Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydraulic Machine
Hydraulic Machine
Uploaded by
Pratik MoyjeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Wind Tunnel ExperimentDocument46 pagesWind Tunnel ExperimentAbhilash Mathew50% (2)
- Rudder DesignDocument11 pagesRudder Designnawan67% (3)
- Reversible Flow Fan: New Product InformationDocument5 pagesReversible Flow Fan: New Product Informationsnow69yNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicEffectsOfPantographs - by Mitsuru Ikeda - RTRIDocument12 pagesAerodynamicEffectsOfPantographs - by Mitsuru Ikeda - RTRIwmplgrcfNo ratings yet
- TDK-humidifier - Element Nebulizer - NB - enDocument5 pagesTDK-humidifier - Element Nebulizer - NB - enKemenesh HNo ratings yet
- Pressure Booster - V GuardDocument2 pagesPressure Booster - V Guardhalderchayan320No ratings yet
- EDGE 650-675 4570 Performance ChartDocument1 pageEDGE 650-675 4570 Performance ChartLeonardo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Series: K5V 200 DT H 100 R 9N 01Document1 pageSeries: K5V 200 DT H 100 R 9N 01Stelian Crisan100% (1)
- Catalogo Servo 1FK7Document6 pagesCatalogo Servo 1FK7José Manuel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Various 3 3" 5" 1000 1" Semi-O 15.12": NS Solids Dia. No. Vanes Discharge Suction Style Speed Impeller DiaDocument1 pageVarious 3 3" 5" 1000 1" Semi-O 15.12": NS Solids Dia. No. Vanes Discharge Suction Style Speed Impeller DiaChunchun MaruNo ratings yet
- BOQ Supply Installation - Construction PowerDocument1 pageBOQ Supply Installation - Construction Powersaravanan .bNo ratings yet
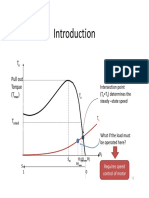
- T Intersection Point (T T) Determines The Steady - State SpeedDocument11 pagesT Intersection Point (T T) Determines The Steady - State SpeedKaone OsupileNo ratings yet
- Thermal Load Effect On Vibration On A Reactor FW Pump 1699692616Document25 pagesThermal Load Effect On Vibration On A Reactor FW Pump 1699692616logicloverNo ratings yet
- 1N5758 Etc PDFDocument3 pages1N5758 Etc PDFPedro lealNo ratings yet
- PLB-0384-4830-ME-0004: ABB India LTDDocument3 pagesPLB-0384-4830-ME-0004: ABB India LTDAlex Labraña RojoNo ratings yet
- Penta KatalogDocument36 pagesPenta KatalogCristian SerbanoiuNo ratings yet
- PompaDocument2 pagesPompaviviNo ratings yet
- PLB-0384-DAT-4830-ME-0005: ABB India LTDDocument3 pagesPLB-0384-DAT-4830-ME-0005: ABB India LTDAlex Labraña RojoNo ratings yet
- SRNE - HF Series - LV - EU - Solar Charge Inverter - Datasheet - 2.1Document1 pageSRNE - HF Series - LV - EU - Solar Charge Inverter - Datasheet - 2.1Lin YutingNo ratings yet
- Motor PassoDocument1 pageMotor PassoHevert TwynsterNo ratings yet
- MM 1150HP WDS6 18.74 PerDocument1 pageMM 1150HP WDS6 18.74 PermajjisatNo ratings yet
- LPS Hybrid AC/DC Features Specification: Solar SubmersibleDocument2 pagesLPS Hybrid AC/DC Features Specification: Solar SubmersibleEric Lee100% (2)
- EEE2003 - Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab: School of Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesEEE2003 - Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab: School of Electrical EngineeringAkshit VSNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Piston PumpDocument19 pagesHydraulic Piston Pumpvodangminhhieu0905960430No ratings yet
