Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 viewsTutorial 4S
Tutorial 4S
Uploaded by
40 Revati Mungelwar1. The document provides 5 practice problems related to mechanics of materials. The problems involve calculating forces, stresses, deflections, and extensions in various loaded structures.
2. The structures include an assembly with end plates under axial loading, joined cylindrical rods with different materials, an aluminum-brass composite exposed to temperature changes, an aluminum rod with an initial gap, and a bolt-nut-spacer assembly.
3. Solutions are provided for calculating stresses induced in a bolt-nut-spacer system when a nut is turned 900 using a spanner.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFDocument2 pagesCEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFEldridge EastNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Mechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesMechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainYogeswaran100% (1)
- ES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALDocument5 pagesES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALGlimmer Dawn Loredo OrdanielNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouscheNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1TanmayNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- 4 - Simple StrainDocument24 pages4 - Simple StrainLorene Ropeta.No ratings yet
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3parmodrtkNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- 212-Chpt 4Document6 pages212-Chpt 4zainabcomNo ratings yet
- Problem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesDocument5 pagesProblem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesClint Charles P. BrutasNo ratings yet
- HW#02Document8 pagesHW#02tozandehjaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1anandNo ratings yet
- Gesm 325a Plate ProblemsDocument4 pagesGesm 325a Plate ProblemsJessa San PedroNo ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFDocument3 pagesEjercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFOscar LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Exercices Non Static Determinated ProblemsDocument2 pagesExercices Non Static Determinated ProblemssesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDenver Nieveras0% (1)
- Simple StressDocument2 pagesSimple StressMariz Ellaine BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Macaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Document13 pagesMacaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Czarina Mae MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarDocument7 pagesProblem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarYatharth KhicharNo ratings yet
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Document6 pagesCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyDocument11 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyHafiz NordinNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressDocument1 pageThermal StressRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Jlim 13Document17 pagesJlim 13Rasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNDocument2 pages2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Axial Members Class WorkDocument2 pagesAxial Members Class WorkKim Book JooNo ratings yet
- Ce003 PsDocument4 pagesCe003 PsJaimeNo ratings yet
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAccount PhoneNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 2020Document5 pagesTutorial 2 2020AntonyNo ratings yet
- Strema Act 2Document42 pagesStrema Act 2James Ryu ZagalaNo ratings yet
- Axial Deformation: Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesAxial Deformation: Strength of MaterialsDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalDocument4 pagesExercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalsesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- IDE 110 W08 Test 1 NameDocument4 pagesIDE 110 W08 Test 1 NameStitch SmithNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Som-Mos-I 205Document4 pagesSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument3 pagesLecture 4 - Statically Indeterminate MembersPaul PatropezNo ratings yet
- SOM Assignment No 2Document4 pagesSOM Assignment No 2suhani mittalNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument3 pagesHandoutssheena Marjorie Cabidog100% (1)
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Document51 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaNo ratings yet
- Strema 102Document4 pagesStrema 102Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument8 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersMo De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Ce6306 16Document3 pagesCe6306 16Arul JONo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet
Tutorial 4S
Tutorial 4S
Uploaded by
40 Revati Mungelwar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pages1. The document provides 5 practice problems related to mechanics of materials. The problems involve calculating forces, stresses, deflections, and extensions in various loaded structures.
2. The structures include an assembly with end plates under axial loading, joined cylindrical rods with different materials, an aluminum-brass composite exposed to temperature changes, an aluminum rod with an initial gap, and a bolt-nut-spacer assembly.
3. Solutions are provided for calculating stresses induced in a bolt-nut-spacer system when a nut is turned 900 using a spanner.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document provides 5 practice problems related to mechanics of materials. The problems involve calculating forces, stresses, deflections, and extensions in various loaded structures.
2. The structures include an assembly with end plates under axial loading, joined cylindrical rods with different materials, an aluminum-brass composite exposed to temperature changes, an aluminum rod with an initial gap, and a bolt-nut-spacer assembly.
3. Solutions are provided for calculating stresses induced in a bolt-nut-spacer system when a nut is turned 900 using a spanner.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesTutorial 4S
Tutorial 4S
Uploaded by
40 Revati Mungelwar1. The document provides 5 practice problems related to mechanics of materials. The problems involve calculating forces, stresses, deflections, and extensions in various loaded structures.
2. The structures include an assembly with end plates under axial loading, joined cylindrical rods with different materials, an aluminum-brass composite exposed to temperature changes, an aluminum rod with an initial gap, and a bolt-nut-spacer assembly.
3. Solutions are provided for calculating stresses induced in a bolt-nut-spacer system when a nut is turned 900 using a spanner.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Tutorial sheet-4
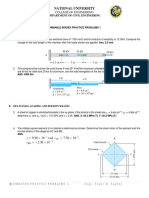
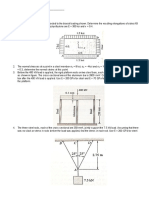
1. The length of the assembly shown decreases by 0.40 mm when an
axial force is applied by means of rigid end plates. Determine (a) the
magnitude of the applied force, (b) the corresponding stress in the
brass core.
2. Two cylindrical rods, one of steel and the other of brass, are
joined at C and restrained by rigid supports at A and E. For
the loading shown and knowing that Es = 200 GPa and Eb =
105 GPa, determine (a) the reactions at A and E, (b) the
deflection of point C.
3. The aluminum shell is fully bonded to the brass core and the
assembly is unstressed at a temperature of 150C. Considering
only axial deformations, determine the stress in the
aluminum when the temperature reaches 1950C.
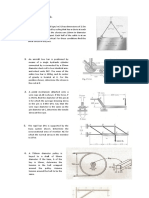
4. At room temperature (200C) a 0.5-mm gap exists between the ends of the rods shown. At a later time
when the temperature has reached 1400C, determine (a) the normal stress in the aluminum rod, (b) the
change in length of the aluminum rod.
