Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Maintenance - Presentation Transcript
General Maintenance - Presentation Transcript
Uploaded by
Padmasiri BandaraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Maintenance - Presentation Transcript
General Maintenance - Presentation Transcript
Uploaded by
Padmasiri BandaraCopyright:
Available Formats
General Maintenance - Presentation Transcript
1. TRAINING ON MAINTENANCE SYSTEM
2. Maintenance Definition
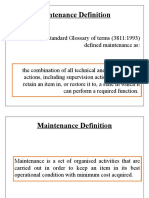
o the combination of all technical and administrative actions, including supervision actions,
intended to retain an item in, or restore it to, a state in which it can perform a required function.
3. Maintenance Definition
o maintenance is a set of organised activities that are carried out in order to keep an item in its
best operational condition with minimum cost acquired.
4. Maintenance Activities
o A ctivities of maintenance function could be either repair or replacement activities, which are
necessary for an item to reach its acceptable productivity condition and these activities, should be carried out
with a minimum possible cost.
5. Maintenance Objectives
o Maintenance objectives should be consistent with and subordinate to production goals.
o The relation between maintenance objectives and production goals is reflected in the action of
keeping production machines and facilities in the best possible condition.
6. Maintenance Objectives
o Maximising production or increasing facilities availability at the lowest cost and at the highest
quality and safety standards.
o Reducing breakdowns and emergency shutdowns.
o Optimising resources utilisation.
o Reducing downtime.
o Improving spares stock control.
7. Maintenance Objectives
o Improving equipment efficiency and reducing scrap rate.
o Minimising energy usage.
o Optimising the useful life of equipment.
o Providing reliable cost and budgetary control.
o Identifying and implementing cost reductions.
8. Maintenance Objectives PLANT M A I N T E N A N C E Reduce Breakdowns Reduce Downtime Improving
Equipment Efficiency Improving Inventory Control Implementing Cost Reduction Maximising Production Optimising
Resources Utilisation Optimising Useful Life of Equipment Minimising Energy Usage Providing Budgetary Control
Figure 2.3 Maintenance Objectives
9. Types of Maintenance MAINTENANCE UNPLANNED MAINTENANCE (REACTIVE) BREAKDOWN
EMERGENCY PLANNED MAINTENANCE (PROACTIVE) CORRECTIVE MAINTENANCE REMEDIAL DEFERRED
PREDECTIVE MAINTENANCE CONDITION - BASED STATISTICAL - BASED PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
ROUTINE RUNNING DESIGN - OUT ENGINEERING SERVICES WINDOW IMPROVEMENT MAINTENANCE
SHUTDOWN CORRECTIVE SHUTDOWN PREVENTIVE SHUTDOWN IMPROVEMENT Shutdown Maintenance
OPPORTU-NITY Figure 2.4 Maintenance Types
10. Types of Maintenance
o Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
o Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o Improvement Maintenance (IM)
o Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
11. Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
o The required repair, replacement, or restore action performed on a machine or a facility after the
occurrence of a failure in order to bring this machine or facility to at least its minimum acceptable condition.
o It is the oldest type of maintenance.
12. Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
o It is subdivided into two types:
Emergency maintenance: it is carried out as fast as possible in order to bring a
failed machine or facility to a safe and operationally efficient condition.
Breakdown maintenance: it is performed after the occurrence of an advanced
considered failure for which advanced provision has been made in the form of repair method, spares,
materials, labour and equipment .
13. Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
o Disadvantages:
o Its activities are expensive in terms of both direct and indirect cost.
o Using this type of maintenance, the occurrence of a failure in a component can cause failures in
other components in the same equipment, which leads to low production availability.
o Its activities are very difficult to plan and schedule in advance.
14. Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
o This type of maintenance is useful in the following situations:
o The failure of a component in a system is unpredictable.
o The cost of performing run to failure maintenance activities is lower than performing other
activities of other types of maintenance.
o The equipment failure priority is too low in order to include the activities of preventing it within
the planned maintenance budget.
15. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o It is a set of activities that are performed on plant equipment, machinery, and systems before the
occurrence of a failure in order to protect them and to prevent or eliminate any degradation in their operating
conditions.
16. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o the maintenance carried out at predetermined intervals or according to prescribed criteria and
intended to reduce the probability of failure or the degradation of the functioning and the effects limited.
17. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o The advantage of applying preventive maintenance activities is to satisfy most of maintenance
objectives.
18. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o The factors that affect the efficiency of this type of maintenance:
o The need for an adequate number of staff in the maintenance department in order to perform
this type of maintenance.
o The right choice of production equipment and machinery that is suitable for the working
environment and that can tolerate the workload of this environment.
o The required staff qualifications and skills, which can be gained through training.
o The support and commitment from executive management to the PM programme.
o The proper planning and scheduling of PM programme.
o The ability to properly apply the PM programme.
19. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o It is good for those machines and facilities which their failure would cause serious production
losses.
o Its aim is to maintain machines and facilities in such a condition that breakdowns and
emergency repairs are minimised.
o Its activities include replacements, adjustments, major overhauls, inspections and lubrications.
20. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o Researchers subdivided preventive maintenance into different kinds according to the nature of
its activities:
o Routine maintenance which includes those maintenance activities that are repetitive and
periodic in nature such as lubrication, cleaning, and small adjustment.
o Running maintenance which includes those maintenance activities that are carried out while the
machine or equipment is running and they represent those activities that are performed before the actual
preventive maintenance activities take place.
21. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
o Opportunity maintenance which is a set of maintenance activities that are performed on a
machine or a facility when an unplanned opportunity exists during the period of performing planned
maintenance activities to other machines or facilities.
o Window maintenance which is a set of activities that are carried out when a machine or
equipment is not required for a definite period of time.
o Shutdown preventive maintenance , which is a set of preventive maintenance activities that are
carried out when the production line is in total stoppage situation.
22. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o In this type, actions such as repair, replacement, or restore will be carried out after the
occurrence of a failure in order to eliminate the source of this failure or reduce the frequency of its occurrence.
23. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types:
o Remedial maintenance , which is a set of activities that are performed to eliminate the source of
failure without interrupting the continuity of the production process.
o The way to carry out this type of corrective maintenance is by taking the item to be corrected out
of the production line and replacing it with reconditioned item or transferring its workload to its redundancy.
24. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o Deferred maintenance , which is a set of corrective maintenance activities that are not
immediately initiated after the occurrence of a failure but are delayed in such a way that will not affect the
production process.
o Shutdown corrective maintenance , which is a set of corrective maintenance activities that are
performed when the production line is in total stoppage situation.
25. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o The main objectives of corrective maintenance are the maximisation of the effectiveness of all
critical plant systems, the elimination of breakdowns, the elimination of unnecessary repair, and the reduction of
the deviations from optimum operating conditions.
o The difference between corrective maintenance and preventive maintenance is that for the
corrective maintenance, the failure should occur before any corrective action is taken.
o Corrective maintenance is different from run to failure maintenance in that its activities are
planned and regularly taken out to keep plant’s machines and equipment in optimum operating condition.
26. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o The way to perform corrective maintenance activities is by conducting four important steps:
o 1. Fault detection.
o 2. Fault isolation.
o 3. Fault elimination.
o 4. Verification of fault elimination.
o In the fault elimination step several actions could be taken such as adjusting, aligning,
calibrating, reworking, removing, replacing or renovation.
27. Corrective Maintenance (CM)
o Corrective maintenance has several prerequisites in order to be carried out effectively:
o Accurate identification of incipient problems.
o Effective planning which depends on the skills of the planners, the availability of well developed
maintenance database about standard time to repair, a complete repair procedures, and the required labour
skills, specific tools, parts and equipment.
o Proper repair procedures.
o Adequate time to repair.
o Verification of repair.
28. Improvement Maintenance (IM)
o It aims at reducing or eliminating entirely the need for maintenance.
o This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types as follows:
o 1. Design-out maintenance which is a set of activities that are used to eliminate the cause of
maintenance, simplify maintenance tasks, or raise machine performance from the maintenance point of view by
redesigning those machines and facilities which are vulnerable to frequent occurrence of failure and their long
term repair or replacement cost is very expensive.
29. Improvement Maintenance (IM)
o 2. Engineering services which includes construction and construction modification, removal and
installation, and rearrangement of facilities.
o 3. Shutdown improvement maintenance , which is a set of improvement maintenance activities
that are performed while the production line is in a complete stoppage situation.
30. Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
o Predictive maintenance is a set of activities that detect changes in the physical condition of
equipment (signs of failure) in order to carry out the appropriate maintenance work for maximising the service
life of equipment without increasing the risk of failure.
o It is classified into two kinds according to the methods of detecting the signs of failure:
Condition-based predictive maintenance
Statistical-based predictive maintenance
31. Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
o Condition-based predictive maintenance depends on continuous or periodic condition monitoring
equipment to detect the signs of failure.
o Statistical-based predictive maintenance depends on statistical data from the meticulous
recording of the stoppages of the in-plant items and components in order to develop models for predicting
failures.
32. Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
o The drawback of predictive maintenance is that it depends heavily on
o information and the correct interpretation of the information.
o Some researchers classified predictive maintenance as a type of preventive maintenance.
o The main difference between preventive maintenance and predictive maintenance is that
predictive maintenance uses monitoring the condition of machines or equipment to determine the actual mean
time to failure whereas preventive maintenance depends on industrial average life statistics.
Electrical Maintenance and Testing of electric power systems is essential to the safe
operation of any electrical system, regardless of its size, type or industry. Electrical worker
inexperience and poor electrical maintenance planning will inevitably result in costly equipment
failure, downtime and productivity losses, not to speak of the risk of electrical safety accidents,
injury and death.
This intense two-day forum provides invaluable information to anyone who wishes to know and
understand the role of electrical maintenance standards, programs and procedures for the optimal
maintenance of electric power systems. The importance of planning, programming and
implementing electrical maintenance practices will be emphasized. This forum also deals with
safety considerations involved in electrical maintenance procedures for all the components of
any electrical system. This will be an interactive forum where the instructor will lead the
discussion between students so to maximze the educational experience.
STANDARDS GOVERNING ELECTRICAL MAINTENANCE
These interactive forums on electrical maintenance standards, procedures and solutions to
electrical maintenance and testing problems will deal with specific issues relating to electrical
testing and troubleshooting procedures and equipment selection.
NETA Standards For Electrical Maintenance
This presentation is designed to alert Canadian electrical maintenance personnel
in utility, industrial, commercial and institutional facilities to the latest
International Electrical Testing Association (NETA) Maintenance and Testing
Specifications. These NETA maintenance specifications cover the suggested field
tests and inspections that are available to assess the suitability for continued service and
reliability of electrical power distribution equipment and systems.
The purpose of these specifications is to assure that tested electrical equipment and systems are
operational and within applicable standards and manufacturer's tolerances and that the equipment
and systems are suitable for continued service. This program will also deal with the important
subject of troubleshooting electrical systems and choosing the proper preventive maintenance
testing equipment and procedures.
NFPA-70b Standard For Electrical Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is the key to reducing accidents, saving lives, and
avoiding costly breakdowns and work stoppages. This latest Edition has been
updated to reflect the latest industry developments and safety strategies. Our
NFPA 70b Electrical Maintenance training course is your best guide for creating
and administering an effective Electrical Preventive Maintenance (EPM) program.
A well-administered EPM program is the surest way to reduce accidents, save lives, and
minimize costly breakdowns and unplanned shutdowns of production equipment Learn about
preventive maintenance for industrial and commercial electrical systems and equipment, and
learn test procedures you can implement at once.
The "NFPA 70b - Recommended Practices For Electrical Equipment Maintenance" is an in-
depth presentation of "Recommended Practices For Electrical Equipment Maintenance". These
recommended practices apply to preventive maintenance for electrical, electronic, and
communication systems and equipment installed in industrial, commercial and institutional
power systems.
CSA Z462 Workplace Electrical Safety - Safety Related Maintenance Requirements
This presentation specifies practical safety-related maintenance requirements for
electrical equipment and installations in the workplaces. These requirements
cover only maintenance directly associated with electrical worker safety.
Who Should Attend
This course is a must for electrical engineers, electrical maintenance personnel,
plant electricians, electrical contractors, power specialists, maintenance managers, consultants
and technologists responsible for the design, construction, installation, inspection, operation, or
maintenance of electrical systems, electrical technicians, inspectors, safety personnel and other
employees responsible for the operation and maintenance of electrical systems in a commercial,
industrial, institutional or utility setting.
