Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Database Environment
3 Database Environment
Uploaded by
Bigu Marius AlinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Database Environment
3 Database Environment
Uploaded by
Bigu Marius AlinCopyright:
Available Formats
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Data
Management
Systems
HDip in Cloud Computing
Lecture: Database Environment Summary
Karl O’Connell
Definitions
• Database: organized collection of logically related data
• Data: stored representations of meaningful objects and
events
– Structured: numbers, text, dates
– Unstructured: images, video, documents
• Information: data processed to increase knowledge in
the person using the data
• Metadata: data that describes the properties and context
of user data
Cork Institute of Technology 1
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
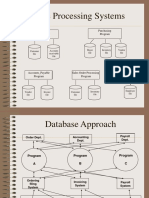
Disadvantages of File Processing
• Program-Data Dependence
– All programs maintain metadata for each file they use
• Duplication of Data
– Different systems/programs have separate copies of the same data
• Limited Data Sharing
– No centralized control of data
• Lengthy Development Times
– Programmers must design their own file formats
• Excessive Program Maintenance
– 80% of information systems budget
Problems with Data Dependency
• Each application programmer must maintain
his/her own data
• Each application program needs to include code
for the metadata of each file
• Each application program must have its own
processing routines for reading, inserting,
updating, and deleting data
• Lack of coordination and central control
• Non-standard file formats
Cork Institute of Technology 2
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Duplicate Data
Problems with Data Redundancy
• Waste of space to have duplicate data
• Causes more maintenance headaches
• The biggest problem:
– Data changes in one file could cause
inconsistencies
– Compromises in data integrity
Cork Institute of Technology 3
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
SOLUTION:
The DATABASE Approach
• Central repository of shared data
• Data is managed by a controlling agent
• Stored in a standardized, convenient
form
Requires a Database Management System (DBMS)
Database Management System
◼ A software system that is used to create, maintain, and provide
controlled access to user databases
Order Filing
System
Invoicing Central database
DBMS
System
Contains employee,
order, inventory,
Payroll pricing, and
System customer data
DBMS manages data resources like an operating system manages hardware resources
Cork Institute of Technology 4
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Advantages of the Database Approach
• Program-data independence
• Planned data redundancy
• Improved data consistency
• Improved data sharing
• Increased application development productivity
• Enforcement of standards
• Improved data quality
• Improved data accessibility and responsiveness
• Reduced program maintenance
• Improved decision support
Costs and Risks of the Database Approach
• New, specialized personnel
• Installation and management cost and
complexity
• Conversion costs
• Need for explicit backup and recovery
• Organizational conflict
10
10
Cork Institute of Technology 5
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Figure 2-1 Components of the Database Environment
11
11
Components of the
Database Environment
• CASE Tools–computer-aided software engineering
• Repository–centralized storehouse of metadata
• Database Management System (DBMS) –software for
managing the database
• Database–storehouse of the data
• Application Programs–software using the data
• User Interface–text and graphical displays to users
• Data/Database Administrators–personnel responsible for
maintaining the database
• System Developers–personnel responsible for designing
databases and software
• End Users–people who use the applications and databases
12
12
Cork Institute of Technology 6
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
The Range of Database Applications
• Personal databases
• Two-tier Client/Server databases
• Multitier Client/Server databases
• Enterprise applications
– Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
– Data warehousing implementations
13
13
14
14
Cork Institute of Technology 7
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Figure 2-2 Two-tier database with local
area network
15
15
Figure 2-3 Three-tiered client/server database
architecture
16
16
Cork Institute of Technology 8
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Enterprise Database Applications
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
– Integrate all enterprise functions (manufacturing,
finance, sales, marketing, inventory, accounting,
