoetin production
Conversion of inactive D-25 Phosphate levels RBC (short lifespan) RBC and Hgb SPLENOMEGALY
hydroxycholecalciferol to & HEMOLYSIS
1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol
Vitamin D Serum calcium levels O2 carry C-P Exacerbating
anemia
Intestinal calcium absorption
ANEMIA
Stimulate PTH release
Calcium reabsorption from bone PTH levels
Calcium in bone Renal failure causes
compensatory mechanisms in
calcium and phosphorus
Demineralization of
bone matrix
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Calcification
Bone becomes fragile
UREMIA (cont.)
Fluid accumulation Retention of sodium chloride; Uremic toxins Ammonia in GIT Urea in infection
renin
Intravascular volume Altered RAAS Uremic fetor Ammonia breath Ammonia concentration
Cardiac workload Angiotensin II
Vasoconstriction Splanchnic arterial vasodilation
HTN Circulatory blood volume
Left ventricular hypertrophy
RAAS activated
Heart failure
Sodium and water retention
Excess fluid shift from IVS to ISS Backflow of fluid and uremic toxins
Systemic edema Accumulation of toxins in bronchioles
Pressure in hepatic veins and PULMONARY EDEMA
in veins draining to peritoneum
ASCITES
UREMIA (cont.)
Inability to Urea crystals Phosphate levels and Size of sweat glands;
excrete urobilin in the skin crystals in the skin activity of oil glands
Gray-bronze skin Uremic frost Pruritus
Perspiration
Dry ski
UREMIA (cont.)
Platelet function impairment Failure to excrete K+ Allerid (idk)
Abnormal clotting activity K+ accumulation Buffering mechanisms
of kidneys
Bleeding tendencies Hyperkalemia Bicarbonate
Accumulation of
Hydrogen ions
K+ diffuses out
UREMIA (cont.)
Uremic toxin presence of FV overload Atrophy and demyelination of nerve fibers
Pericardium is affected Neuropathy
Inflammation and fibrin formation Peripheral nerve involvement
Fibrin accumulation Motor and sensory nerve conduction
Pericardium surfaces coated Restless
with fibrous exudate leg syndrome
Vascular collagen tissue deposition Burning
feet syndrome
Fibrous pericardium encases the heart
Pericarditis
You might also like
- Indonesia Market Outlook 2024 by NielsenIQ & MECDocument37 pagesIndonesia Market Outlook 2024 by NielsenIQ & MECdiancahayanii100% (1)
- AML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case StudiesDocument5 pagesAML Gold - Precious Metal Sector Case Studiesjabir pkNo ratings yet
- DVH8090Document2 pagesDVH8090aulin64_845645735No ratings yet
- Pathology ReviewDocument26 pagesPathology ReviewSafiya James100% (1)
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DengueKevin50% (2)
- Red Flags For AutismDocument3 pagesRed Flags For AutismHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Schem DiagramDocument9 pagesSchem DiagramDATO-ON JOANA PAULANo ratings yet
- Schematic DiagramDocument9 pagesSchematic DiagramDATO-ON JOANA PAULANo ratings yet
- Activity On Renal DiseasesDocument6 pagesActivity On Renal DiseasesRicca Christyl SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseaseDocument6 pagesRenal DiseaseyeonjiNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Infection, On TheDocument3 pagesStreptococcus Infection, On TheMonica DomingoNo ratings yet
- Disorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pageDisorder Etiology: Acute GlomerulonephritisChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec - Renal DiseasesDocument6 pagesAUBF Lec - Renal Diseasescdsteenkamp18No ratings yet
- Glomerular Diseases: Pathogenesis of Glomerular Diseases Progression of Glomerular DiseasesDocument6 pagesGlomerular Diseases: Pathogenesis of Glomerular Diseases Progression of Glomerular DiseasesSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Quality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningDocument15 pagesQuality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- LEC AUBF Renal-Diseases MIDTERMS 02Document3 pagesLEC AUBF Renal-Diseases MIDTERMS 02Jashmine May TadinaNo ratings yet
- Stras Renal DiseaseDocument3 pagesStras Renal Diseaseacer14appleNo ratings yet