BONUS FEATURES
FREE (CD Format) -- 252-Page NETA "2007 Specifications Standard For Electrical Maintenance
Testing" (Value $275)
FREE (CD Format) -- 227-Page NFPA 70B "Recommended Practice for Electrical Equipment
Maintenance"(Value $50)
FREE -- 100-Page Electrical Maintenance and Testing Handbook (Value $25)
You might also like
- Test Bank For Marketing 20th Edition William M Pride o C FerrellDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Marketing 20th Edition William M Pride o C FerrellstephenhuepjotNo ratings yet
- HR (Summer Internship Project)Document49 pagesHR (Summer Internship Project)Nishant67% (12)
- Month-End Walkthrough Diagnostic QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesMonth-End Walkthrough Diagnostic QuestionnaireMaria Danice Angela100% (1)
- Types of MaintenanceDocument10 pagesTypes of MaintenanceAbishek JainNo ratings yet
- Total Productive Maintenance For Organisational EffectivenessFrom EverandTotal Productive Maintenance For Organisational EffectivenessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Sample Bus As Questionbank 2005Document5 pagesSample Bus As Questionbank 2005eco2dayNo ratings yet
- LEC1-Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1-Maintenance DefinitionMilin SutharNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesChapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering Notesodeke aronNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Installation of Machinery: (Meng 5231)Document21 pagesMaintenance and Installation of Machinery: (Meng 5231)Milion dugumaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVaraGoudNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument25 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- Southern Range Nyanza LTDDocument17 pagesSouthern Range Nyanza LTDspindles2No ratings yet
- MGT MNT PLN PRST2NDDraftDocument139 pagesMGT MNT PLN PRST2NDDraftchibssa alemayehuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1pptDocument46 pagesChapter 1pptEjizen LowNo ratings yet
- LEC1 Maintenance DefinitionDocument31 pagesLEC1 Maintenance DefinitionSaba ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Study On Maintenance Process and Maintenance ToolsDocument17 pagesStudy On Maintenance Process and Maintenance ToolsKawsar AlamNo ratings yet
- Medical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-RumaimaDocument28 pagesMedical Equipment Maintenance: Dr. Mahmoud Al-Rumaimaمحمد الاشولNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument23 pagesMaintenance DefinitionMekonnen AyalNo ratings yet
- ME2037 Maintenance EngineeringDocument51 pagesME2037 Maintenance EngineeringVicky Vignesh100% (1)
- Me6012 - Maintenance EngineeringDocument13 pagesMe6012 - Maintenance EngineeringIyswaryaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering Q&a PDFDocument27 pagesMaintenance Engineering Q&a PDFRaviggg100% (3)
- Types of maintenanceDocument8 pagesTypes of maintenancemehtatreedaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument36 pagesMaintenance DefinitionakanawNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 2 Mark PDFDocument38 pagesMaintenance 2 Mark PDFSaravanan HNo ratings yet
- ME2037 Maintenance EngineeringDocument46 pagesME2037 Maintenance Engineeringrp0212100% (2)
- Topic 1 - Maintenance System LatestDocument77 pagesTopic 1 - Maintenance System LatestAfhnan TemiziNo ratings yet
- Maintenance QBDocument43 pagesMaintenance QBajitsssNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument46 pagesMaintenance Engineering Questions and Answersakbar_mdhNo ratings yet
- ME2037 - Maintenance Engineering (Eighth Semester Mech) Question BankDocument20 pagesME2037 - Maintenance Engineering (Eighth Semester Mech) Question BankSK NAGOOR VALINo ratings yet
- Lec1-Maintenance Definition 1Document35 pagesLec1-Maintenance Definition 1searetekeste20102014No ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance and Replacement Models: Chapter - 1Document38 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance and Replacement Models: Chapter - 1engineer engrNo ratings yet
- ME6012-Maintenance-Engineering 2 MarksDocument14 pagesME6012-Maintenance-Engineering 2 MarksAravind SelvaNo ratings yet
- Akif 2Document41 pagesAkif 2tazeem_akifNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Medical EquipmentDocument33 pagesMaintenance of Medical EquipmentAbe CyberCrewPlusDotmy100% (1)
- Maintenance ManagementDocument14 pagesMaintenance ManagementAasishPatilNo ratings yet
- 1-Chapter One: IntroductionDocument15 pages1-Chapter One: IntroductionIsmailNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6: Maintenance of Machine ToolsDocument9 pagesUNIT 6: Maintenance of Machine ToolsAchal NimjeNo ratings yet
- Maintenence BasicsDocument51 pagesMaintenence BasicsKarim Magdy100% (2)
- 0 MaintenanceDocument35 pages0 MaintenanceMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- I. Discuss The Needs For MaintenanceDocument3 pagesI. Discuss The Needs For MaintenancePrem Kumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- CH 1 MaintenanceDocument26 pagesCH 1 MaintenanceTewodros DereseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceAzimZakwanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument50 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVinitSinhaNo ratings yet