- Curva 2Document1 pageCurva 2Luis FernandoNo ratings yet
- 8 Centrifugal Compressor PerformanceDocument28 pages8 Centrifugal Compressor PerformanceHazem Ramdan100% (1)
- CasappaDocument44 pagesCasappaback1949No ratings yet
- Water Turbine and Its TypesDocument7 pagesWater Turbine and Its TypesprakashNo ratings yet
- Perfomance Curve BFP HP Ip PDFDocument2 pagesPerfomance Curve BFP HP Ip PDFRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Motor m55sp 2k eDocument2 pagesMotor m55sp 2k ebLesaLmeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Flow Instruments: Flow Switches & Indicators Delta Tube - Averaging Pitot TubeDocument3 pagesAn Overview of Flow Instruments: Flow Switches & Indicators Delta Tube - Averaging Pitot TubegiridharNo ratings yet
- Tons Tons: CAPWAP (R) 2014-3 Licensed To PT Teno IndonesiaDocument3 pagesTons Tons: CAPWAP (R) 2014-3 Licensed To PT Teno IndonesiaAdiitPuutraNo ratings yet
- BasicformulasDocument2 pagesBasicformulasAhmad SabraNo ratings yet
- X ErCharProtDocument10 pagesX ErCharProtNavaneethakrishnan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Relief Valve: RD-162A-X-Y-ZDocument1 pageRelief Valve: RD-162A-X-Y-ZMichał A.No ratings yet
- Smoke Ventilators F400 / 120: Smoke Air Ventilator High-Performance ResilientDocument11 pagesSmoke Ventilators F400 / 120: Smoke Air Ventilator High-Performance ResilientBachir BachirNo ratings yet
- Performance Chart Theoretical Working Point: CGT/4-900-6/32 15KW (400V50HZ) IE3 V5Document3 pagesPerformance Chart Theoretical Working Point: CGT/4-900-6/32 15KW (400V50HZ) IE3 V5Ishan RanganathNo ratings yet
- Series CA: Magnetic Drive Centrifugal PumpDocument2 pagesSeries CA: Magnetic Drive Centrifugal Pumphanni86No ratings yet
- 1002 A Series Variable Displacement Piston PumpsDocument48 pages1002 A Series Variable Displacement Piston PumpsLuis Enrique López LeónNo ratings yet
- Ecma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Document2 pagesEcma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Anil JindalNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Pumps and TurbinesDocument48 pagesTopic 4: Pumps and TurbinesKeJeNo ratings yet
- Autocad Homework 2Document10 pagesAutocad Homework 2chroeun sokayNo ratings yet
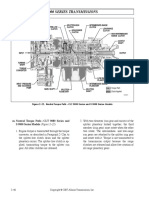
- Description and Operation: M. Neutral Torque Path - CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Document10 pagesDescription and Operation: M. Neutral Torque Path - CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Rodrigo SantanderNo ratings yet
- From-Pttr by Sami: Single Line Instalation Electrical 1-1apDocument1 pageFrom-Pttr by Sami: Single Line Instalation Electrical 1-1apSiti Iyaroh dearni SaragihNo ratings yet
- Flygt Catalogue Grosses Pompes EnglishDocument102 pagesFlygt Catalogue Grosses Pompes EnglishAlexander MedinaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Inlet Feed and Gas Outlet Nozzles Momentum + Liquid Outlet Nozzle Velocity LimitsDocument1 pageRecommended Inlet Feed and Gas Outlet Nozzles Momentum + Liquid Outlet Nozzle Velocity LimitsHadi VeyseNo ratings yet
- Bellin - Inglese Eccentric Screw PumpDocument8 pagesBellin - Inglese Eccentric Screw PumpAlexis ValleNo ratings yet