- Aubf Ut Disorder Transes FinalsDocument2 pagesAubf Ut Disorder Transes FinalsElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Mychelle MenesNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Body Fluids w8Document3 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Body Fluids w8Cheska ReyesNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases NotesDocument4 pagesRenal Diseases NotesJanine CabreraNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeDocument8 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeMichael HusainNo ratings yet
- 7 Renal Disease StudentDocument34 pages7 Renal Disease Studentrbm121415chyNo ratings yet
- Complications of Burn-Raga ManduaruDocument12 pagesComplications of Burn-Raga ManduaruperoksidaseNo ratings yet
- 7 AUBF Lec 7Document6 pages7 AUBF Lec 7Marlyn BorilloNo ratings yet
- UWorld Notes Step 2 CKDocument11 pagesUWorld Notes Step 2 CKSamah Khan67% (3)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeDocument9 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeAjeng DwiNo ratings yet
- Renal Diseases - BSMLS OLFUDocument15 pagesRenal Diseases - BSMLS OLFUMitch IbayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Glomerular DiseasesDocument8 pagesChapter 8 Glomerular DiseasesDIVINE GRACE FLORITA PEPITONo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeDocument8 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeWenny A. YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Sean Dominique C. Maghinay GU1: Medical HXDocument5 pagesSean Dominique C. Maghinay GU1: Medical HXSean Dominique Cruz MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Postgraduate Medical Journal May 2003Document9 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Postgraduate Medical Journal May 2003Sa7arNo ratings yet
- Renal and Metabolic DiseasesDocument5 pagesRenal and Metabolic DiseasesAry OuiNo ratings yet
- AUB - Renal DiseasesDocument2 pagesAUB - Renal DiseasesJeanne RodiñoNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument2 pagesNephritic Syndromevalari8069No ratings yet
- Renal DiseaseDocument4 pagesRenal DiseaseApril Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticeDocument8 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Best PracticegibsonrajanNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis EngDocument43 pagesGlomerulonephritis EngNosirova ManijaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Acetylneuraminic Acid Hydrolase Deficiency Causing NEPHROSIALIDOSIS, Produce FSGSDocument4 pagesAcetylneuraminic Acid Hydrolase Deficiency Causing NEPHROSIALIDOSIS, Produce FSGSนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseasesDocument7 pagesRenal DiseasesXyleene Jency Bien IINo ratings yet
- Aubf RenaallllllllDocument7 pagesAubf RenaallllllllMarienel PingolNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseaseDocument5 pagesRenal DiseasefeajhanineladagaNo ratings yet
- Necrotising Fascitis: Recent Advances in Surgery 39Th EditionDocument36 pagesNecrotising Fascitis: Recent Advances in Surgery 39Th EditionPraveen CpNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Doi: 10.1136/pmj.79.930.206Document9 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis: Doi: 10.1136/pmj.79.930.206mariuz01No ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefoxitinDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefoxitinShaniah DawaNo ratings yet
- Mohamad, Ayah S. Pathophysiology of Maradi's Condition: Salmonella TyphiDocument2 pagesMohamad, Ayah S. Pathophysiology of Maradi's Condition: Salmonella TyphiPIXIEPETERNo ratings yet
- NEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidDocument20 pagesNEPHROTIC SYNDROME - HamidAbdul Hamid OmarNo ratings yet
- Glomerular Disorders - GlomerulonephrtisDocument56 pagesGlomerular Disorders - GlomerulonephrtisValerie Suge-MichiekaNo ratings yet
- SD Nefritico PostgradDocument9 pagesSD Nefritico PostgradMacarena GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- GLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Document8 pagesGLOMERULONEPHRITIS (Bright's Disease)Anjitha K. JNo ratings yet
- Renal PathDocument71 pagesRenal PathSuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- AUBF FinalsDocument62 pagesAUBF FinalsAlthea Jam Grezshyl GaloNo ratings yet