human resources)
• Data Warehouse
– Integrated decision support system derived from
various operational databases
17
17
Figure 2-4 Evolution of database technologies
18
18
Cork Institute of Technology 9
Karl O'Connell HDIP - 2019
Enterprise Data Model
• First step in database development
• Specifies scope and general content
• Overall picture of organizational data at high level of
abstraction
• Entity-relationship diagram
• Descriptions of entity types
• Relationships between entities
• Business rules
19
19
Cork Institute of Technology 10
You might also like
- Scheme of Work: Cambridge Lower Secondary Digital Literacy 0082 Stage 8Document42 pagesScheme of Work: Cambridge Lower Secondary Digital Literacy 0082 Stage 8SamiyaNo ratings yet
- Jeffrey A. Hoffer, V. Ramesh, Heikki Topi: Modern Database Management 12 EditionDocument63 pagesJeffrey A. Hoffer, V. Ramesh, Heikki Topi: Modern Database Management 12 EditionAndrew LinNo ratings yet
- Examples of Database Applications: Introduction To DatabasesDocument11 pagesExamples of Database Applications: Introduction To DatabasesBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Mr. Sohaib LatifDocument28 pagesInstructor: Mr. Sohaib LatifHafsa KhanNo ratings yet
- Information Management ReviewerDocument13 pagesInformation Management ReviewerJax RozenNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 - IntroductionDocument37 pagesLecture-1 - IntroductionJaveria TahirNo ratings yet
- Information ManagementDocument18 pagesInformation ManagementorchuchiNo ratings yet
- Database Ch-1Document7 pagesDatabase Ch-1gebriyeNo ratings yet
- DCIT 24 ReviewerDocument16 pagesDCIT 24 ReviewerORACION, Mark GerlexNo ratings yet
- The Database EnvironmentDocument3 pagesThe Database EnvironmentJax RozenNo ratings yet
- B. Overview of DatabasesDocument35 pagesB. Overview of DatabasesTonmoy BiswasNo ratings yet
- DB 1Document29 pagesDB 1aishaNo ratings yet
- DatabaseDocument45 pagesDatabasewaqas08No ratings yet
- DatabaseOverviewDocument101 pagesDatabaseOverviewbabjeereddyNo ratings yet
- Lectures32606 31061 SixDocument60 pagesLectures32606 31061 SixSucharita SahaNo ratings yet
- Discovering Computers 2011: Living in A Digital WorldDocument62 pagesDiscovering Computers 2011: Living in A Digital WorldJohny DoelNo ratings yet
- CIS Module 2 - Classic Data Center - ModiDocument67 pagesCIS Module 2 - Classic Data Center - Modinishtha sethiNo ratings yet
- Fodb Reviewer PrelimDocument5 pagesFodb Reviewer PrelimCerica BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: By-Karan Tiwari Bca 2 SemesterDocument14 pagesDatabase Management System: By-Karan Tiwari Bca 2 Semesterflying ostrichNo ratings yet
- Database Design & ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design & ManagementyohoNo ratings yet
- Asdf WefefDocument30 pagesAsdf Wefefbattal2023513No ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Database EnvironmentDocument25 pagesModule 1 - The Database EnvironmentPatrick RomanNo ratings yet
- AMS PresentationDocument24 pagesAMS PresentationShowkat HossainNo ratings yet
- PART 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument34 pagesPART 1 - The Database Environment and Development ProcessMike AntolinoNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument64 pagesDatabase Management SystemSamiksha SainiNo ratings yet
- Slide MIS - Chap 6Document10 pagesSlide MIS - Chap 6Hằng NgôNo ratings yet
- College of Science and TechnologyDocument34 pagesCollege of Science and TechnologyCynthia UmubyeyiNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: Chapter TwoDocument55 pagesManagement Information System: Chapter Twoobsinan dejeneNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document32 pagesCH 1pir zadaNo ratings yet
- dATA Base LectureDocument32 pagesdATA Base LectureJessiNo ratings yet
- Information Management 2Document25 pagesInformation Management 2orchuchiNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To DatabasesDocument35 pages1 Introduction To DatabasesBricious Mulimbi100% (1)
- DatabaseDocument11 pagesDatabaseksylviakinyanjui2No ratings yet
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument35 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramSweety RaniNo ratings yet
- Rdbms III SemDocument80 pagesRdbms III Semsms948072No ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document20 pagesLecture 02Islam SaleemNo ratings yet
- Database NotesDocument81 pagesDatabase NotesEmma mutaurwaNo ratings yet
- "Database Systems": Book: Modern Database ManagementDocument35 pages"Database Systems": Book: Modern Database ManagementRimsha AwanNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Business: Bba, Semester 2 Database Management Systems, Module - I Ms Bhawana GuptaDocument35 pagesAmity School of Business: Bba, Semester 2 Database Management Systems, Module - I Ms Bhawana GuptaMukulDabasNo ratings yet