5. A 100 mm long steel bolt of 10 mm diameter having a thread pitch of 1.6 mm
passes concentrically through a copper spacing tube of internal and external
diameters of 12 and 18 mm, respectively, as shown in Figure. If the nut is
initially tightened up by hand so that it does not cause any stress in the
spacing tube. Determine the stresses induced in the tube and in the bolt if a
spanner is then used to turn the nut through 900. The moduli of elasticity for
steel and copper are 209 and 100 GPa, respectively.
(Ans: bolt 386.835 MPa; tube 214.911 MPa )
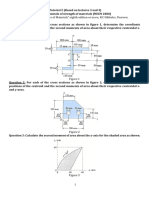
Practice problems
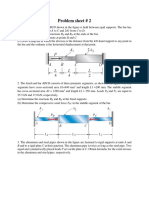
1. Determine the forces in the four legs of a square table (see
Fig.), produced by the load P acting at point A. The top of the
table and the floor are assumed absolutely rigid and the legs
are attached to the floor so that they can undergo tension as
well as compression.
(Ans: X P(1/ 4 e / a 2);Y P / 4; Z P(1/ 4 e / a 2) )
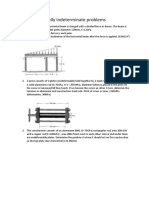
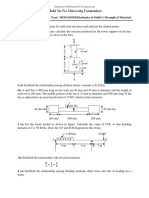
1. A round bar, of length L, tapers uniformly from radius r1 at one end to radius r2 at the other. Show that the extension
produced by a tensile axial load P is PL /(2 Er1 ) if r2 = 2r1. Compare this extension with that of a uniform cylindrical
2
bar having a radius equal to the mean radius of the tapered bar. (Ans: 8/9)
You might also like
- CEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFDocument2 pagesCEMDEF40 - Practice Problems 1 PDFEldridge EastNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- Mechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesMechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainYogeswaran100% (1)
- ES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALDocument5 pagesES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALGlimmer Dawn Loredo OrdanielNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouscheNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1TanmayNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesDocument24 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members & Thermal StressesBuddy SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- 4 - Simple StrainDocument24 pages4 - Simple StrainLorene Ropeta.No ratings yet
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3parmodrtkNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets Strength of Materials 1Document3 pagesProblem Sets Strength of Materials 1Ho BiNo ratings yet
- 212-Chpt 4Document6 pages212-Chpt 4zainabcomNo ratings yet
- Problem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesDocument5 pagesProblem Set: Strain and Thermal StressesClint Charles P. BrutasNo ratings yet
- HW#02Document8 pagesHW#02tozandehjaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1anandNo ratings yet
- Gesm 325a Plate ProblemsDocument4 pagesGesm 325a Plate ProblemsJessa San PedroNo ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFDocument3 pagesEjercicios en Clase Deformaciones PDFOscar LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Note Chapt IIDocument27 pagesNote Chapt IIRitesh KishoreNo ratings yet
- Exercices Non Static Determinated ProblemsDocument2 pagesExercices Non Static Determinated ProblemssesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartDocument2 pagesStrength of Materials: at Least TWO Questions From Each PartnvnrevNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 2.1 and 2.2 PDFDenver Nieveras0% (1)
- Simple StressDocument2 pagesSimple StressMariz Ellaine BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Macaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Document13 pagesMacaraeg, Czarina Mae B. Bsabe 3-1 Quiz No.4Czarina Mae MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarDocument7 pagesProblem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarYatharth KhicharNo ratings yet
- CE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17Document6 pagesCE 6306 / Strength of Materials Mechanical Engineering 2016-17amdevaNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyDocument11 pagesStatically Indeterminate Members (Axially Loaded Only: F F FyHafiz NordinNo ratings yet
- Thermal StressDocument1 pageThermal StressRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Jlim 13Document17 pagesJlim 13Rasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNDocument2 pages2-d. Statically Indeterminate Members: Ans. 3330 KNJasleneDimarananNo ratings yet
- Axial Members Class WorkDocument2 pagesAxial Members Class WorkKim Book JooNo ratings yet
- Ce003 PsDocument4 pagesCe003 PsJaimeNo ratings yet
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAccount PhoneNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 2020Document5 pagesTutorial 2 2020AntonyNo ratings yet
- Strema Act 2Document42 pagesStrema Act 2James Ryu ZagalaNo ratings yet
- Axial Deformation: Strength of MaterialsDocument10 pagesAxial Deformation: Strength of MaterialsDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- Shearing DeformationDocument21 pagesShearing DeformationRyan Joseph Rabino100% (1)
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Exercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalDocument4 pagesExercises Axial Forces and Deformation + TranversalsesNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- IDE 110 W08 Test 1 NameDocument4 pagesIDE 110 W08 Test 1 NameStitch SmithNo ratings yet
- Simple Stress and StrainDocument3 pagesSimple Stress and StrainManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Som-Mos-I 205Document4 pagesSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument3 pagesLecture 4 - Statically Indeterminate MembersPaul PatropezNo ratings yet
- SOM Assignment No 2Document4 pagesSOM Assignment No 2suhani mittalNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument3 pagesHandoutssheena Marjorie Cabidog100% (1)
- Strength WorksheetDocument9 pagesStrength WorksheetHabtamu GetaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Document51 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies: Engr. Ramir C. Del Mundo February 06, 2021Joshua DariaNo ratings yet
- Strema 102Document4 pagesStrema 102Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate MembersDocument8 pagesStatically Indeterminate MembersMo De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Ce6306 16Document3 pagesCe6306 16Arul JONo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet