Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna VS Rna
Dna VS Rna
Uploaded by
Creepy GrinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dna VS Rna
Dna VS Rna
Uploaded by
Creepy GrinCopyright:
Available Formats
GUARIN, VAUGHN ROMEO GEN BIO 2NDQ MODULE 2
GRADE 11-SID MISS MIAN PATALINGHUG
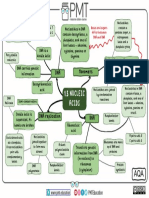
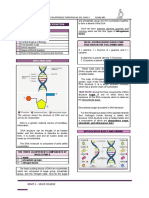
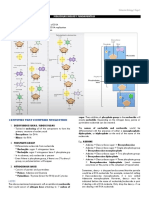
DNA VS. RNA
DNA RNA
FUNCTION: FUNCTION:
DNA replicates and stores genetic information. It is RNA converts the genetic information contained
a blueprint for all genetic information contained SIMILARILITES within DNA to a format used to build proteins, and
within an organism. then moves it to ribosomal protein factories.
SUGAR: both are perhaps the most important
SUGAR:
molecules in cell biology,
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, which contains one responsible for the storage and
RNA contains ribose sugar molecules, without the
reading of genetic information that
less hydroxyl group than RNA’s ribose underpins all life hydroxyl modifications of deoxyribose.
They are both linear polymers,
consisting of sugars, phosphates and STRAND:
STRAND
bases.
DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix. Both DNA and RNA store genetic RNA only has one strand,
but like DNA, is made up of
information.
These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. DNA and RNA are both large nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands.
Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar biological polymers. RNA sometimes forms a secondary double helix structure,
Both DNA and RNA consists of sugar,
molecule and a nitrogenous base. nitrogenous bases, and a phosphate but only intermittently.
backbone.
On both molecules, guanine and
nitrogenous bases:
cytosine pair with each other (are
nitrogenous bases:
adenine (A) complementary). adenine (A)
guanine (G)
guanine (G)
thymine (T)
uracil (U)
cytosine (C) cytosine (C)
You might also like
- Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5Document1 pageBiological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5RanaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Nucleic AcidsDocument1 page1.5 Nucleic AcidsBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument2 pagesDNA Vs RNAMegat AmirulNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Nucleic AcidsDocument13 pages4.4 Nucleic Acidsrovicvaldenor97No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidsShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 10Document4 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 10Ma. Jhysavil ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesFunctions of Nucleic Acids Are:: Nucleic Acids Consist of Either One or Two Long Chains of Two Types of Nucleic AcidsveloNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Pro Synth PPTDocument17 pagesUnit 8 Pro Synth PPTERLIE ROSE VERGARANo ratings yet
- DNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonDocument6 pagesDNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- DLP 3Document15 pagesDLP 3princessspbsedscicsuandrewsNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYheyyouNo ratings yet
- Week4 Heredity Inheritance-And-Variation DNADocument30 pagesWeek4 Heredity Inheritance-And-Variation DNAperlasirisalthea22No ratings yet
- Nucleotide BiochemDocument27 pagesNucleotide BiochemHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument8 pagesNucleic AcidhbmbzfnttpNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- PoppletDocument1 pagePoppletapi-688178924No ratings yet
- DNA RNA: DefinitionDocument1 pageDNA RNA: Definitionkatrina668No ratings yet
- PHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerDocument8 pagesPHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument12 pagesBiomoleculesPRADEEP CNo ratings yet
- Mtap I - Molbio - NotesDocument30 pagesMtap I - Molbio - NotesKath CamacamNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document4 pagesUnit 6Leen Al-FouzanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesMarie WrightNo ratings yet
- Nu Cleo ShitDocument4 pagesNu Cleo ShitPretty Grace101No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisJo JoNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesDocument6 pagesNucleotides,: Roles of RNA MoleculesGizelle Mae Pasiol-MacayanNo ratings yet
- Identification of Novel Components of NAD-utilizing Metabolic Pathways and Prediction of Their Biochemical FunctionsDocument18 pagesIdentification of Novel Components of NAD-utilizing Metabolic Pathways and Prediction of Their Biochemical FunctionsGuillermo Domínguez HuertaNo ratings yet
- Mine - SylBioGr10Document11 pagesMine - SylBioGr10Suzan.FilizNo ratings yet
- Science10 q3 - Mod4.1 Week4 Protein-Synthesis v4-1Document11 pagesScience10 q3 - Mod4.1 Week4 Protein-Synthesis v4-1Mhira MuliNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids 4Document4 pagesNucleic Acids 4Edgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Essential Idea: The Structure of DNA Allows Efficient Storage of Genetic InformationDocument26 pagesEssential Idea: The Structure of DNA Allows Efficient Storage of Genetic InformationReeya WhabiNo ratings yet
- 2024 FS RECOVERY ATP Life Sciences GR 12 (Exam Guidelines 2021) - 17 Jan 2024Document11 pages2024 FS RECOVERY ATP Life Sciences GR 12 (Exam Guidelines 2021) - 17 Jan 2024Reitumetse MolefeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesNucleic Acidslim.angelyne0126No ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument16 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAady.rogo.plnnpNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Midterm TransesDocument17 pagesBiochem Lec Midterm Transescathryna gaylanNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- Transcription Diagrams BlankDocument5 pagesTranscription Diagrams BlankAlejandro MartínezNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument28 pagesDNA Vs RNALeilani Joy Rivera GabitoNo ratings yet
- Formal Rep 1Document6 pagesFormal Rep 1PATRICIA RAE ENDAYANo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Dna and Cental Dogma 1Document3 pagesLecture Notes Dna and Cental Dogma 1antonettenakpilNo ratings yet
- Bio212 2024 L13 Introduction To Molecular GeneticsDocument20 pagesBio212 2024 L13 Introduction To Molecular GeneticsGrace DiswaiNo ratings yet
- Bio211 L9 Nucleic AcidsDocument22 pagesBio211 L9 Nucleic Acidsmoketesharon50No ratings yet
- Activity 1 DNA RNADocument1 pageActivity 1 DNA RNAAvelino JohnmarcNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Mining Financial FlowDocument1 pageMining Financial FlowCreepy GrinNo ratings yet
- Theology Quarter 2Document18 pagesTheology Quarter 2Creepy GrinNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Module 2Document8 pagesEarth Science Module 2Creepy GrinNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2nd Quarter Module 2Document8 pagesEarth Science 2nd Quarter Module 2Creepy GrinNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 2nd Quarter Module 2Document8 pagesEarth Science 2nd Quarter Module 2Creepy GrinNo ratings yet
- Composite Polyester: Polymer EngineeringDocument22 pagesComposite Polyester: Polymer EngineeringYasser AshourNo ratings yet
- Oxygen BarrierDocument20 pagesOxygen BarrierKarina ArdizziNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- BIOPLASTIKDocument8 pagesBIOPLASTIKChristine Ulina Tarigan SilangitNo ratings yet
- Hdpe Raffia ManufactyuerfDocument18 pagesHdpe Raffia Manufactyuerfjemish limbaniNo ratings yet
- Ceresana Brochure Market-Study Ethylene 2nd Ed.Document7 pagesCeresana Brochure Market-Study Ethylene 2nd Ed.Zahid FarooqNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 6.10.15Document31 pagesPresentation1 6.10.15Paramasivam VeerappanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition BuckinghamDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition BuckinghamglendavictoriabbkNo ratings yet
- Processing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsDocument3 pagesProcessing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsJason WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Unit 01 Chemical Basis of Life 2Document11 pagesGrade 10 Science Unit 01 Chemical Basis of Life 2rpubuduniNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem 3 LG 5.6 Review of Nucleic Acids Structure and Functions (Part I)Document7 pagesSLG Chem 3 LG 5.6 Review of Nucleic Acids Structure and Functions (Part I)franzachilleslindayagNo ratings yet
- Polymers - 20Document60 pagesPolymers - 20MnkNo ratings yet
- Cat Stepn Components MS21266 BACG20Z Data SheetDocument2 pagesCat Stepn Components MS21266 BACG20Z Data SheetFariz FadzuanNo ratings yet
- CH 27.8 PlasticsDocument95 pagesCH 27.8 PlasticsSmruti Ranjan PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Lost Foam CastingDocument2 pagesLost Foam CastingKirti MehtaNo ratings yet
- What Is Polyester Fiber? What Is Understood by Thermoplastic and Thermoset Polyester?Document5 pagesWhat Is Polyester Fiber? What Is Understood by Thermoplastic and Thermoset Polyester?MOJAHID HASAN Fall 19No ratings yet
- Permintaan Barang Polyoshika - UpdateDocument32 pagesPermintaan Barang Polyoshika - Updaterahman ihsanNo ratings yet
- On Modified BitumenDocument19 pagesOn Modified BitumenTejeshwini SNo ratings yet
- WWW Alibaba Com Product Detail Virgin Recycled HDPE LDPE LLDPE Resin 50034948234 HTML SPM A2700 7724838 2017115 147 270d15cf9xf0iwDocument4 pagesWWW Alibaba Com Product Detail Virgin Recycled HDPE LDPE LLDPE Resin 50034948234 HTML SPM A2700 7724838 2017115 147 270d15cf9xf0iwMauricio JonguitudNo ratings yet
- Rubber & Plastics - CompaniesDocument10 pagesRubber & Plastics - CompaniesMario StrašniNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 9 PDFcarlette11No ratings yet
- Automotive - Presentation - Plastics-3rd June-2015 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Document108 pagesAutomotive - Presentation - Plastics-3rd June-2015 (Compatibility Mode) (Repaired)Annavarapu Gopalakrishna100% (1)
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument6 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyNiar Ar-RahmahNo ratings yet
- Ldpe Process TechnologyDocument7 pagesLdpe Process Technologysswoo8245No ratings yet
- Bio PackagingDocument36 pagesBio PackagingarisyaNo ratings yet
- CHM-203 Biomolecules 2.1Document10 pagesCHM-203 Biomolecules 2.1Mihir IyerNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2023-02-08 at 4.56.21 PMDocument7 pagesWhatsApp Image 2023-02-08 at 4.56.21 PMNew GlobalNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2772397621000319 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S2772397621000319 MainJOSHUA MEDRANONo ratings yet
- Nukleotida, DNA, RNA OKDocument42 pagesNukleotida, DNA, RNA OKSylvia AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Write The Letter of The Best Answer On The Space ProvidedAdrian BrillantesNo ratings yet