- Ziegler Fire Pump FPN 1000 - 10-1000 - 15-1000 - EnglDocument2 pagesZiegler Fire Pump FPN 1000 - 10-1000 - 15-1000 - EnglSatria 'igin' Girindra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue - 2022Document4 pagesGeneral Catalogue - 2022gautamNo ratings yet
- Enric Pardo, Mike Staines, Zhenan Jiang, Neil Glasson, Bob BuckleyDocument1 pageEnric Pardo, Mike Staines, Zhenan Jiang, Neil Glasson, Bob BuckleymikeNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument11 pagesJointsThyaga RajNo ratings yet
- TMS Turbomaschinen Service EnglDocument12 pagesTMS Turbomaschinen Service EnglMehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- K3 V280 SpecsDocument1 pageK3 V280 SpecsJuan AcostaNo ratings yet
- Motor m42sp 5 e PDFDocument1 pageMotor m42sp 5 e PDFBryan BlancoNo ratings yet
- 9000 Series Transmissions: M. Neutral Torque Path-CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Document10 pages9000 Series Transmissions: M. Neutral Torque Path-CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)amin chaabenNo ratings yet
- HEURISTICSDocument6 pagesHEURISTICSlordyNo ratings yet
- Gas Velocity CalculatorDocument5 pagesGas Velocity CalculatoresutjiadiNo ratings yet
- Perseverance SpecSheet Simba M4CDocument3 pagesPerseverance SpecSheet Simba M4C马建乐No ratings yet
- Kill Sheet ANA 103Document19 pagesKill Sheet ANA 103Chirica George-CatrinelNo ratings yet
- Transformer On-Load Tap-Changer Control Relay: M M M M M M MDocument2 pagesTransformer On-Load Tap-Changer Control Relay: M M M M M M MshekooferiahiNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Loads Panelboard Ante TataDocument1 pageSchedule of Loads Panelboard Ante TataEDGARDO JR. DIGALNo ratings yet
- Politeknik MalayDocument6 pagesPoliteknik MalaybrianlaksonoNo ratings yet
- Simple Descriptions of ValvesDocument46 pagesSimple Descriptions of ValvesAhmed AlhinaiNo ratings yet
- M 389 ContentDocument52 pagesM 389 ContentokahertaberNo ratings yet
- Storage and Conveying of Bulk SolidsDocument5 pagesStorage and Conveying of Bulk SolidsjijiakdkclsikfdsNo ratings yet
- NPSHADocument5 pagesNPSHAjokishNo ratings yet
- CEESI High Water Cut PaperDocument29 pagesCEESI High Water Cut PaperhaitoecheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Dimensional Analysis Modeling and Similitude PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 7 Dimensional Analysis Modeling and Similitude PDFAbera Mamo100% (1)
- Hydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCDocument1 pageHydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCIwanTiaraMotorNo ratings yet
- Curva de Performance 4 Bombas - Recomendação WEIRDocument1 pageCurva de Performance 4 Bombas - Recomendação WEIRJoão Paulo Augusto MacedoNo ratings yet
- CHE 314 - 2 Mechanics of ParticlesDocument33 pagesCHE 314 - 2 Mechanics of ParticlesAbdulrahim SegirNo ratings yet
- Darcy's LawDocument10 pagesDarcy's LawJunaid ArifNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Control Valve FisherDocument9 pagesData Sheet Control Valve FisherFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2hariharanbookNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Analysis of A Blended Wing Body AircraftDocument18 pagesAerodynamic Analysis of A Blended Wing Body Aircraftsohaibumer2001No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Heat Transfer EnhancementDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Heat Transfer Enhancementfyr5efrr100% (1)