- #5 Maintenance CostDocument49 pages#5 Maintenance CostKhoirul Be100% (1)
- Plant Maintenance & Checklist: Anirbit Chowdhury Asst Manager - PMVDocument37 pagesPlant Maintenance & Checklist: Anirbit Chowdhury Asst Manager - PMVAnirbitNo ratings yet
- MEP 283 Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesMEP 283 Lecture NotesPkay TandohNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 19meDocument104 pagesMaintenance 19meawaiszulfiqar050No ratings yet
- Ce 2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Document15 pagesCe 2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Abera MamoNo ratings yet
- Ce 2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Document15 pagesCe 2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Charan Tej Rudrala100% (1)
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument21 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part IKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Maintanance Engg MaterialDocument58 pagesMaintanance Engg MaterialSiva KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: (Shashank Tilak)Document7 pagesOperations Management: (Shashank Tilak)Vijay Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chap. OneDocument26 pagesChap. OnesitoawNo ratings yet
- Maintenace 2Document37 pagesMaintenace 2fekadeNo ratings yet
- Maintenance TypesDocument15 pagesMaintenance TypesShalini YadavNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDocument37 pagesMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- Subject: Production and Operations Management Unit 5: Maintenance and Waste ManagementDocument6 pagesSubject: Production and Operations Management Unit 5: Maintenance and Waste ManagementAnonymous yL88JjNo ratings yet
- Local Presentation On CBM - Iipm, IndiaDocument54 pagesLocal Presentation On CBM - Iipm, IndiaFreddie Asiedu LarbiNo ratings yet
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Practical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneFrom EverandPractical, Made Easy Guide To Building, Office And Home Automation Systems - Part OneNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- KirloskarDocument81 pagesKirloskarSumit SonkarNo ratings yet
- 2011 Vol 5 No 2Document13 pages2011 Vol 5 No 2Nipun SharmaNo ratings yet
- OrderingDocument2 pagesOrderingSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- SEBoK 18 Part5Document123 pagesSEBoK 18 Part5simbamike100% (1)
- SAP HR AND HRM Interview Questions and Answers: Learning IT Courses Has Never Been This EasyDocument28 pagesSAP HR AND HRM Interview Questions and Answers: Learning IT Courses Has Never Been This EasyAhmed AshrafNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ND Human Resources MGT OmnibusDocument138 pagesSyllabus ND Human Resources MGT OmnibusFaith MbeveNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ii:: AIC Netbooks: Optimizing Product AssemblyDocument7 pagesCase Study Ii:: AIC Netbooks: Optimizing Product Assemblymuskaan bhadadaNo ratings yet
- Master in Talent Development Human ResourcesDocument24 pagesMaster in Talent Development Human ResourcesPRANEETHNo ratings yet
- Office of The Sangguniang Bayan: Hon. Clemente Castro Firmalino, JRDocument10 pagesOffice of The Sangguniang Bayan: Hon. Clemente Castro Firmalino, JRRod CastroNo ratings yet
- Brand Equity 10Document3 pagesBrand Equity 10Suyash MayekarNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesManagerial Economics Multiple Choice QuestionsNeha Sngh100% (1)
- Overview of FMCG SectorDocument2 pagesOverview of FMCG SectorSandip NayekNo ratings yet
- Converged Systems Sales PlaybookDocument12 pagesConverged Systems Sales PlaybookPeter Stone100% (3)
- Idi Sai - Handbook Final v2Document191 pagesIdi Sai - Handbook Final v2Shota JamburidzeNo ratings yet
- Mba ProspectusDocument24 pagesMba Prospectusmadan.htNo ratings yet
- Appex CaseDocument5 pagesAppex CaseRajveer100% (3)
- HRMiS Report2Document100 pagesHRMiS Report2Sachin Mehta100% (1)
- 7 Elements of A Strategic PlanDocument7 pages7 Elements of A Strategic PlanSabyasachi KarNo ratings yet
- JD Fabric SourcingDocument2 pagesJD Fabric SourcingSnig KavNo ratings yet
- SDM Module 4Document52 pagesSDM Module 4Harsh Vardhan100% (1)
- Making The Case For The Added Value Chain - Xid-1202168 - 1Document8 pagesMaking The Case For The Added Value Chain - Xid-1202168 - 1christianNo ratings yet
- Full Funnel WorkshopDocument52 pagesFull Funnel WorkshopIsmael BriascoNo ratings yet
- Vokurka 2000Document13 pagesVokurka 2000Ikhsan MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Pure Competition in The Short Run: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument17 pagesPure Competition in The Short Run: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinPowerpoint XtremeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Concept and OrigionDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship Concept and OrigionabrarNo ratings yet
- Employee Benefits in Small Medium EnterprisesDocument8 pagesEmployee Benefits in Small Medium EnterprisesRehab ShaikhNo ratings yet





























































![Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/235162742/149x198/2a816df8c8/1709920378?v=1)


