- I.M. 1 3 NormalizationDocument14 pagesI.M. 1 3 Normalizationkencyron.abentinoNo ratings yet
- Database 2 - C309 3mise: SyllabusDocument17 pagesDatabase 2 - C309 3mise: SyllabusJapanNo ratings yet
- Big Data AnalyticsDocument25 pagesBig Data Analyticsb210871No ratings yet
- Data Warehouse ComponentsDocument26 pagesData Warehouse Componentsdurai muruganNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 - Introduction To Database SystemsDocument40 pagesLecture - 1 - Introduction To Database Systemsmazenezzat666No ratings yet
- 1st Week Database-SystemsDocument59 pages1st Week Database-SystemsrubasaleeeeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 - Introduction To DBDocument30 pages6.1 - Introduction To DBmansorNo ratings yet
- Database Systems Chapter 1Document6 pagesDatabase Systems Chapter 1marlee_musniNo ratings yet
- Ch11Document23 pagesCh11Izme SaadNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Database Management SystemDocument12 pagesEvolution of Database Management SystemsambashivaraoNo ratings yet
- DBS Overview and DBSDLCDocument48 pagesDBS Overview and DBSDLCerikikinyamagohaNo ratings yet
- Information Management Systems (ECSE211L) : (Introduction of IMS)Document42 pagesInformation Management Systems (ECSE211L) : (Introduction of IMS)hardikNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 DBDocument30 pagesChapter-1 DBShaggYNo ratings yet
- FDS ReviewerDocument16 pagesFDS ReviewerSecuretech Security Systems PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Database Management Systems: George Klington. ADocument18 pagesDatabase Management Systems: George Klington. AklingtonNo ratings yet
- Module V (Database Management System)Document43 pagesModule V (Database Management System)Divisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Modern Database ManagementDocument9 pagesModern Database ManagementShermeen AdnanNo ratings yet
- DBS NotesDocument85 pagesDBS NotesOmary HajiNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Database SystemsDocument74 pages1 - Introduction To Database SystemsYasemin GövezNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument92 pagesBig DataAylin KorogluNo ratings yet
- Databases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationFrom EverandDatabases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Information Storage and Management: Storing, Managing, and Protecting Digital Information in Classic, Virtualized, and Cloud EnvironmentsFrom EverandInformation Storage and Management: Storing, Managing, and Protecting Digital Information in Classic, Virtualized, and Cloud EnvironmentsEMC Education ServicesNo ratings yet
- H+ Sport CustomersDocument42 pagesH+ Sport CustomersBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 8 Unit TestingDocument25 pages8 Unit TestingBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- H+ Sport OrdersDocument13 pagesH+ Sport OrdersBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 10 BackupDocument18 pages10 BackupBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 9 File ManagementDocument16 pages9 File ManagementBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 10 Methodologies BasicConceptsDocument21 pages10 Methodologies BasicConceptsBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 11 Methodologies XP ScrumDocument17 pages11 Methodologies XP ScrumBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- How To Make ButterDocument2 pagesHow To Make ButterBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 12 Configuration+managementDocument33 pages12 Configuration+managementBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 6 - B - Personas OverviewDocument40 pages6 - B - Personas OverviewBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 9 LifecycleModelingDocument34 pages9 LifecycleModelingBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 2 ModelingwithUMLDocument28 pages2 ModelingwithUMLBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 7 System TestingDocument21 pages7 System TestingBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 3 ModelingWithUMLDocument25 pages3 ModelingWithUMLBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 4 Traditional REDocument29 pages4 Traditional REBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- L10a - ExceptionsDocument25 pagesL10a - ExceptionsBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- IT Solutions Architecture 1st Lab ReportDocument31 pagesIT Solutions Architecture 1st Lab ReportBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 17Document34 pagesPHP 17Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 15Document34 pagesPHP 15Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- L10b - SoftwareQualityDocument35 pagesL10b - SoftwareQualityBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 13Document57 pagesPHP 13Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 12Document24 pagesPHP 12Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 01Document30 pagesPHP 01Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 07Document20 pagesPHP 07Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 03Document50 pagesPHP 03Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 09Document62 pagesPHP 09Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 02Document47 pagesPHP 02Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- PHP 04Document59 pagesPHP 04Bigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- 05afile SystemsDocument40 pages05afile SystemsBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- SOFT7006 Operating Systems: 5. ConcurrencyDocument79 pagesSOFT7006 Operating Systems: 5. ConcurrencyBigu Marius AlinNo ratings yet
- Informatica Metadata Manager Data Sheet 6792 DatasheetDocument4 pagesInformatica Metadata Manager Data Sheet 6792 DatasheetsvmglpNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing FundamentalsDocument527 pagesData Warehousing FundamentalsMadan Mohan0% (1)
- Harmony 17 Premium Reference GuideDocument1,186 pagesHarmony 17 Premium Reference GuideTwenti FoorNo ratings yet
- Deep WebDocument53 pagesDeep WebAnil StevensNo ratings yet
- Osb ConceptsDocument5 pagesOsb ConceptsDivyaNo ratings yet
- Athena Basics - Key Concepts - The Athena GuideDocument6 pagesAthena Basics - Key Concepts - The Athena GuidePatricia FillipsNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Practices: MicroservicesDocument42 pagesPatterns and Practices: MicroservicesIlama Sto100% (1)
- Pérez Garbín 75357 Inmaculada Perez Garbin Smart Stores Technology 784051 761594907Document118 pagesPérez Garbín 75357 Inmaculada Perez Garbin Smart Stores Technology 784051 761594907Amazing ThingsNo ratings yet
- VideoCleaner Users GuideDocument27 pagesVideoCleaner Users GuideMuhammad Syimir YusofNo ratings yet
- OLM Tables and ERDDocument16 pagesOLM Tables and ERDSyed Farhan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Competency Center: Best Practices To Deliver REAL Business ValueDocument41 pagesBusiness Intelligence Competency Center: Best Practices To Deliver REAL Business ValueGirish GroverNo ratings yet
- Xiv 11.5.1 XcliDocument704 pagesXiv 11.5.1 XcliMuthu LNo ratings yet
- Paleoenvironment of Europe in The LGMDocument3 pagesPaleoenvironment of Europe in The LGMPablo CulebrasNo ratings yet
- Setting Up Database Based MDS Repository in Weblogic 12cDocument10 pagesSetting Up Database Based MDS Repository in Weblogic 12cPriya JayaramanNo ratings yet
- DCIT 305: Databases Fundamentals: Session 1: Introduction To Database FundamentalsDocument47 pagesDCIT 305: Databases Fundamentals: Session 1: Introduction To Database FundamentalsSey JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Integration of Oracle Intermedia Text With DspaceDocument5 pagesIntegration of Oracle Intermedia Text With DspacememoNo ratings yet
- Scrivener Manual Win LetterDocument267 pagesScrivener Manual Win Letternod284No ratings yet
- Whitepaper Workday Technology Platform Devt ProcessDocument20 pagesWhitepaper Workday Technology Platform Devt ProcessdharmaNo ratings yet
- RMAN (Script Overview)Document22 pagesRMAN (Script Overview)raajiNo ratings yet
- Credit Scoring SASDocument42 pagesCredit Scoring SASjavierkztNo ratings yet
- SAP - Customer Exit Implementation For Decoupled Framework Info TypesDocument9 pagesSAP - Customer Exit Implementation For Decoupled Framework Info TypesBumblefreakNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Land Asset Management in Ghana A Shared Responsibility and Recipe For Good GovernanceDocument16 pagesOptimizing Land Asset Management in Ghana A Shared Responsibility and Recipe For Good GovernanceMuhammad Maulidin NazibNo ratings yet
- Geospatial SoaDocument83 pagesGeospatial Soajulialau10No ratings yet
- Tacl A 00544Document23 pagesTacl A 00544Brent BaumgartnerNo ratings yet
- How To Collect ICT Statistics Using Household Surveys - The ITU Manual On ICT Household SurveysDocument10 pagesHow To Collect ICT Statistics Using Household Surveys - The ITU Manual On ICT Household SurveysDiah YuniartiNo ratings yet
- Hexaware Guidewire Data Migration WP MadhurVirmaniDocument9 pagesHexaware Guidewire Data Migration WP MadhurVirmaniSowbhagya VaderaNo ratings yet
- MTDATA Installation and DemoDocument2 pagesMTDATA Installation and DemoAbraão Santos SilvaNo ratings yet
- Product & Solutions Overview: Ananda Rajagopal VP, Product Line ManagementDocument37 pagesProduct & Solutions Overview: Ananda Rajagopal VP, Product Line ManagementCCIE DetectNo ratings yet