- Esp PVT-PropertiesDocument17 pagesEsp PVT-PropertiesJSN179No ratings yet
- Rexroth Axial Piston Fluids Tellus Bajo de ShellDocument8 pagesRexroth Axial Piston Fluids Tellus Bajo de ShellJill WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Modern Helicopter AerodynamicsDocument53 pagesModern Helicopter AerodynamicsAulia®100% (1)
- Elbow Flow MeasurementDocument3 pagesElbow Flow Measurementsandeep lal100% (1)
- SOP Testing Procedure For Ball Valve-API 6D-1Document16 pagesSOP Testing Procedure For Ball Valve-API 6D-1Ponco Setiyo PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Hvws System For 10 Mva TransformerDocument26 pagesHvws System For 10 Mva Transformershashi ranjanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-I - LAB: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesMechanics of Materials-I - LAB: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAmmar Naseer GhummanNo ratings yet
- Exp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctDocument7 pagesExp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctKawar Abid100% (1)
- LdoDocument12 pagesLdoAnonymous YcAZv5qF67No ratings yet
- Mecheng 325 Exam Study GuideDocument3 pagesMecheng 325 Exam Study GuideAnthony KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Seepage 1 PDFDocument16 pagesSeepage 1 PDFRadifan Halif100% (1)
- CGE536 - EH2433B Group & Lab Session SEPT 2018 PDFDocument1 pageCGE536 - EH2433B Group & Lab Session SEPT 2018 PDFJohan AliffNo ratings yet
- YAMADA Engineering Handbook 2014Document141 pagesYAMADA Engineering Handbook 2014ToyinNo ratings yet
Hydraulic Machine
Hydraulic Machine
Uploaded by
Pratik MoyjeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydraulic Machine
Hydraulic Machine
Uploaded by
Pratik MoyjeCopyright:
Available Formats
Model Relationship for Turbine Specific speed classification of pumps
Turbine
Name Type Type of
Energy
Ns (MKS) Head Discharge Direction of
flow
Dimensional Diamensionless FLOW DIRECTION SPEED DIMENSION
Pelton wheel Impulse Kinetic 10-35 High Low(Q<1000 LPM) Tangential
Parameter Parameter SPECIFIC SPEED
turbine (250 to 1000m)
(Single jet) Radial Low 10-30
P
Peloton wheel Impulse Kinetic 35-60 High Low Tangential Medium 30-50
turbine
(multiple jet)
(250 to 1000 m) flow runner N P
1. NS = 1. Ns = High 50-80
Francis Reaction Kinetic + 60-300 Medium Medium Inward Radial (H)5 / 4 gH)5/4
Turbine Pressure (60 to 150 m) (1000-10000) LPM Mixed flow Mixed Flow 80-160
(Modern Francis)
Q Q Axial Flow 160-450
Kaplan & Reaction Kinetic + 300-1000 Low High(Q>10000LPM) Axial flow 2. CQ = 2. CQ =
Propeller
turbine
Pressure (< 30 m) ND3 D3 Types of Pump Range of Head
Classificationaccording to energy available at input
H gh Low head pump upto 15m head
3. CH = 3. CH = Medium head pump 15 m to 40 m
Impulse turbine Reaction Turbine N 2 D2 2 D 2 High head pump above 40 m
1. Input energy is only 1. Input energy is kinetic energy + pressure energy P P
kinetic energy 4. CP = 4. CP = N Q T 1 (L3T 1 )1/ 2
2. Pressure remains constant 2. pressure drop takes place. N D5
3
3 D5 Specific speed (Ns) = 3/ 4 L3 / 4T 3 / 2
throughout the working
(H m ) L3 / 4
& which is equal to atmospheric. Here, N S = Specific speed, CQ = Discharge coefficient
3. Useful for high head & low discharge 3. Useful for low head & high discharge
C H = Head coefficient, CP = Power coefficient ir or
ervod
4. Degree of reaction is zero. 4. Degree of reaction not zero.
5. No draft tube 5. Draft tube is present. es
R pon
6. Example Pelton wheel 6. Example (i) Francis Turbine 2
(ii) kaplan & propeller Turbine. w – Angular speed = , N – No. of revolution/minute Dam
Surge chamber
Gross power Net power Power Power H – Head (m), P – Power
from from developed obtained Penstock Motor Generator
reservoir reservoir by from
(Water power) runner shaft (BHP) Turbine
Draft Tube
Entrance of Turbine
Reservoir spiral casing runner Shaft
Tail Water
Cross section through a pumped storage plant Pond
Head loss in Mechanical
(a) Hydraulic losses
penstock losses
(i) Eddy formation Fluid Path
(i) Blade friction
(iii) Friction in draft (a) Pelton (Impulse): Head race (Dam) Penstock Nozzle Bucket
tube Generator
(iv) Energy contained losses (Blades) Runner Tail race
by water leaving Property Centrifugal pump Reciprocating pump (b) Reaction turbine (Kaplan & francis): Head race Penstock Casing
draft tube Guide vanes Moving vanes Runner Draft tube Tail
Flow Continuous and smooth Fluctuating and pulsating
(b) Leakage losses
Maintenance cost Less More race.
Generator Running Speed Can run at high speed Cann’t run at high speed For turbine : water power > Runner power > shaft power
Starting torque More Less For pump : Shaft power > Impeller power > Water power
For Reaction Turbine Wear and Tear Less More
Pumps in series: Q = Constant, Increase Head, Total Hm = n Hm
Efficiency Less More
Turbine Speed ratio Flow ratio No. of vanes Pumps in parallel: Hm = Constant, Increase discharge, Total Q = n Q
Floor area Smaller Large
Indicator diagram is the graph between the pressure head in the cylinder
m Suction and delivery valve Not necessary Necessary
Pelton 0.4–0.5 0 15 Cost Less Four times of C.P.
& the distance travelled by the piston flow inner dead centre for one com-
2 plete revolution of the crank, work done by pump is proportional to the
Mechanism Impeller Piston
Francis 0.6–0.9 0.15–0.3 25 to 30 Discharge High Low area of indicator diagram.
Kaplan & 1.8–2.5 0.6–0.9 3 to 8 Priming Required Not required Hydraulic RAM (It work on the principle of water hammer) is a device
Propeller Problem Cavitation Water seperation used to lift small quantity of water to a larger height when a large quan-
tity is available at smaller height. It does not need any external power
Head Vs discharge and Power Vs discharge realtionship like electricity.
CIVIL ENGINEERING
Forward
ne
ROCKET CHART
ne
curve vane
va
d va
FOR QUICK REVISION
Radial vane ia l
ad
Power
CIVIL BOOSTER - Dnt trust us, Just Check it’s content & Then Go for it - ( LEAVE THE
wa r
R
Head
REST, GET THE BEST ) . Available on amazon flipkart. Zero Error book with BEST Content
For
Backward vane
ward
curve vane Back
Discharge Discharge
You might also like
- Wind Tunnel ExperimentDocument46 pagesWind Tunnel ExperimentAbhilash Mathew50% (2)
- Rudder DesignDocument11 pagesRudder Designnawan67% (3)
- Reversible Flow Fan: New Product InformationDocument5 pagesReversible Flow Fan: New Product Informationsnow69yNo ratings yet
- AerodynamicEffectsOfPantographs - by Mitsuru Ikeda - RTRIDocument12 pagesAerodynamicEffectsOfPantographs - by Mitsuru Ikeda - RTRIwmplgrcfNo ratings yet
- TDK-humidifier - Element Nebulizer - NB - enDocument5 pagesTDK-humidifier - Element Nebulizer - NB - enKemenesh HNo ratings yet