- Case Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyDocument24 pagesCase Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyFrances GrefalNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument28 pagesGlomerulonephritisqayyum consultantfpscNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lecture-I FINDocument8 pagesAUBF Lecture-I FINChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chapter7Document43 pagesMidterm Chapter7Frances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DengueDocument1 pagePathophysiology DenguePLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- Sem 4Document8 pagesSem 4Bea EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatingDocument3 pagesPathophysiology: Predisposing PrecipitatinggizelleNo ratings yet
- PATHOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOLOGYJasellePanteNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoNo ratings yet
- Coliseum ReadingDocument2 pagesColiseum Readingrosember lopezNo ratings yet
- SACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Document4 pagesSACABAYA 2024 Sports Rules & Forms (Football)Travis DavisNo ratings yet
- Caste Disabilities Removal Act, 1850Document2 pagesCaste Disabilities Removal Act, 1850Naresh AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law: Requisites For ValidityDocument19 pagesAdministrative Law: Requisites For ValidityDeb BagaporoNo ratings yet
- Sworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net WorthDocument4 pagesSworn Statement of Assets, Liabilities and Net Worthjohn welsonNo ratings yet
- What Are PineberriesDocument5 pagesWhat Are PineberrieskeithNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Learning Environment On Academic Performance From Students PerspectiveRolly JameroNo ratings yet
- Most Important Idioms and PhrasesDocument65 pagesMost Important Idioms and PhrasesRAVINDRA BHADU 6ANo ratings yet
- Get Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Document113 pagesGet Set Go! 5. Workbook (PDFDrive)Maureen BravoNo ratings yet
- Paleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeDocument13 pagesPaleolithic: Rehistoric Estern UropeAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Quick Install Yealink Vp530 enDocument2 pagesQuick Install Yealink Vp530 enfastoreldaNo ratings yet
- HNNE Term Proforma Front Sheet 2008 With InstructionsDocument4 pagesHNNE Term Proforma Front Sheet 2008 With InstructionsMaribel MuevecelaNo ratings yet
- 「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構Document38 pages「山場」與「岩韻」:武夷茶的風土條件與市場價値結構szeon100% (1)
- Achievements:: 'The Spirit of Wipro' Is Best Represented Through The Following Three StatementsDocument3 pagesAchievements:: 'The Spirit of Wipro' Is Best Represented Through The Following Three StatementsNitesh R ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Situational Leadership in EducationDocument22 pagesSituational Leadership in EducationRoss Thorburn100% (1)
- Early AdulthoodDocument1 pageEarly AdulthoodCherry BobierNo ratings yet
- Makalah Huawei Learning Cloud User GuidDocument45 pagesMakalah Huawei Learning Cloud User GuidhazirafatmarinaNo ratings yet
- Translation and Language Teaching - Malmkjaer, K.Document5 pagesTranslation and Language Teaching - Malmkjaer, K.Igara OliveiraNo ratings yet
- RETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsDocument4 pagesRETDEM - Wearing of Appropriate PPEsYo MamaNo ratings yet
- Zombie: The Coil RulebookDocument137 pagesZombie: The Coil RulebookGnomeMadeIon100% (4)
- HanumanstaleDocument449 pagesHanumanstaleBhaskar Gundu100% (2)
- Science5 Q4 Module5 Week5 18pDocument18 pagesScience5 Q4 Module5 Week5 18praymondcapeNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFDocument8 pagesMohamed Atef Mohamed Abdelrhman Arab (Report - 2) PDFdragon for pc gamesNo ratings yet
- Shaun Allen - Why - Summer - Makes - Us - Lazy-Teacher-12Document6 pagesShaun Allen - Why - Summer - Makes - Us - Lazy-Teacher-12Shaun AllenNo ratings yet
- Vatican Council II - Constitutions, Decrees - Austin FlanneryDocument533 pagesVatican Council II - Constitutions, Decrees - Austin FlanneryIoan PAICUNo ratings yet
- Sample Bar Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesSample Bar Exam QuestionsslydogchuckNo ratings yet