- Pressure Booster - V GuardDocument2 pagesPressure Booster - V Guardhalderchayan320No ratings yet
- EDGE 650-675 4570 Performance ChartDocument1 pageEDGE 650-675 4570 Performance ChartLeonardo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Series: K5V 200 DT H 100 R 9N 01Document1 pageSeries: K5V 200 DT H 100 R 9N 01Stelian Crisan100% (1)
- Catalogo Servo 1FK7Document6 pagesCatalogo Servo 1FK7José Manuel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Various 3 3" 5" 1000 1" Semi-O 15.12": NS Solids Dia. No. Vanes Discharge Suction Style Speed Impeller DiaDocument1 pageVarious 3 3" 5" 1000 1" Semi-O 15.12": NS Solids Dia. No. Vanes Discharge Suction Style Speed Impeller DiaChunchun MaruNo ratings yet
- BOQ Supply Installation - Construction PowerDocument1 pageBOQ Supply Installation - Construction Powersaravanan .bNo ratings yet
- T Intersection Point (T T) Determines The Steady - State SpeedDocument11 pagesT Intersection Point (T T) Determines The Steady - State SpeedKaone OsupileNo ratings yet
- Thermal Load Effect On Vibration On A Reactor FW Pump 1699692616Document25 pagesThermal Load Effect On Vibration On A Reactor FW Pump 1699692616logicloverNo ratings yet
- 1N5758 Etc PDFDocument3 pages1N5758 Etc PDFPedro lealNo ratings yet
- PLB-0384-4830-ME-0004: ABB India LTDDocument3 pagesPLB-0384-4830-ME-0004: ABB India LTDAlex Labraña RojoNo ratings yet
- Penta KatalogDocument36 pagesPenta KatalogCristian SerbanoiuNo ratings yet
- PompaDocument2 pagesPompaviviNo ratings yet
- PLB-0384-DAT-4830-ME-0005: ABB India LTDDocument3 pagesPLB-0384-DAT-4830-ME-0005: ABB India LTDAlex Labraña RojoNo ratings yet
- SRNE - HF Series - LV - EU - Solar Charge Inverter - Datasheet - 2.1Document1 pageSRNE - HF Series - LV - EU - Solar Charge Inverter - Datasheet - 2.1Lin YutingNo ratings yet
- Motor PassoDocument1 pageMotor PassoHevert TwynsterNo ratings yet
- MM 1150HP WDS6 18.74 PerDocument1 pageMM 1150HP WDS6 18.74 PermajjisatNo ratings yet
- LPS Hybrid AC/DC Features Specification: Solar SubmersibleDocument2 pagesLPS Hybrid AC/DC Features Specification: Solar SubmersibleEric Lee100% (2)
- EEE2003 - Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab: School of Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesEEE2003 - Electromechanical Energy Conversion Lab: School of Electrical EngineeringAkshit VSNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Piston PumpDocument19 pagesHydraulic Piston Pumpvodangminhhieu0905960430No ratings yet
- Curva 2Document1 pageCurva 2Luis FernandoNo ratings yet
- 8 Centrifugal Compressor PerformanceDocument28 pages8 Centrifugal Compressor PerformanceHazem Ramdan100% (1)
- CasappaDocument44 pagesCasappaback1949No ratings yet
- Water Turbine and Its TypesDocument7 pagesWater Turbine and Its TypesprakashNo ratings yet
- Perfomance Curve BFP HP Ip PDFDocument2 pagesPerfomance Curve BFP HP Ip PDFRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Motor m55sp 2k eDocument2 pagesMotor m55sp 2k ebLesaLmeNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Flow Instruments: Flow Switches & Indicators Delta Tube - Averaging Pitot TubeDocument3 pagesAn Overview of Flow Instruments: Flow Switches & Indicators Delta Tube - Averaging Pitot TubegiridharNo ratings yet
- Tons Tons: CAPWAP (R) 2014-3 Licensed To PT Teno IndonesiaDocument3 pagesTons Tons: CAPWAP (R) 2014-3 Licensed To PT Teno IndonesiaAdiitPuutraNo ratings yet
- BasicformulasDocument2 pagesBasicformulasAhmad SabraNo ratings yet
- X ErCharProtDocument10 pagesX ErCharProtNavaneethakrishnan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Relief Valve: RD-162A-X-Y-ZDocument1 pageRelief Valve: RD-162A-X-Y-ZMichał A.No ratings yet
- Smoke Ventilators F400 / 120: Smoke Air Ventilator High-Performance ResilientDocument11 pagesSmoke Ventilators F400 / 120: Smoke Air Ventilator High-Performance ResilientBachir BachirNo ratings yet
- Performance Chart Theoretical Working Point: CGT/4-900-6/32 15KW (400V50HZ) IE3 V5Document3 pagesPerformance Chart Theoretical Working Point: CGT/4-900-6/32 15KW (400V50HZ) IE3 V5Ishan RanganathNo ratings yet
- Series CA: Magnetic Drive Centrifugal PumpDocument2 pagesSeries CA: Magnetic Drive Centrifugal Pumphanni86No ratings yet
- 1002 A Series Variable Displacement Piston PumpsDocument48 pages1002 A Series Variable Displacement Piston PumpsLuis Enrique López LeónNo ratings yet
- Ecma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Document2 pagesEcma L1221BR3 PD02 05172016Anil JindalNo ratings yet
- Topic 4: Pumps and TurbinesDocument48 pagesTopic 4: Pumps and TurbinesKeJeNo ratings yet
- Autocad Homework 2Document10 pagesAutocad Homework 2chroeun sokayNo ratings yet
- Description and Operation: M. Neutral Torque Path - CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Document10 pagesDescription and Operation: M. Neutral Torque Path - CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Rodrigo SantanderNo ratings yet
- From-Pttr by Sami: Single Line Instalation Electrical 1-1apDocument1 pageFrom-Pttr by Sami: Single Line Instalation Electrical 1-1apSiti Iyaroh dearni SaragihNo ratings yet
- Flygt Catalogue Grosses Pompes EnglishDocument102 pagesFlygt Catalogue Grosses Pompes EnglishAlexander MedinaNo ratings yet
- Recommended Inlet Feed and Gas Outlet Nozzles Momentum + Liquid Outlet Nozzle Velocity LimitsDocument1 pageRecommended Inlet Feed and Gas Outlet Nozzles Momentum + Liquid Outlet Nozzle Velocity LimitsHadi VeyseNo ratings yet
- Bellin - Inglese Eccentric Screw PumpDocument8 pagesBellin - Inglese Eccentric Screw PumpAlexis ValleNo ratings yet
- Ziegler Fire Pump FPN 1000 - 10-1000 - 15-1000 - EnglDocument2 pagesZiegler Fire Pump FPN 1000 - 10-1000 - 15-1000 - EnglSatria 'igin' Girindra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- General Catalogue - 2022Document4 pagesGeneral Catalogue - 2022gautamNo ratings yet
- Enric Pardo, Mike Staines, Zhenan Jiang, Neil Glasson, Bob BuckleyDocument1 pageEnric Pardo, Mike Staines, Zhenan Jiang, Neil Glasson, Bob BuckleymikeNo ratings yet
- JointsDocument11 pagesJointsThyaga RajNo ratings yet
- TMS Turbomaschinen Service EnglDocument12 pagesTMS Turbomaschinen Service EnglMehmet ErenNo ratings yet
- K3 V280 SpecsDocument1 pageK3 V280 SpecsJuan AcostaNo ratings yet
- Motor m42sp 5 e PDFDocument1 pageMotor m42sp 5 e PDFBryan BlancoNo ratings yet
- 9000 Series Transmissions: M. Neutral Torque Path-CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)Document10 pages9000 Series Transmissions: M. Neutral Torque Path-CLT 9880 Series and S 9800 Series Models (Figure 2-22)amin chaabenNo ratings yet
- HEURISTICSDocument6 pagesHEURISTICSlordyNo ratings yet
- Gas Velocity CalculatorDocument5 pagesGas Velocity CalculatoresutjiadiNo ratings yet
- Perseverance SpecSheet Simba M4CDocument3 pagesPerseverance SpecSheet Simba M4C马建乐No ratings yet
- Kill Sheet ANA 103Document19 pagesKill Sheet ANA 103Chirica George-CatrinelNo ratings yet
- Transformer On-Load Tap-Changer Control Relay: M M M M M M MDocument2 pagesTransformer On-Load Tap-Changer Control Relay: M M M M M M MshekooferiahiNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Loads Panelboard Ante TataDocument1 pageSchedule of Loads Panelboard Ante TataEDGARDO JR. DIGALNo ratings yet
- Politeknik MalayDocument6 pagesPoliteknik MalaybrianlaksonoNo ratings yet
- Simple Descriptions of ValvesDocument46 pagesSimple Descriptions of ValvesAhmed AlhinaiNo ratings yet
- M 389 ContentDocument52 pagesM 389 ContentokahertaberNo ratings yet
- Storage and Conveying of Bulk SolidsDocument5 pagesStorage and Conveying of Bulk SolidsjijiakdkclsikfdsNo ratings yet
- NPSHADocument5 pagesNPSHAjokishNo ratings yet
- CEESI High Water Cut PaperDocument29 pagesCEESI High Water Cut PaperhaitoecheNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Dimensional Analysis Modeling and Similitude PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 7 Dimensional Analysis Modeling and Similitude PDFAbera Mamo100% (1)
- Hydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCDocument1 pageHydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Wlu HC Hu C HLB Blu BLC WLCIwanTiaraMotorNo ratings yet
- Curva de Performance 4 Bombas - Recomendação WEIRDocument1 pageCurva de Performance 4 Bombas - Recomendação WEIRJoão Paulo Augusto MacedoNo ratings yet
- CHE 314 - 2 Mechanics of ParticlesDocument33 pagesCHE 314 - 2 Mechanics of ParticlesAbdulrahim SegirNo ratings yet
- Darcy's LawDocument10 pagesDarcy's LawJunaid ArifNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Control Valve FisherDocument9 pagesData Sheet Control Valve FisherFIRMANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2hariharanbookNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Analysis of A Blended Wing Body AircraftDocument18 pagesAerodynamic Analysis of A Blended Wing Body Aircraftsohaibumer2001No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Heat Transfer EnhancementDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Heat Transfer Enhancementfyr5efrr100% (1)
- Esp PVT-PropertiesDocument17 pagesEsp PVT-PropertiesJSN179No ratings yet
- Rexroth Axial Piston Fluids Tellus Bajo de ShellDocument8 pagesRexroth Axial Piston Fluids Tellus Bajo de ShellJill WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Modern Helicopter AerodynamicsDocument53 pagesModern Helicopter AerodynamicsAulia®100% (1)
- Elbow Flow MeasurementDocument3 pagesElbow Flow Measurementsandeep lal100% (1)
- SOP Testing Procedure For Ball Valve-API 6D-1Document16 pagesSOP Testing Procedure For Ball Valve-API 6D-1Ponco Setiyo PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Hvws System For 10 Mva TransformerDocument26 pagesHvws System For 10 Mva Transformershashi ranjanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-I - LAB: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesMechanics of Materials-I - LAB: Department of Mechanical EngineeringAmmar Naseer GhummanNo ratings yet
- Exp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctDocument7 pagesExp6 Air Flow Velocity and Pressure Coefficient Around The 90o Rectangular DuctKawar Abid100% (1)
- LdoDocument12 pagesLdoAnonymous YcAZv5qF67No ratings yet
- Mecheng 325 Exam Study GuideDocument3 pagesMecheng 325 Exam Study GuideAnthony KimberlyNo ratings yet
- Seepage 1 PDFDocument16 pagesSeepage 1 PDFRadifan Halif100% (1)
- CGE536 - EH2433B Group & Lab Session SEPT 2018 PDFDocument1 pageCGE536 - EH2433B Group & Lab Session SEPT 2018 PDFJohan AliffNo ratings yet
- YAMADA Engineering Handbook 2014Document141 pagesYAMADA Engineering Handbook 2014ToyinNo ratings yet